Non-volatile sequent modular memory, data storage and reading method
A technology for data storage and data storage, which is applied in the direction of static memory, read-only memory, digital memory information, etc., can solve the problems of high power consumption, slow speed, low repeatable reading and writing times, etc., so as to improve the reading and writing speed and reduce the The effect of power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
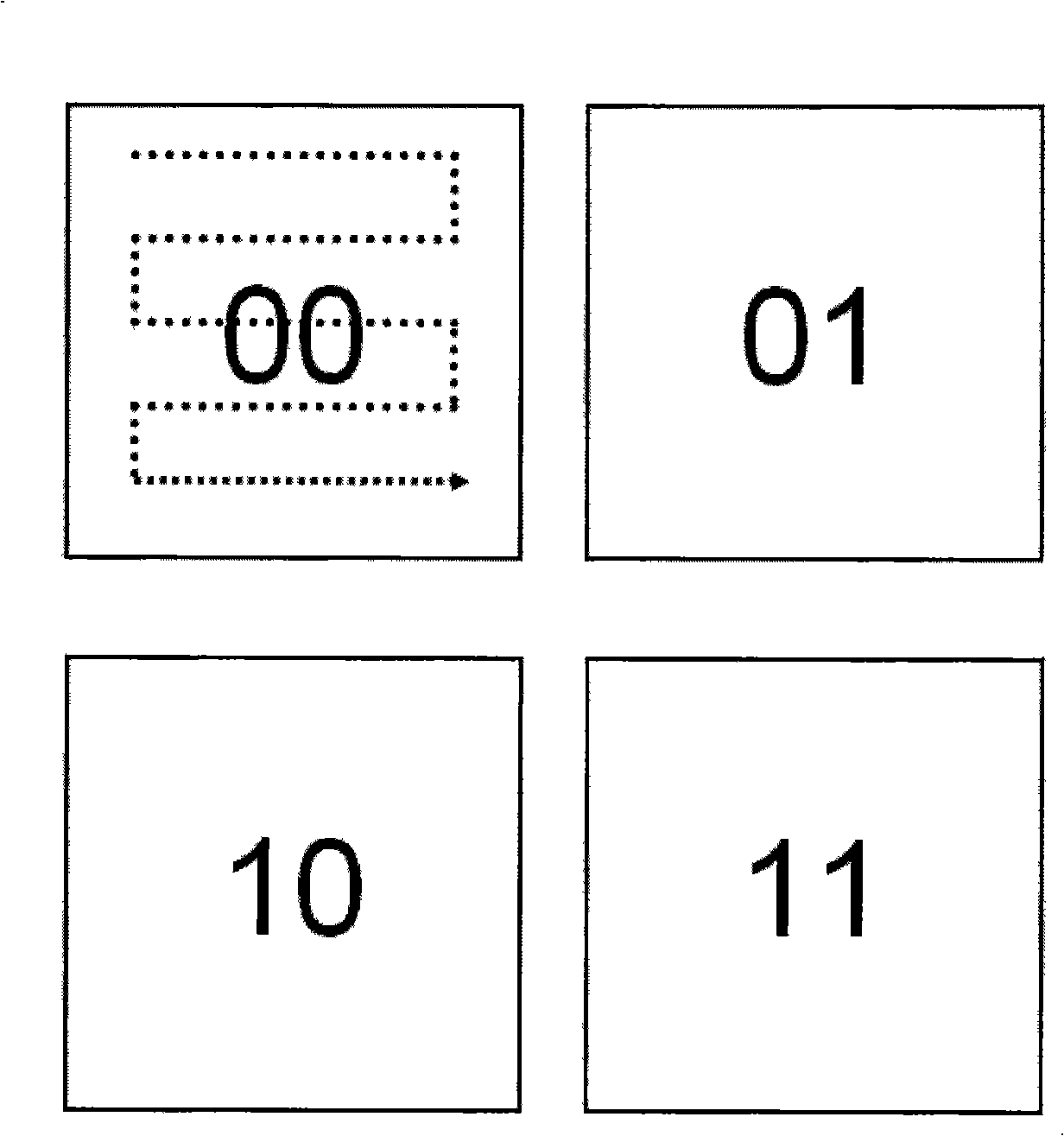
[0039] figure 1 A new type of non-volatile modular sequential memory is shown. First, the memory is divided, and each memory block is given a common address, and each memory block has only one address. The random reading and writing method is adopted between the storage blocks, and the sequential reading and writing method is adopted inside the storage block.
[0040] The storage method is as follows:
[0041] A11. The data to be stored points to a storage block.
[0042] A12. Store data in order.
[0043] A13. Complete the storage data operation.
