Patents
Literature
35 results about "Equilibrium potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Equilibrium potential. (Science: physiology) The membrane potential at which a particular type of ion or other particle does not diffuse through the membrane in either direction.
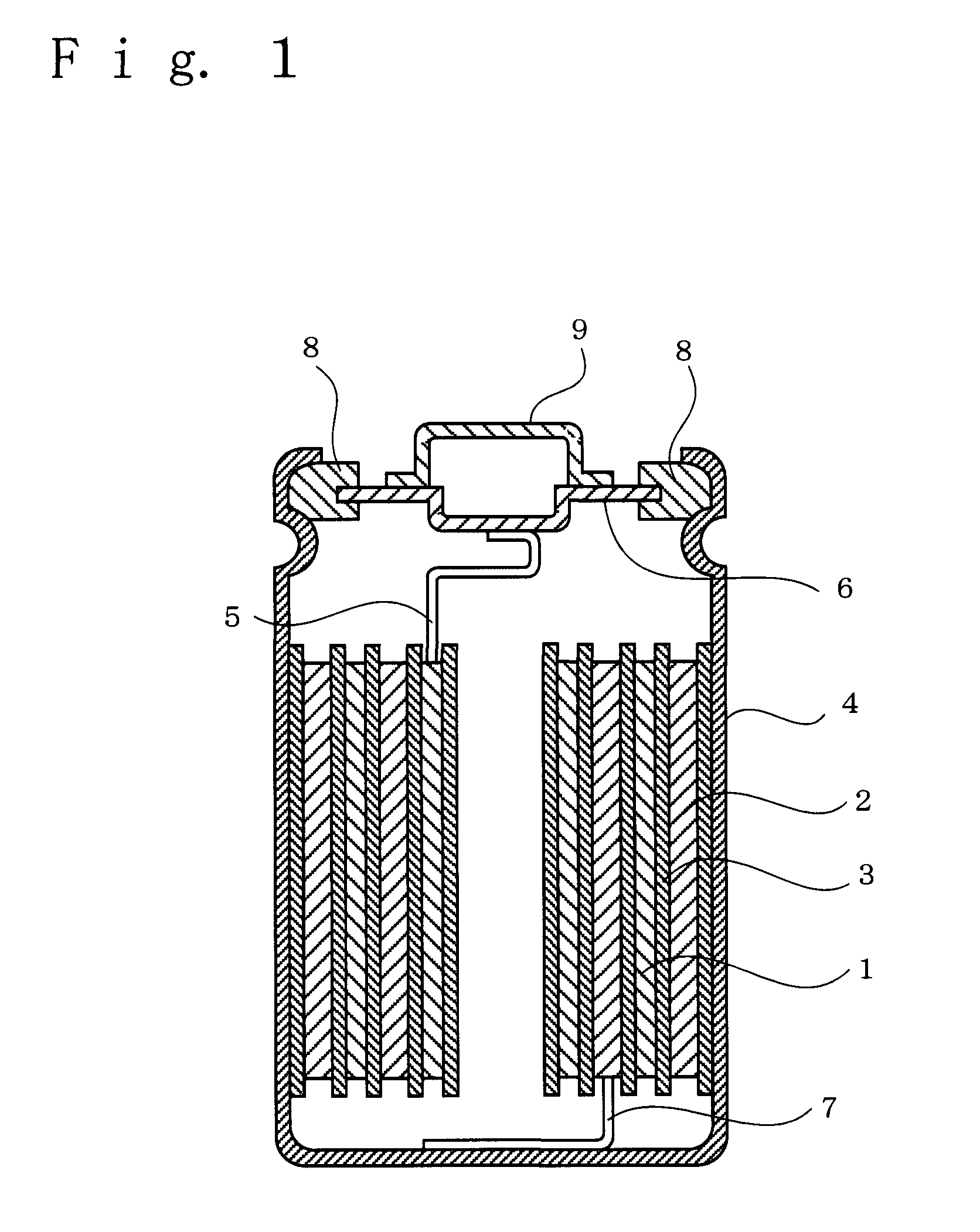
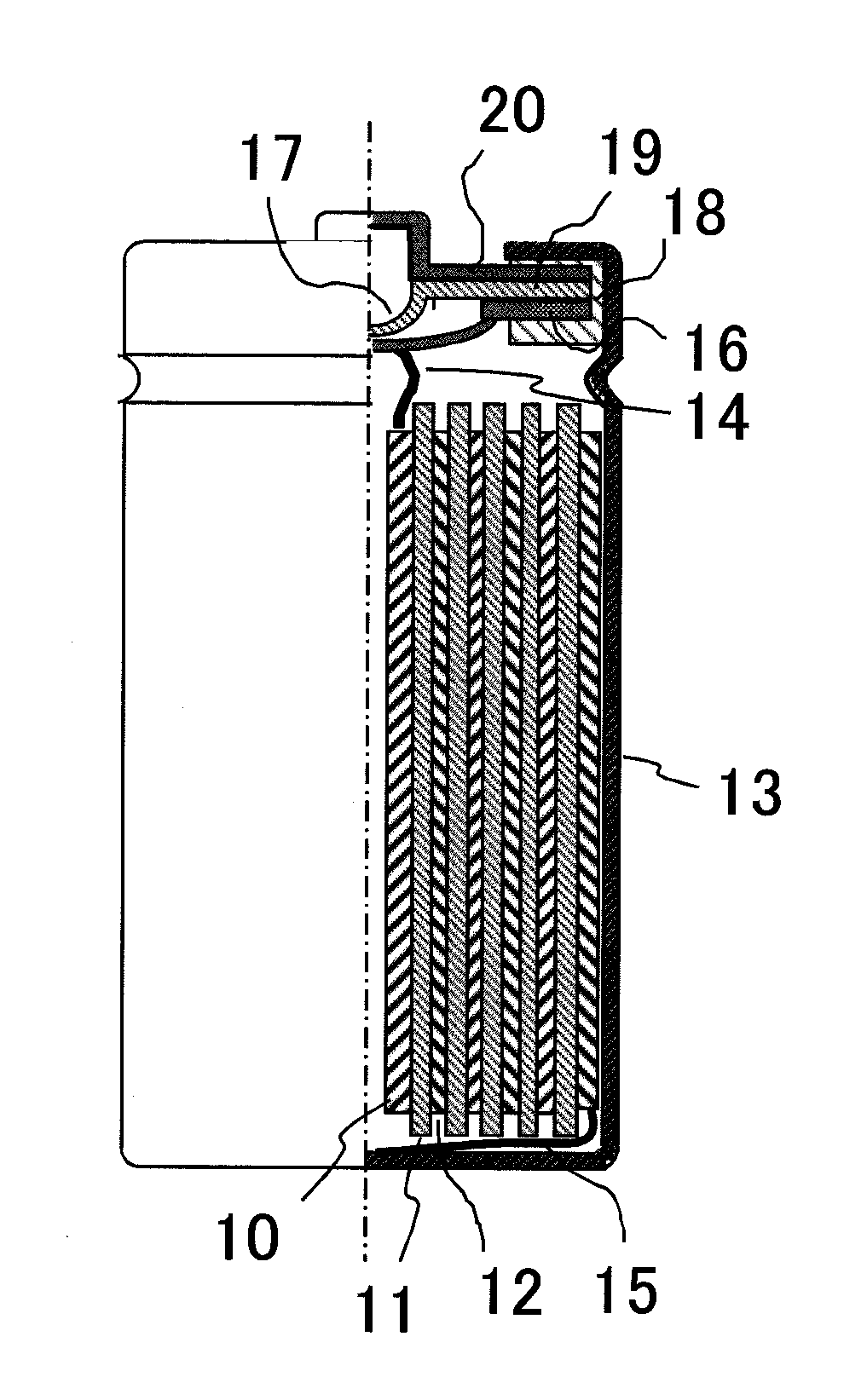
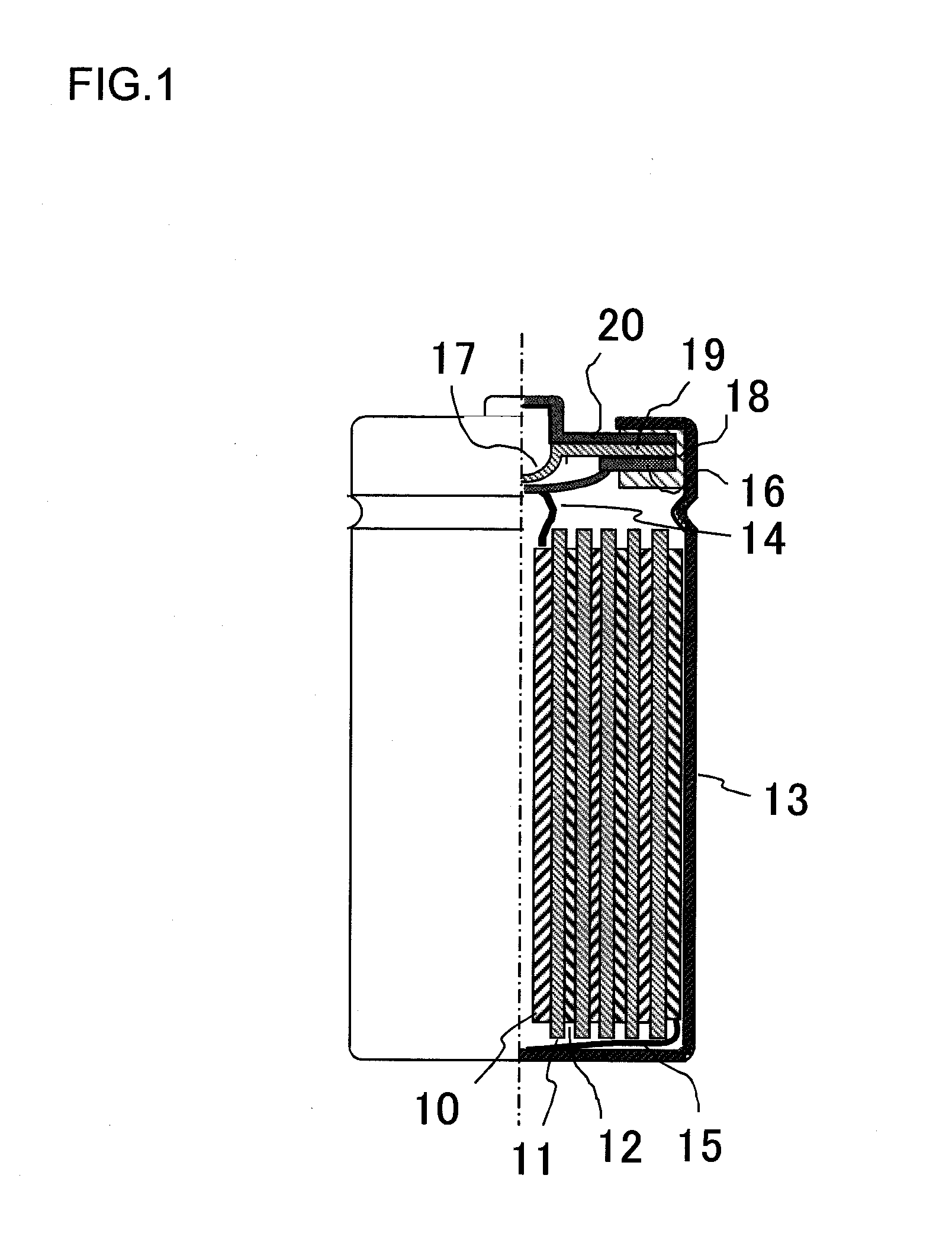
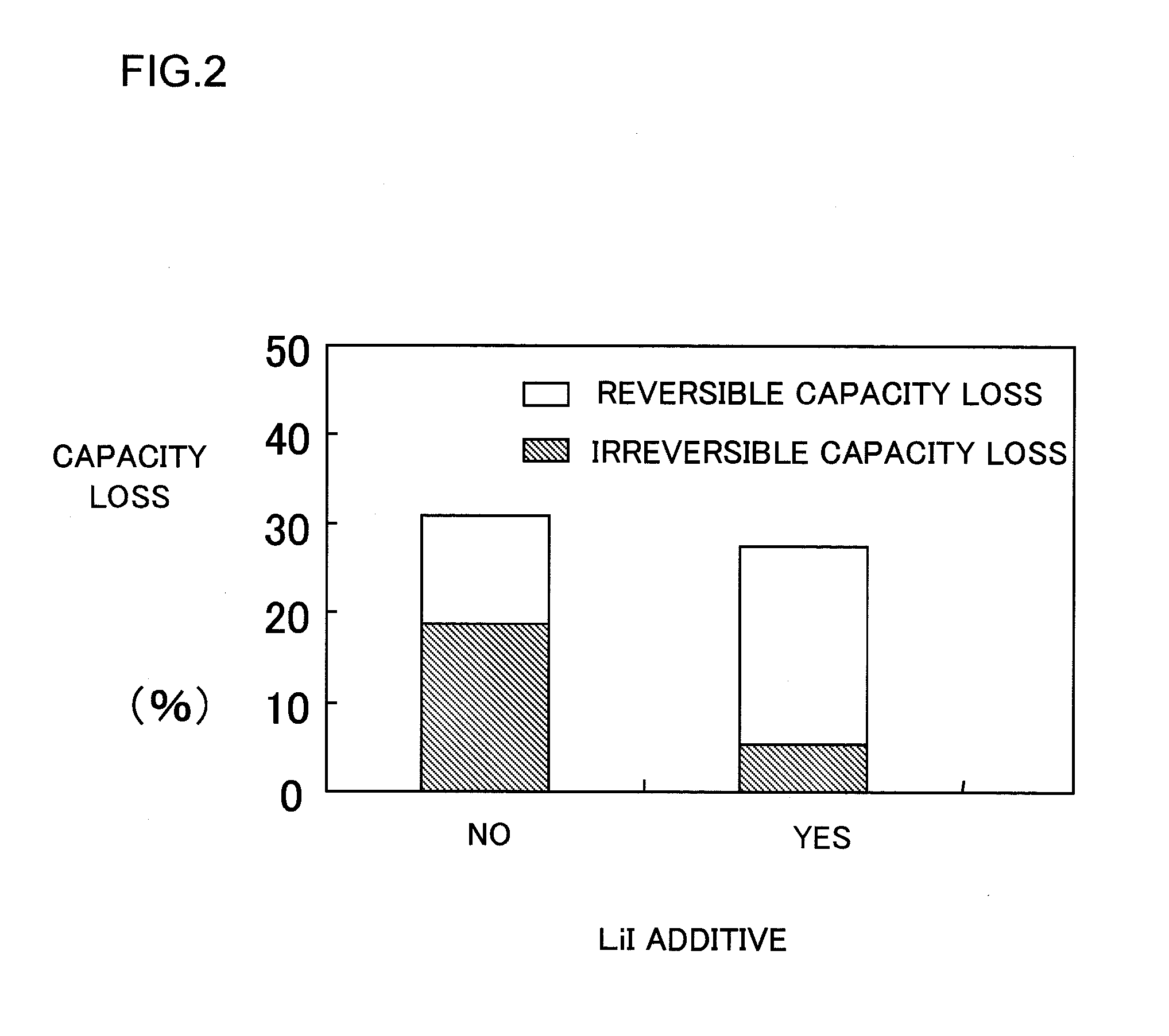
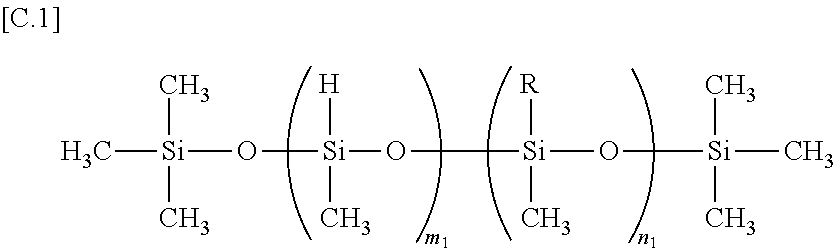
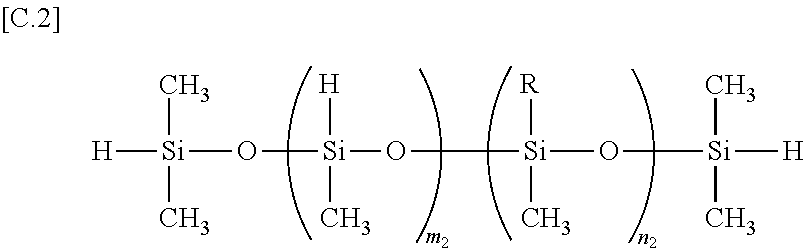
Non-aqueous electrolyte for secondary battery and non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
ActiveUS20100035162A1Inhibit excessive decompositionAvoid decompositionOrganic electrolyte cellsLi-accumulatorsEquilibrium potentialCarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery comprising a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a separator, and a non-aqueous electrolyte, wherein the non-aqueous electrolyte comprises a non-aqueous solvent and lithium salt as an electrolyte, and wherein the non-aqueous solvent contains chain fluorinated carboxylic acid ester represented by the formula CH3COOCH2CH3-xFx (wherein x is 2 or 3) and a film forming chemical decomposed in the range of +1.0 to 3.0 V based on an equilibrium potential between metal lithium and lithium ion.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Non-aqueous electrolyte for secondary battery and non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
ActiveUS8097368B2Decrease is limitedInhibitory responseOrganic electrolyte cellsLi-accumulatorsEquilibrium potentialCarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery comprising a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a separator, and a non-aqueous electrolyte, wherein the non-aqueous electrolyte comprises a non-aqueous solvent and lithium salt as an electrolyte, and wherein the non-aqueous solvent contains chain fluorinated carboxylic acid ester represented by the formula CH3COOCH2CH3-xFx (wherein x is 2 or 3) and a film forming chemical decomposed in the range of +1.0 to 3.0 V based on an equilibrium potential between metal lithium and lithium ion.
