Single-phase grounding fault determining, protecting method and system of neutral-point uneffective earthed electric grid
A single-phase ground fault and non-effective grounding technology, which is applied to emergency protection circuit devices, fault locations, and emergency protection circuit devices for limiting overcurrent/overvoltage, and can solve misjudgments or missed judgments of high-resistance ground faults , unable to provide effective protection, misunderstanding of single-phase ground fault judgment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
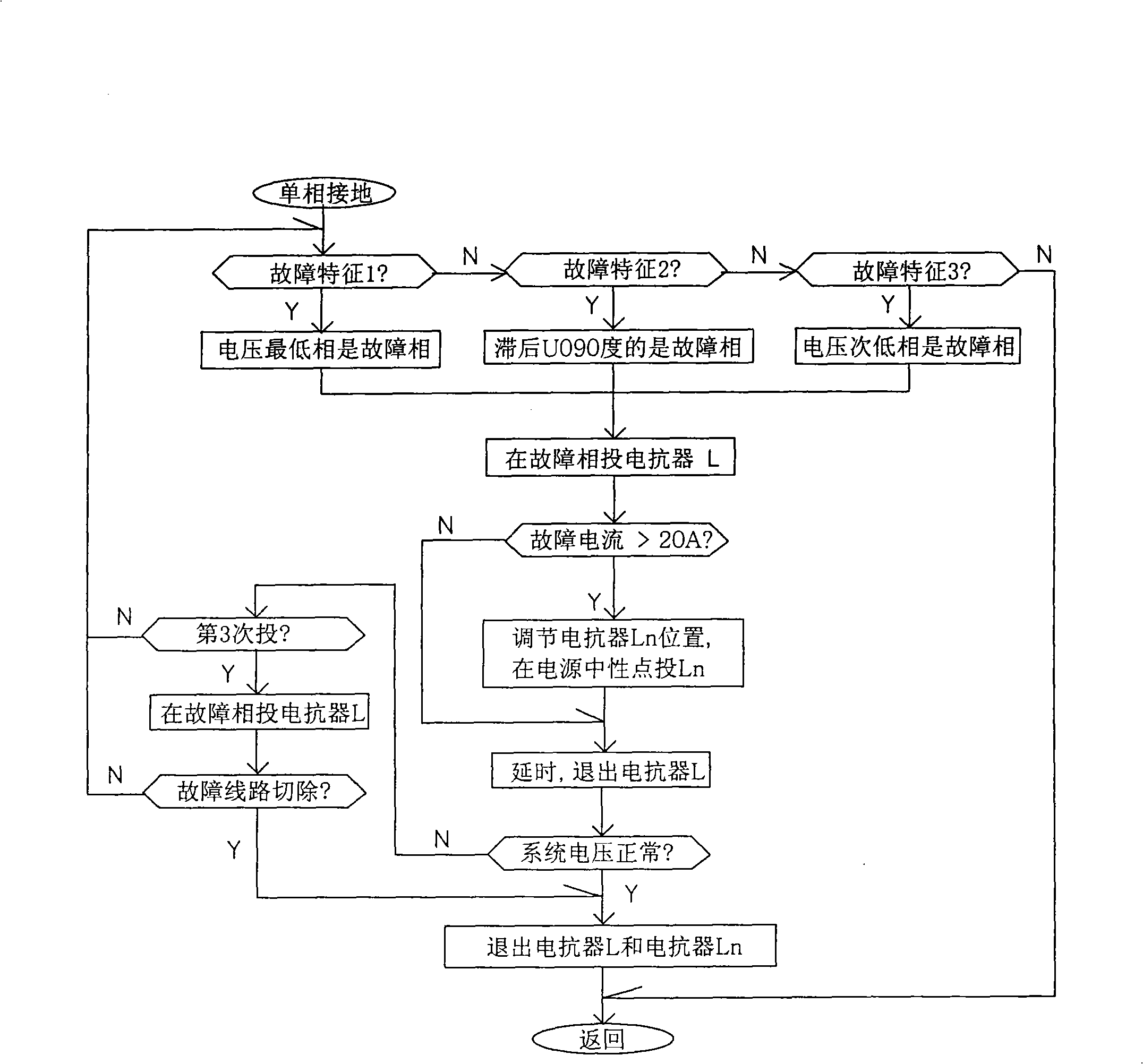
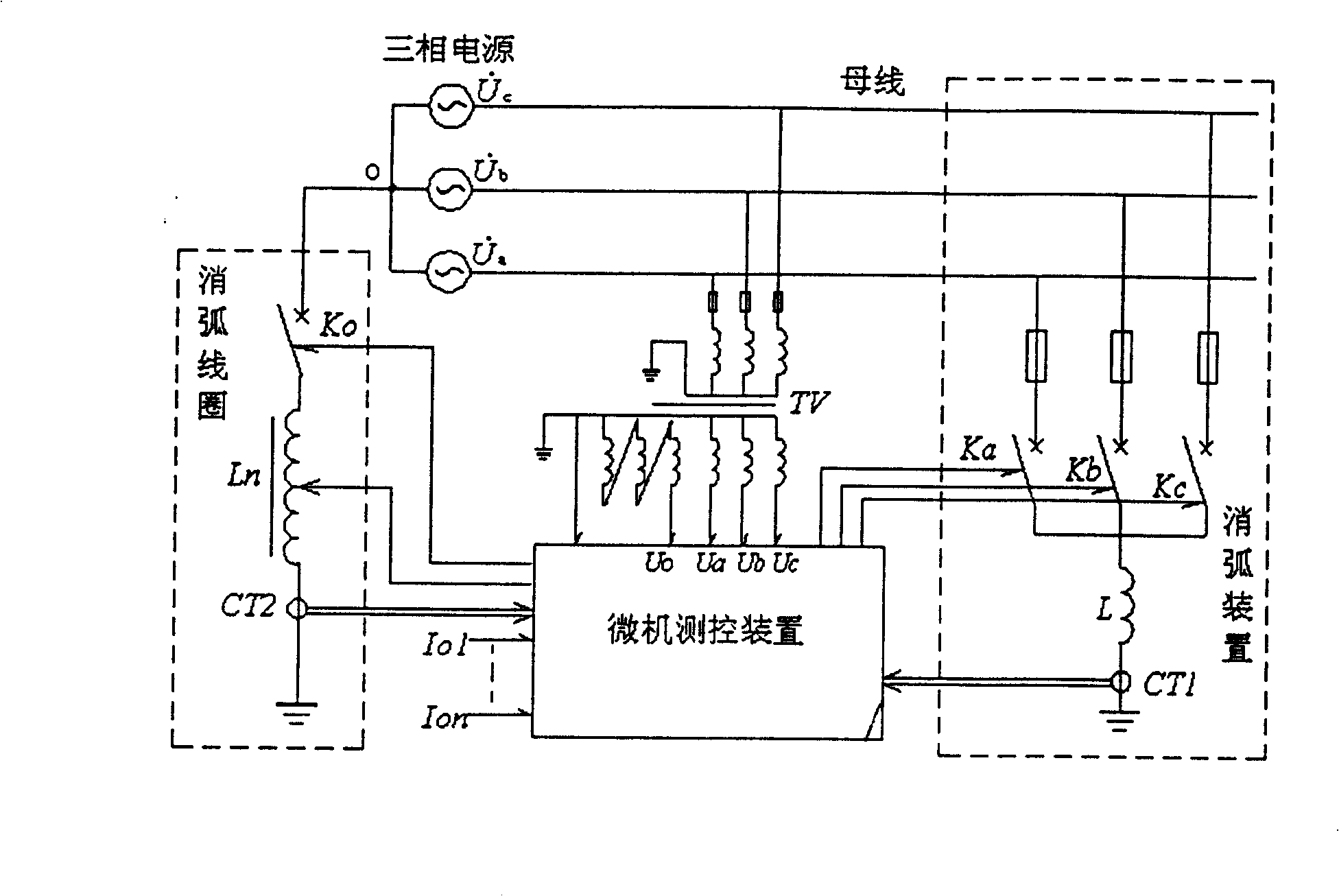
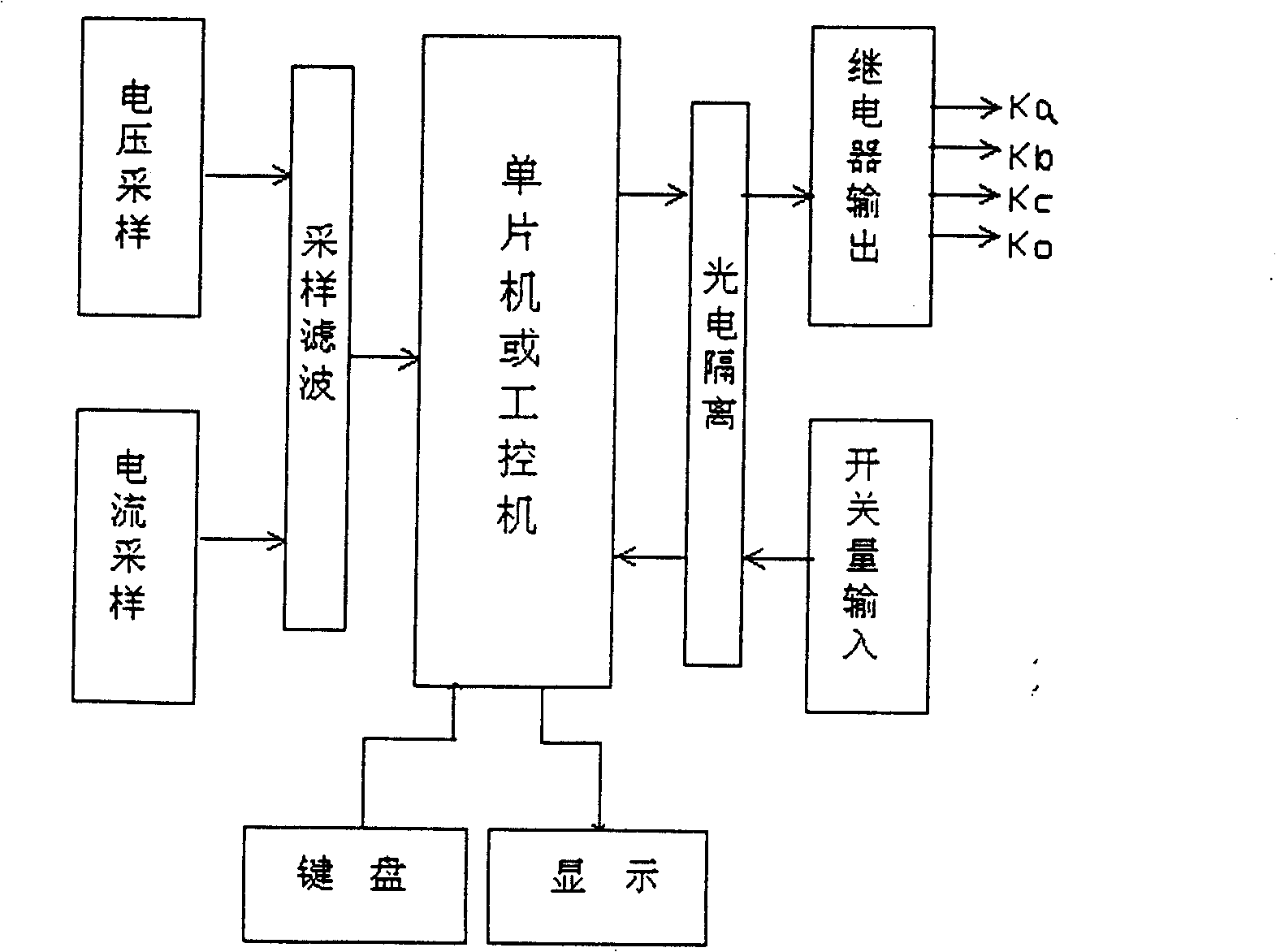
[0038] When single-phase grounding occurs in a 6kV neutral point non-effectively grounded grid system, the measured zero-sequence voltage is 2kV, while the normal phase voltage of the system is 3.6kV. It can be seen from the discrimination method described in claim 1 that the single-phase The ground fault satisfies the condition of characteristic area 1, therefore, it can be judged that the lowest phase of the three-phase voltage is the fault phase at this time, and immediately put into ground protection on the busbar of this phase (the ground