Nonvolatile semiconductor storage device and method for operating same
A storage device, non-volatile technology, applied in information storage, static memory, read-only memory, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0071] First, referring to FIG. 8 to FIG. 14, the common non-selection voltage V WE / 2 is given for the first embodiment of the unselected word line and the unselected bit line.
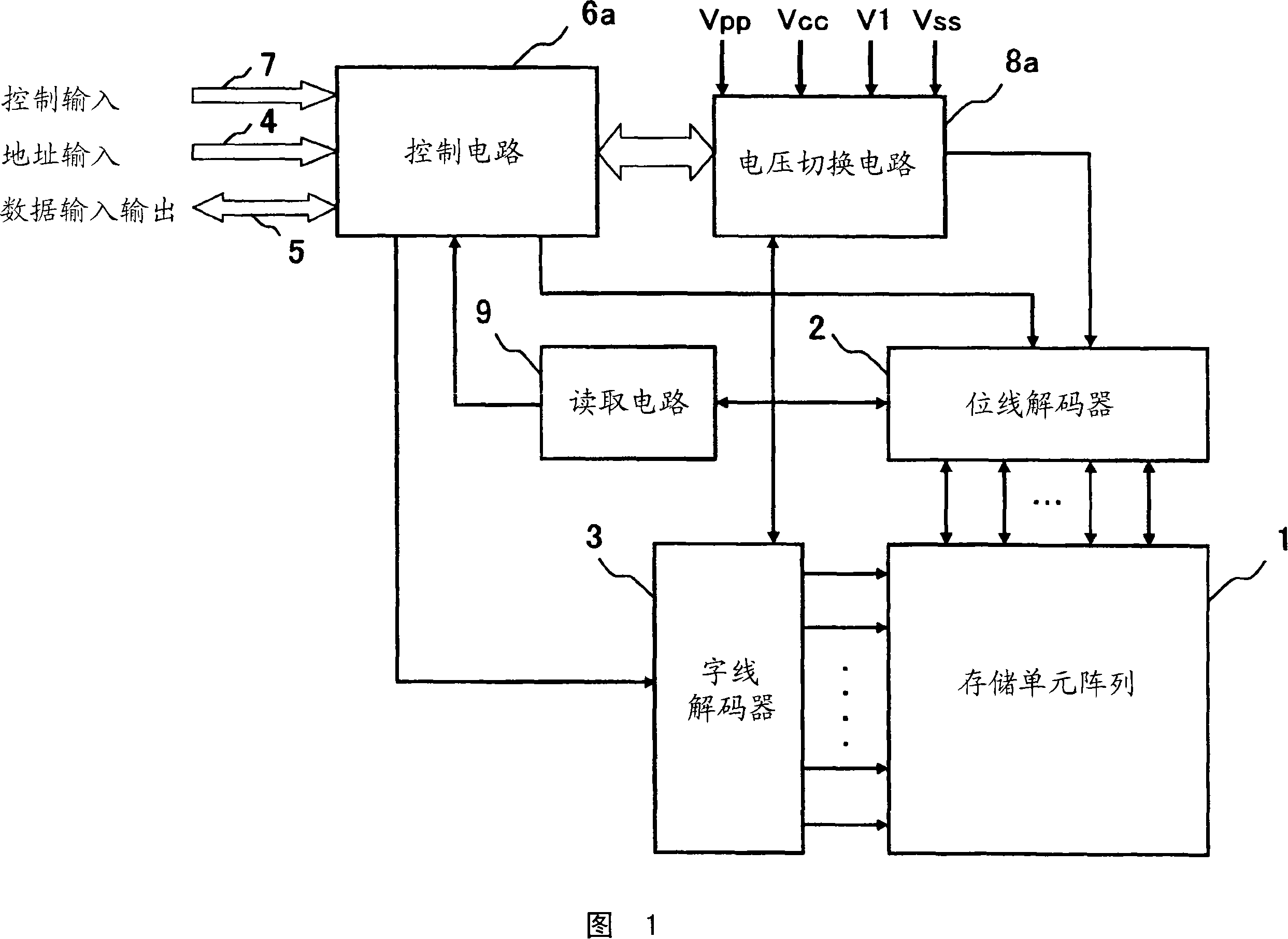
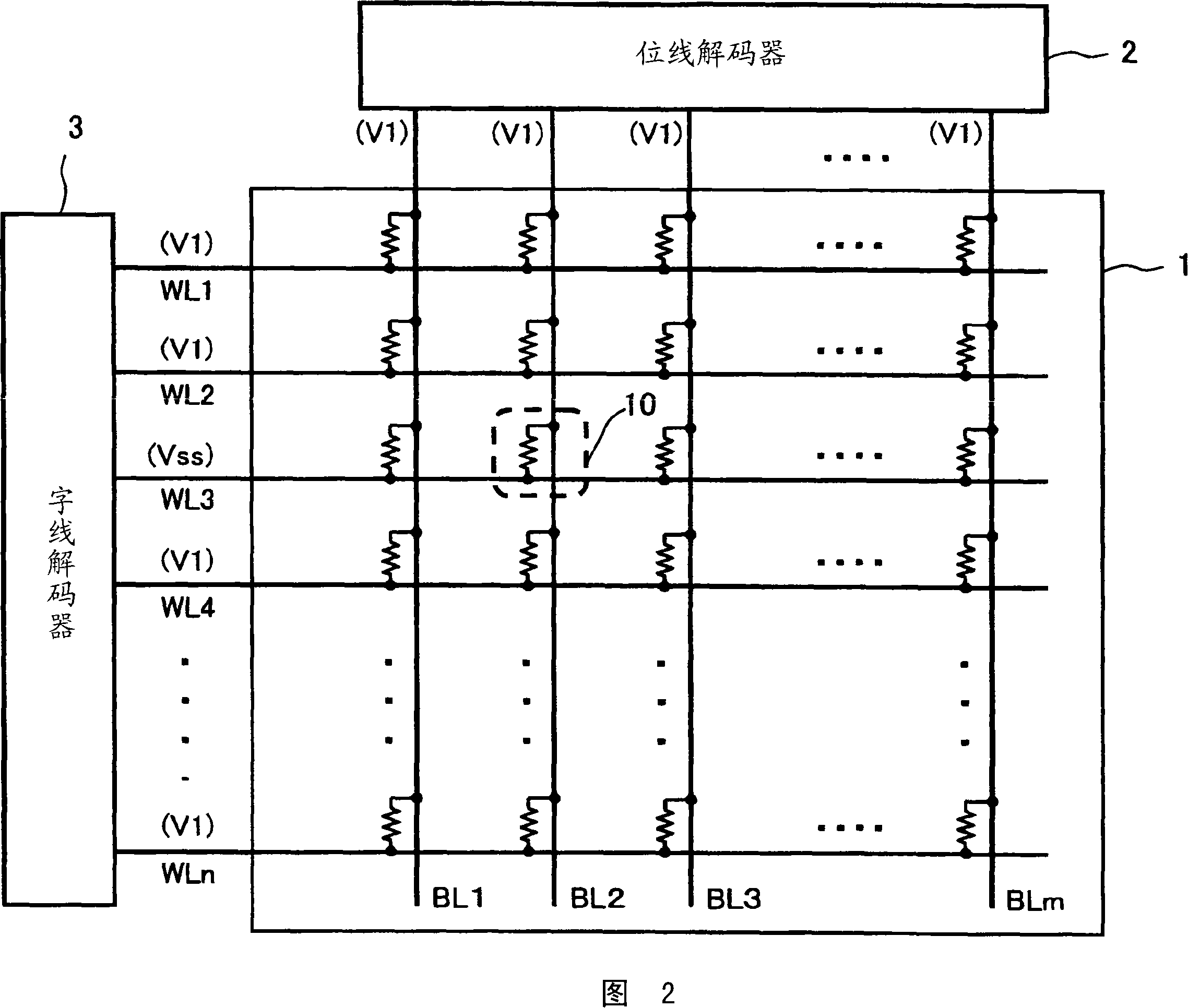
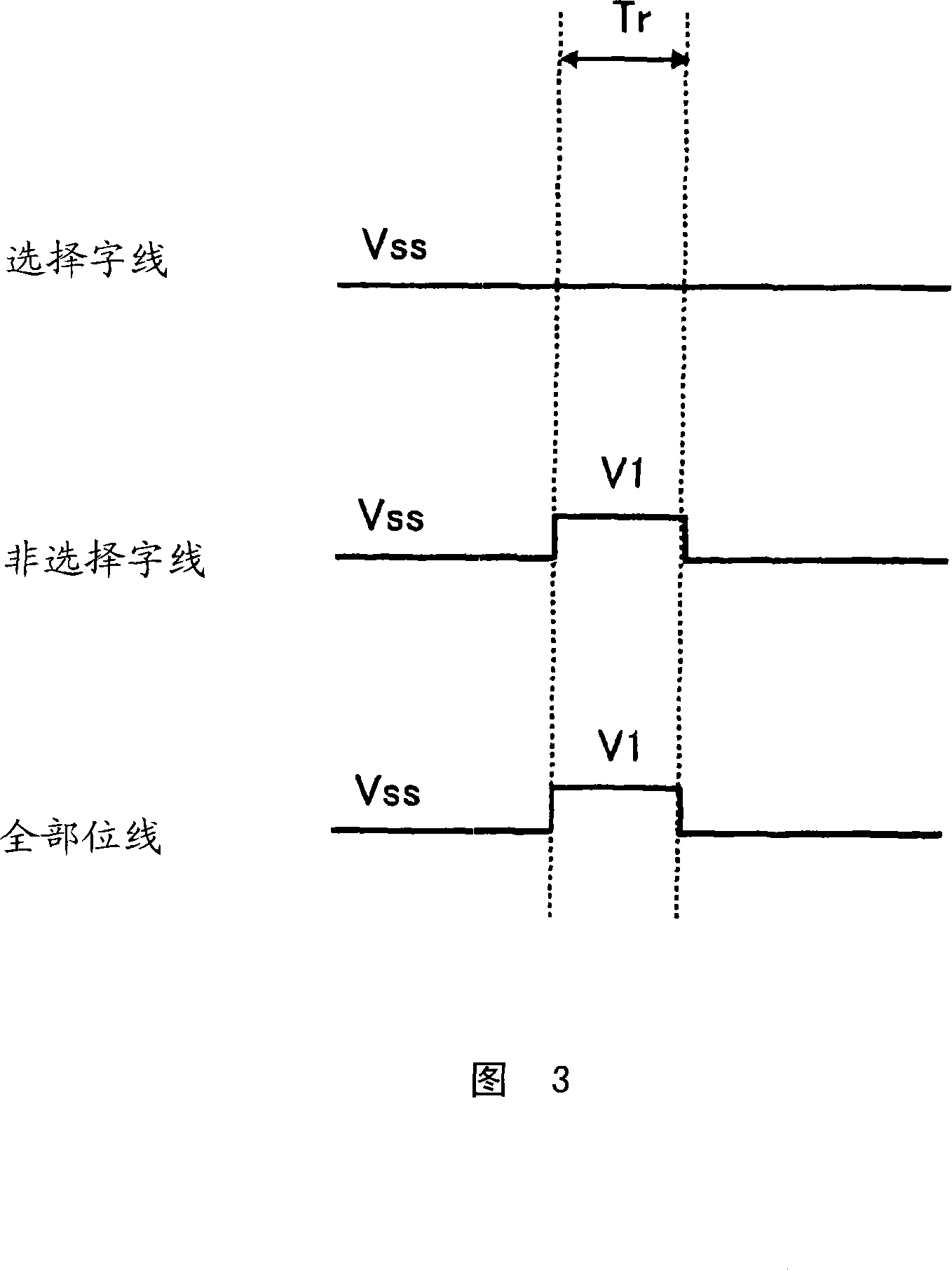
[0072] Fig. 8 is a block configuration diagram showing the functional configuration of the device of the present invention. In FIG. 8 , common reference numerals are assigned to common parts with conventional nonvolatile semiconductor memory devices. As shown in FIG. 8, for the device of the present invention, the memory cell array 1 in which the 1R-type memory cells are arranged in a matrix illustrated in FIG. 9 has a bit line decoder 2, a word line decoder 3, and a voltage switching circuit 8d around , the reading circuit 9 and the control circuit 6d. Basically, it has the same structure as the conventional