[0044] The readout method is as follows:
[0045] B11. Find the storage data address
[0046] B12. Read out the data sequentially.
[0047] B13. Complete the data readout operation.
Embodiment 2
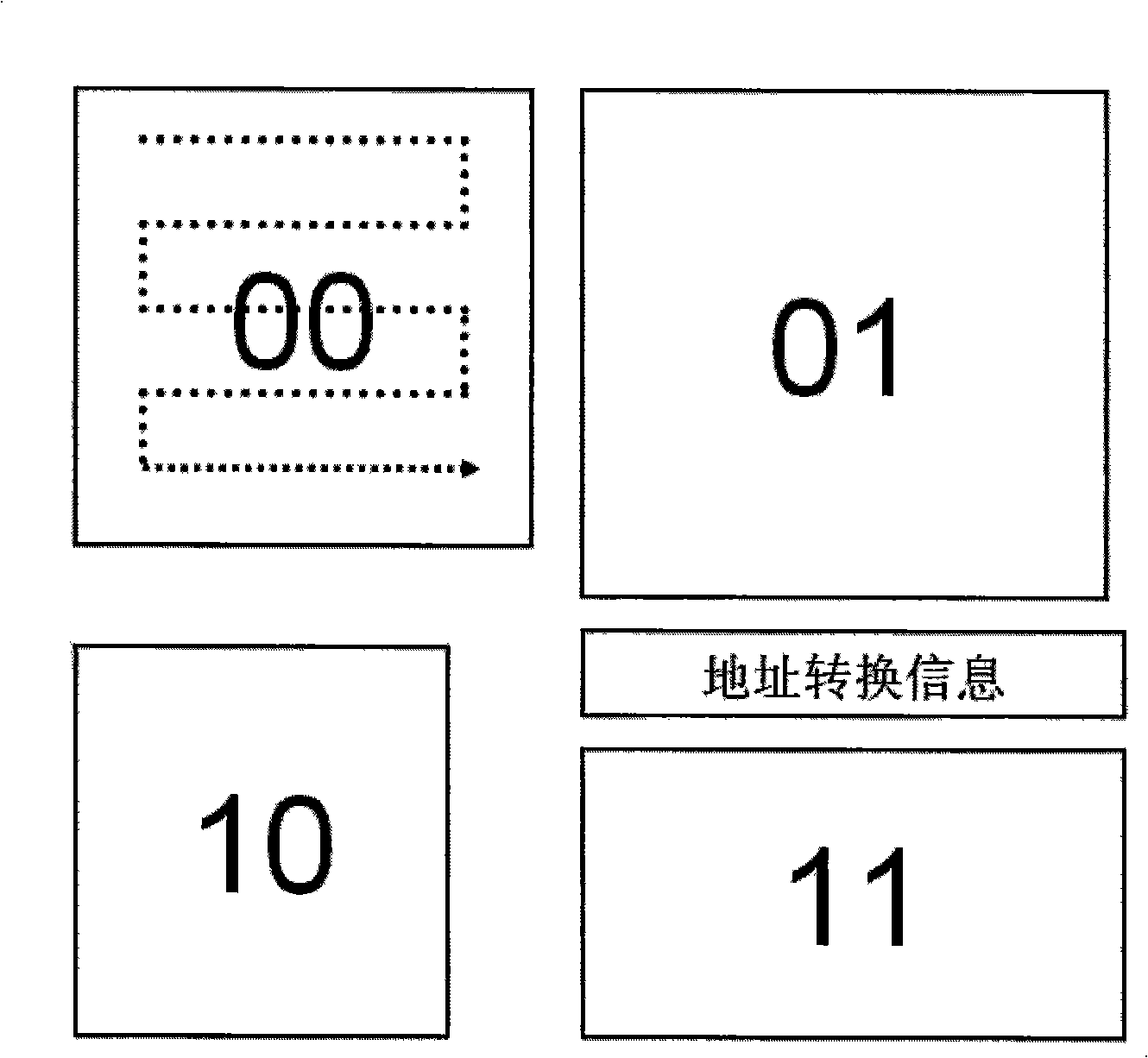
[0049] figure 2 An alternative to non-volatile block-style sequential storage is shown. Pre-evaluate the amount of data to be written, store data with a large amount of data in a storage block with a large capacity, and store data with a small amount of data in a storage block with a small capacity. This method should be divided into different sizes for the memory chip. Each memory block is marked with an address. In the process of storing data, first evaluate the amount of data to be stored. If the amount of data reaches a certain value, the address of the data is automatically converted to a specific storage block, and the conversion information is recorded in another non-volatile block. in the permanent storage block. In the readout process, the address conversion information is read out first, and then the data is read out according to the address conversion information.
[0050] The storage method is as follows:
[0051] A21. Evaluate the data to be stored.
