Piezo-electricity drive type optical lens
An optical lens, piezoelectric drive technology, applied in the field of optical lens, to achieve the effect of simplifying the sturdiness, simplifying the components, and easy to assemble
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
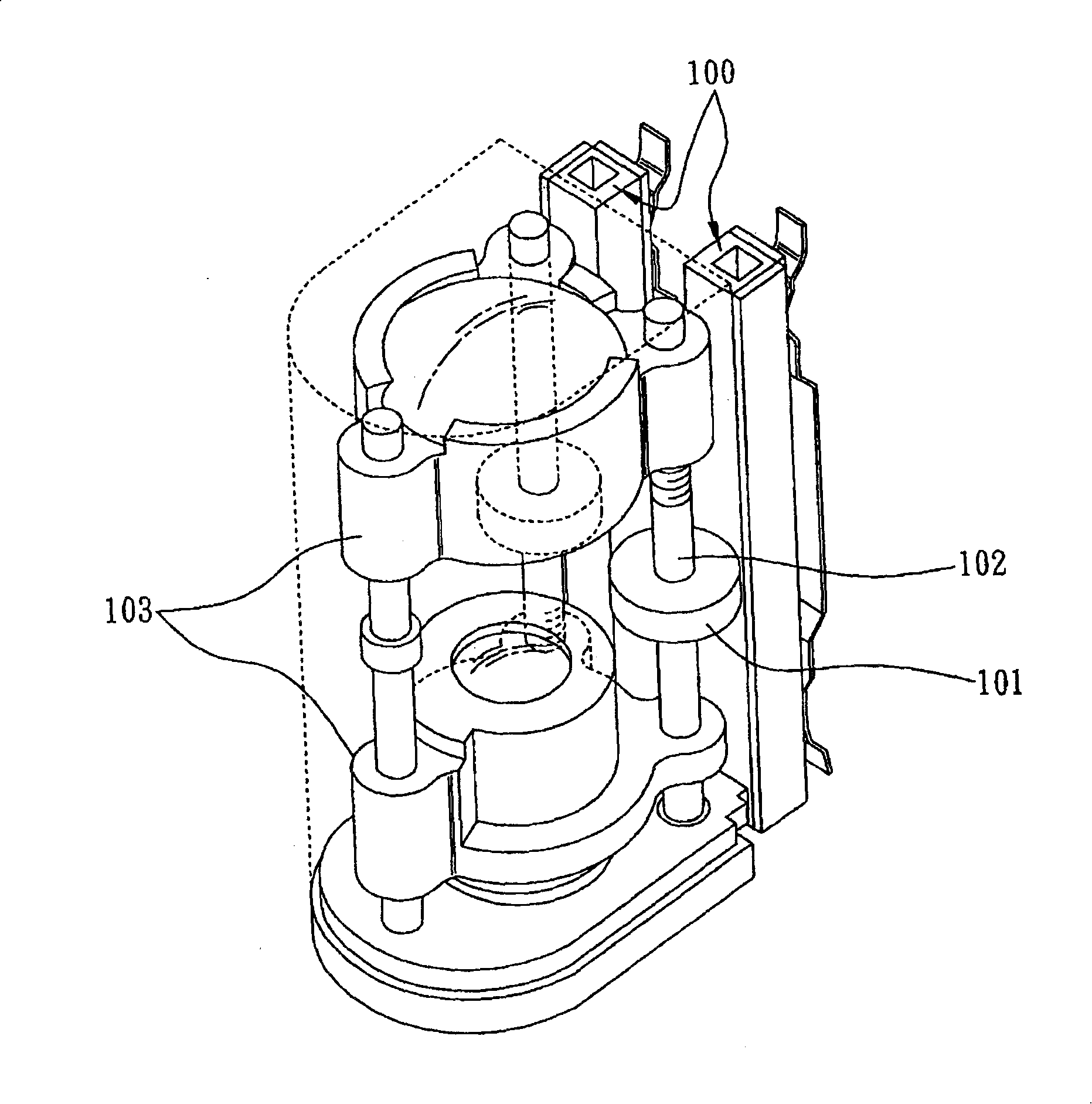
[0077] like Figure 5 As shown in FIG. 6 , the present invention provides a piezoelectric-driven optical lens, which includes a lens body 2 , a piezoelectric actuator 3 for providing driving force, and a position sensing device 4 for sensing position changes. The lens body 2 at least has a hollow seat body 21 communicating with the outside to form a light hole 211, a lens barrel 22 positioned in the hollow seat body 21 that can move axially along the axis of the light hole 211, and fixed to the lens barrel 22 and mirror group 23 corresponding to the axis of the optical hole 21. The piezoelectric actuator 3 is disposed between the hollow base body 21 and the lens barrel 22 for driving the lens barrel 22 to move axially relative to the hollow base body 21 for zooming. The position sensing device 4 is arranged in the hollow seat 21 to sense the axial position of the lens barrel 22 relative to the hollow seat 21, thereby simplifying the piezoelectric-driven optical lens to overco...