Owner:KANTO DENKA IND CO LTD +1
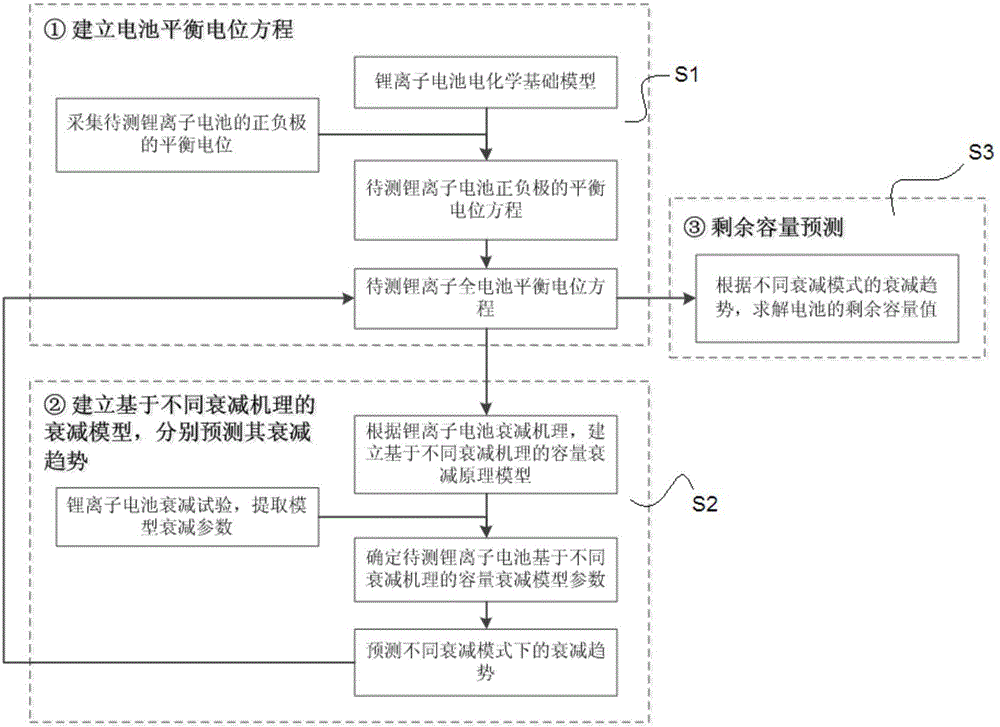
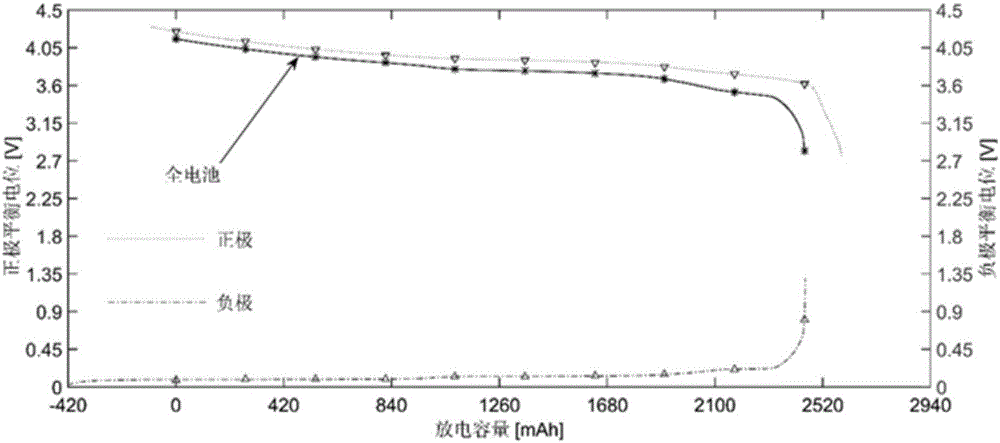
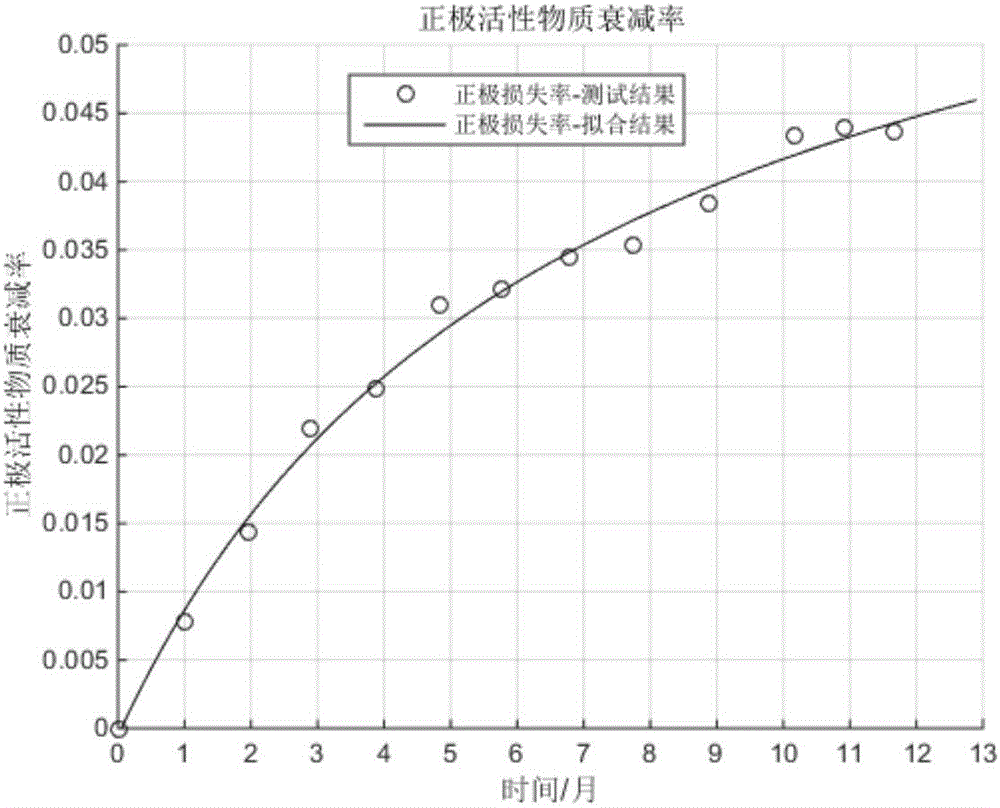
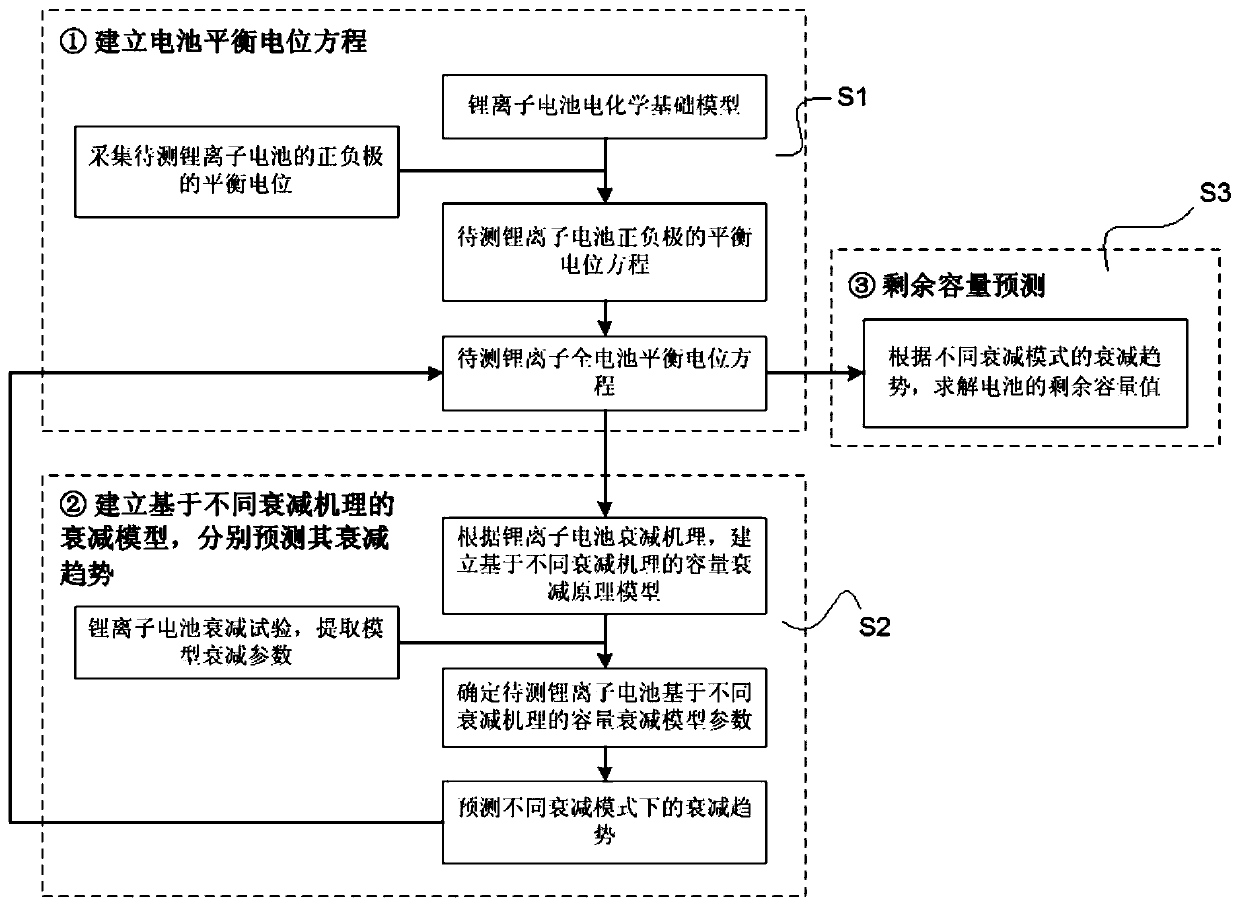
Method for forecasting service life of lithium ion battery based on capacity attenuation mechanism decomposition analysis
ActiveCN106383324AShrinkage test timeReduce test sampleElectrical testingEquilibrium potentialPredictive methods
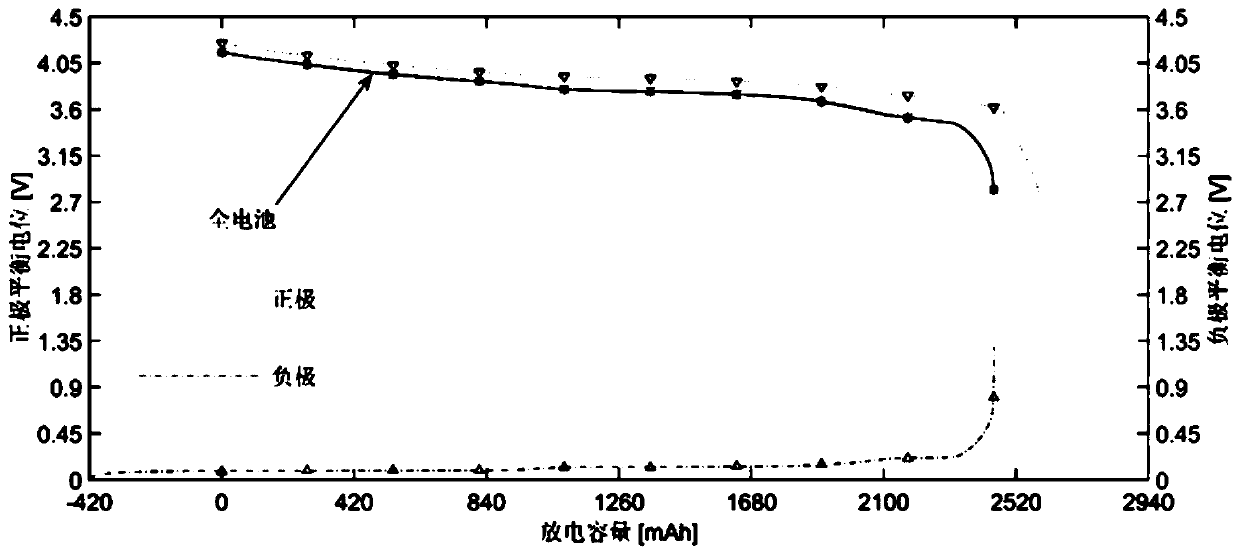
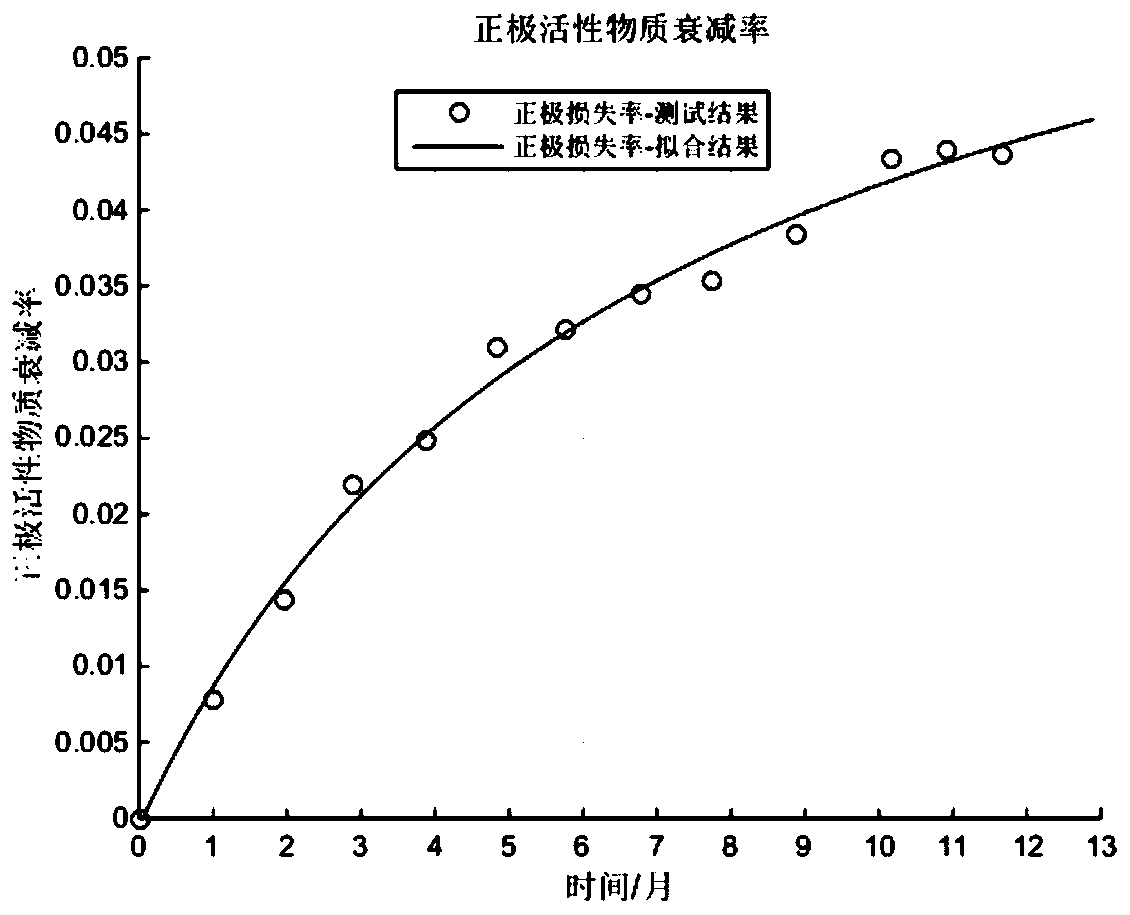
The invention discloses a method for forecasting service life of a lithium ion battery based on capacity attenuation mechanism decomposition analysis. The method comprises the following steps: step one, establishing an equilibrium potential equation of a lithium ion battery to be tested by subtracting equilibrium potentials of positive and negative electrodes with combination of test data of the lithium ion battery to be tested, and then carrying out polarization modification to obtain the equilibrium potential equation; step two, establishing a multi-attenuation-mode decomposition model based on different attenuation mechanisms of the lithium ion battery, establishing a multi-attenuation-mode fitting equation of the lithium ion battery to be tested through a short-term aging test and forecasting attenuation trend; and step three, substituting a forecasting result of the multi-attenuation-mode fitting equation into the equilibrium potential equation of the lithium ion battery to be tested, and forecasting residual capacity. Through the service life forecasting method for carrying out decomposition analysis of different attenuation modes based on different capacity attenuations of the lithium ion battery, the problem that simple extrapolation is carried out according to the experiment test data or the attenuation of the service life of the lithium ion battery is simply ascribed to the single electrochemical mechanism is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI POWER ENERGY STORAGE BATTERY SYST ENG TECH +1
Electrochemical detection method for corrosion degree of steel reinforcing bar in concrete
InactiveCN102706933AReduce disturbanceEasy and fast testingMaterial electrochemical variablesEquilibrium potentialPower flow
The invention discloses an electrochemical detection method for the corrosion degree of a steel reinforcing bar in concrete. The electrochemical detection method comprises the following steps of: (1) respectively and correspondingly connecting the steel reinforcing bar, a counter electrode and a reference electrode which are arranged in a concrete sample with an electrochemical workstation to form a three-electrode testing system; (2) opening the electrochemical workstation for carrying out polarization test and recording anodic polarization current at the ending moment of the polarization; (3) calculating the corrosion current density icorr of the steel reinforcing bar; and (4) comparing the corrosion current density icorr of the steel reinforcing bar, which is calculated in the third step, with an internal standard value to judge whether the steel reinforcing bar is corroded or not. According to the method for determining the corrosion current density of the steel reinforcing bar in the concrete, an equilibrium potential is used as an initial polarization potential; according to the polarization mode, the distorsion of the measured polarization curve is avoided; an polarization potential amplitude is reasonable, so that the disturbance on the steel reinforcing bar is smaller; subsequent fitting processing for test data is avoided; the simplicity, convenience and quickness in test are realized; and the electrochemical detection method is suitable for engineering application.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and system for detecting single electrode potential of battery
ActiveCN104391159AEasy to measureImprove accuracyCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical testingEquilibrium potentialElectrode potential
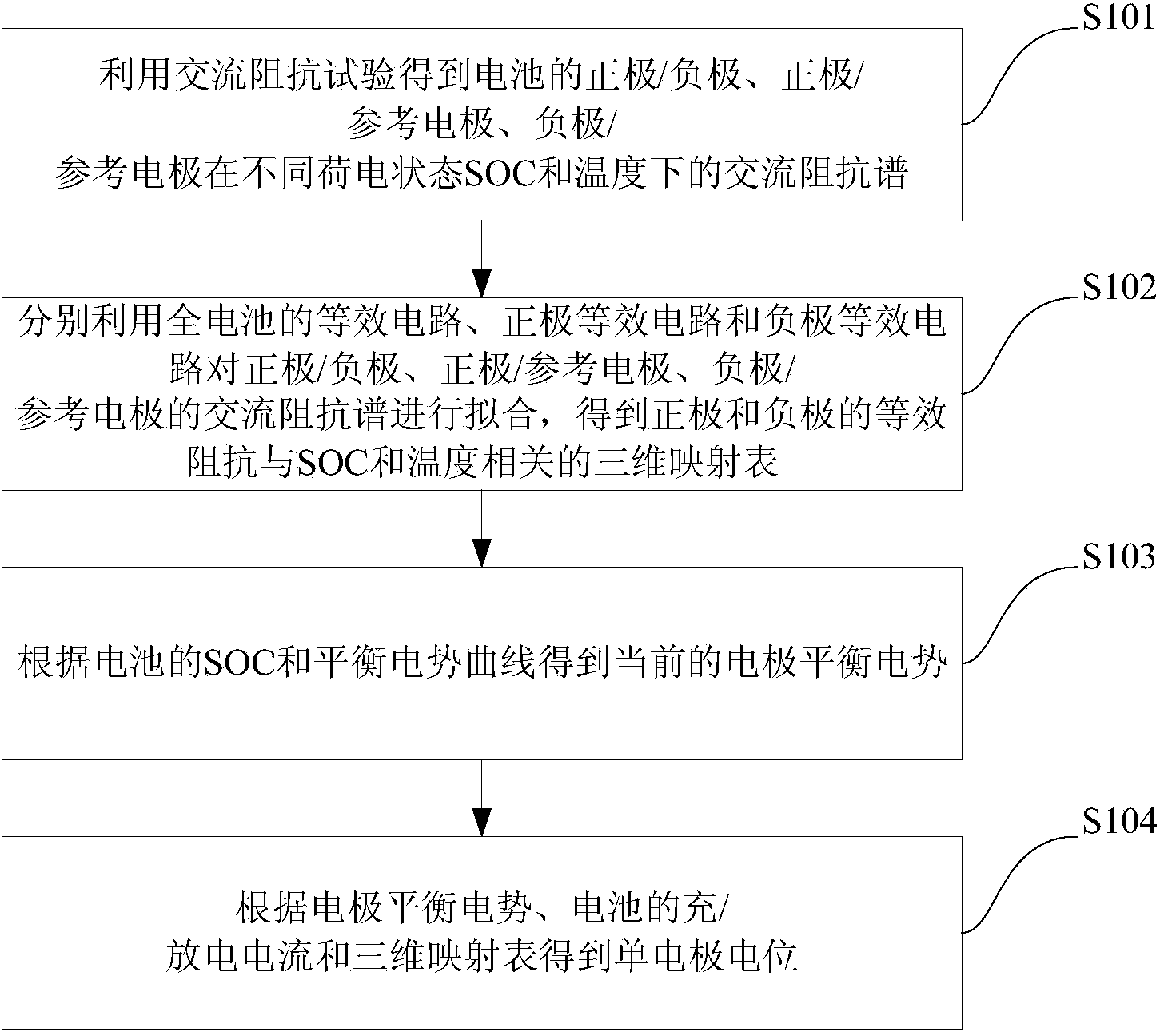
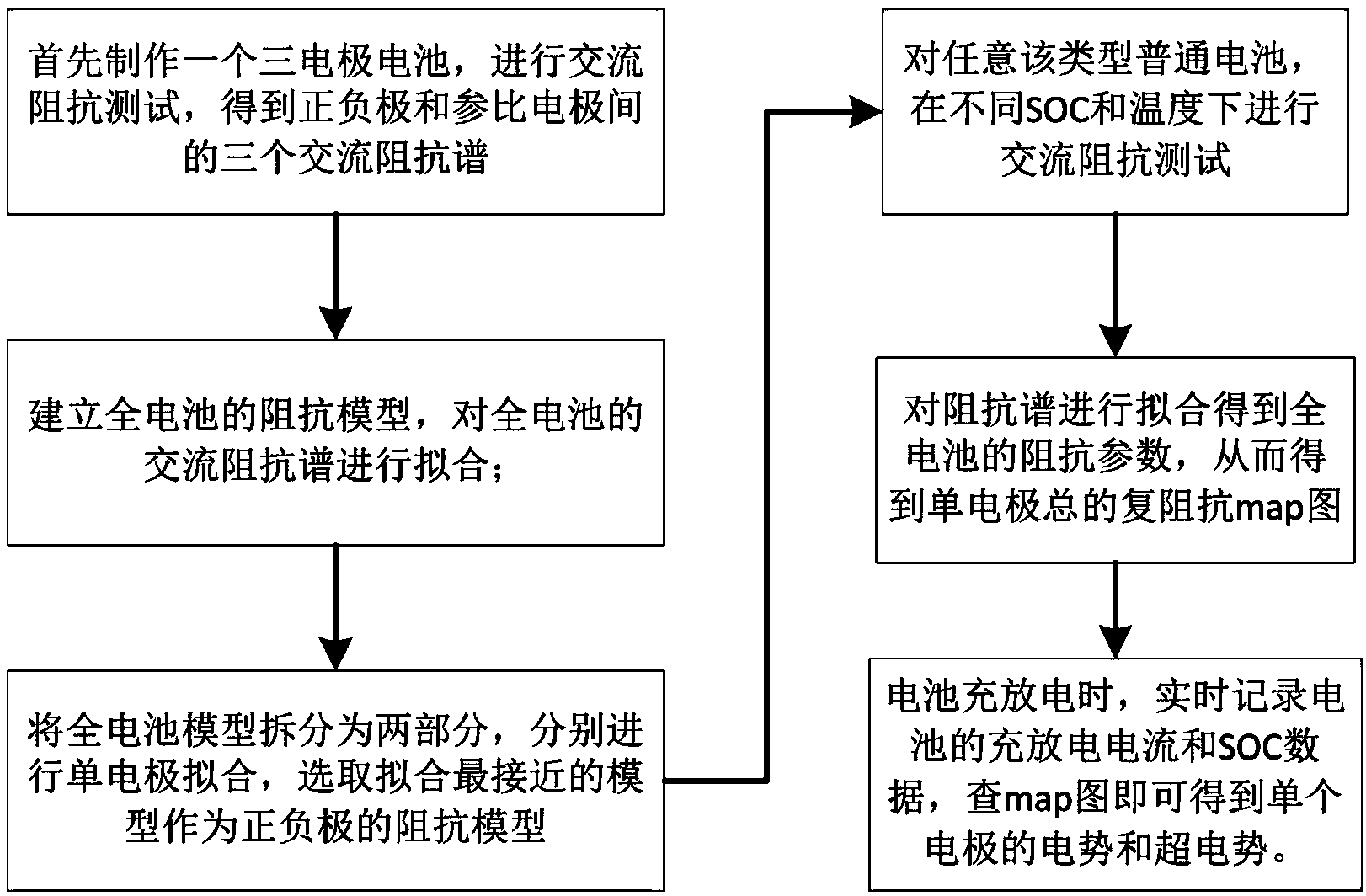
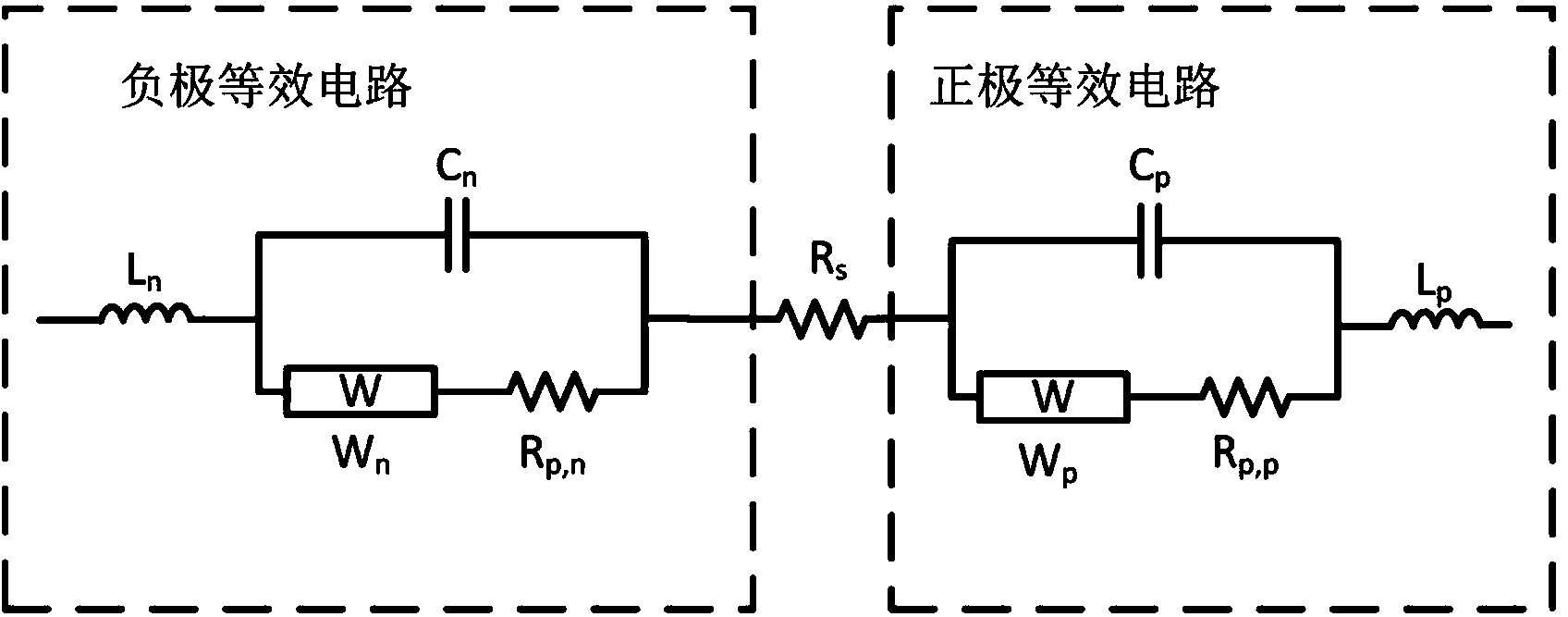
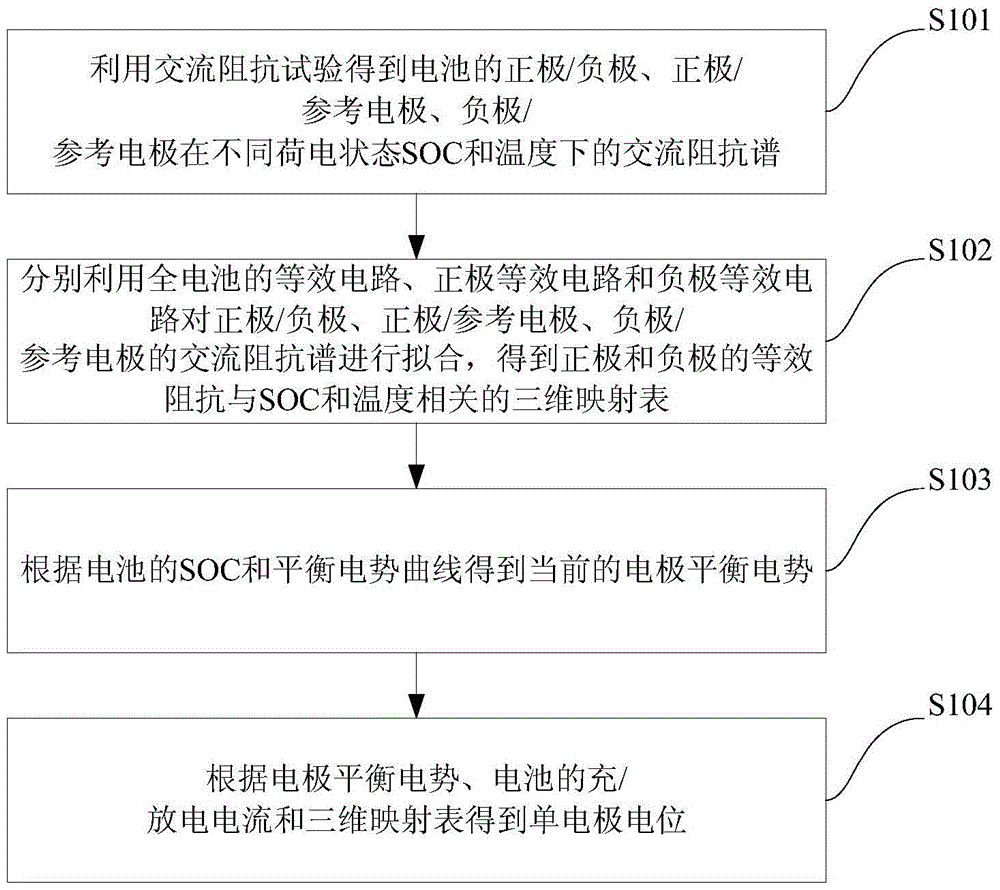
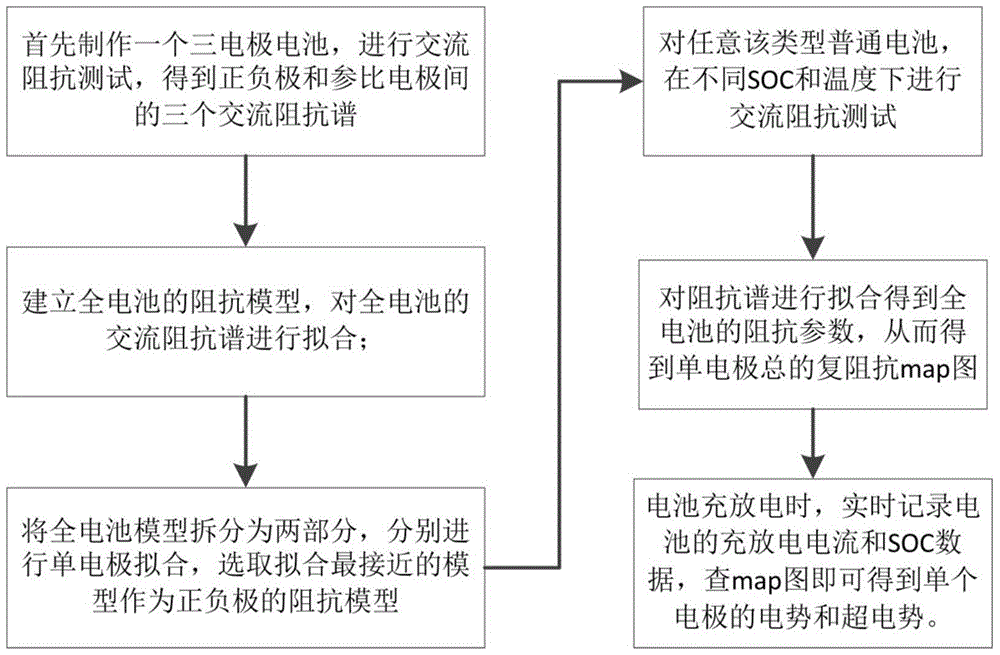
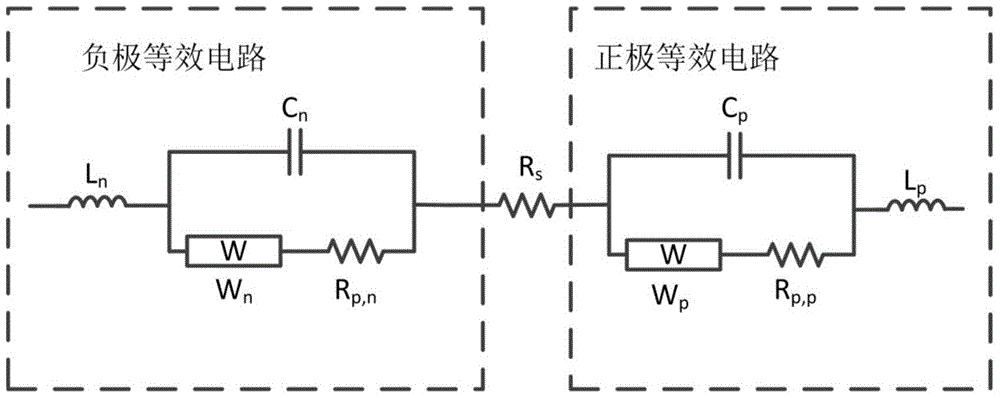
