Design method for diamond knife tool for processing Fresnel lens
A diamond tool and Fresnel lens technology, applied in stone processing tools, stone processing equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of principle processing errors, large loss of light energy, and reduce the optical efficiency of Fresnel lenses, etc., to achieve The effect of eliminating the principle error and reducing the loss of light energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
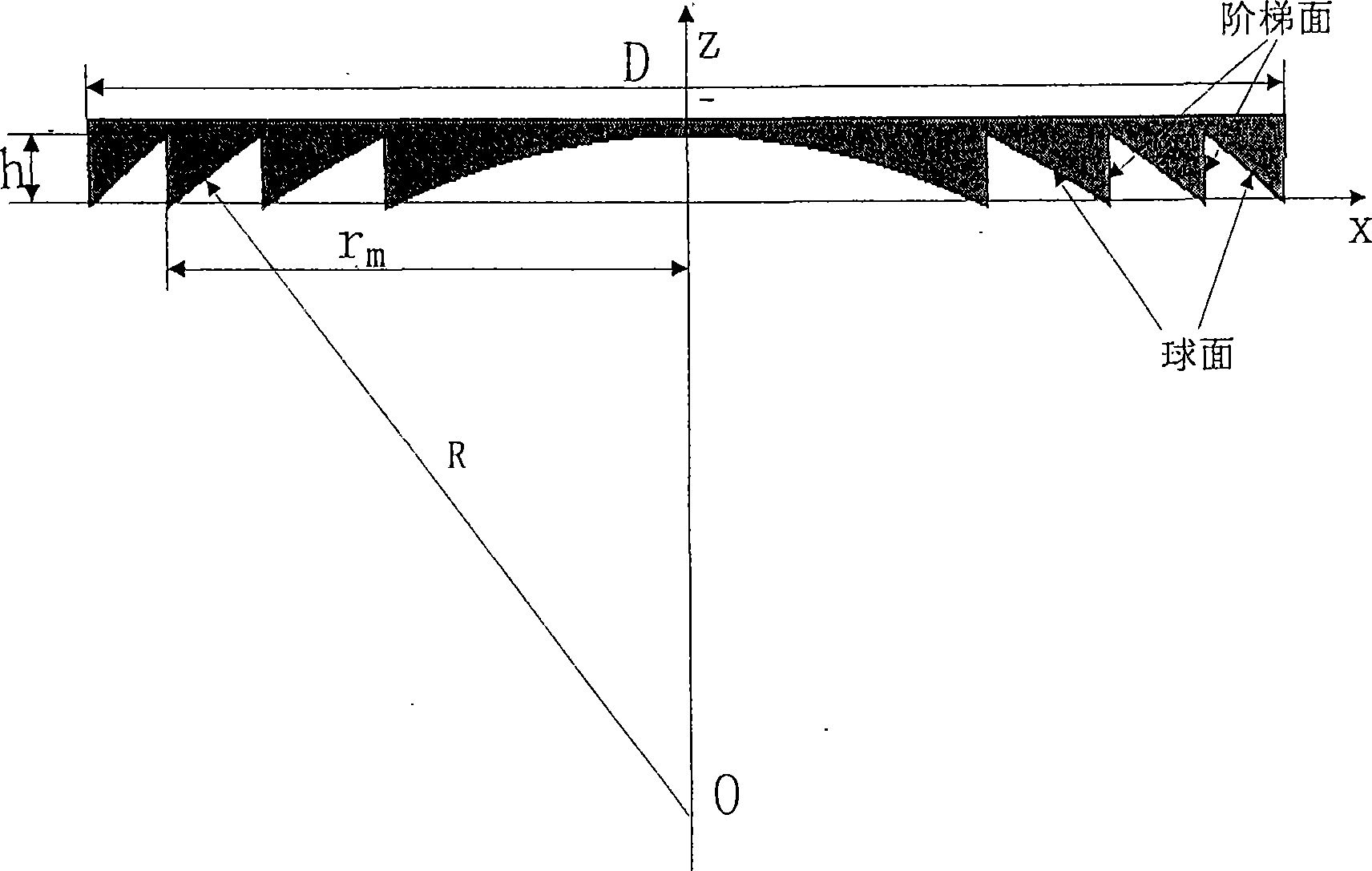
[0022] Embodiment 1, combining figure 1 , the design parameters of the Fresnel lens are: focal length f, workpiece diameter D, design light wavelength λ 0 , phase depth factor M, medium refractive index n. According to the related design formula of Fresnel lens:
[0023] Number of belts that can be processed m = ( D 2 ) 2 2 M λ 0 f
[0024] Maximum relief depth h = M λ 0 Δ n 0
[0025] The annulus radius of the mth annulus r m = 2 mM ...
