Optical encoder and electronic equipment
An encoder and optical technology, which is applied in the field of optical encoders, can solve the problems of difficult miniaturization of the encoder module, increased current consumption, and unsuitability for use, and achieve the effect of simplifying electrical wiring and realizing miniaturization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
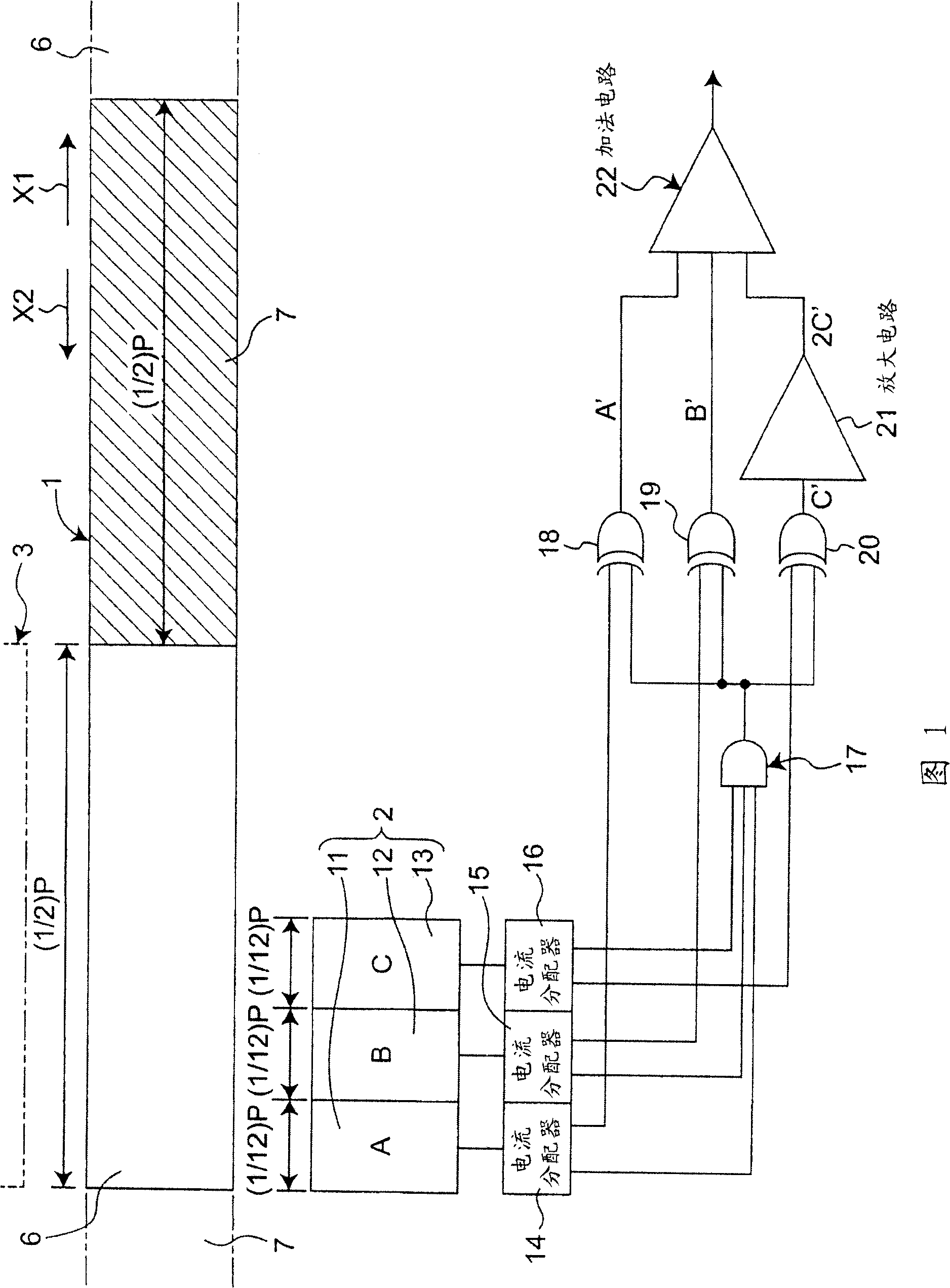
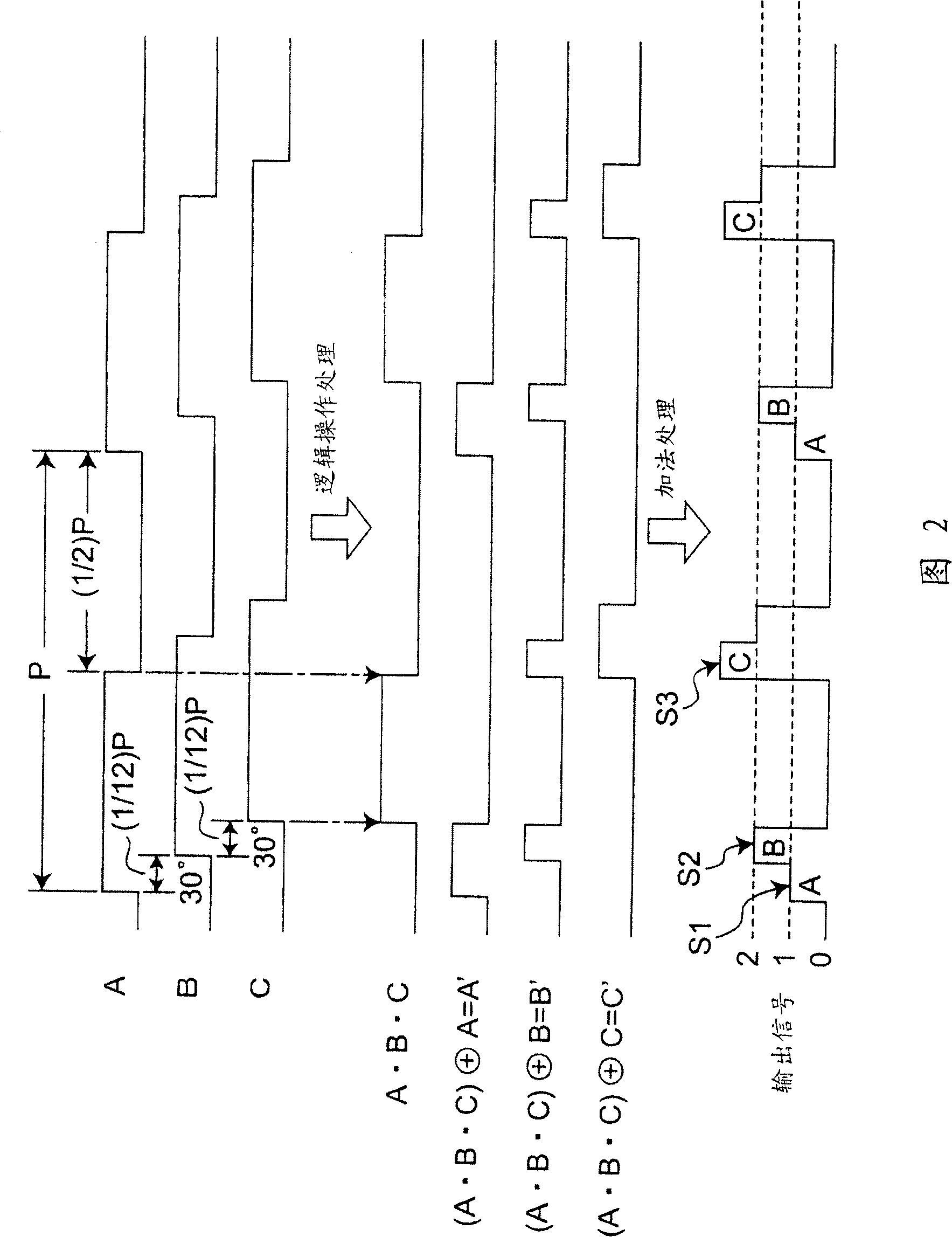
[0067] FIG. 1 shows a first embodiment of an optical encoder of the present invention. This first embodiment includes a moving body 1 , a light receiving unit 2 and a light emitting unit 3 . The light emitting unit 3 is constituted by a light emitting element such as an LED (Light Emitting Diode). The light receiving unit 2 has three light receiving elements 11 to 13 . In addition, the moving body 1 can move in a direction indicated by an arrow X1 or X2, and light-on portions 6 and light-off portions 7 are alternately arranged in the moving direction. If the arrangement pitch of the light-on portions 6 is P, the size (width dimension) in the moving direction of the light-on portions 6 and the light-off portions 7 is (1 / 2)P. The above-mentioned light-on portion 6 passes the light from the light-emitting unit 3 to the light-receiving unit 2 side, and on the other hand, the light-off portion 7 does not pass the light from the light-emitting unit 3 to the light-receiving unit 2 ...