The invention discloses a method for detecting single electrode potential of a battery. The method comprises the following steps: an AC impedance test is used for acquiring AC impedance spectrums of a positive electrode / negative electrode, a positive electrode / reference electrode and a negative electrode / reference electrode of the battery in different states of charge (SOC) and at different temperatures; an equivalent circuit, a positive electrode equivalent circuit and a negative electrode equivalent circuit of the total battery are respectively used to fit the AC impedance spectrums of the positive electrode / negative electrode, the positive electrode / reference electrode and the negative electrode / reference electrode, and a related three-dimensional mapping table between equivalent impedance of the positive electrode and the negative electrode and the SOC and the temperature is obtained; the current electrode equilibrium potential is obtained according to the SOC of the battery and a equilibrium potential curve; and the single electrode potential is obtained according to the electrode equilibrium potential, charging / discharging current sum of the battery and the three-dimensional mapping table. The electrode potential of a common battery can be directly and conveniently measured, and accuracy of the measurement result is improved. The invention also provides a system for detecting single electrode potential of a battery.
Owner:BEIJING KEY POWER TECH
Multilayer conductive film, current collector using same, battery and bipolar battery
ActiveUS9601780B2Disadvantageous spaceDisadvantageous weightFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsElectrode potentialEquilibrium potential
A multilayer conductive film includes a layer 1 including a conductive material containing a polymer material 1 having an alicyclic structure and conductive particles 1 and a layer 2 including a material having durability against positive electrode potential. The multilayer conductive film has stability in an equilibrium potential environment in a negative electrode and stability in an equilibrium potential environment in a positive electrode, has low electric resistance per unit area in the thickness direction, and has excellent barrier properties for a solvent of an electrolytic solution. A battery including a current collector employing the multilayer conductive film can achieve both weight reduction and durability.
Owner:KANEKA CORP +1
Lithium ion secondary battery
InactiveUS20110027662A1Loss of capacityCapacity lossSolid electrolyte cellsLi-accumulatorsEquilibrium potentialLithium
A lithium ion secondary battery includes: a cathode that stores / releases lithium ion at a potential not lower than an oxidation-reduction equilibrium potential between halogen ion and halogen; an anode that stores / releases lithium ion, preferably containing carbon; and a non-aqueous electrolytic solution composed of a non-aqueous solvent having dissolved therein an electrolyte. The non-aqueous electrolytic solution contains lithium halide or a halogen molecule. Instead of the non-aqueous electrolytic solution, a polymer solid electrolyte containing lithium halide or halogen molecule may be used.
Owner:HITACHI VEHICLE ENERGY
High concentration zinc and vanadium redox cell
The invention discloses a high concentration zinc and vanadium redox cell. According to the invention, the novel zinc vanadium oxidation reduction cell is characterized in that a vanadium ion solution is taken as an anode active substance, zinc and a zinc ion solution are taken as an cathode active substance, wherein the equilibrium potential is 1.76 V under a standard state, the open-circuit voltage is 1.7 - 2.0 V under a charging state. The vanadium ions of the vanadium ion solution are existed as quintavalence and quadrivalence (V(I), V(IV)), and the total vanadium concentration can reach to 4.0 mol / L, a solvent is inorganic acid or organic acid. The zinc ion solution is a zinc ion electrolyte containing organic acid or inorganic acid. The organic acid is methanesulfonic acid or sulfamic acid. The inorganic acid is sulfuric acid or nitric acid. The high energy concentration redox cell can be exploited according to the invention.
Owner:周成壁
Multilayer conductive film, current collector using same, battery and bipolar battery
ActiveUS20140186699A1Decrease in battery performanceHigh output densityFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsEquilibrium potentialElectrical resistance and conductance
