Coated cemented carbide endmill
A cutting tool and coating technology, applied in the direction of coating, tools for lathes, metal material coating process, etc., can solve problems such as chipping and breaking of cutting edges
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0056]Uncoated cutting tools, WC-10% Co inserts for turning ISO type CNMG120408 were cleaned and subjected to a PVD coating process according to the following. The blades were loaded into a reactive arc evaporation type PVD apparatus chamber containing six metal evaporation sources arranged in pairs. The blade further undergoes a triple rotation to coat it evenly. One pair of evaporators had Ti metal targets and the other two had AlTi alloy targets with a compositional atomic ratio Al / Ti of 2. The chamber is evacuated, followed by heating and plasma etching steps to further clean the knives and condition the blade surface by removing excess binder from the blade surface. TiN and (Ti,Al)N alloy layers were deposited at a temperature of 600°C by metal evaporation while maintaining a partial pressure of nitrogen in the coater, and using appropriate selection of active evaporation sources and ratios. Process conditions in the deposition step are as follows:
[0057] Table 1
...
example 2
[0067] Inserts from Example 1 were subjected to a coating process using the parameters according to Table 3 to deposit an additional interlayer of the second type.
[0068] table 3
[0069] Floor
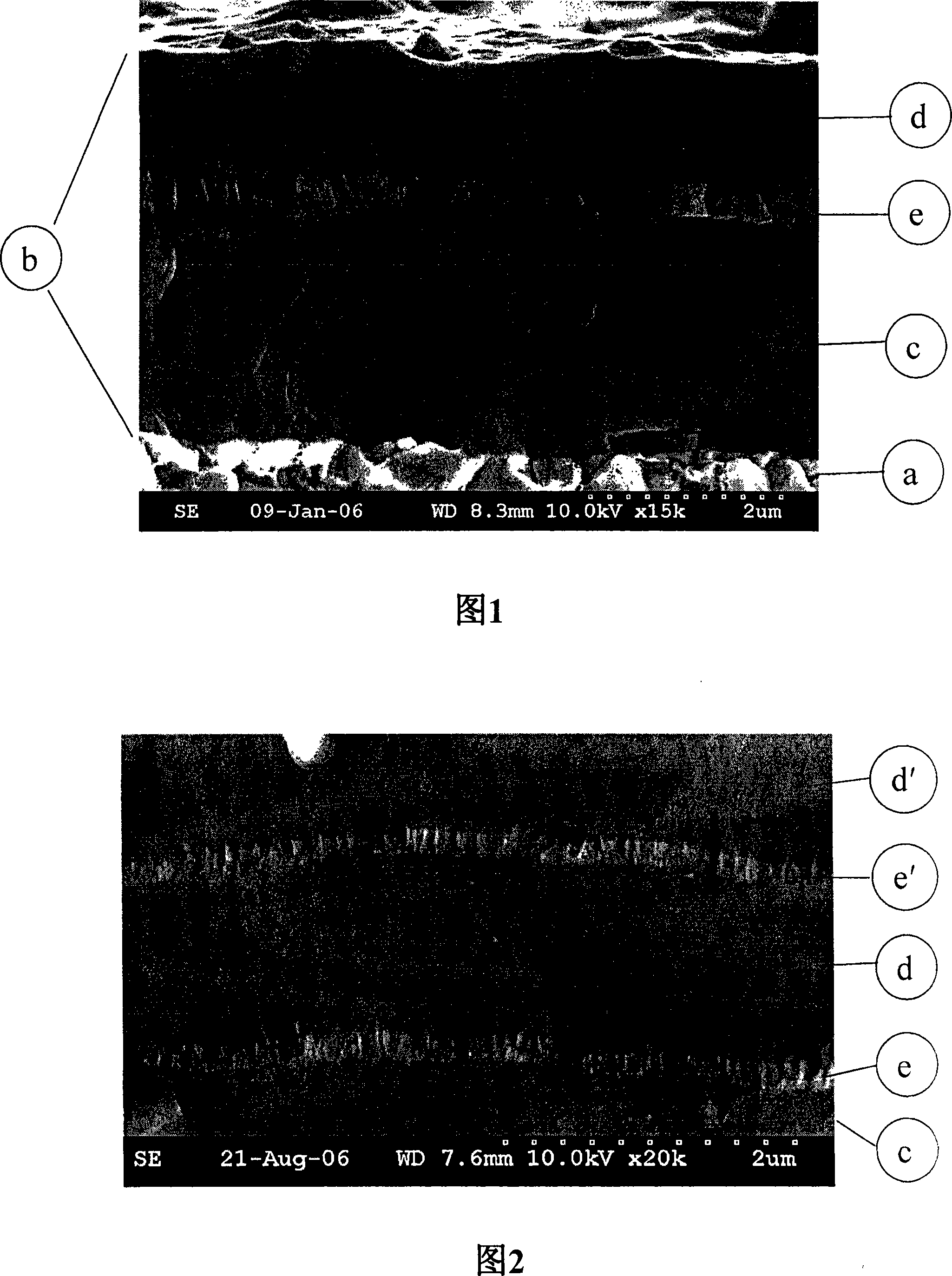
[0070] The fractured cross-section of the coating is shown in the SEM micrograph in FIG. 2 .
[0071] Inserts were analyzed using the same technique as in Example 1. The results are shown in Table 4.
[0072] Table 4
[0073] Floor
[0074] * Estimates made on measurements of a single layer coating deposited under the same conditions and having a composition and thickness consistent with that of the layer. After deposition of layers e and d, it is desired that the residual stress of layer c remain at substantially the same stress level.
example 3
[0076] The coating according to example 1 was deposited to a thickness of 4.2 μm on a solid carbide ball nose end mill with a diameter of 10 mm. A similar end mill with the same cemented carbide composition was coated with a prior art (Ti,Al)N single layer coating with an Al / Ti atomic ratio of 2.0 and a thickness of 2.9 μm . The two end mill variants were evaluated in a dry milling test for profile milling of 1.2379 steel with a hardness of HRC58. The cutting speed is 170m / min, the feed speed is 0.12mm / tooth, and the cutting amount is a p =a e = 0.2 mm. The tool life (expressed in milling distance m) up to the maximum wear amount of 0.40 mm is shown in Table 5. The results show that the coatings of the invention have superior performance in demanding milling operations on superhard steels.
[0077] table 5
[0078] Coated solid carbide end mill test
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com