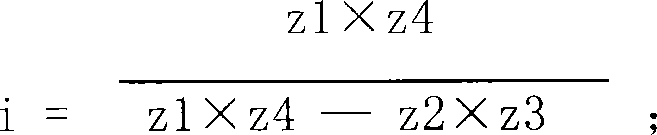Decelerator for control motor
A technology of reducer and support bearing, applied in the direction of controlling mechanical energy, electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve the problems of long working time, fast wear, and reduce gear efficiency, and achieve long service life, high transmission efficiency, and easy installation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
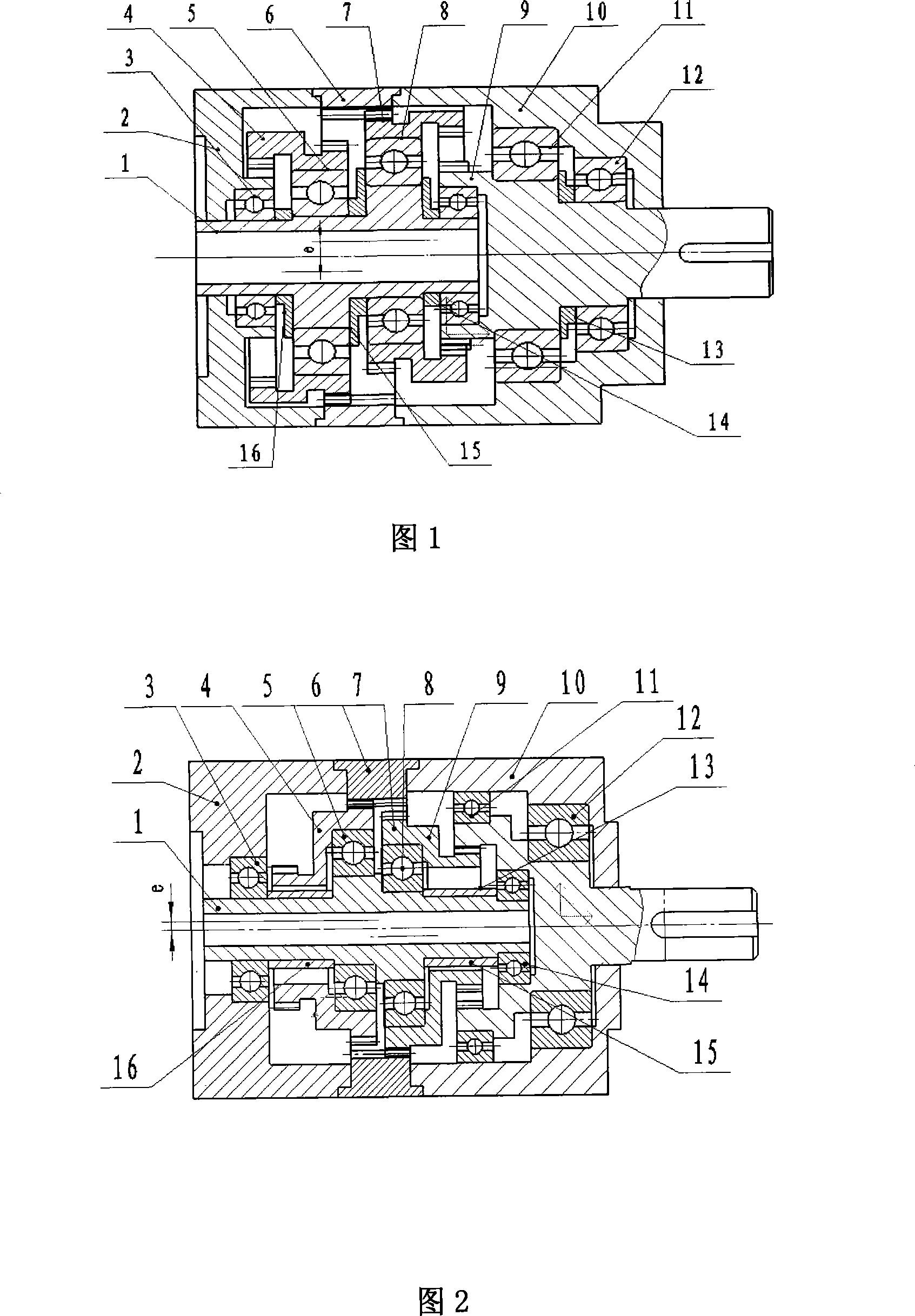
[0014] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, a reducer for controlling a motor consists of an input shaft 1, stepped planetary gears 4 and 7 (the stepped planetary gears 4 and 7 are composed of an external gear and an internal gear), an internal gear 6, an output shaft 9, and a right casing Body 10, left housing 2, support bearings 3,14 of input shaft 1, support bearings 5,8 of two stepped planetary gears 4,7, and support bearings 11,12 of output shaft 9 constitute. Among the figure, 13,15,16 all are retaining rings.