A multilayer conductive film includes a layer 1 including a conductive material containing a polymer material 1 having an alicyclic structure and conductive particles 1 and a layer 2 including a material having durability against positive electrode potential. The multilayer conductive film has stability in an equilibrium potential environment in a negative electrode and stability in an equilibrium potential environment in a positive electrode, has low electric resistance per unit area in the thickness direction, and has excellent barrier properties for a solvent of an electrolytic solution. A battery including a current collector employing the multilayer conductive film can achieve both weight reduction and durability.
Owner:KANEKA CORP +1
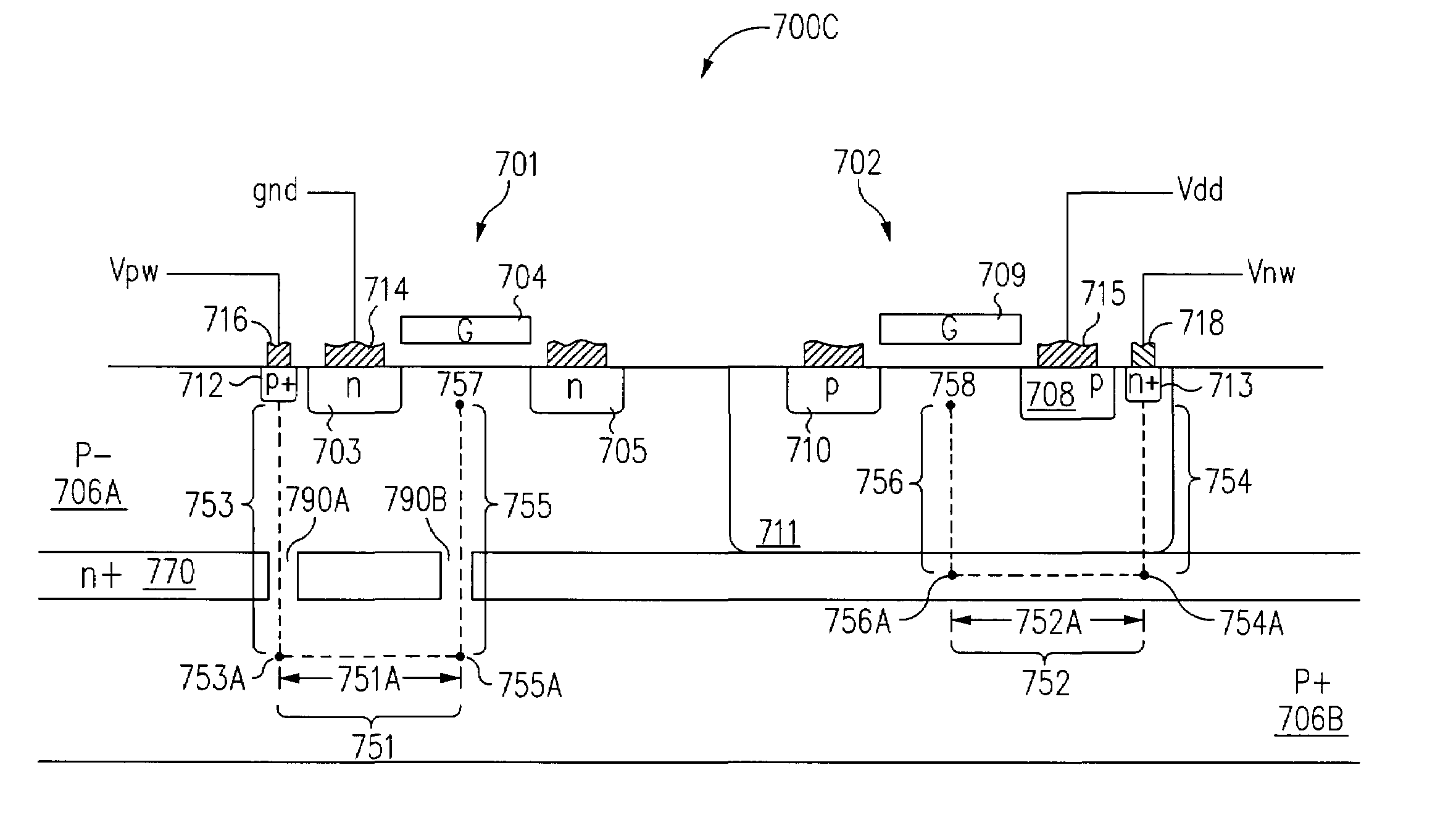
Device including a resistive path to introduce an equivalent RC circuit
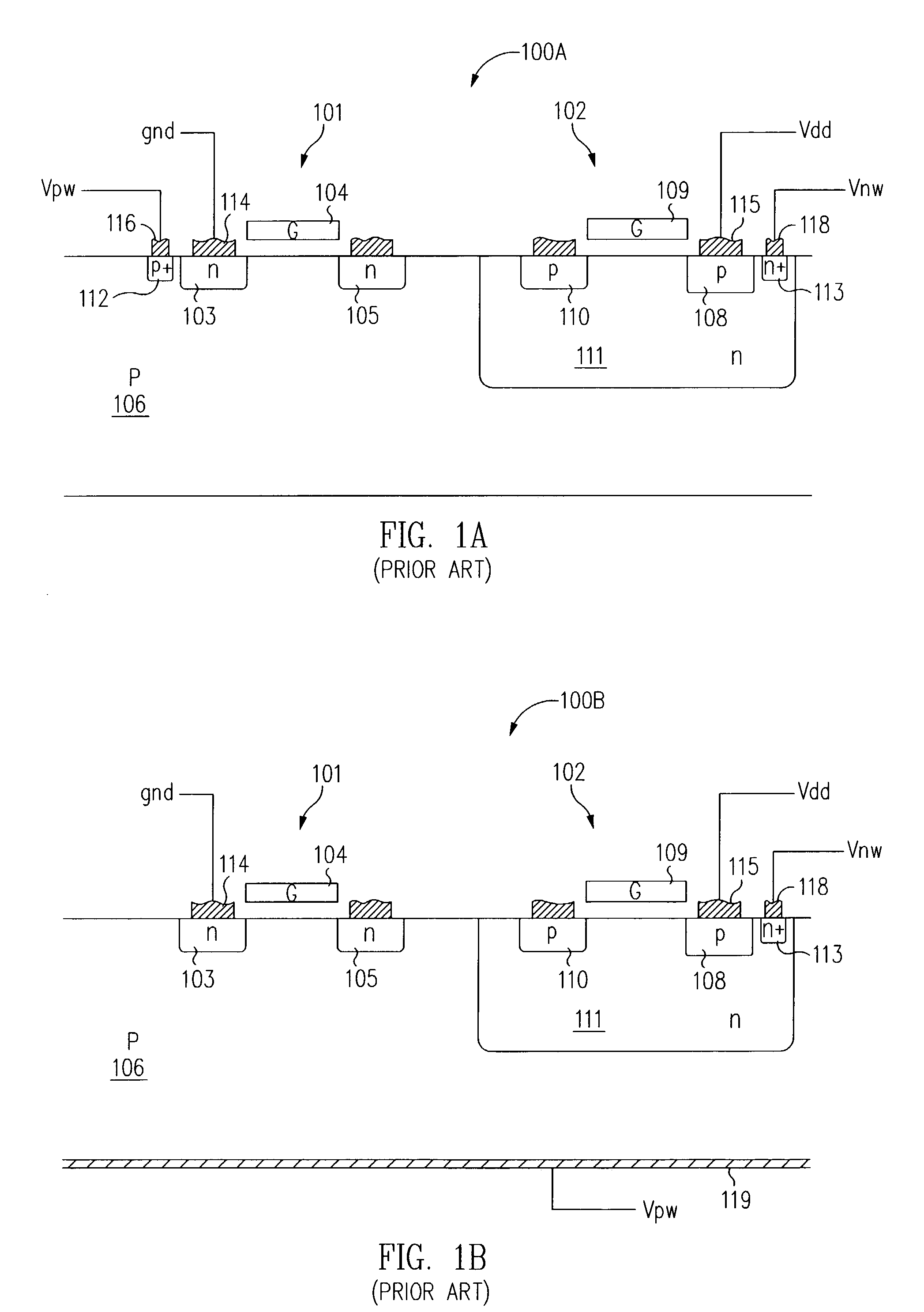
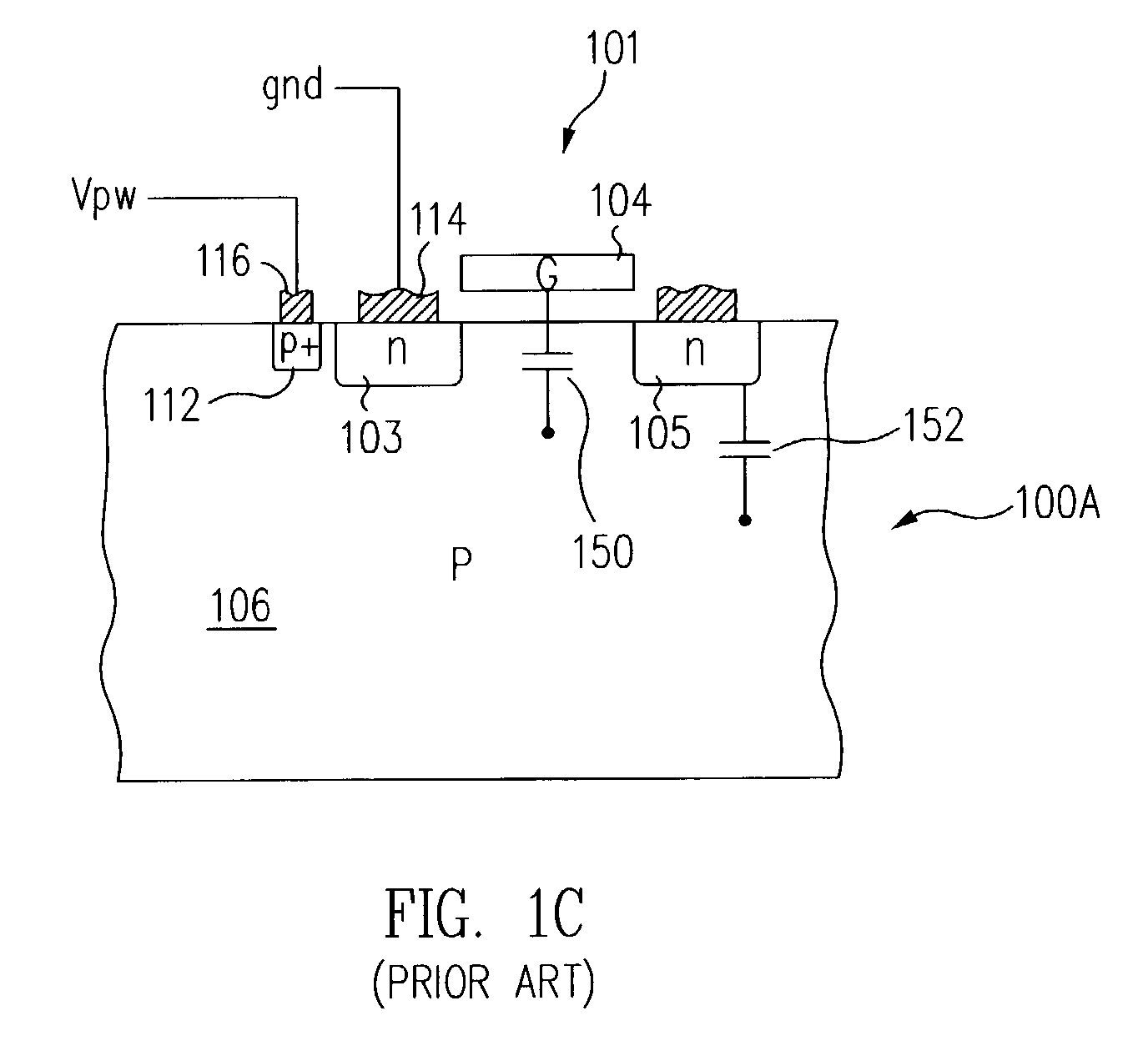
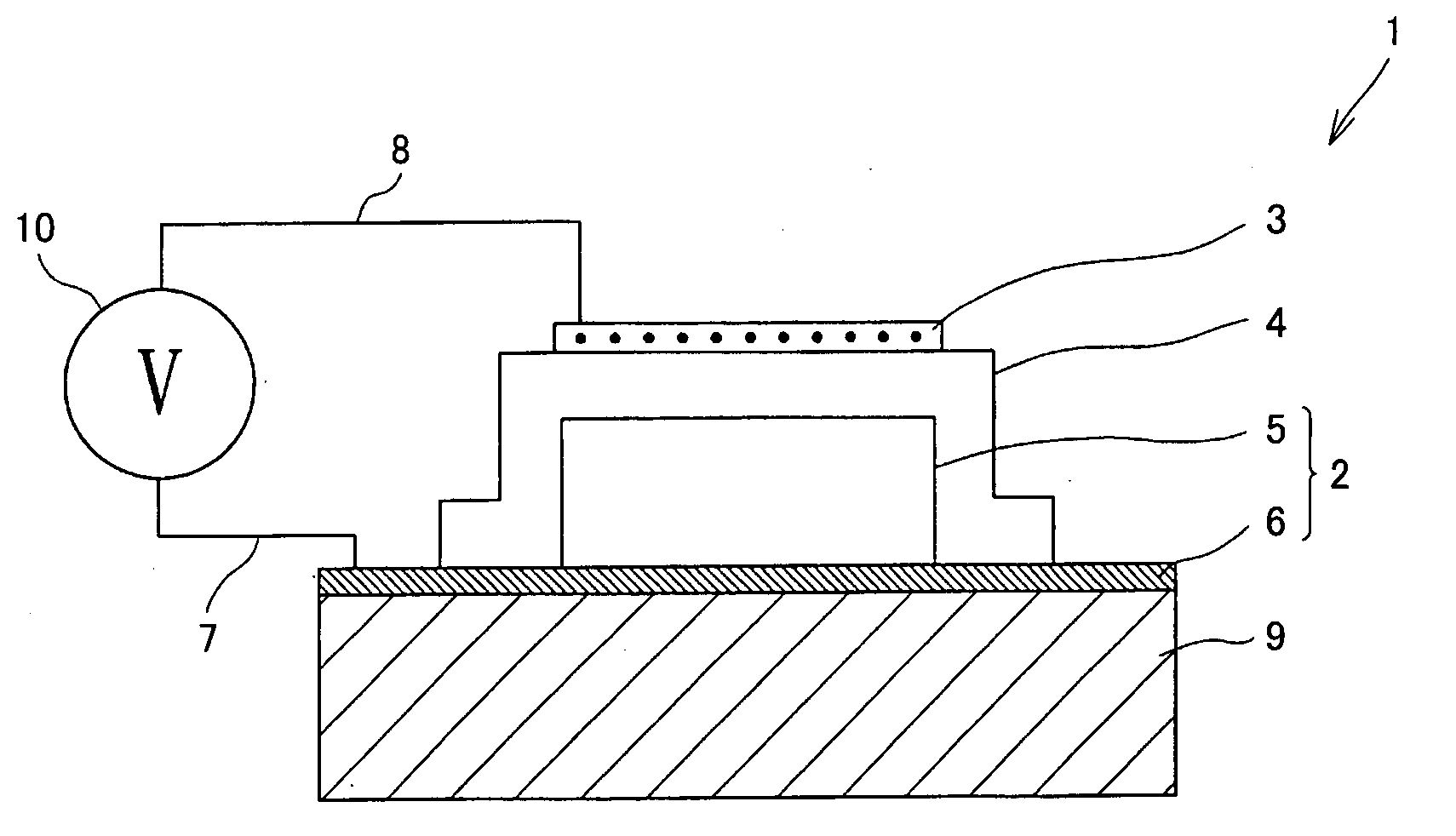
InactiveUS6965151B2Lower threshold voltageRaise the threshold voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceEquilibrium potential
Structures for providing devices that include resistive paths specifically designed to provide a predetermined resistance between the bulk material of the device and a well tie contact. By providing a resistive path, an equivalent RC circuit is introduced to the device that allows the bulk material potential to track the gate potential, thereby advantageously lowering the threshold voltage as the device turns on and raising the threshold voltage as the device turns off. In addition, the introduction of the resistive path also allows the bulk material potential to be controlled and stabilize at an equilibrium potential between switching events.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
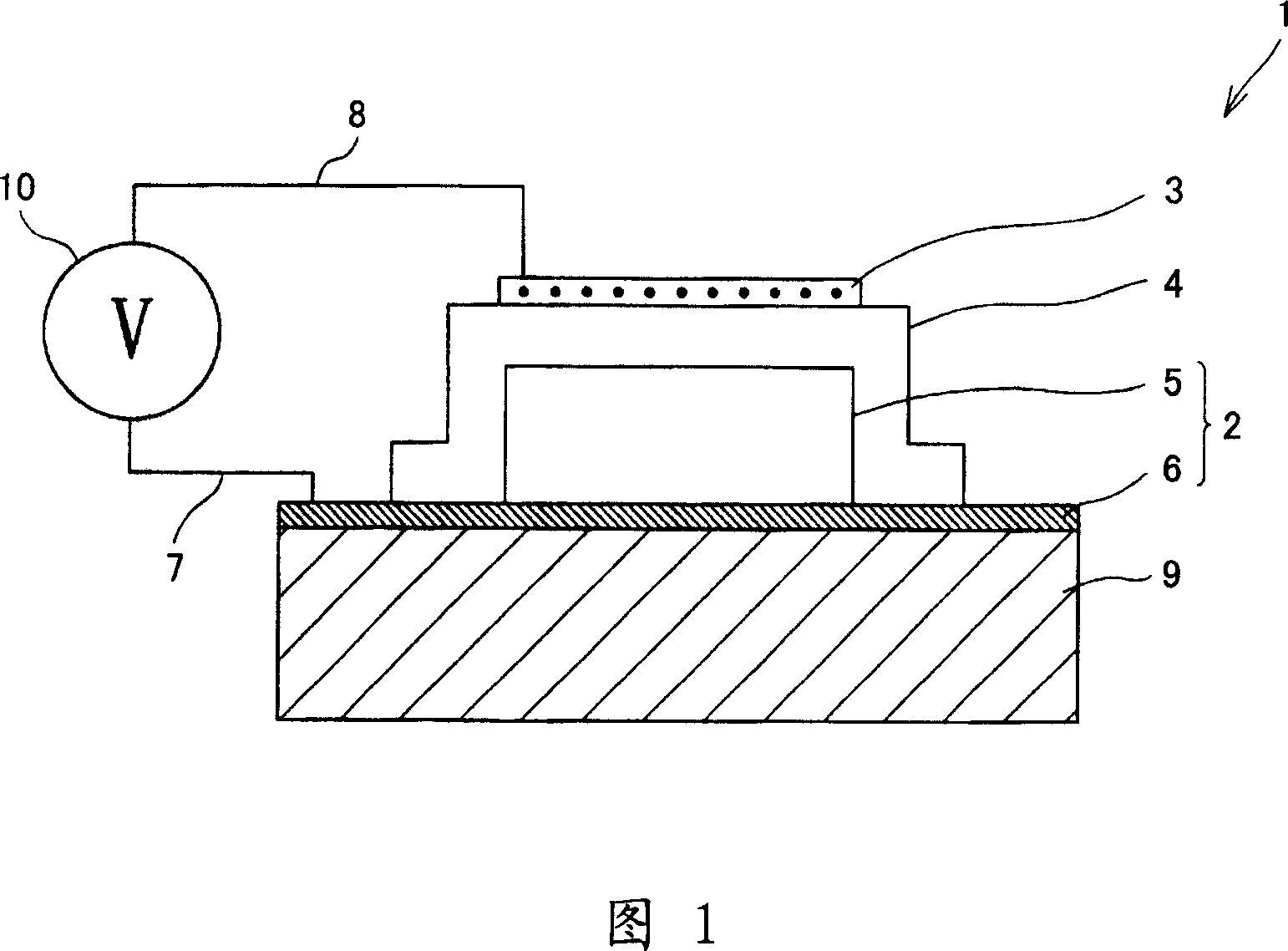
Gas sensor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080053827A1Improve stabilityHigh responsibilityLine/current collector detailsGas analyser construction detailsEquilibrium potentialLithium
With a gas sensor comprising a structure including a reference pole having a reference material and an electronic conductive material and a sensing pole having a sensing material and an electronic conductive material provided through a solid electrolyte in which the said solid electrolyte, the said reference material and the said sensing material are constituted of lithium ionic conductors and a method of manufacturing the same, an equilibrium potential gas sensor employing a solid electrolyte operable at a low temperature not more than 200° C., particularly at the room temperature, not influenced by moisture or the like and excellent in age-based stability with high measurement sensitivity as well as high responsibility and a method of manufacturing the same can be provided.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method for evaluating secondary battery
InactiveUS20110074430A1Ensure correct executionReduced measurement timeFinal product manufactureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEquilibrium potentialDiffusion
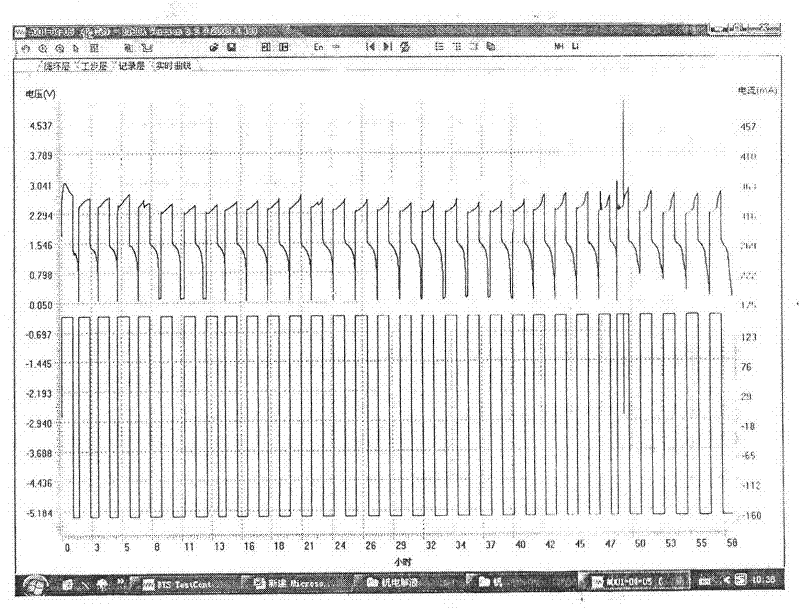
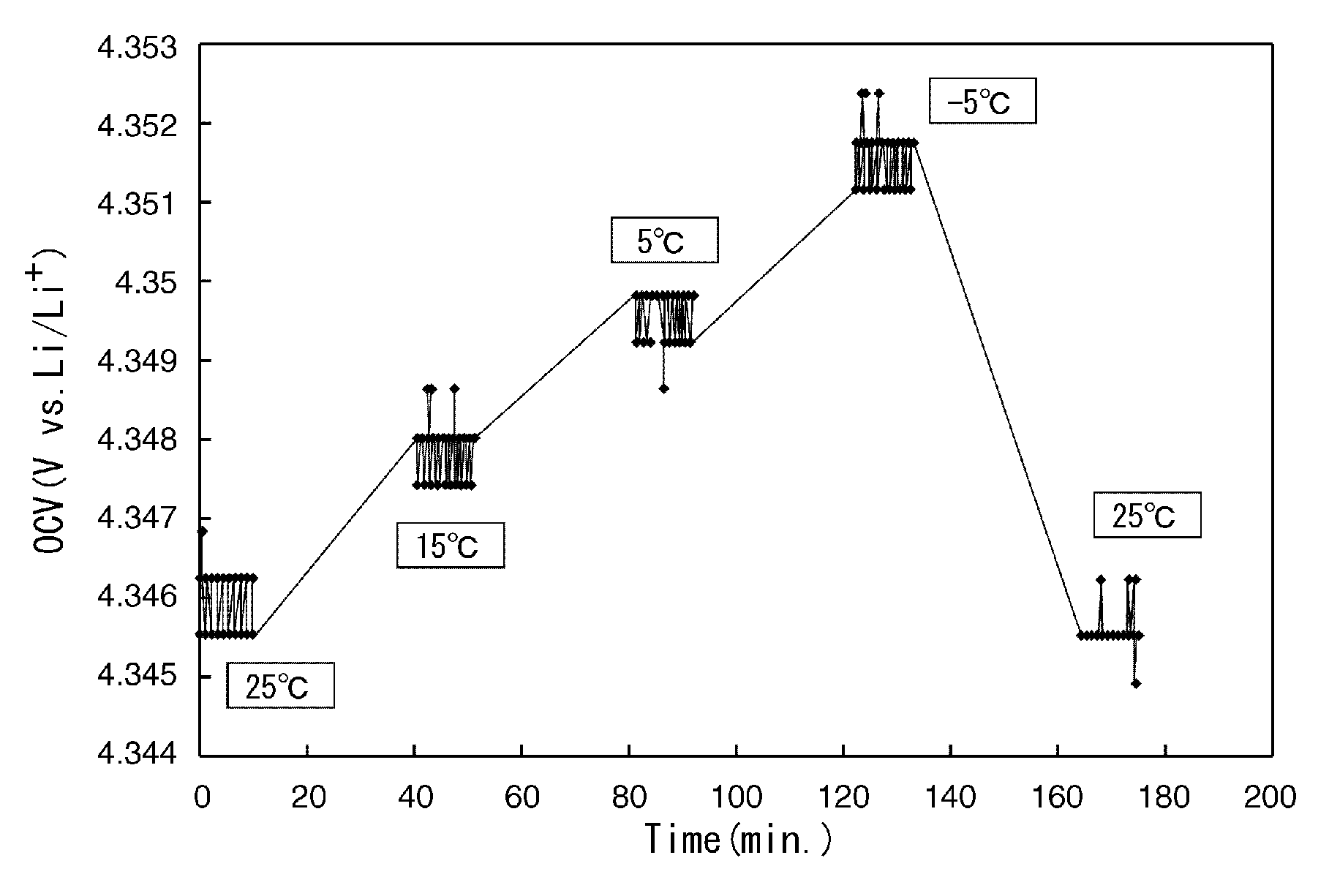
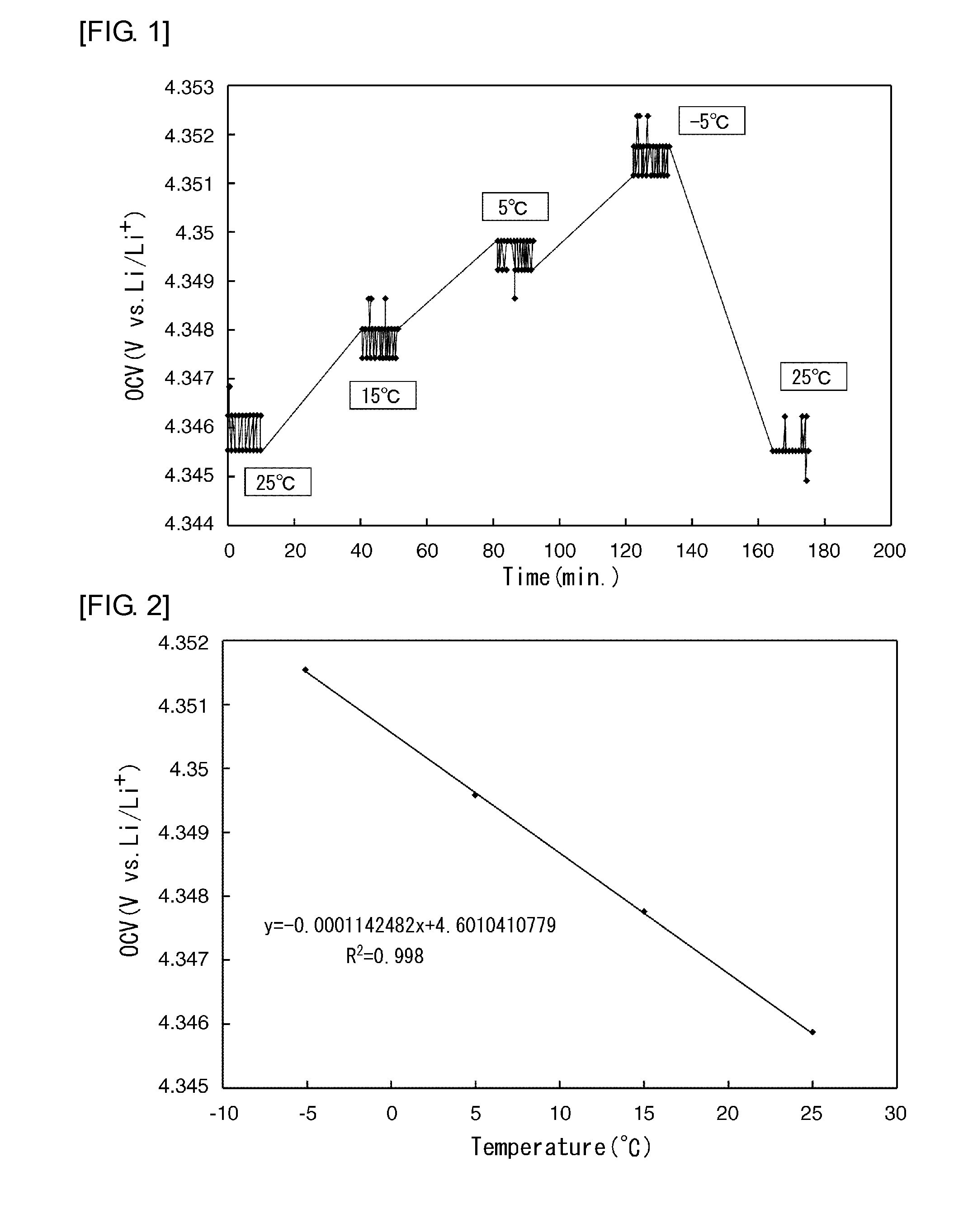
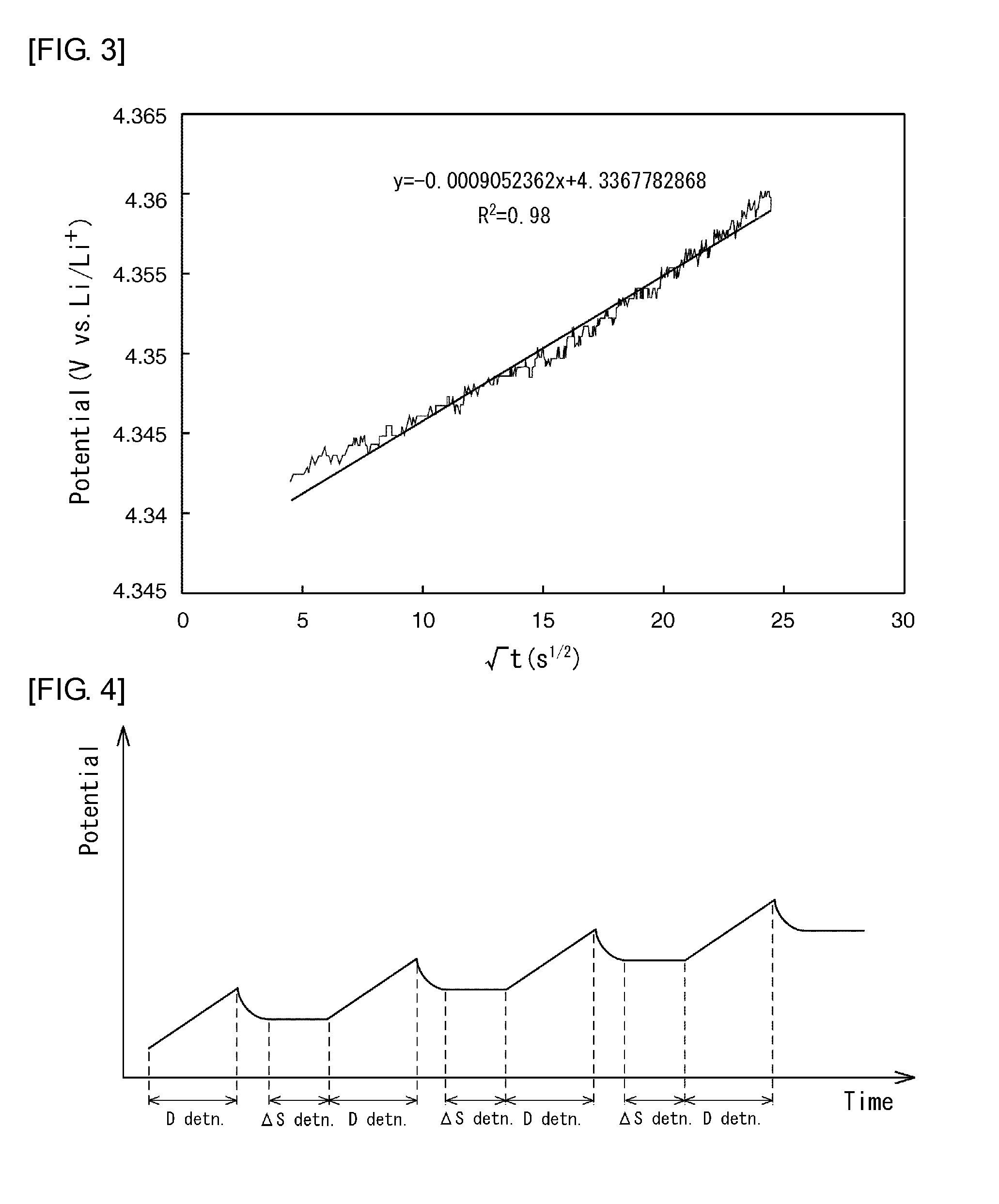
A method for evaluating a secondary battery includes repeatedly performing: an open circuit voltage measurement step of measuring the open circuit voltage of the secondary battery to be evaluated at each of a plurality of temperatures; a potential change measurement step of measuring, after the open circuit voltage measurement step, the potential change in the secondary battery while changing the state of charge of the secondary battery; and an equilibrium potential measurement step of measuring the equilibrium potential of the secondary battery after the potential change measurement step. An entropy variation in each of the different states of charge is calculated based on the open circuit voltages at the plurality of temperatures measured in the state of charge, and a chemical diffusion coefficient in each of the different states of charge is calculated based on the equilibrium potential of the secondary battery and the potential change in the secondary battery both measured in the state of charge. The secondary battery is evaluated based on the entropy variations and the chemical diffusion coefficients in the different states of charge.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Semiconductor structure and process thereof
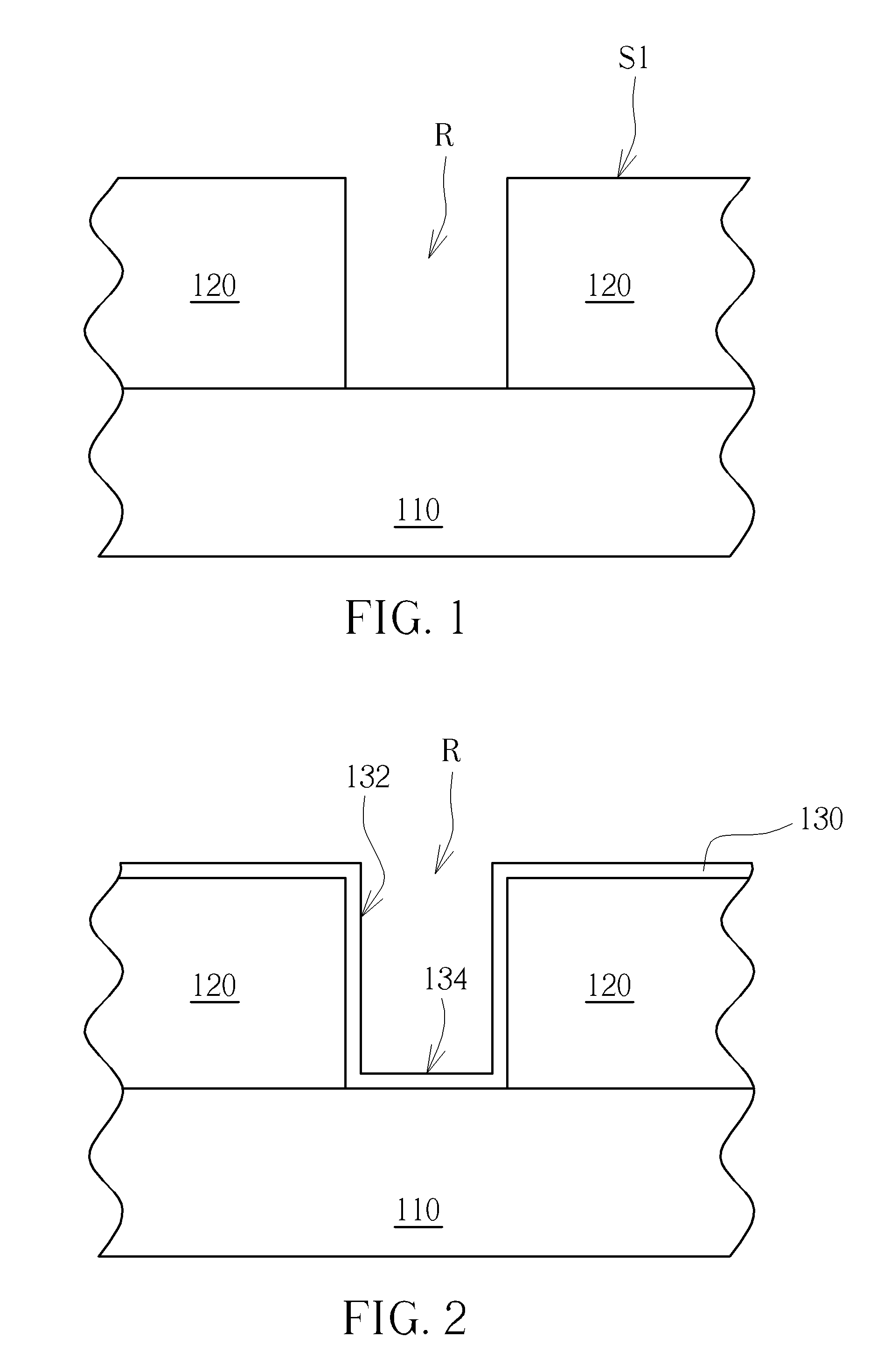
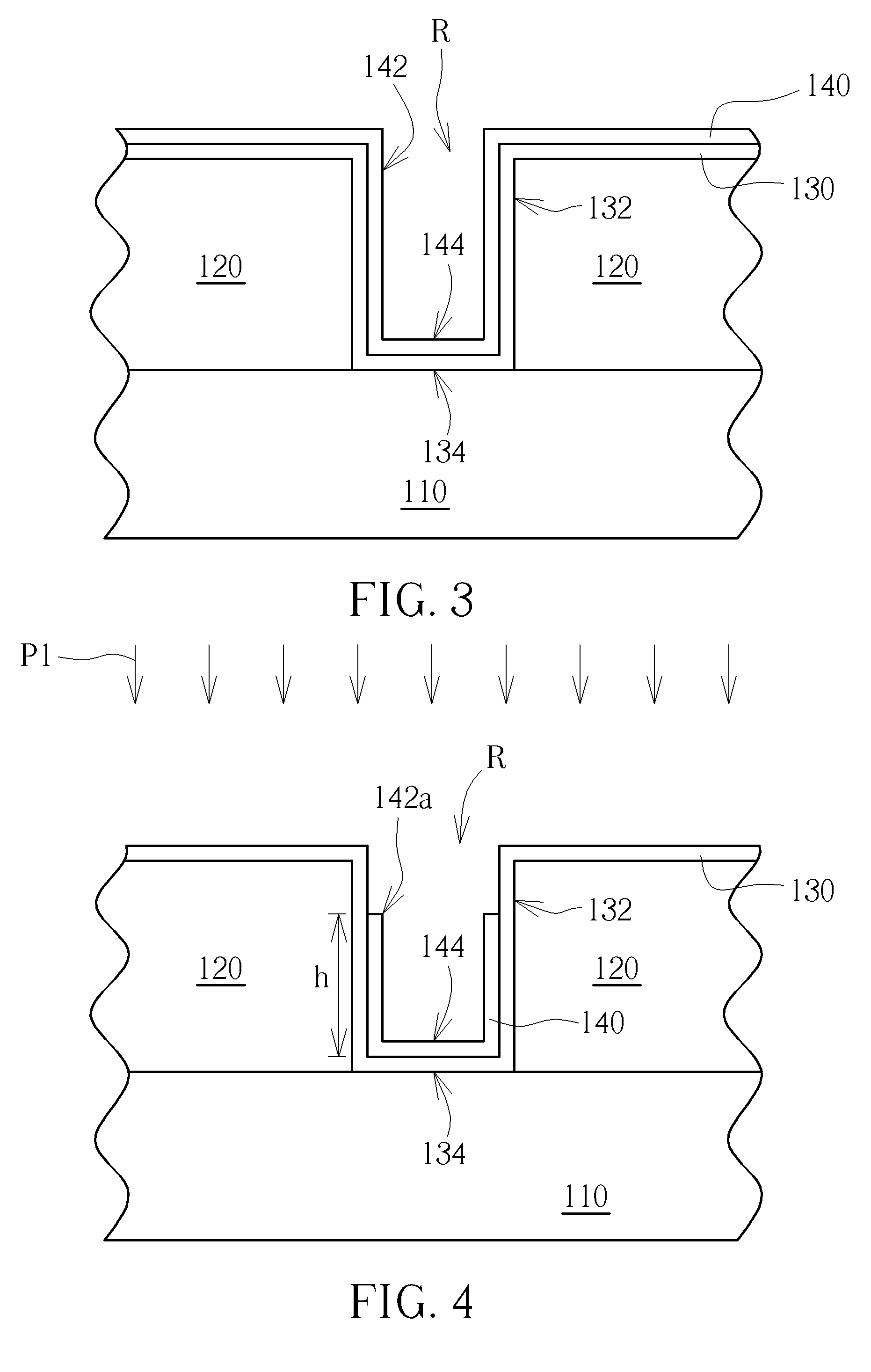
InactiveUS20160336269A1Easy to fillReduce galvanic corrosionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEquilibrium potentialSemiconductor structure
