TiO2 nanometer pore array material preparation method and uses thereof
A nanopore array, titanium-based technology, applied in the growth of polycrystalline materials, chemical instruments and methods, crystal growth, etc., can solve the problems affecting the stability of titanium-based TiO nanotube array materials, photoelectric catalytic performance, electrochemical performance and related properties. , nanotube array film and substrate peeling, nanotube and substrate cracking or breaking, etc., to achieve the effect of shortened migration path, good optoelectronic and electrical properties, and strong mechanical force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
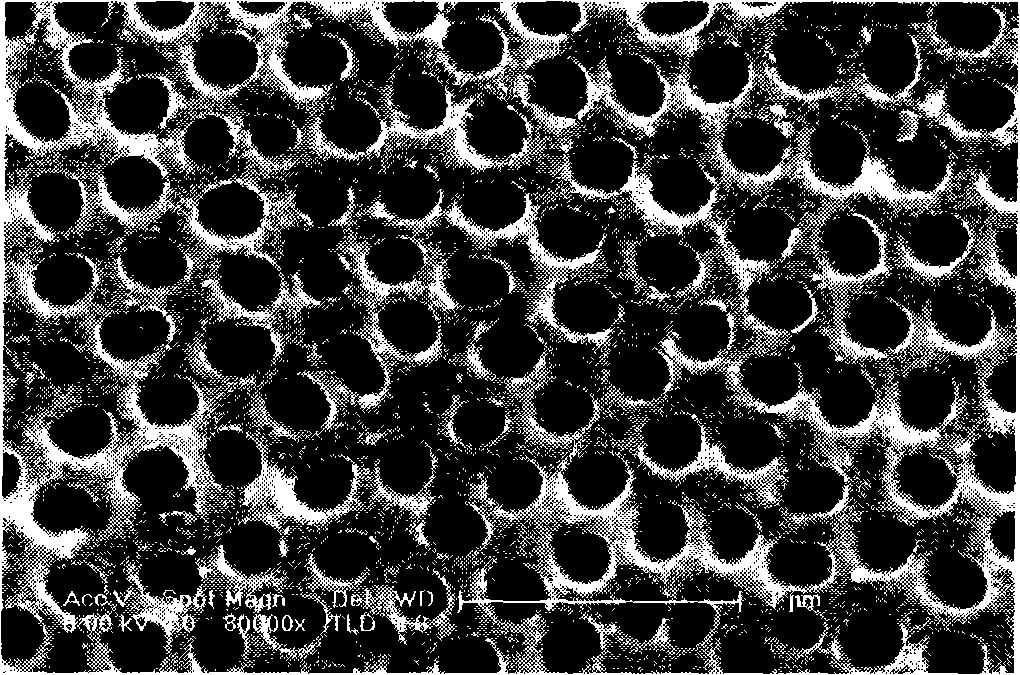
[0018] The cleaned pure titanium sheet (>99.9%) is used as an anode, and the platinum sheet is used as a counter electrode, and placed in a hydrofluoric acid-dimethylsulfoxide electrolyte solution containing 5 wt% of fluorine (mass ratio, the same as in the following examples) Anodize the titanium sheet. The applied voltage is 40V, and the anodizing time is 70h. After the preparation, the titanium sheet is removed, and the excess loose film on the surface of the titanium sheet is removed by ultrasonic method, and TiO with a pore diameter of about 180nm and a pore depth of about 55nm can be obtained. 2 Nanohole array structure, its surface morphology can be seen in figure 1 .
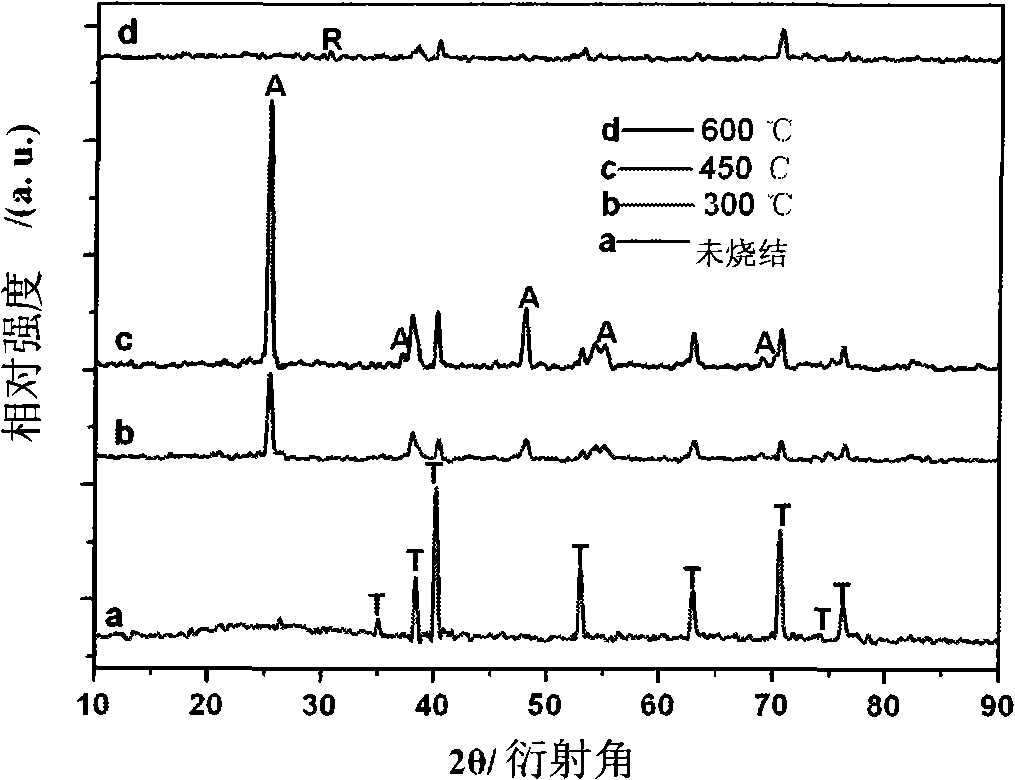
[0019] Sinter the material at a temperature range of 450°C for 3 hours, and anatase phase TiO can be obtained after cooling 2 Nanopore array electrode materials, see image 3 c.
