Colour active matrix displays
An active matrix and color technology, applied in the field of color active matrix display equipment, can solve the problems that are not suitable for forming displays, etc., and achieve the effect of simple unit formation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
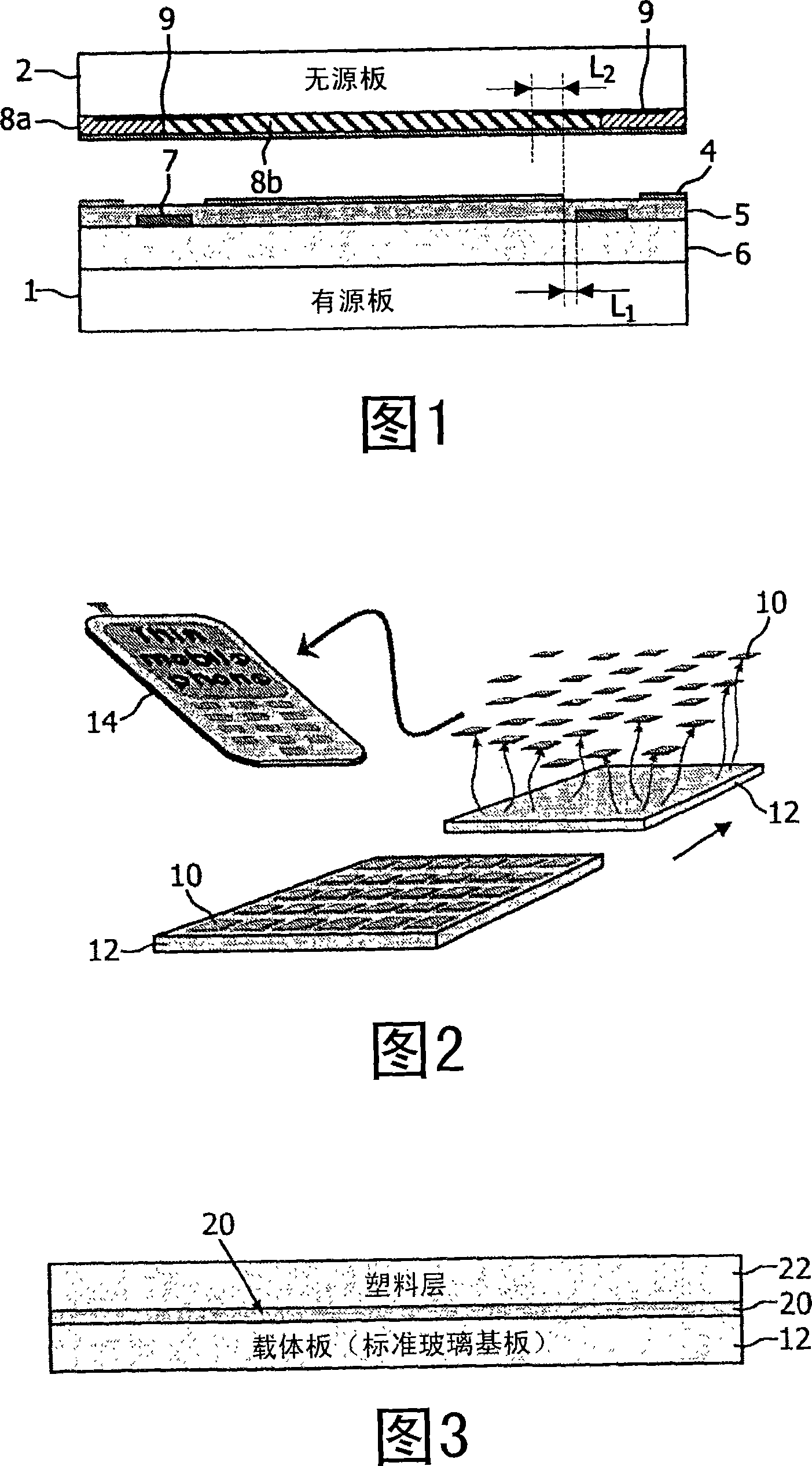
[0062] Figure 2 schematically shows the manufacture of a (not yet published) plastic display proposed by the applicant, showing the final separation stage. The completed display 10 is separated from the glass substrate 12 and subsequently used in a device such as a mobile phone 14 .
[0063] Figure 3 is used to explain the basic manufacturing concept and shows a glass carrier plate 12 with an a-Si separation layer 20 and a plastic layer 22 which acts as a plastic substrate. This substrate structure can form the basis for active and passive boards. FIG. 3 only shows one display substrate, but actually there will be many display units on the large glass substrate, as shown in FIG. 2 .
[0064] The separation layer 20 may be a thin layer of a-Si, which is deposited on the glass substrate 12 before adding the plastic layer 22 . The a-Si separation layer is applied by PECVD, for example, and may have a thickness of 10 to 50 nm. A laser separation process can be used to activate ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com