A semiconductor process includes the following steps. A dielectric layer having a recess is formed on a substrate. A barrier layer is formed to cover the recess, thereby the barrier layer having two sidewall parts. A conductive layer is formed on the barrier layer by an atomic layer deposition process, thereby the conductive layer having two sidewall parts. The two sidewall parts of the conductive layer are pulled down. A conductive material fills the recess and has a part contacting the two sidewall parts of the barrier layer protruding from the two sidewall parts of the conductive layer, wherein the equilibrium potential difference between the barrier layer and the conductive layer is different from the equilibrium potential difference between the barrier layer and the conductive material. Moreover, the present invention also provides a semiconductor structure formed by said semiconductor process.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Oxide-ion sensor for use in a molten-salt based electrochemical reduction process
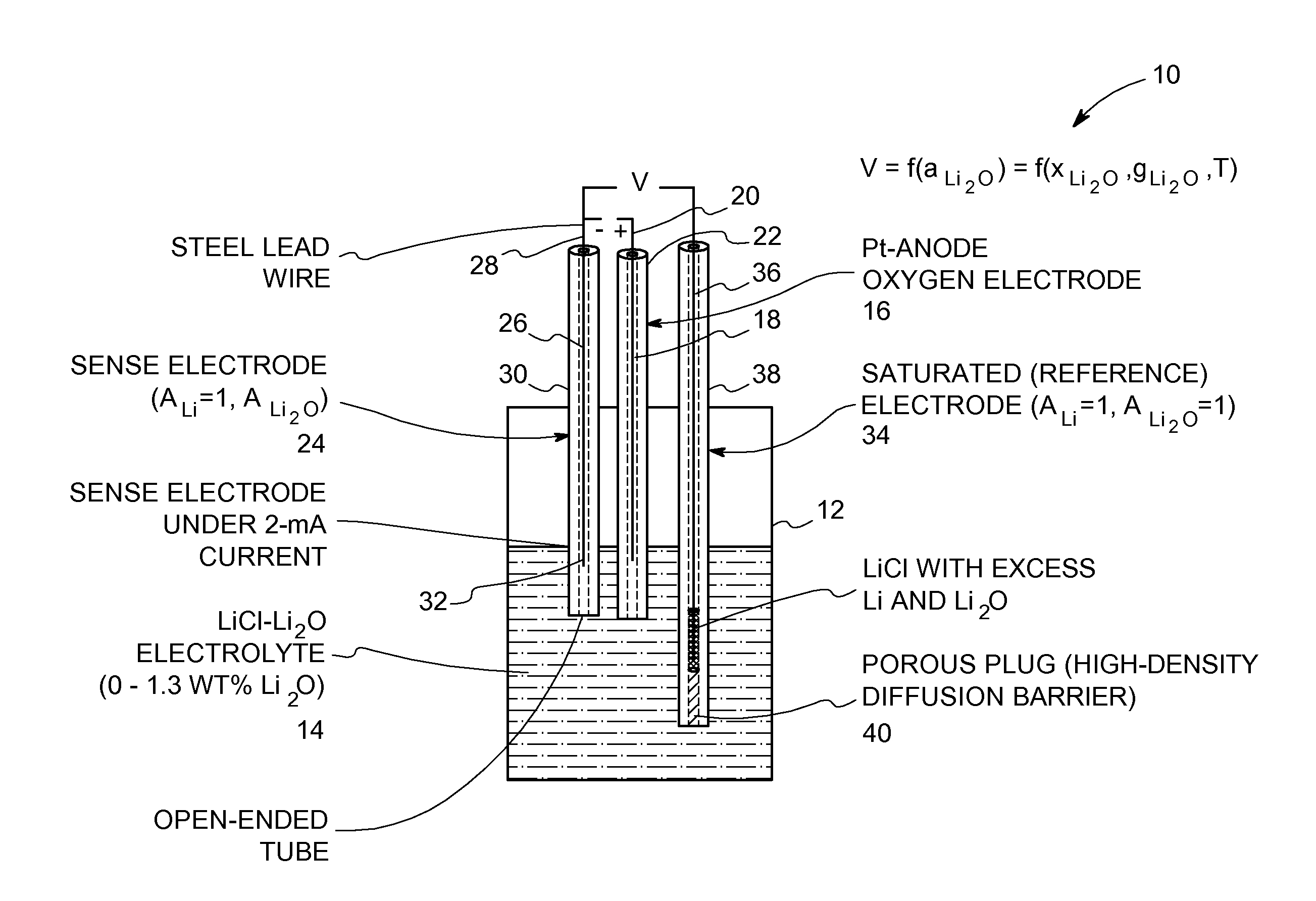
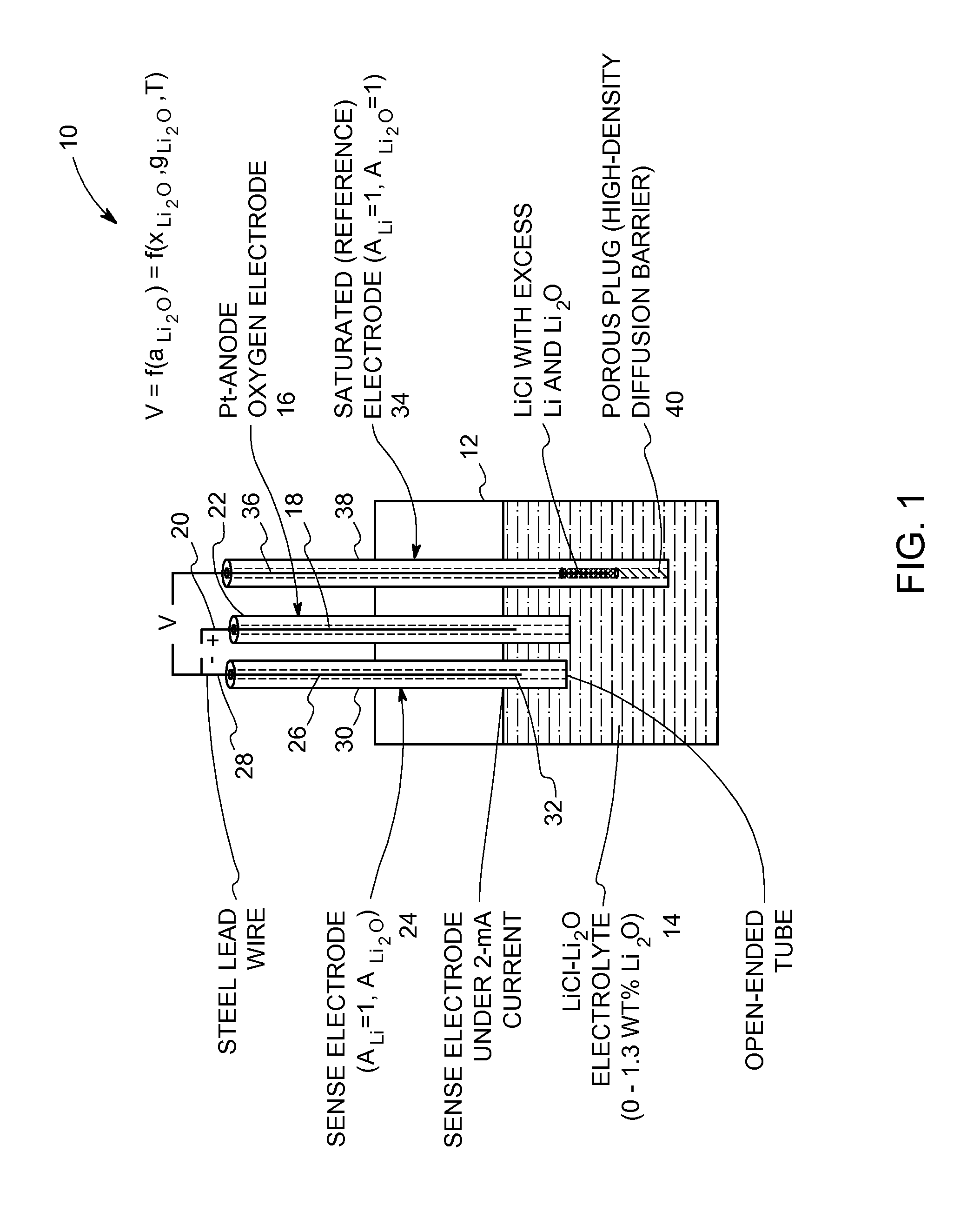
InactiveUS20110108439A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementEquilibrium potentialMolten salt
An oxide-ion sensor includes an oxygen electrode, a sense electrode and a saturated (reference) electrode. The sense electrode is operated at a substantially constant current for determining an instantaneous value of a dissolved oxide-ion concentration in the molten salt electrolyte. The saturated electrode is used to determine a reference value of the dissolved oxide-ion concentration in the molten salt electrolyte. A dissolved oxide-ion concentration in the molten salt electrolyte is continuously monitored in-situ during the molten-salt based electrochemical reduction process by determining an equilibrium potential between the sense electrode and the saturated electrode with the sense electrode carrying a small current in a circuit that is completed using the oxygen electrode. In another embodiment, the dissolved oxide-ion concentration in the molten salt electrolyte is continuously monitored in-situ by determining an electrochemical impedance of the molten salt electrolyte using a pair of bare current-carrying conductors and a frequency response analyzer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Gas sensor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveCN101135661AExcellent stability over timeHigh measurement sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGas analyser construction detailsLithiumEquilibrium potential
With a gas sensor comprising a structure including a reference pole having a reference material and an electronic conductive material and a sensing pole having a sensing material and an electronic conductive material provided through a solid electrolyte in which the said solid electrolyte, the said reference material and the said sensing material are constituted of lithium ionic conductors and a method of manufacturing the same, an equilibrium potential gas sensor employing a solid electrolyte operable at a low temperature not more than 200 DEG C, particularly at the room temperature, not influenced by moisture or the like and excellent in age-based stability with high measurement sensitivity as well as high responsibility and a method of manufacturing the same can be provided.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Annular flow electrochemical cell for measurements online
Owner:CENT PARA LA INVESTIGACION CIENTIFICO TECHCO PARA LA MINERIA CICITEM
Method for removing phosphorus from sewage on basis of magnesium alloy corrosion
The invention discloses a method for removing phosphorus from sewage on the basis of magnesium alloy corrosion. The method comprises the steps of immersing a magnesium alloy plate containing a certainmass of magnesium in wastewater rich in nitrogen and phosphorus, and recovering precipitated magnesium ammonium phosphate after a period of time. Since equilibrium potential (-2.37V) is relatively low, a magnesium metal is very easily corroded and dissolved out in an aqueous solution system; and magnesium ions required by crystallization of magnesium ammonium phosphate are provided by the slow corrosion of the magnesium alloy and react with ammonium and phosphate pre-existing in the wastewater to generate a magnesium ammonium phosphate crystal for resource recycling of phosphorus and nitrogen.