no. 2 approach
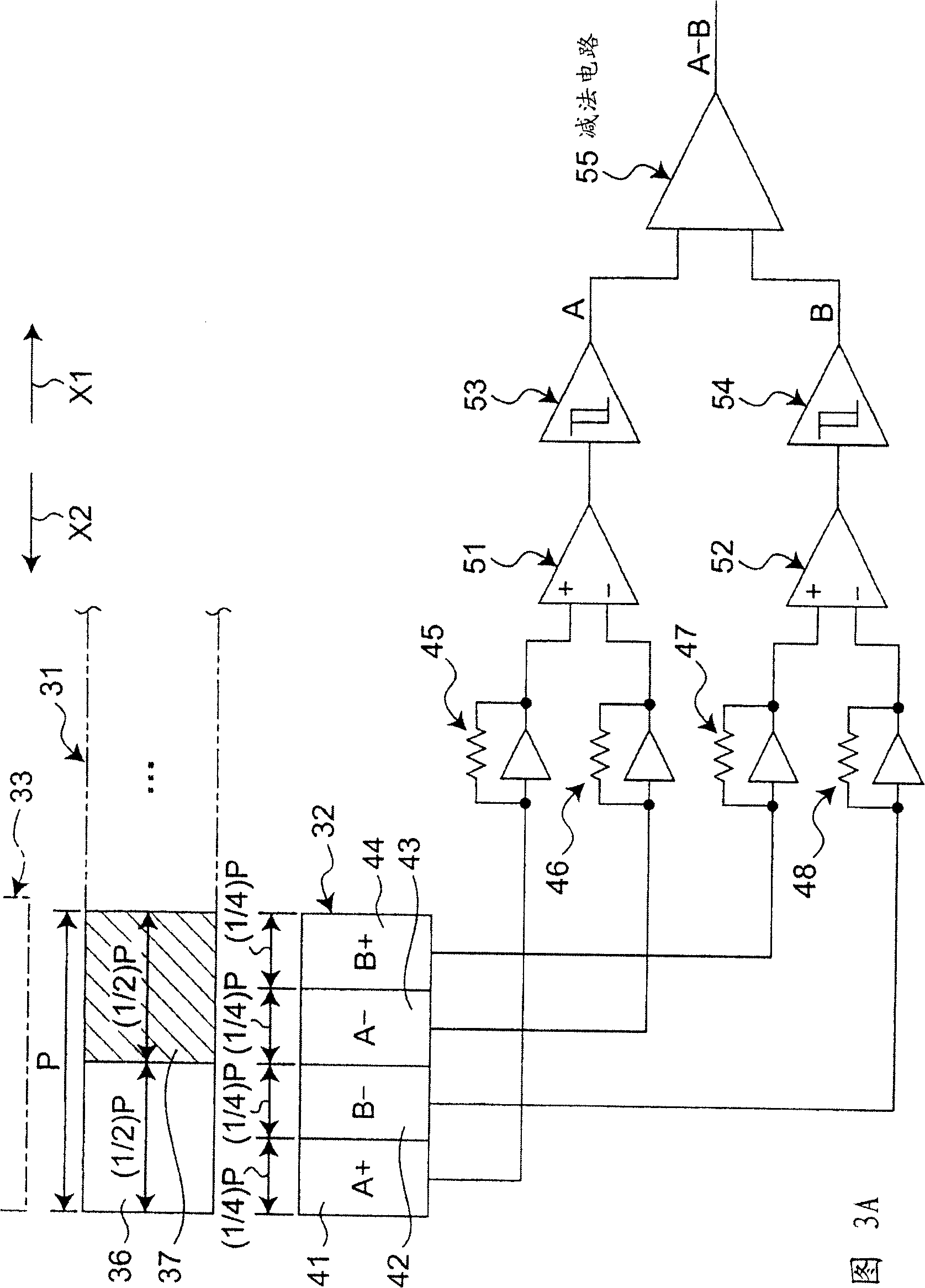
[0074] Next, FIG. 3A shows a second embodiment of the optical encoder of the present invention. This second embodiment includes a moving body 31 , a light receiving unit 32 and a light emitting unit 33 . The light emitting unit 33 is constituted by a light emitting element such as an LED (Light Emitting Diode).
[0075] The light receiving unit 32 has four light receiving elements 41 to 44 . In addition, the moving body 31 can move in the direction indicated by the arrow X1 or X2, and the light-on portions 36 and the light-off portions 37 are alternately arranged in the moving direction. If the arrangement pitch of the light-on portions 36 is P, the size (width dimension) in the moving direction of the light-on portions 36 and the light-off portions 37 is (1 / 2)P. The above-mentioned light-on portion 36 passes light from the light-emitting unit 33 to the light-receiving unit 32 side, and on the other hand, the light-off portion 37 does not pass light from the light-emitting u...
no. 3 approach
[0088] Next, FIG. 5 shows a third embodiment of the optical encoder of the present invention. The third embodiment differs from the second embodiment in that an exclusive OR circuit 61 and an AND circuit are connected between the AD converters 53, 54 and the subtraction circuit 55 of the second embodiment. 62, and a comparison unit 66 is connected to the output terminal of the subtraction circuit 55. Therefore, the third embodiment is the same as the second embodiment in that it includes the movable body 31 , the light receiving unit 32 , the light emitting unit 33 , and the current-voltage converting units 45 to 48 shown in FIG. 3A . Therefore, in this third embodiment, the same reference numerals are given to the same parts as those of the second embodiment, and the description will be given mainly on the parts different from the second embodiment.
[0089] As shown in FIG. 5 , in the third embodiment, the output line 67 of the AD converter 53 and the output line 68 of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com