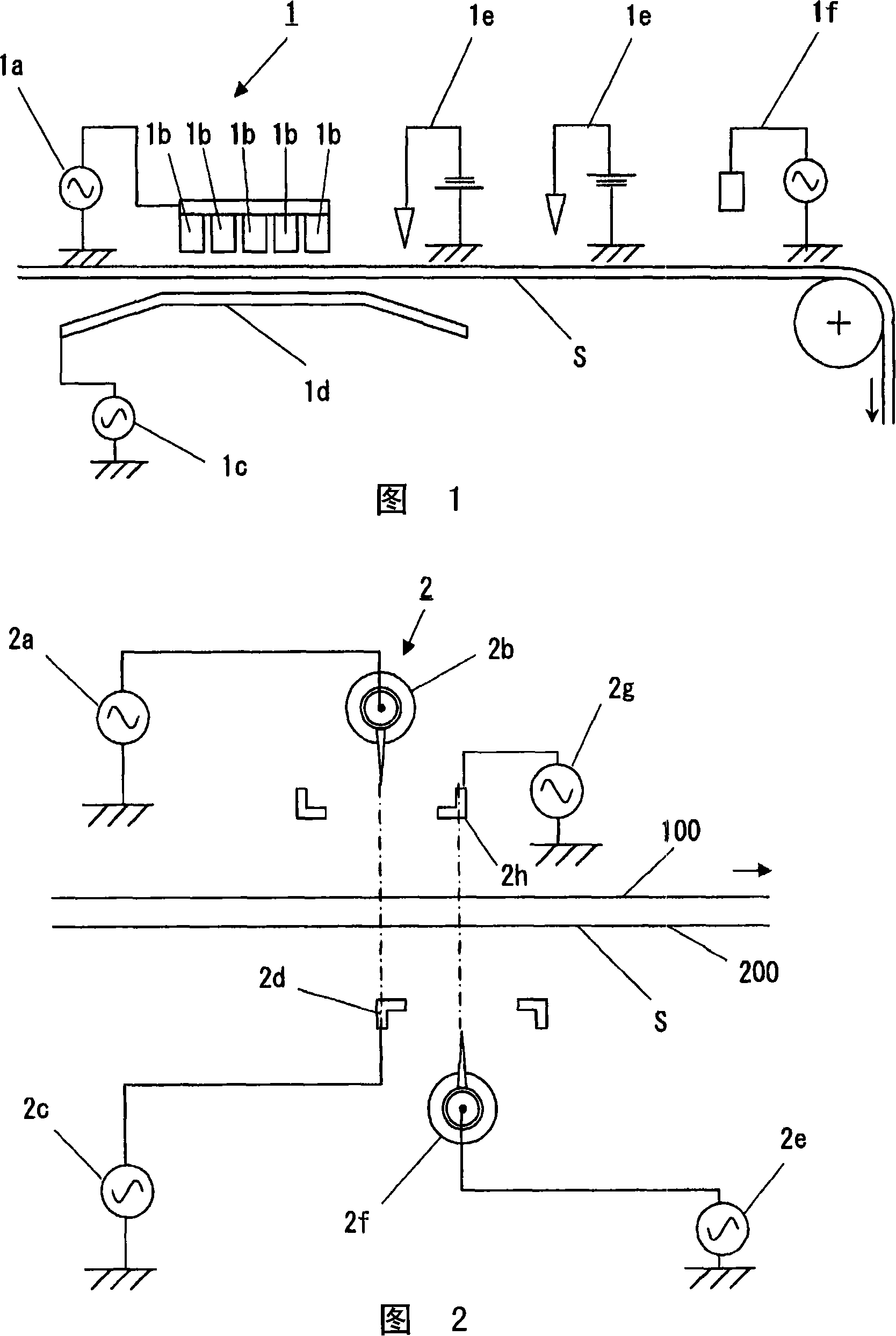
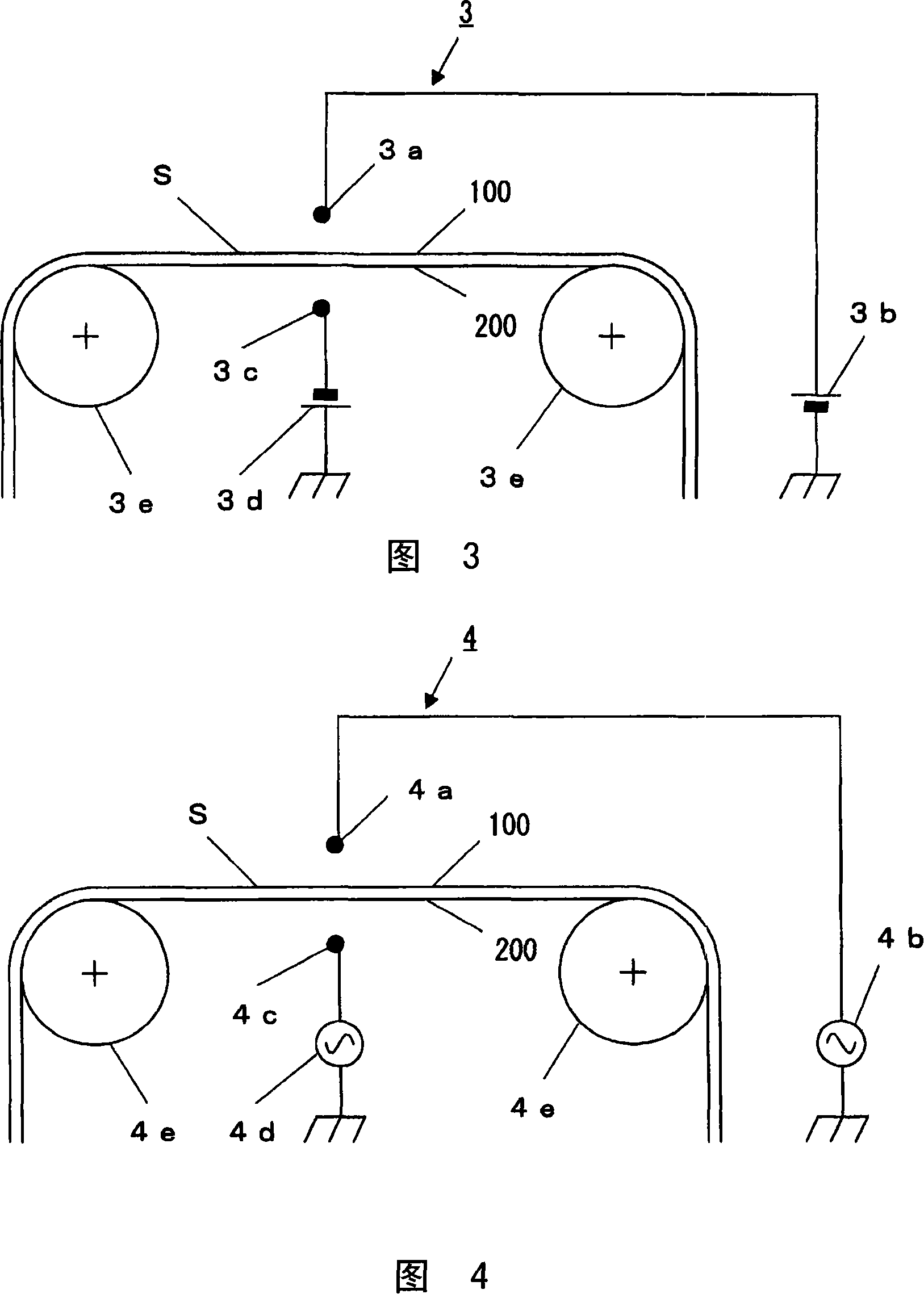
Neutralizing device, neutralizing method and production method of electric-insulating sheet
An electrical insulation and sheet technology, applied in corona discharge devices, electrical components, static electricity, etc., can solve the problems of uneven positive and negative charging, uneven adhesion of ink or coating agent, and inability to eliminate static spots.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
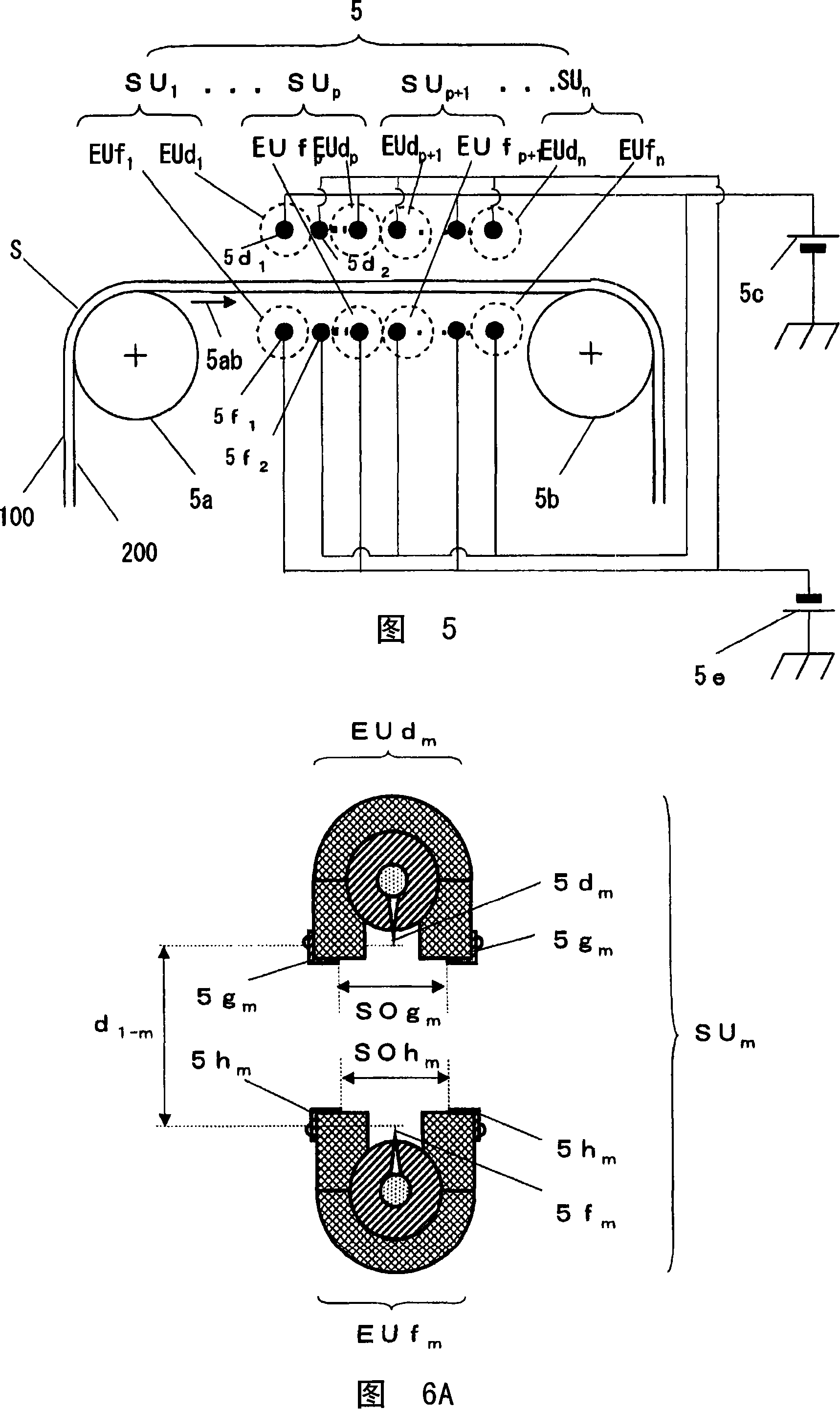
[0391] In the static elimination device 5 shown in FIG. 5 , a biaxially stretched polyethylene terephthalate film S (Lumira-38S28 manufactured by Toray Co., Ltd.; Film A-1) As an electrically insulating sheet S, the film S was moved at the speed u [unit: m / min] shown in Table 1. For the raw film A-1, as shown in FIG. 10 , periodic charging was performed at a period of 1.1 to 1.2 mm along the moving direction of the film S within a range of 10 mm in the width direction of the film S as shown in FIG. 10 .