[0015] The input shaft 1 is supported by the first support bearing 3 and the second support bearing 14 respectively in the inner hole of the left housing 2 and the left end of the output shaft 9. There are two pairs of eccentric circles with a circumferential difference of 180° in the middle of the input shaft 1. The third support bearing 5 and the fourth support bearing 8 are installed on the circle, the inner hole of the stepped planetary gear 4 is sleeved on t...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Embodiment 2: The difference from the first structure is that the teeth on the two-step planetary gears 4 and 7 are all external teeth, and the left end of the output shaft 9 has a ring of internal teeth, and the rest of the structure is the same as the first structure.
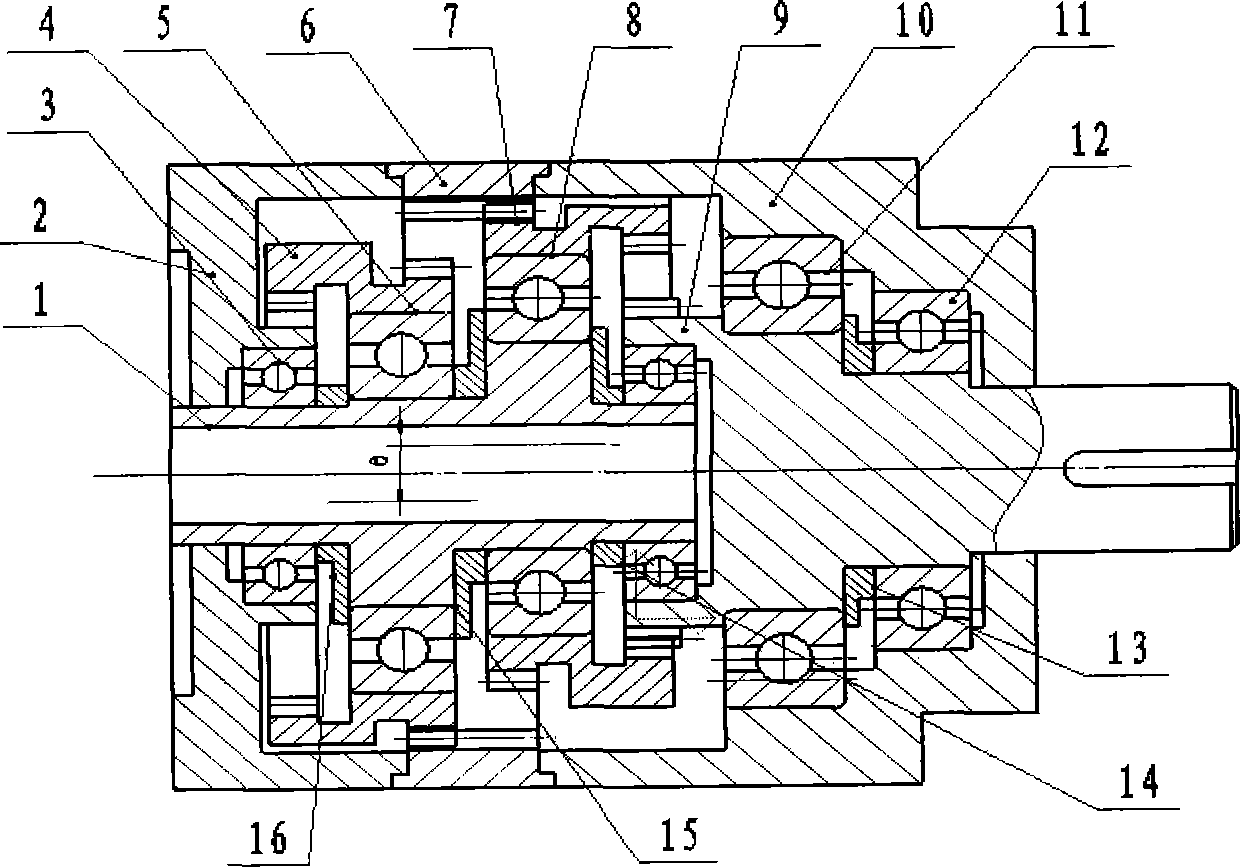
[0021] Depend on figure 2 As shown: the reducer mainly includes the input shaft 1, the first stepped planetary gear 4, the second stepped planetary gear 7, the internal gear 6 and the output shaft 9, and the first support bearing 3 and the second support for supporting the input shaft 1 The bearing 14 is used to support the third support bearing 5 and the fourth support bearing 8 of the two-step planetary gears 4 and 7 , and is used to support the fifth support bearing 11 and the sixth support bearing 12 of the output shaft 9 . Among the figure, 2 is the right housing, 10 is the left housing, and 13 is a retaining ring.
[0022] The input shaft 1 is supported by the first support bearing 3 and the se...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Embodiment 3: Figures are omitted, the two-stage planetary gears are both external gears, and the modulus difference between the first-stage and second-stage gears in the two-stage internal and external gear meshing is 0.25, such as 1.25 for the first stage and 1.5 for the second stage , by adjusting the displacement coefficient x to ensure that the center distance between the two pairs of gears is e.
[0029] transmission ratio i = z 1 × z 4 z 1 × z 4 - z 2 × z 3 ; zi and z3 are the external teeth of the stepped planetary gear, z2 is the internal tooth of the internal gear 6; z4 is the internal tooth fixed on the output shaft.
[0030] z1=z3, when z4-z2=1, then: transmissi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com