Owner:深圳市中涛环保工程技术有限公司
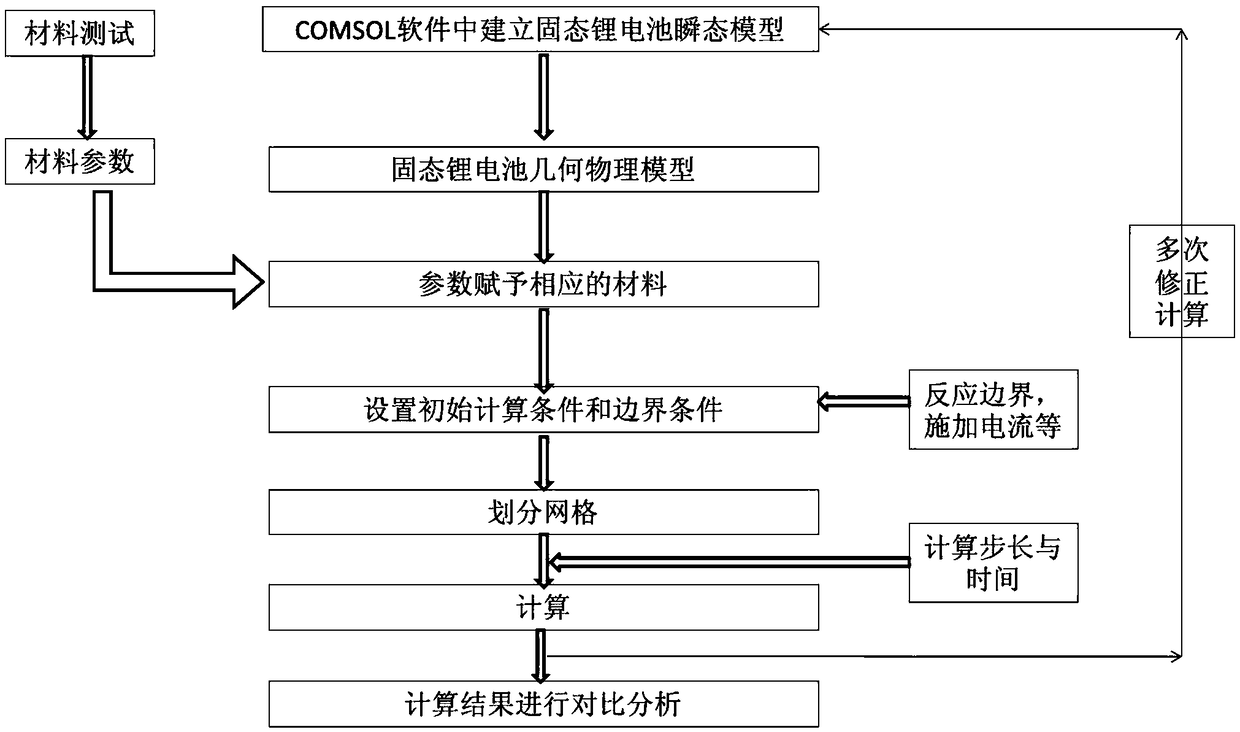
COMSOL model-based manufacturing method of solid-state lithium battery
ActiveCN108875145ASave costsShorten the timeFinal product manufactureSecondary cellsEquilibrium potentialPhysical model
The invention relates to a COMSOL model-based manufacturing method of a solid-state lithium battery, and belongs to the technical field of chemical power supply. The COMSOL model-based manufacturing method of the solid-state lithium battery includes: 1) obtaining property data of battery material through alternating-current impedance, a galvanostatic intermittent titration technique, cyclic voltammetry or an equilibrium potential curve electrochemical-method, and calculating and obtaining parameters of the battery material; 2) using COMSOL electrochemical-modules and PDE modules to establish atransient model of the solid-state lithium battery; 3) establishing geometric physical models of the solid-state lithium battery, and assigning parameters of the step 2) to corresponding material areas, 4) setting initial calculation conditions and boundary conditions; 5) dividing meshes, and carrying out calculation, wherein a one-dimensional physical model adopts a point mesh, a two-dimensionalphysical model adopts a rectangular mesh, and a three-dimensional physical model adopts a thin-plate-type cuboid mesh; and 6) carrying out comparative analysis on calculation results of different process parameters. According to the method, theoretical guidance on solid-state lithium battery design is realized, costs and time are saved, and promotion and application of the solid-state lithium battery are facilitated.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
Method for measuring non-protein nitrogen content in tobacco
InactiveCN101382516AThe assay method has fewer stepsFew stepsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEquilibrium potentialCopper
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGDONG IND
Magnesium ion battery negative electrode material prepared by manganese acetate tetrahydrate glycerol solvent method
InactiveCN109659556AEasy to makeEasy to manufactureCell electrodesSecondary cellsEquilibrium potentialMANGANESE ACETATE
The invention discloses a magnesium ion battery negative electrode material prepared by a manganese acetate tetrahydrate glycerol solvent method. The method comprises the steps: removing crystalline water in manganese acetate tetrahydrate through a glycerol solvothermal method to obtain anhydrous manganese acetate of a layered structure; manufacturing an electrode plate, and assembling a magnesiumion semi-battery. Electrochemical test results show that anhydrous manganese acetate has electrochemical reversible magnesium storage performances, wherein the reaction equilibrium potential is about0.87V (vs.Mg / Mg2+), the first discharge capacity can reach 63.5 mAh / g, the circulation capacity and the electrochemical reversibility are superior to those of manganous oxide. The method can avoid the generation of magnesium metal column crystals which may cause potential safety hazards, and the method has good research and development prospects.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
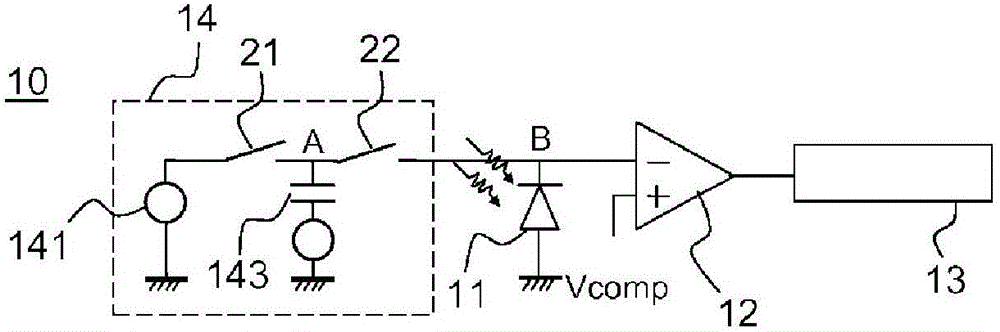
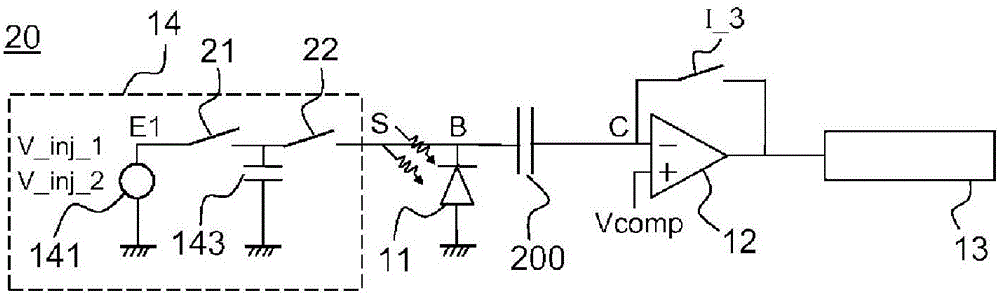
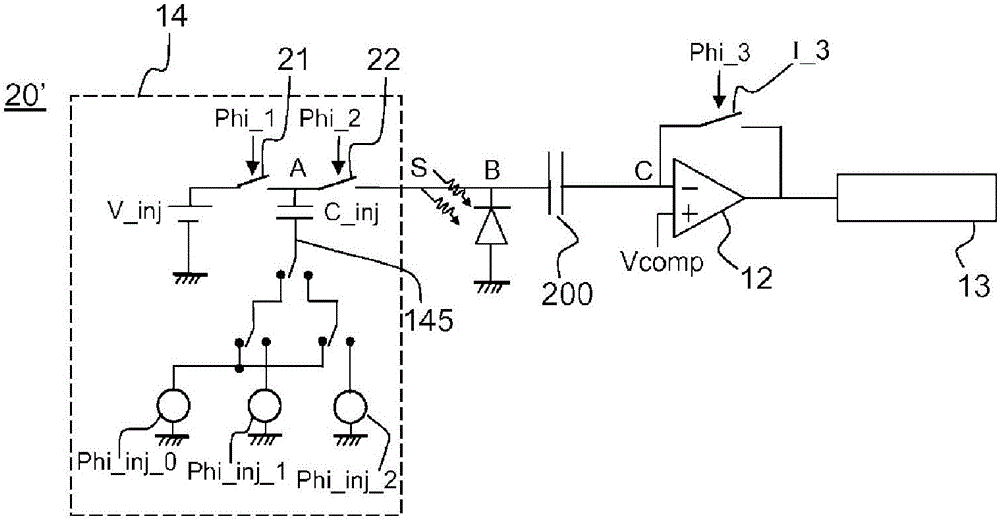
Electronic charge injection circuit for radiation detector
ActiveCN105849590APulse generatorRadiation intensity measurementCharge injectionEquilibrium potential
The invention relates to an electronic read circuit for a radiation detector comprising: an element (11) sensitive to the radiation, an injection circuit, able to inject a charge at one terminal of the sensitive element (11), the injection circuit (14) extending between at least one input terminal and one output terminal, the output terminal being able to be connected to said sensitive element (11), the injection circuit (14) being able to produce a charge under the effect of a trigger pulse. The injection circuit is able to inject a first charge when an input terminal is connected to a first input potential and a second charge when an input terminal is connected to a second input potential (Vinj2, Phiinj)). The circuit comprises means for storing a difference between an output potential of the injection circuit (14), called equilibrium potential, and a reference potential, such that the second charge depends on the second input potential and on said equilibrium potential.
Owner:原子能和辅助替代能源委员会 +1
System and method for microbial/photocoupled reduction of carbon dioxide to produce methane
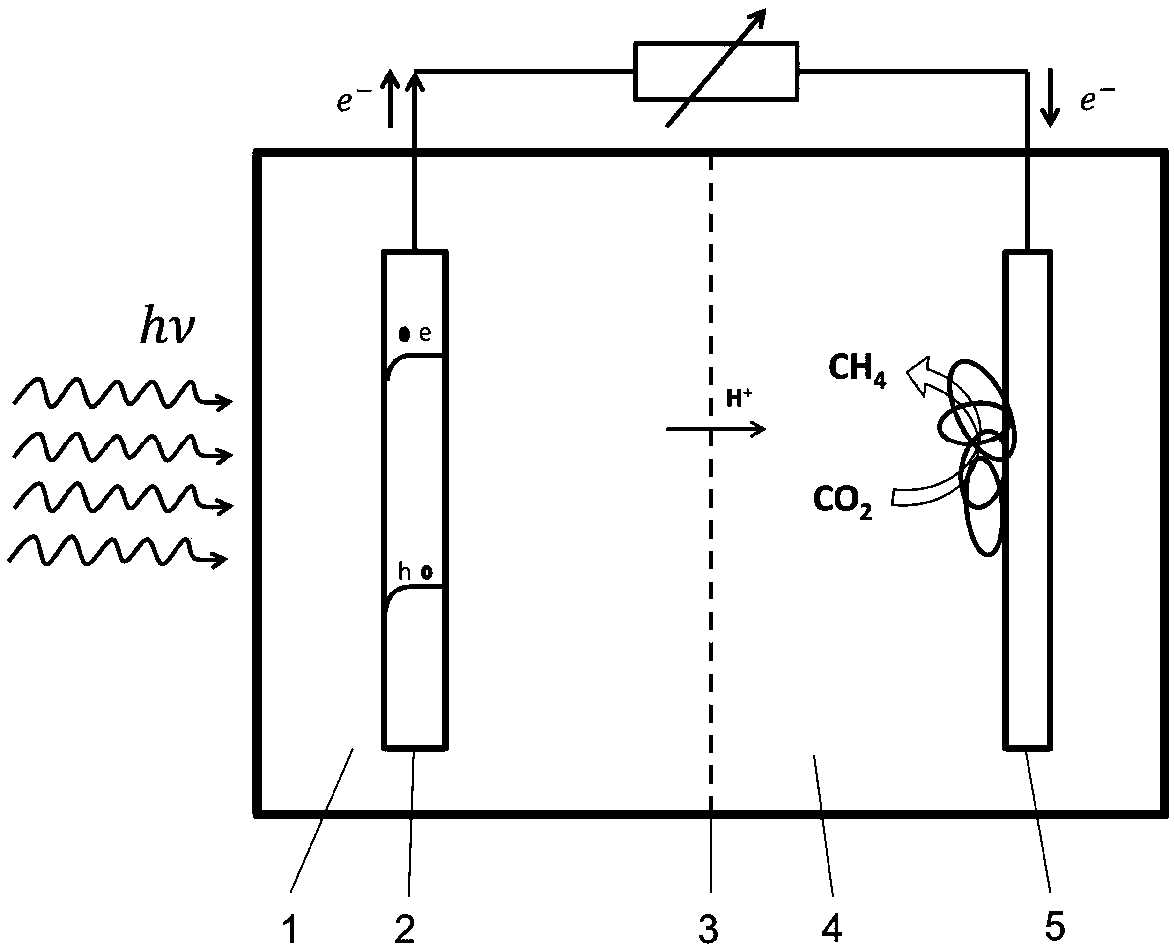
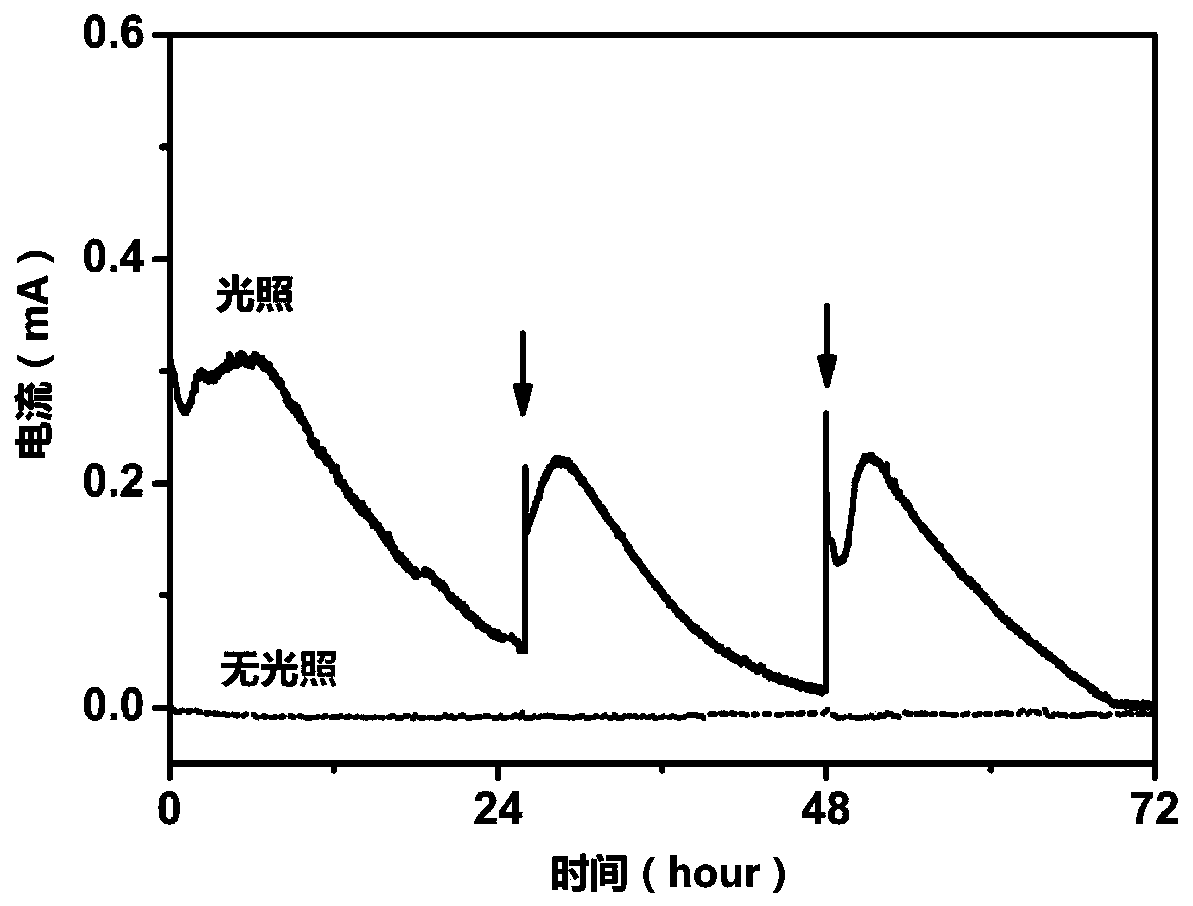
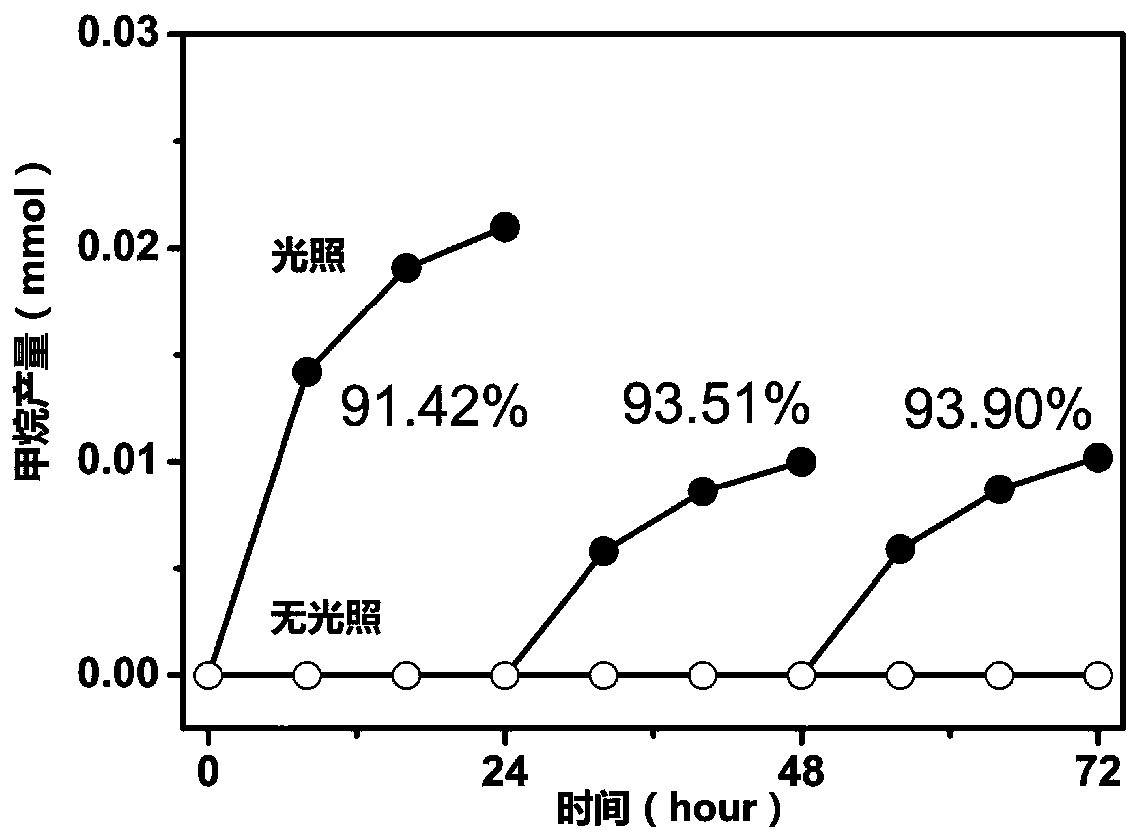
ActiveCN106947688BLow costTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesApparatus sterilizationEquilibrium potentialCathode
The invention discloses a system and a method for reducing CO2 to produce methane through microorganism / photoelectric-coupling. The system herein includes an anode chamber and a cathode chamber, which are respectively filled with an anode solution and a cathode solution; a cation exchange membrane is disposed between the anode chamber and the cathode chamber. The system is also characterized in that a photo-anode is disposed in the anode chamber, wherein an n-type semiconductor serves as a photocatalyst on the photo-anode. The conduction band potential of the n-type semiconductor, under any pH value, is lower than the redox equilibrium potential of CO2 / CH4; meanwhile, the valence band potential of the n-type semiconductor is higher than the redox equilibrium potential of H2O / O2; a bio-cathode is arranged in the cathode chamber, wherein electrochemical active methanogens are adhered to the surface of the bio-cathode. The microorganisms can directly acquire electrons from the electrode to reduce CO2 and produce the methane, so that CO2 and microorganism conversion is achieved by means of solar energy. The system and the method have great application prospect.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
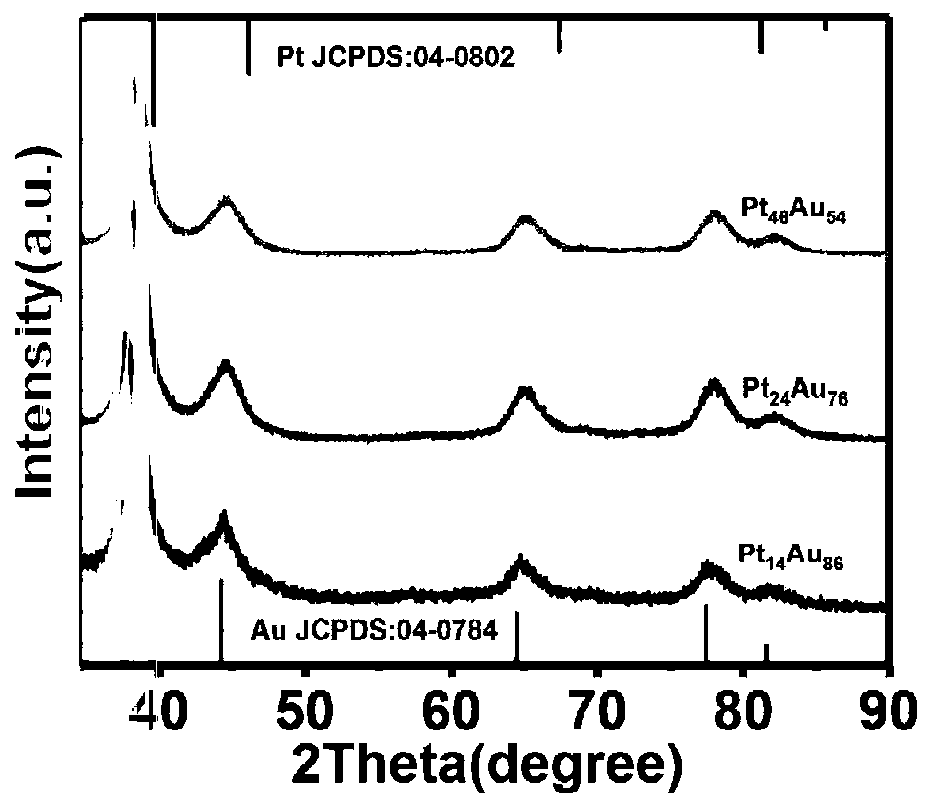
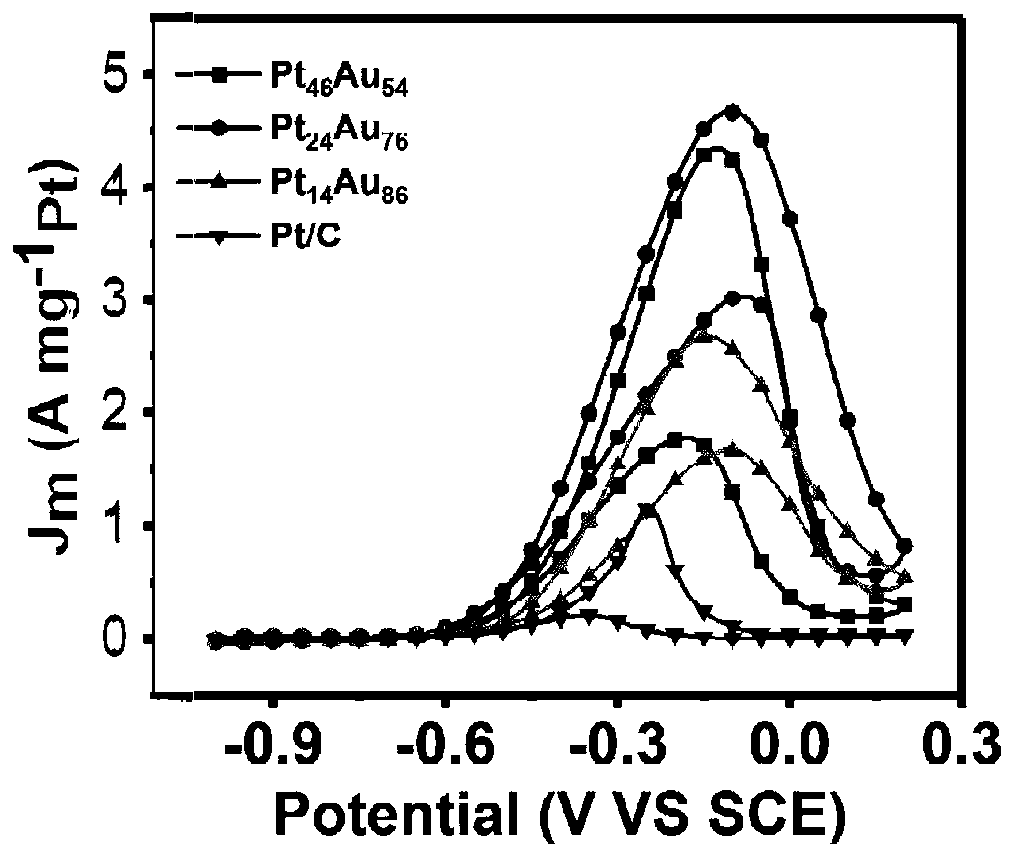
PtAu nano catalyst with controllable active site spacing and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110165227AImprove electrocatalytic performanceChange atomic distributionCell electrodesFuel cellsNano catalystEquilibrium potential
The invention discloses a PtAu nano catalyst with a controllable active site spacing and a preparation method thereof. The method comprise steps that platinum acetylacetonate, chloroauric acid, tri-n-octylphosphine oxide, oleylamine and octadecene are mixed under the nitrogen atmosphere and are stirred to a clear state; the solution is then heated and subjected to temperature insulation, reactionis completed, after natural cooling and centrifugal washing, the PtAu nano catalyst having the controllable active site spacing is obtained. The method is advantaged in that in the preparation process, the equilibrium potential of the two types of precursor salt is evened by the tri-n-octylphosphine oxide, two elements are co-reduced, atomic distribution of a surface of the nano crystal is effectively changed by adjusting an input ratio of acetylacetonate platinum and chloroauric acid and utilizing surface atomic reconstruction induced by high temperature, the Pt-Au active site spacing is shortened, the Pt-Au distance is regulated to greatly improve activity and stability of the PtAu nano catalyst in methanol oxidation reaction, and the catalyst can further be used in oxygen reduction reaction.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Sand grinding modification method of lithium ion battery mineral negative electrode material