no. 2 example
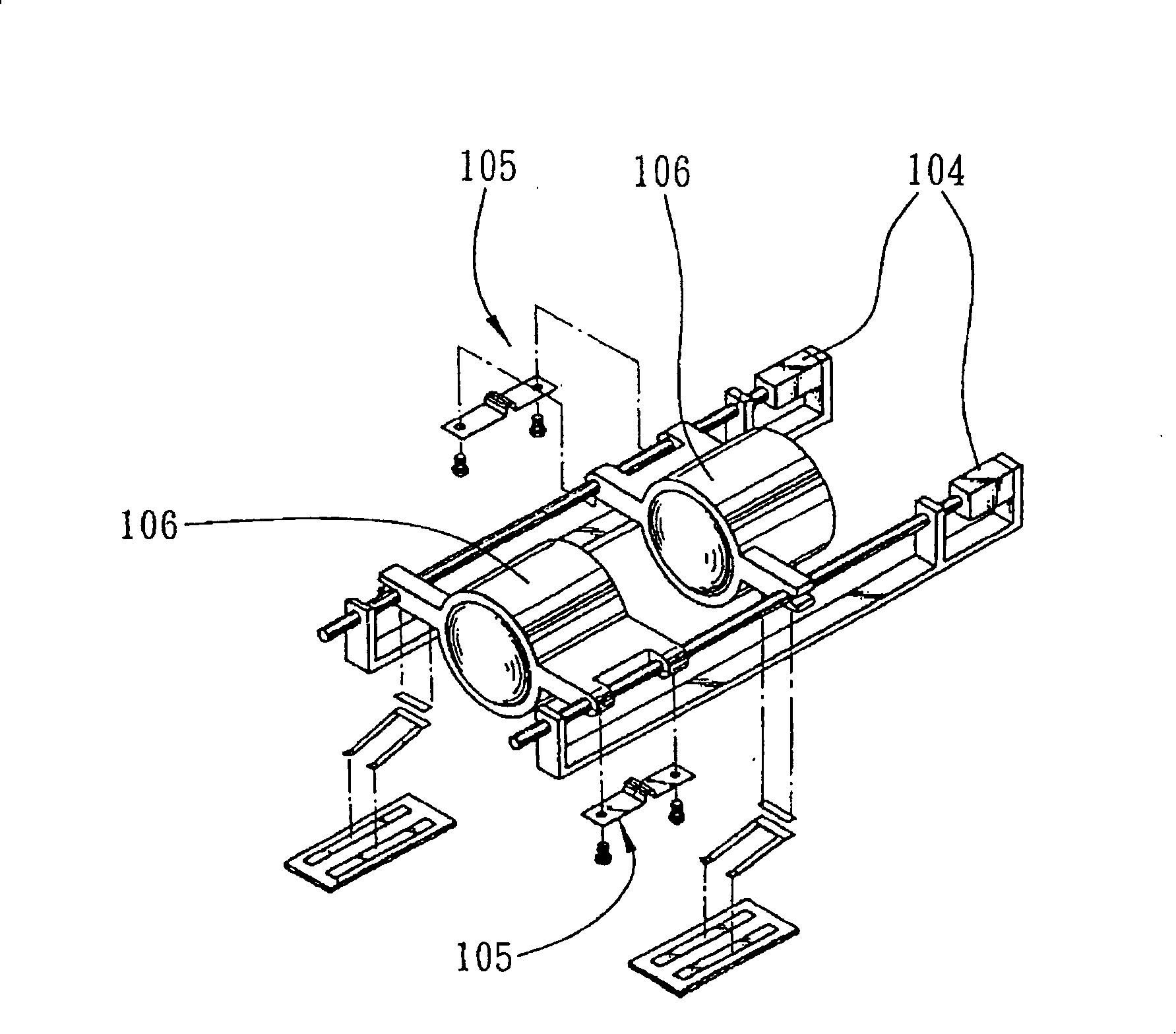
[0090] Please refer to Fig. 7, the difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is only in the design and arrangement position of the piezoelectric actuator 3', and the hollow base 21, lens barrel 22, lens group 23, and the design of the position sensing device 4 are roughly the same, and only part of the structural design of the piezoelectric actuator 3' has been adjusted to the configuration position, so the same part will not be described repeatedly, and the component symbols will not be redefined. In order not to go into too much detail, only the differences are described below, which are hereby explained.