nonvolatile semiconductor memory device shown in FIG. 1 . The difference from the structure of the conventional nonvolatile semiconductor memory device shown in FIG. 1 is that the voltages ap...
no. 2 approach
[0088] Next, referring to FIG. 15 to FIG. 21 , the first method of providing the ground voltage Vss as a common non-selected voltage to the non-selected word line and the non-selected bit line in each storage operation of writing, erasing, and reading of the device of the present invention is described. Two implementation modes.
[0089] Fig. 15 is a block configuration diagram showing the functional configuration of the device of the present invention according to the second embodiment. In FIG. 15 , the parts common to the conventional nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and the first embodiment are denoted by common reference numerals and described. As shown in FIG. 15, for the device of the present invention, the memory cell array 1 in which the 1R-type memory cells are arranged in a matrix illustrated in FIG. 16 has a bit line decoder 2, a word line decoder 3, and a voltage switching circuit 8e around , the reading circuit 9 and the control circuit 6e. The structure ...
no. 3 approach
[0102] Then, with reference to FIG. 22 to FIG. 28 , it is explained that in each storage operation of writing, erasing, and reading of the device of the present invention, the writing voltage V is provided to the non-selected word line and the non-selected bit line. WE 1 / 3 of the common first non-selection voltage V WE / 3 of the third embodiment.
[0103] Fig. 22 is a block configuration diagram showing the functional configuration of the device of the present invention according to the third embodiment. In FIG. 22 , the parts common to the conventional nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and the first embodiment are denoted by common reference numerals and described. As shown in FIG. 22, for the device of the present invention, a bit line decoder 2, a word line decoder 3, a voltage switching circuit 8f, Read circuit 9 and control circuit 6f. The structure is basically the same as that of the conventional nonvolatile semiconductor memory device shown in FIG. 1 and the f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com