InactiveCN109647584AEasy to crushHigh electrochemical reversibilityCell electrodesSecondary cellsElectrochemical responseMicro nano
The invention discloses a sand grinding modification method of a lithium ion battery mineral negative electrode material. The method is characterized in that two stages of grinding, namely planetary ball grinding and sand grinding, are carried out on natural zinc concentrate to obtain a micro-nano zinc concentrate negative electrode material, wherein the particle size of the negative electrode material is less than 100 nm, moreover, agglomerates exist, and the BET specific surface area of the negative electrode material is larger than 27 m<2> / g; and an electrode is manufactured by using the negative electrode material, acetylene black and PVDF at the mass ratio of 7:2:1, a lithium battery is assembled, an electrochemical performance test shows that the micro-nano zinc concentrate negativeelectrode material has good electrochemical reaction reversibility, the reaction equilibrium potential is about 1.2 V (vs. Li / Li<+>), the first-time discharge specific capacity is 736 mAh / g or above,and the specific capacity of the 50th-time charge and discharge cycle is 513 mAh / g or above. According to the method, micro-nano crushing of the zinc concentrate can be easily realized, so that the electrochemical performance of the zinc concentrate used as the lithium ion battery negative electrode material is remarkably improved, and a relatively good practical application value is achieved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
A Lithium-ion Battery Life Prediction Method Based on Capacity Fading Mechanism Decomposition Analysis
ActiveCN106383324BShrinkage test timeReduce test sampleElectrical testingEquilibrium potentialDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for forecasting service life of a lithium ion battery based on capacity attenuation mechanism decomposition analysis. The method comprises the following steps: step one, establishing an equilibrium potential equation of a lithium ion battery to be tested by subtracting equilibrium potentials of positive and negative electrodes with combination of test data of the lithium ion battery to be tested, and then carrying out polarization modification to obtain the equilibrium potential equation; step two, establishing a multi-attenuation-mode decomposition model based on different attenuation mechanisms of the lithium ion battery, establishing a multi-attenuation-mode fitting equation of the lithium ion battery to be tested through a short-term aging test and forecasting attenuation trend; and step three, substituting a forecasting result of the multi-attenuation-mode fitting equation into the equilibrium potential equation of the lithium ion battery to be tested, and forecasting residual capacity. Through the service life forecasting method for carrying out decomposition analysis of different attenuation modes based on different capacity attenuations of the lithium ion battery, the problem that simple extrapolation is carried out according to the experiment test data or the attenuation of the service life of the lithium ion battery is simply ascribed to the single electrochemical mechanism is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI POWER ENERGY STORAGE BATTERY SYST ENG TECH +1
Preparation method of manganous oxide negative electrode material of magnesium ion battery
InactiveCN109638277AHigh theoretical specific capacityImprove securityCell electrodesCapacitanceEquilibrium potential
The invention discloses a preparation method of a manganous oxide negative electrode material of a magnesium ion battery. According to the method, the manganous oxide negative electrode material withelectrochemically reversible magnesium-storing performance is prepared through a manganous oxalate pyrolysis method, wherein the reaction equilibrium potential of the material is 0.87V(vs.Mg / Mg<2+>),the granularity of a pyrolysis product under the temperature of 400 DEG C ranges from 30nm to 50nm, the first discharge specific capacity is 39.6mAh / g, the ratio of pseudocapacitance capacity in the specific capacity is large, the redox peak current of the material is slowly lowered along with increase of cycles, and the specific capacity of the material is slowly lowered along with rising of pyrolysis temperature. The method has advantages in terms of granularity control and specific capacity increase of the manganous oxide negative electrode material and is possibly subjected to practical application in the future.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Conductive film, current collector using same, battery and bipolar battery
ActiveUS10230112B2Disadvantageous spaceDisadvantageous weightSingle bars/rods/wires/strips conductorsFinal product manufactureEquilibrium potentialElastomer
A conductive film includes a layer 1 formed by a conductive material 1 that includes a polymer material 1 containing any of (1) an amine and an epoxy resin (where the epoxy resin and the amine are mixed in a ratio of 1.0 or more in terms of the ratio of the number of active hydrogen atoms in the amine with respect to the number of functional groups in the epoxy resin), (2) a phenoxy resin and an epoxy resin, (3) a saturated hydrocarbon polymer having a hydroxyl group, and (4) a curable resin and an elastomer and conductive particles 1. The conductive film has excellent stability in an equilibrium potential environment in a negative electrode and low electric resistance per unit area in the thickness direction. A multilayer conductive film including the conductive film achieves excellent interlayer adhesion, and using them as a current collector enables the production of a battery satisfying both weight reduction and durability.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
A high-concentration zinc-vanadium redox battery
The invention discloses a high concentration zinc and vanadium redox cell. According to the invention, the novel zinc vanadium oxidation reduction cell is characterized in that a vanadium ion solution is taken as an anode active substance, zinc and a zinc ion solution are taken as an cathode active substance, wherein the equilibrium potential is 1.76 V under a standard state, the open-circuit voltage is 1.7 - 2.0 V under a charging state. The vanadium ions of the vanadium ion solution are existed as quintavalence and quadrivalence (V(I), V(IV)), and the total vanadium concentration can reach to 4.0 mol / L, a solvent is inorganic acid or organic acid. The zinc ion solution is a zinc ion electrolyte containing organic acid or inorganic acid. The organic acid is methanesulfonic acid or sulfamic acid. The inorganic acid is sulfuric acid or nitric acid. The high energy concentration redox cell can be exploited according to the invention.