[0052...
Embodiment 3
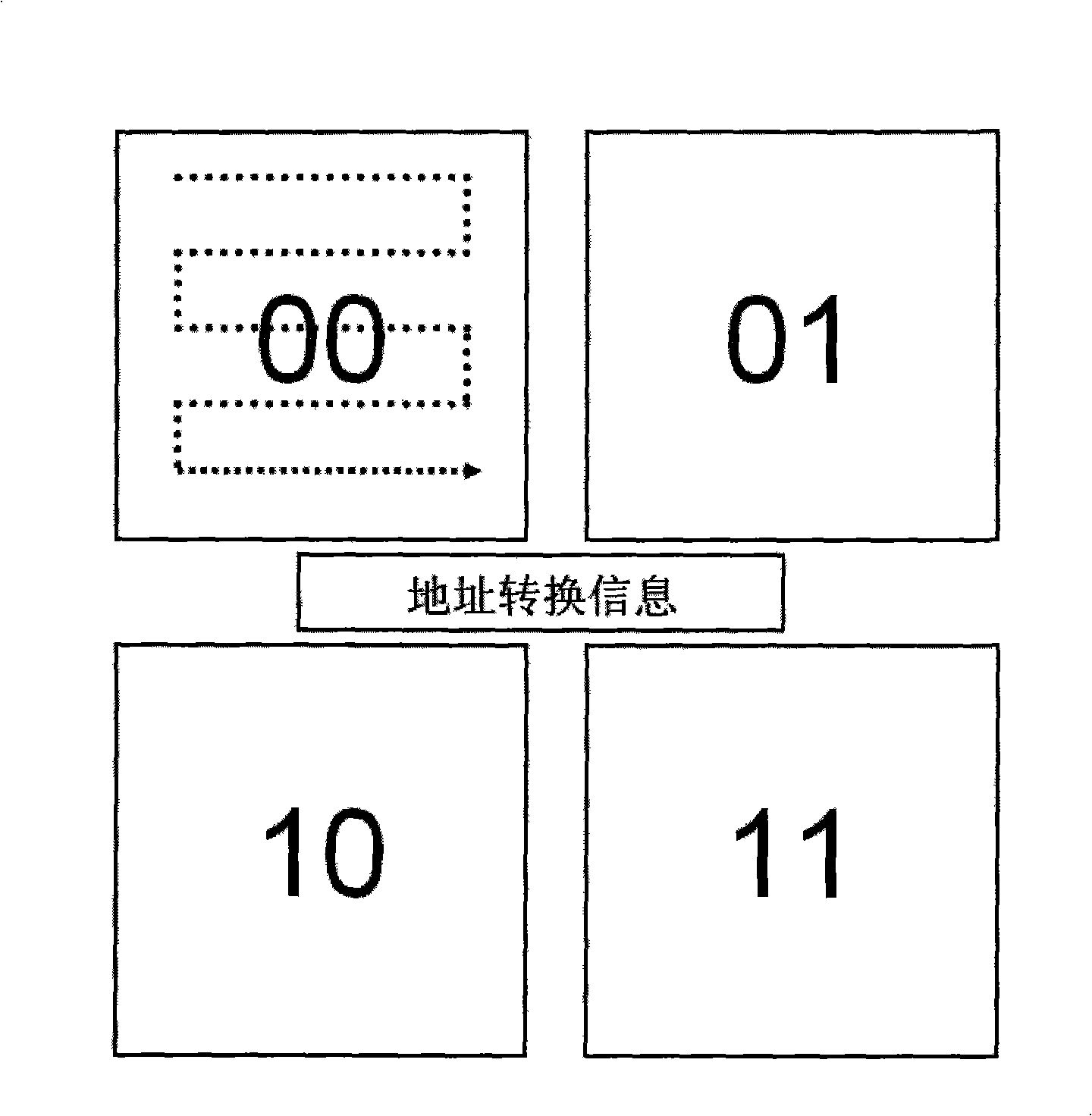
[0061] image 3 An alternative to non-volatile block-style sequential storage is shown. Pre-evaluate the amount of data to be written, and if the amount of data is large, divide and store the amount of data into two or more different storage blocks. In the process of storing data, firstly evaluate the amount of data to be stored. If the amount of data reaches a certain value, the data amount is divided and stored, and the address conversion information of the divided storage is stored in another non-volatile memory block. In the readout process, the address conversion information is read out first, and then the data is read out according to the address conversion information.
[0062] The storage method is as follows:
[0063] A31. Evaluate the data to be stored.
[0064] A32. If the amount of data is large, divide and store the amount of data into two or more different storage blocks. The address is converted into a suitable storage block, and the address conversion infor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com