Embodiment 2
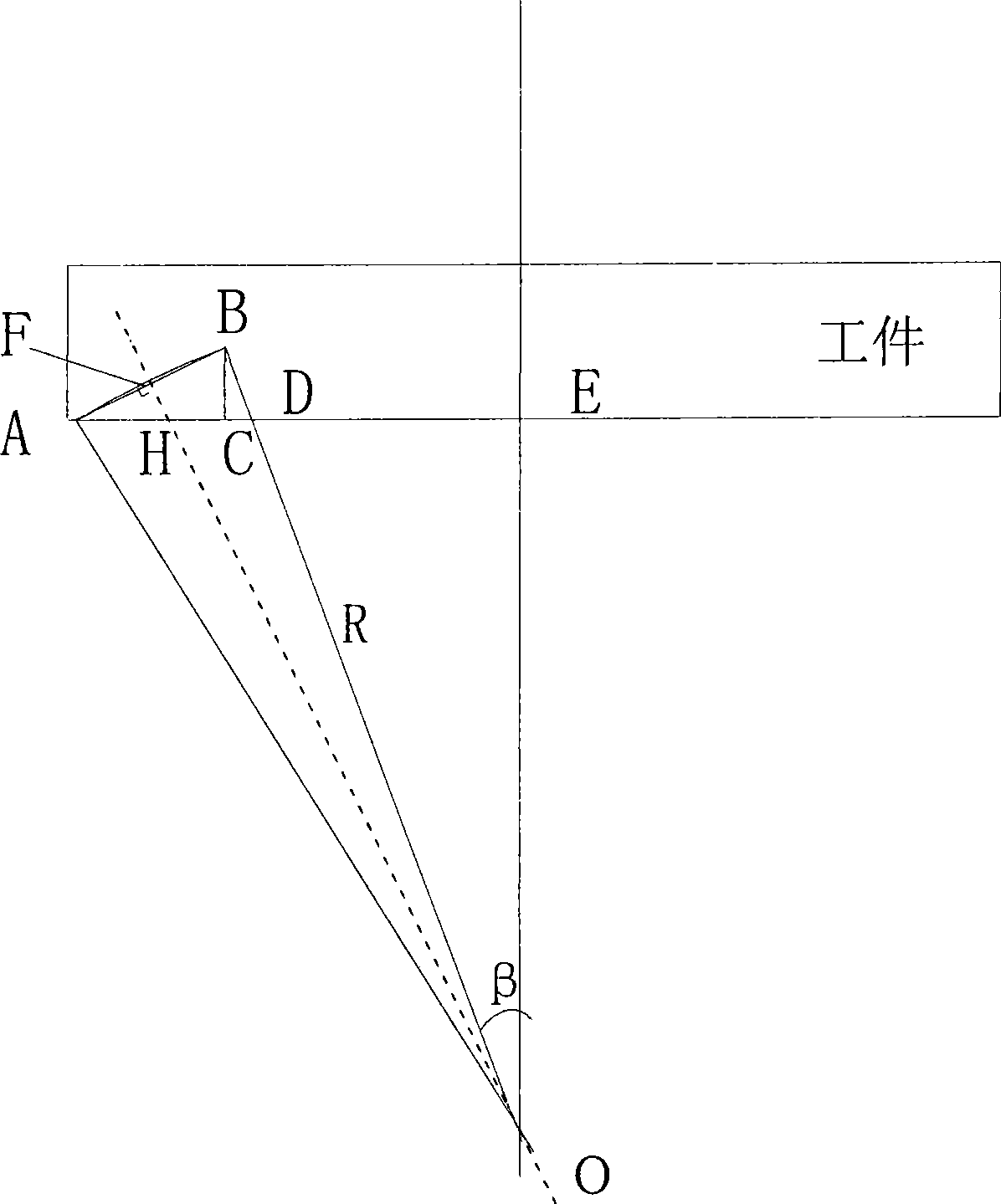
[0026] Example 2, combined with figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 , Figure 6 , the present invention a kind of diamond cutter design method of processing Fresnel lens, described diamond cutter parameter design is as follows:
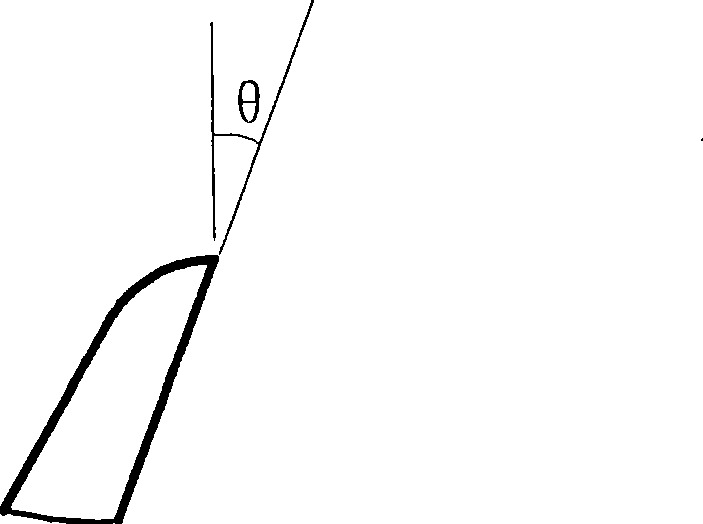
[0027] The design and calculation process of the deflection angle θ: when the tool swing angle is required to process the stepped surface of the outermost ring belt, the radius R of the spherical surface on the ring belt needs to be obtained first. According to the design parameters of the Fresnel lens, the coordinates of each point, A(r max ,0), B(r max-1 , h), C(r max-1 ,0), Then the slope of the line AB k = BC AC . The equation of the straight line FO can be expressed as y = - 1 k x + b , Substitute the coordinates of points k and F to obtain t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com