Owner:周成壁
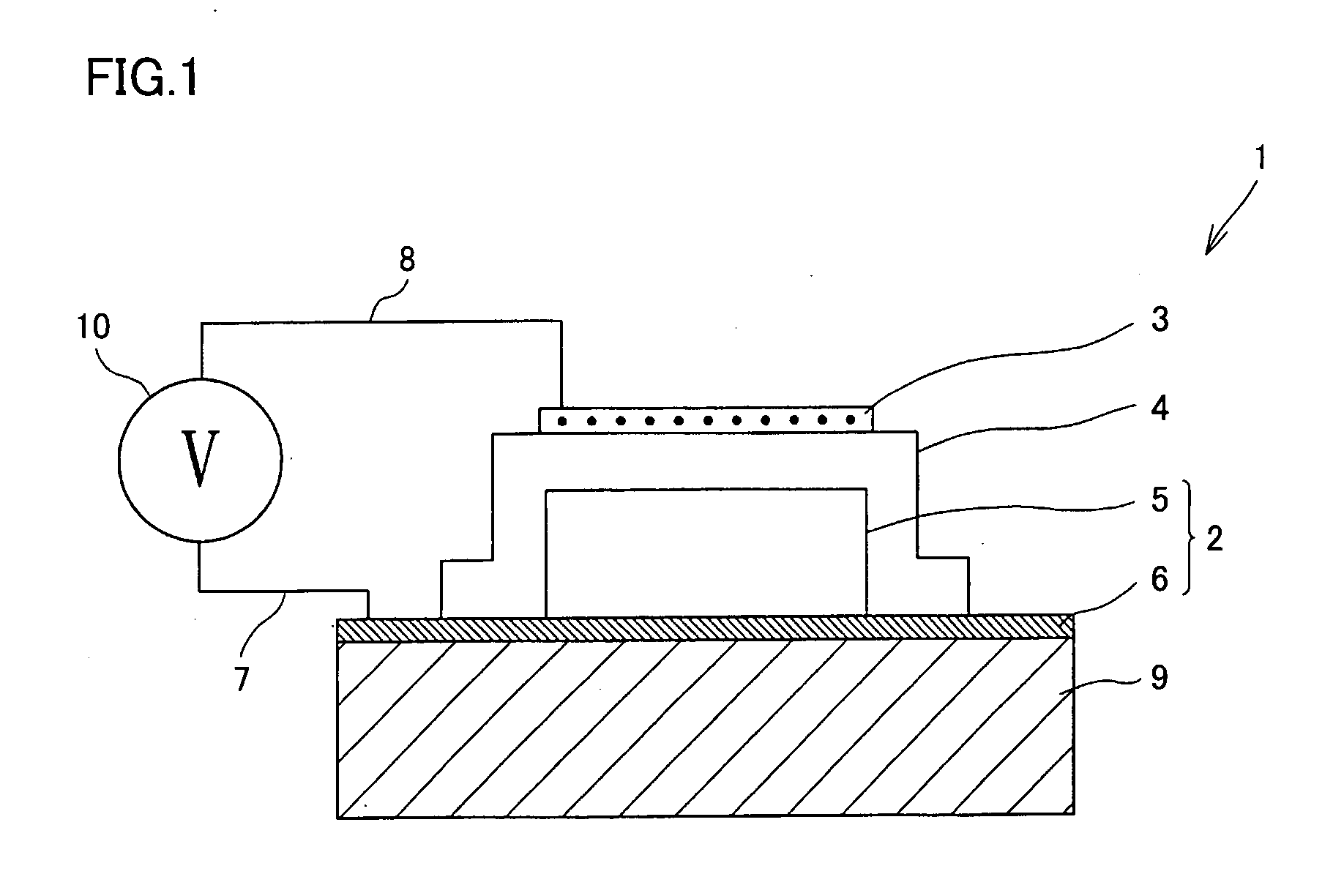
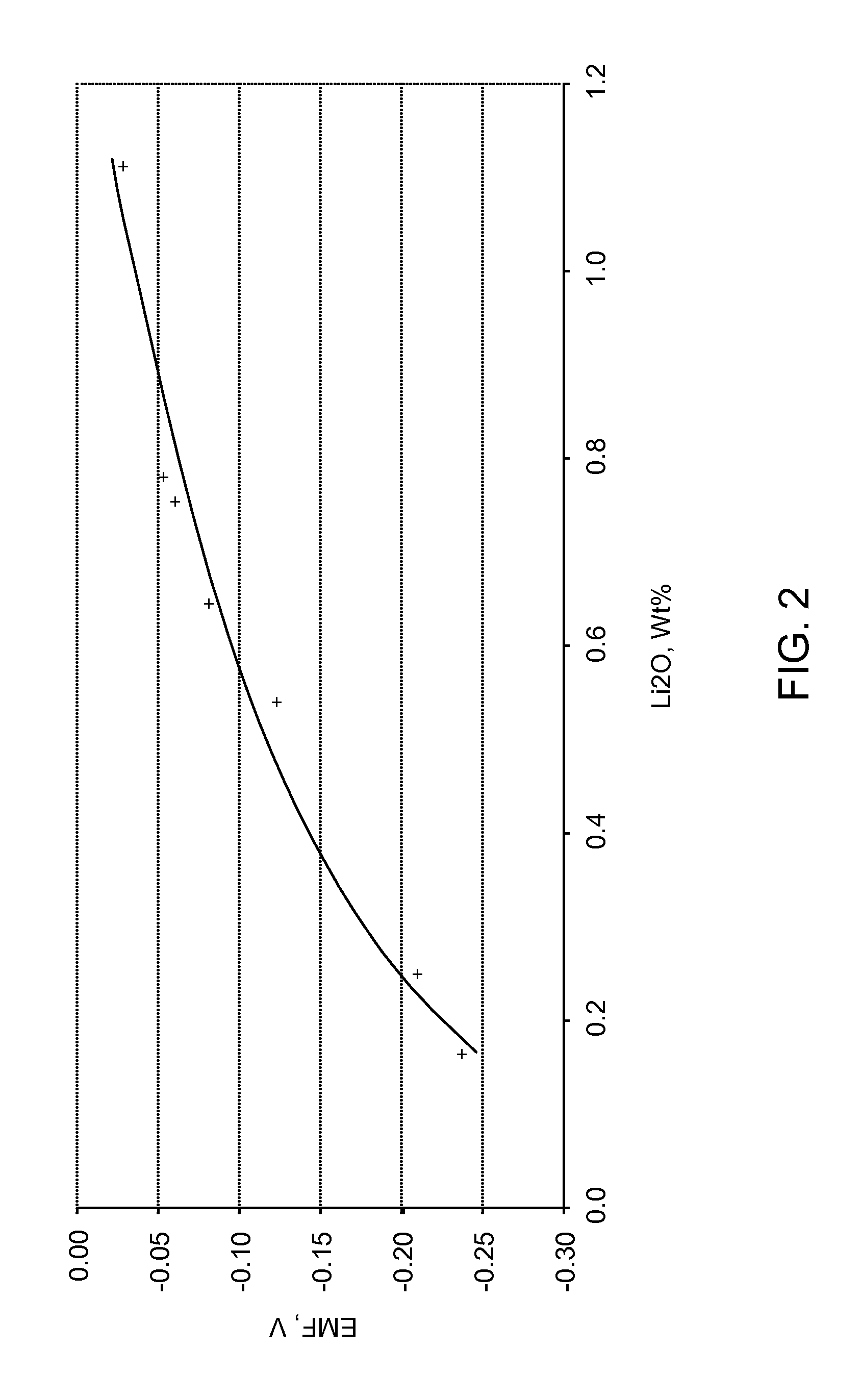
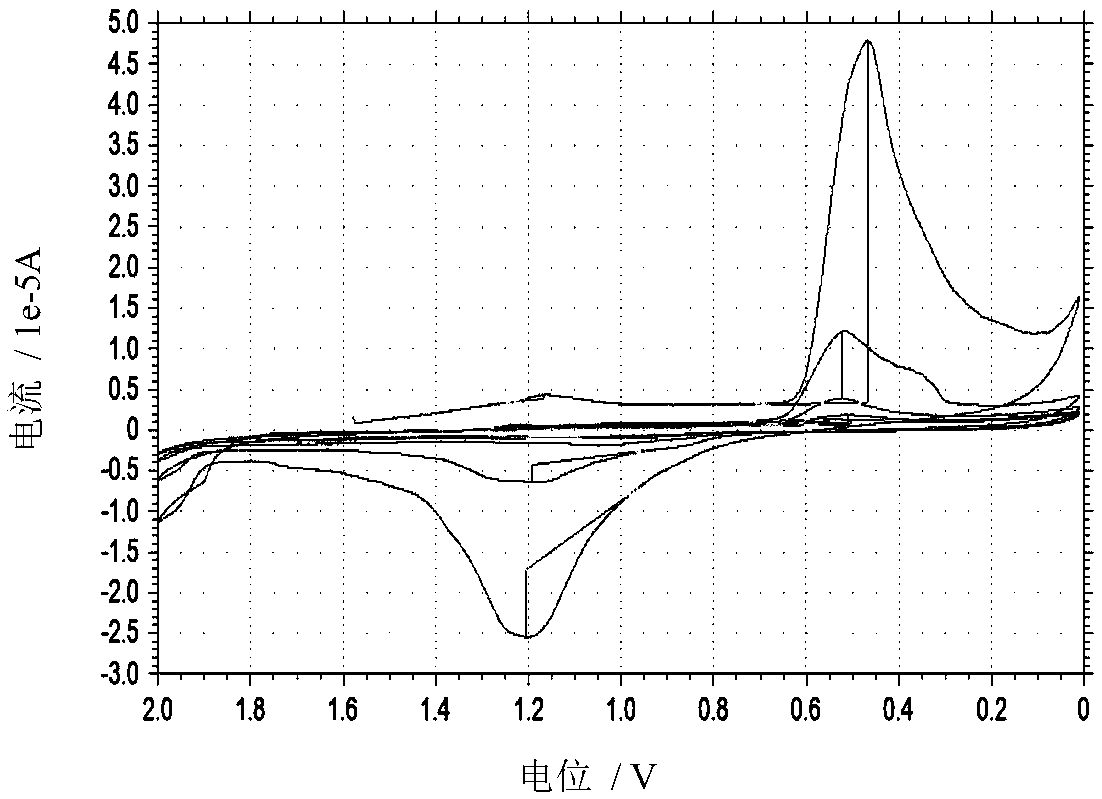
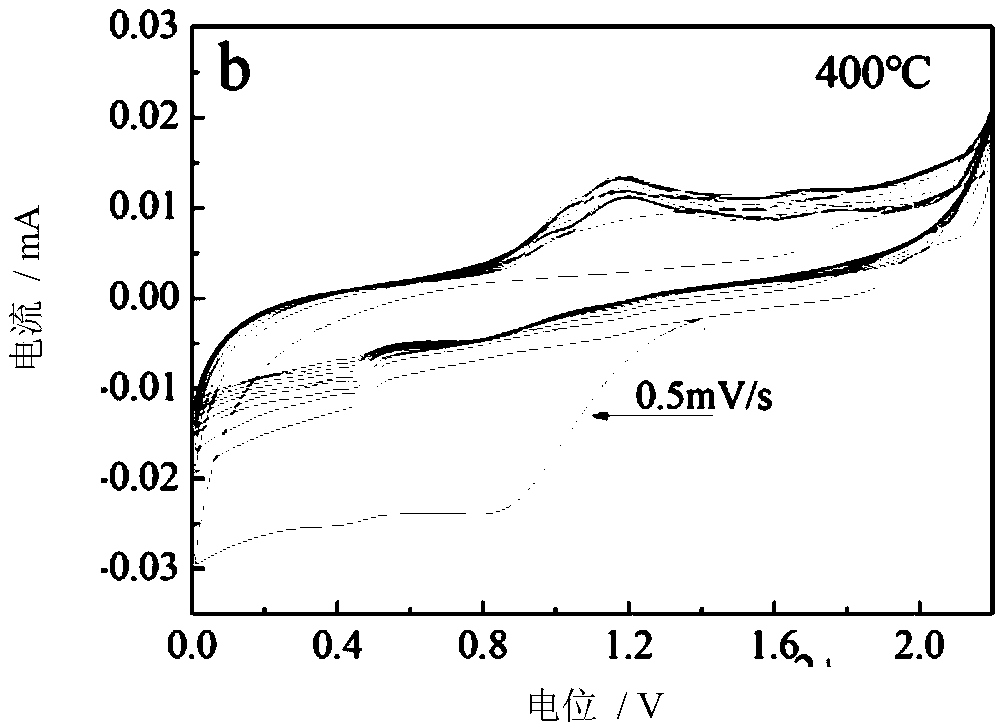
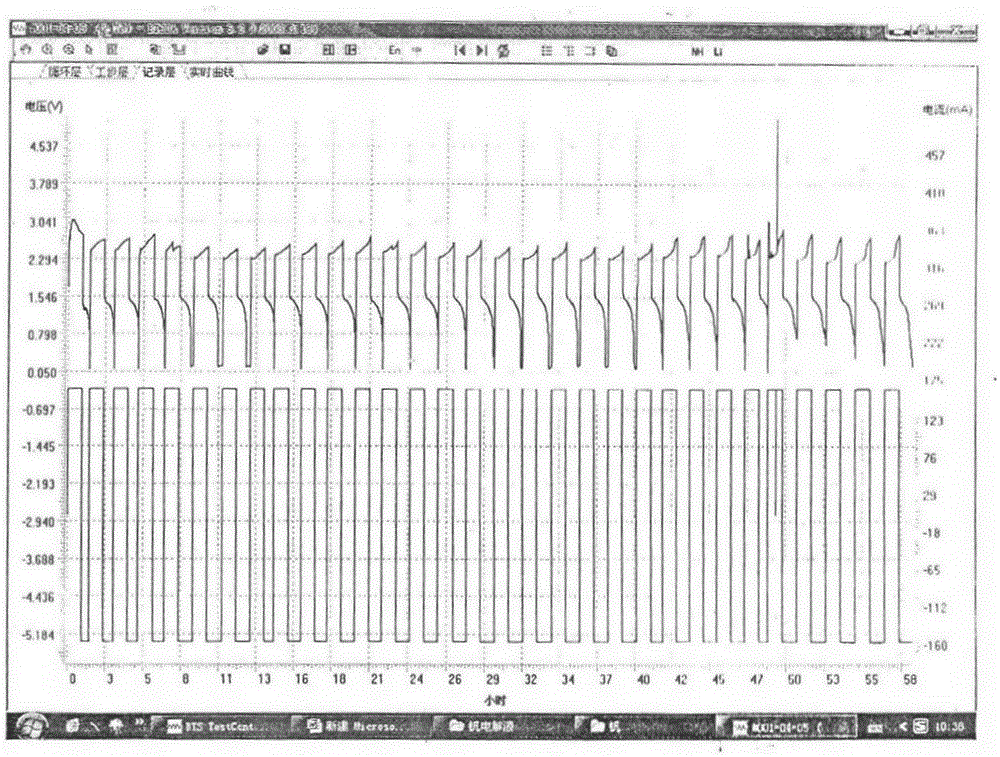
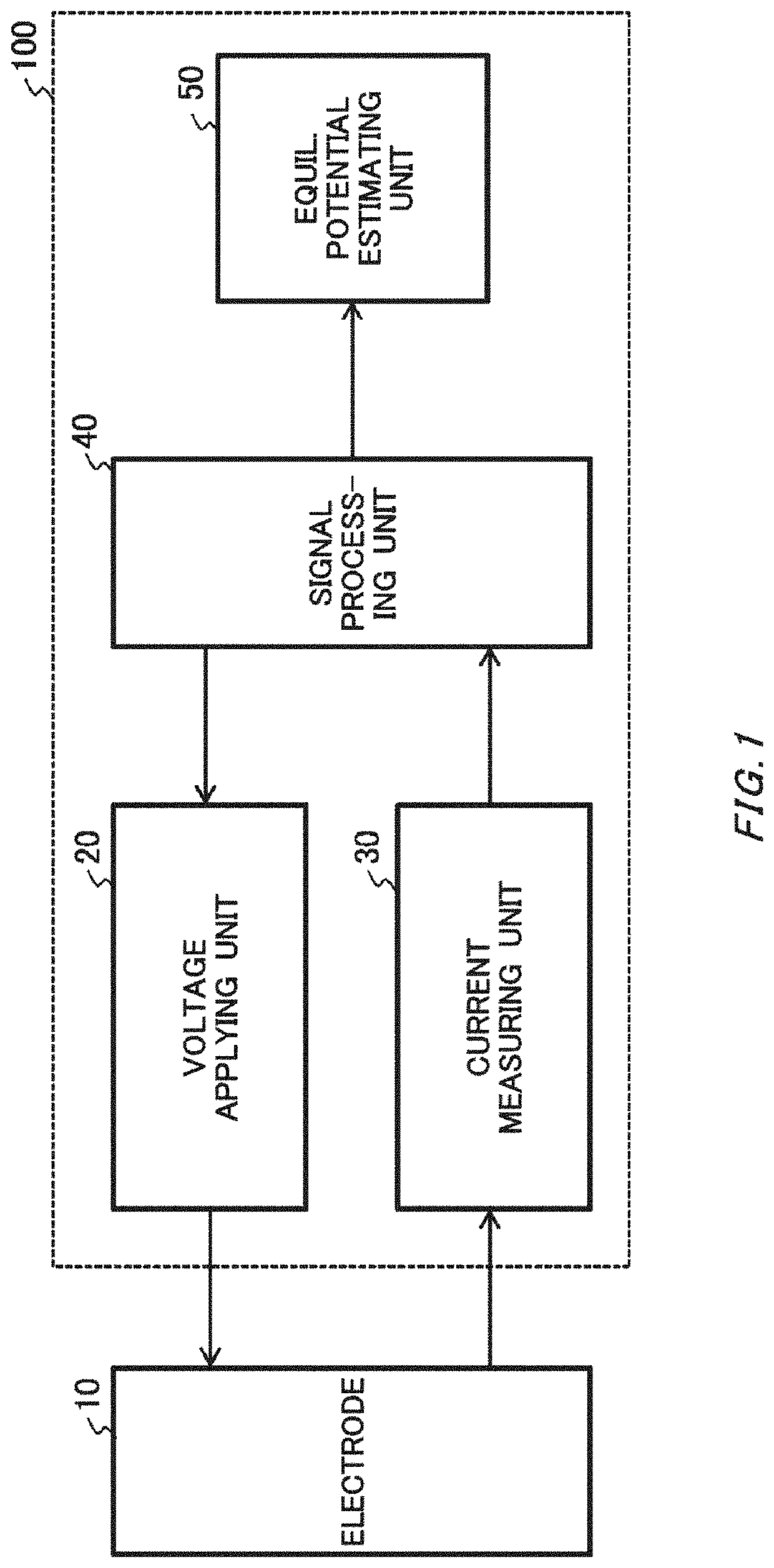
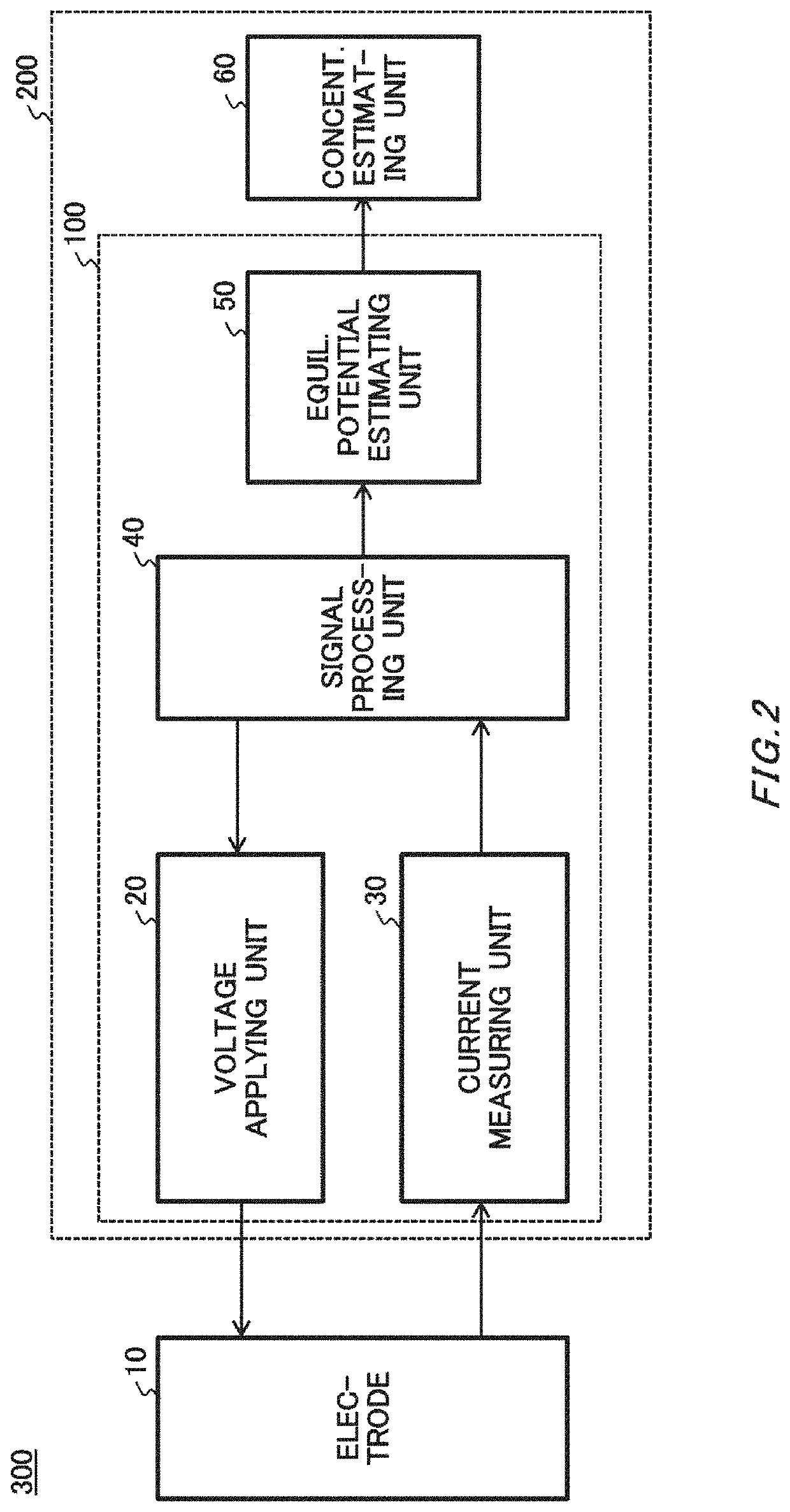
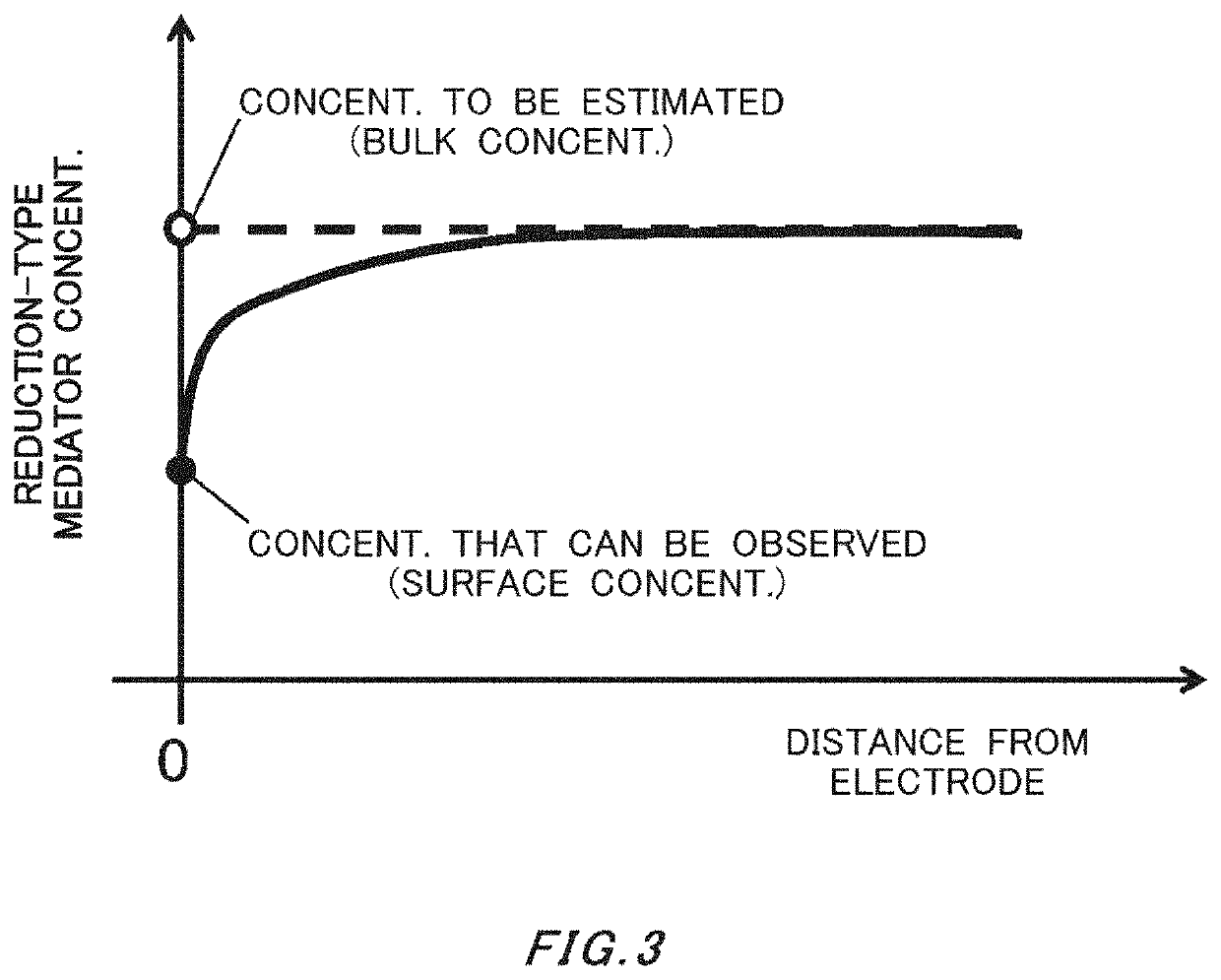
Equilibrium potential estimating method, equilibrium potential estimating device, concentration estimating device, program, medium and blood sugar estimating device
ActiveUS10641730B2Water treatment parameter controlMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEquilibrium potentialElectrode Contact
An oxidation-reduction substance equilibrium potential estimating method is provided, the method including:applying a voltage to an electrode contacting a sample containing an oxidation-reduction substance and sweeping the voltage;measuring a current flowing through the electrode;if an integrated value of the current becomes a value within a reference range, determining whether to sweep the voltage in an opposite direction to a sweep direction in the previous sweeping or to terminate sweeping of the voltage;if it is determined to terminate sweeping of the voltage, estimating an oxidation-reduction substance equilibrium potential at a value of the voltage; andif it is determined to sweep the voltage, sweeping the voltage in an opposite direction to a sweep direction in the previous sweeping.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Method and system for detecting single electrode potential of battery
ActiveCN104391159BCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical testingEquilibrium potentialElectrical battery
Owner:BEIJING KEY POWER TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com