Embodiment 2
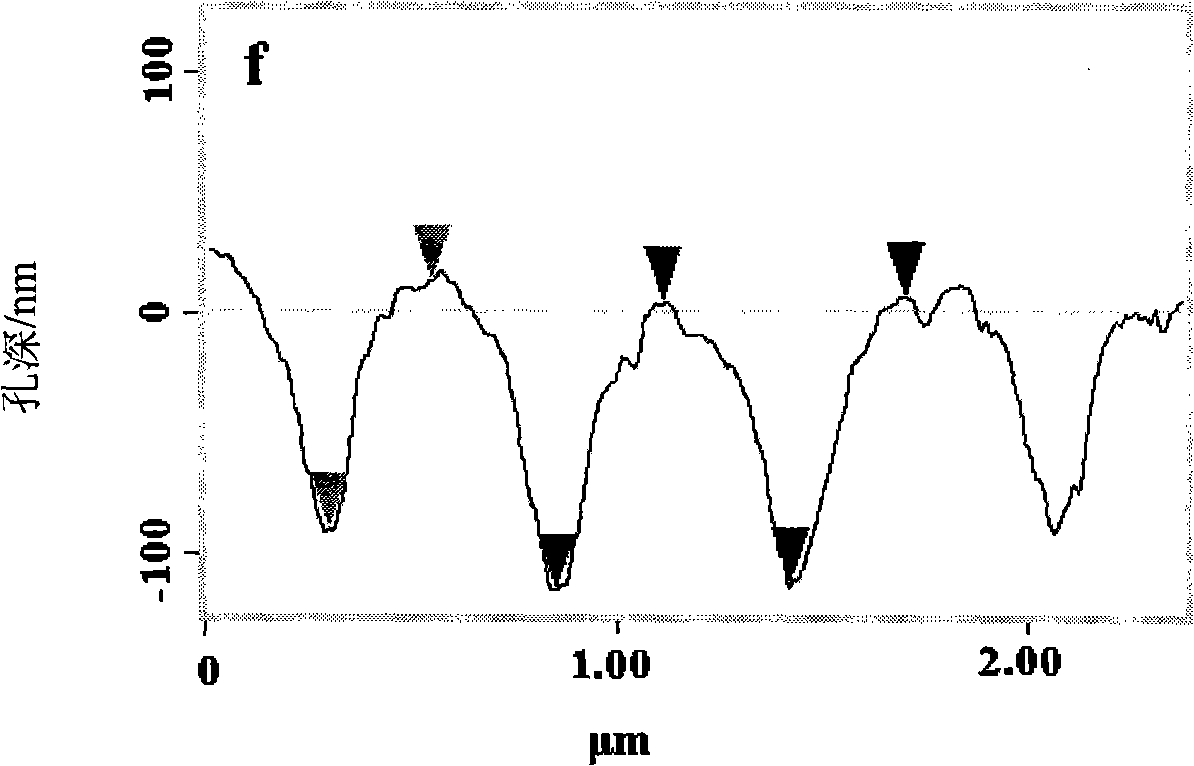
[0021] The cleaned pure titanium sheet (>99.9%) is used as an anode, and the platinum sheet is used as a counter electrode, and is placed in a hydrofluoric acid-dimethyl sulfoxide electrolyte solution containing 5 wt% of fluorine for anodic oxidation. The applied voltage is 60V, and the anodizing time is 75h. After the preparation, the titanium sheet is removed, and the loose film on the surface of the titanium sheet is removed by mechanical vibration, and TiO with a pore diameter of about 300nm and a pore depth of 100nm can be obtained. 2 Nanohole array material, pores deep figure 2 .
[0022] The sample was sintered in the temperature range of 300 °C for 15 hours, and the anatase phase TiO could be obtained after cooling 2 Nanopore array electrode materials.
Embodiment 3
[0024] The cleaned pure titanium sheet (>99.9%) is used as an anode, and the platinum sheet is used as a counter electrode, which is placed in a hydrofluoric acid-dimethylformamide electrolyte containing 1% fluorine for anodic oxidation. The applied voltage is 20V, and the anodizing time is 40h. After the preparation, the titanium sheet is removed, and the loose film on the surface layer of the titanium sheet is removed by ultrasonic method, and TiO with a pore diameter of about 80nm and a pore depth of 25nm can be obtained. 2 Nanopore Array Materials.
[0025] The sample was sintered at 700°C for 0.5h, and after cooling, TiO in the rutile phase was obtained. 2 Nanopore array electrode materials.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hole depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com