[0392] Arrow TD in FIG. 10 indicates the width direction of the film S, and arrow MD indicates the moving direction of the film S. As shown in FIG. The distribution of the equilibrium potential on the back surface of the first surface of the periodically charged part (the AA' portion in FIG. 10 ) is shown in FIG. 11 , which is along the moving direction of the thin film S, centered at 0 V, and has an amplitude of 270 V (charges on each surface Density amplitude of 190μC / m 2...
Embodiment 2
[0420] In the static elimination device 5 shown in FIG. 5 , a biaxially stretched polyethylene terephthalate film S (Lumira-75T10 manufactured by Toray Co., Ltd., manufactured by Toray Co., Ltd. Film B and raw film C) were used as the electrical insulating sheet S, and the film S was moved at 300 m / min.
[0421] The raw film B is a film that is charged so that positive and negative charges are alternately arranged at a period of 5 mm along the moving direction of the film S on the first surface of the film S, and the absolute values of the positive and negative peaks of the equilibrium potential on the back surface Up to 560V (480 to 560V), i.e., the amplitude of the charge density is up to 396μC / m 2 (340 to 396μC / m 2 ), at the same position in the in-plane direction, the polarity of the first surface and the polarity of the second surface of the thin film S are opposite polarities, and the equilibrium potential of the first surface and the equilibrium potential of the seco...
Embodiment 3
[0429] Apply a positive voltage to the first ion generating electrode (apply negative voltage to the second ion generating electrode) from the most upstream (first) to the sixth static elimination unit in the moving direction of the film S, and the potential difference between the ion generating electrodes is positive, and the potential difference between the ion generating electrodes is positive. The seventh and eighth static elimination units were the same as in Example 2 except that a negative voltage was applied to the first ion generating electrodes (a positive voltage was applied to the second ion generating electrodes), and the potential difference between the ion generating electrodes was negative. Table 2 shows the results of static elimination evaluation of the raw film B and the raw film C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com