protection can be grounded through the reactor L, or other methods grounding), if the fault current is less than 20A, the reactor Ln will not be used, and only the switch-on reactor L will complete the protection; if it is greater than 20A, the reactor Ln will be adjusted to an appropriate position according to the current value measured by CT2 to drive the high voltage The switch Ko is closed, and the neutral point of the power supply is...
example 2
[0040] When single-phase grounding occurs in a 6kV neutral point non-effectively grounded power grid system, the measured zero-sequence voltage is 1.8kV, while the normal phase voltage of the system is 3.6kV. It can be seen from the discrimination method described in claim 1 that the single The phase-to-ground fault satisfies the condition of characteristic area 2. Therefore, it can be judged that the phase voltage lagging behind the zero-sequence voltage by 90° at this time is the fault phase, and the grounding protection is immediately put into use on the busbar of this phase (the grounding protection can be grounded through the reactor L, or other means of grounding), if the fault current is less than 20A, the reactor Ln will not be put into use, and only the switching-off reactor L will complete the protection; if it is greater than 20A, the reactor Ln will be adjusted to an appropriate position according to the current value measured by CT2 , drive the high-voltage switch ...
example 3
[0042] When single-phase grounding occurs in a 6kV neutral point non-effectively grounded grid system, the measured zero-sequence voltage is 1.2kV, while the normal phase voltage of the system is 3.6kV. It can be seen from the discrimination method described in claim 1 that the single The phase-to-ground fault satisfies the condition of characteristic area 3, therefore, it can be judged that the second lowest phase of the three-phase voltage is the fault phase at this time, and immediately put into ground protection on the busbar of this phase (the ground protection can be grounded through the reactor L, or grounding in other ways), if the fault current is less than 20A, the reactor Ln will not be put into use, and only the switch-on reactor L will complete the protection; if it is greater than 20A, the reactor Ln will be adjusted to an appropriate position according to the current value measured by CT2, Drive the high-voltage switch Ko to close, ground the neutral point of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com