[0091] As shown in Figure 7, the lens body 2 also includes a wear-resistant part 26 located outside the lens barrel 22, and the piezoelectric actuator 3' is fixed on the inner surface of the hollow seat body 21, and makes the wear-resistant The part 26 is kept in contact with the piezoelectric actuator 3', that is, the wear-resistant part 26 is fixed to ...
no. 3 example
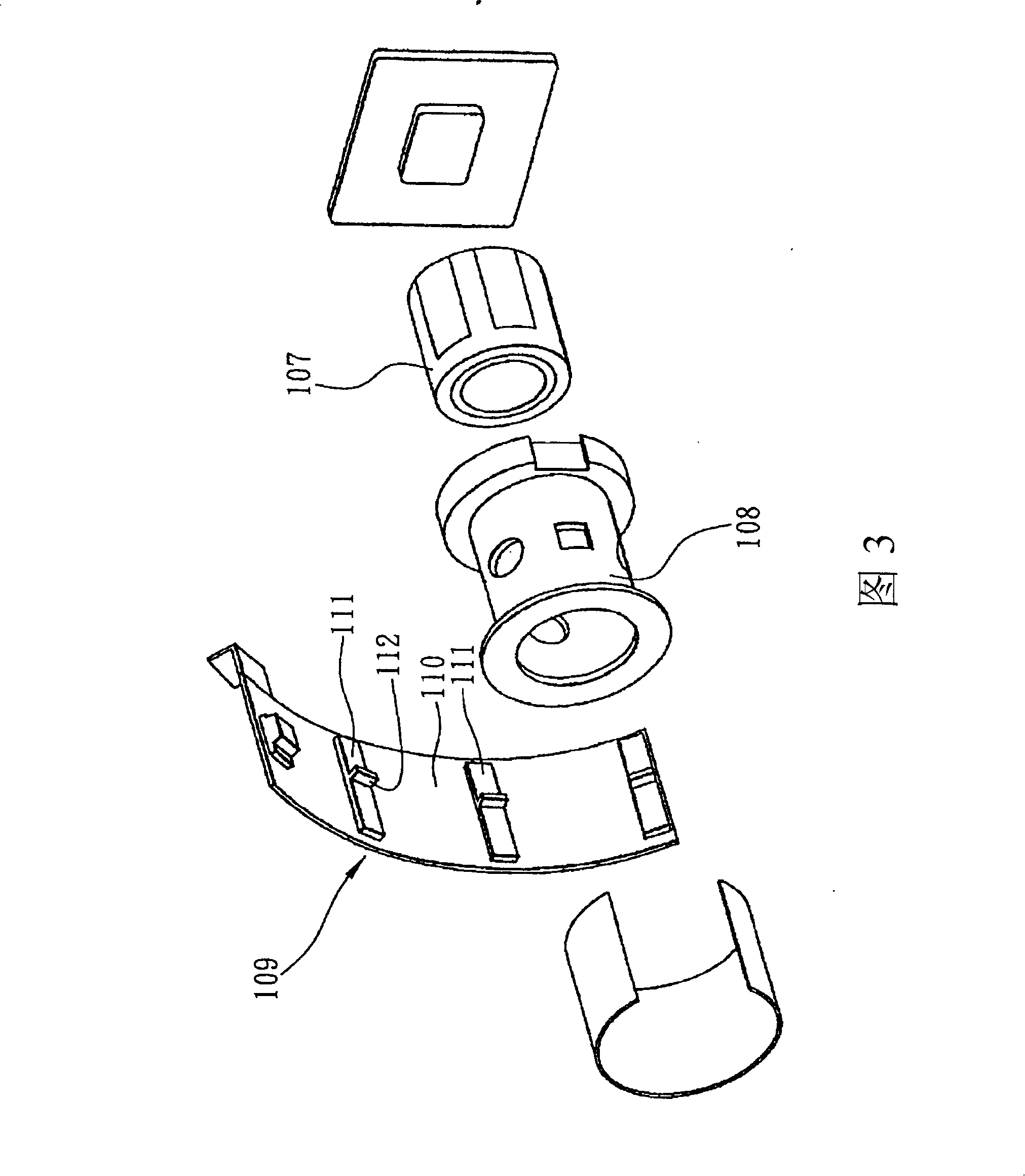
[0093] Please refer to Fig. 8, the difference between the present embodiment and the second embodiment is only in the design and arrangement position of the piezoelectric actuator 3", and the hollow seat body 21, lens barrel 22, lens group 23, And the design of the position sensing device 4 is the same, so the same part will not be described repeatedly, and the component symbols will not be redefined, so as not to repeat it too much. Only the differences will be described below, which is hereby explained.
[0094] As shown in FIG. 8 , the lens body 2 also includes a wear-resistant part 26 located on the outside of the lens barrel 22, and the piezoelectric actuator 3" includes a wear-resistant part 26 fixed on the outside 22 of the lens barrel and is relatively far away from the wear-resistant part 26. The prestressing device 32", and the piezoelectric stator 31" fixed on the inner surface of the hollow seat body 21 and kept in contact with the wear-resistant part 26, at the sam...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com