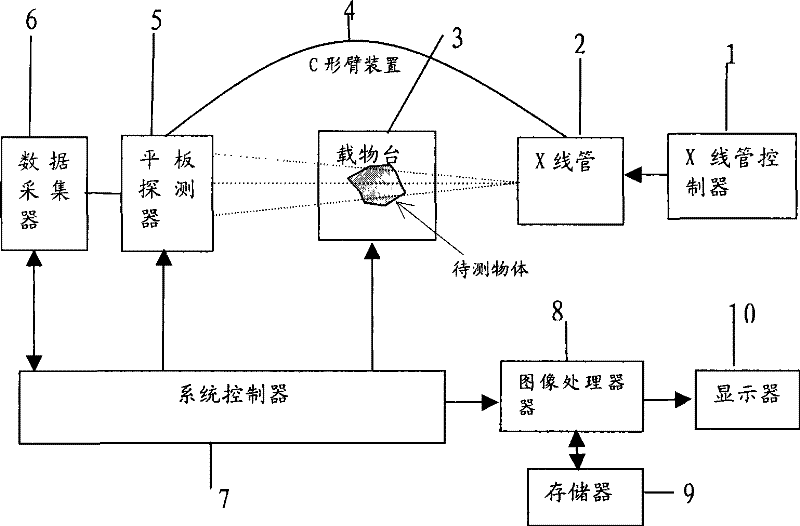
Method and system of X ray image three-dimensional reconstruction
A three-dimensional reconstruction and X-ray technology, which is applied in the field of medical image processing, can solve the problems that it is inconvenient for doctors to observe comprehensively, and cannot obtain a multi-angle or three-dimensional image of the subject, so as to achieve the effect of comprehensive observation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
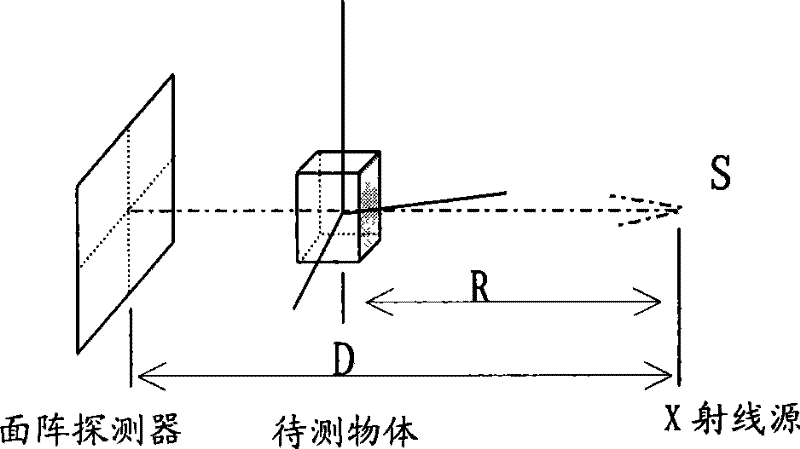
[0035] see figure 2 , first measure or calibrate the X-ray imaging system parameters D, R, d 0 . D is the distance between the X-ray source S and the area array detector, R is the distance between the X-ray source S and the rotation center axis of the object to be measured, d 0 is the pixel pitch of the area array detector (the supplier of the area array detector can provide this parameter).
[0036] see image 3 , to rotate the X-ray imaging system or the stage, so that the imaging system and the object on the stage undergo relative circular or helical motion, and perform image sampling. S is the X-ray tube, which moves along a circular track (sampling circle), and the track of the area array detector opposite to it is also a circle (in the case of a C-arm, the area array detector and the X-ray tube will be in the movement on the same sampling circle). The object to be measured is placed on the stage, the centerline SO of the X-ray cone ray beam passes through the centr...
Embodiment 2
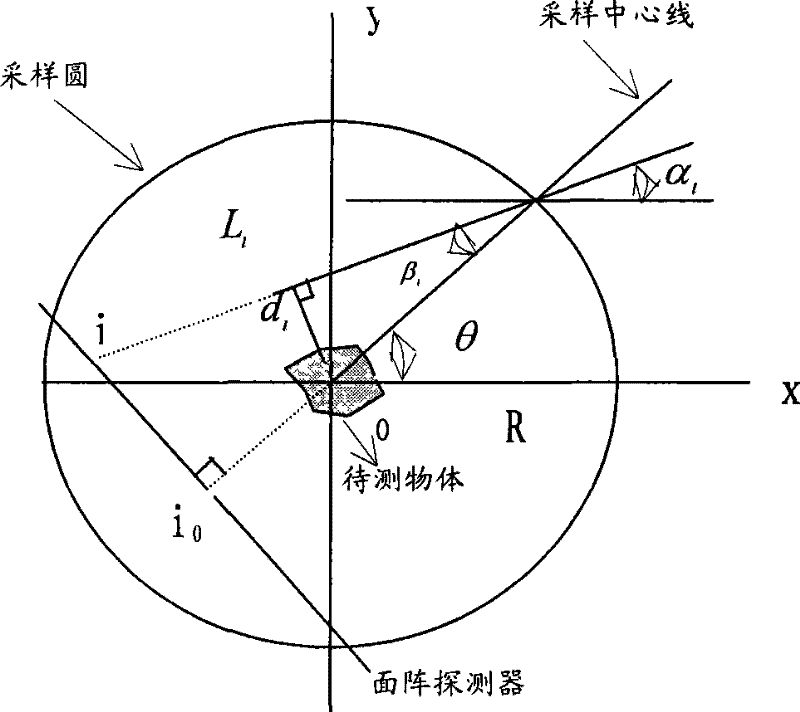
[0050] see Figure 4 , S is the X-ray tube, which moves along a circular trajectory (sampling circle), and the trajectory of the area array detector opposite to it is also a circle (in the case of a C-arm, the area array detector and the X-ray tube will be moving on the same sampling circle). The object to be measured is placed on the stage, the centerline SO of the X-ray cone ray beam passes through the central axis of rotation and is perpendicular to the area array detector, intersecting i 0 , corresponding to the i-th projection image 0 Column of pixels, a non-central line L of the X-ray cone beam i Point i on the intersecting surface array detector corresponds to the i-th column pixel of the projected image, and the ray L i The angle with the centerline SO is β i , the angle between the central line SO and the reference axis (X axis) is θ. A frame of image I(θ) is collected at every θ angle, and the collected image data is compressed and stored in computer memory as r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com