Cyanobacteria modified by gene engineering and use thereof for producing ethanol
A technology of cyanobacteria and bacterium Synechocystis, which can be used in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, application, etc., and can solve the problem of insufficient ethanol production concentration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
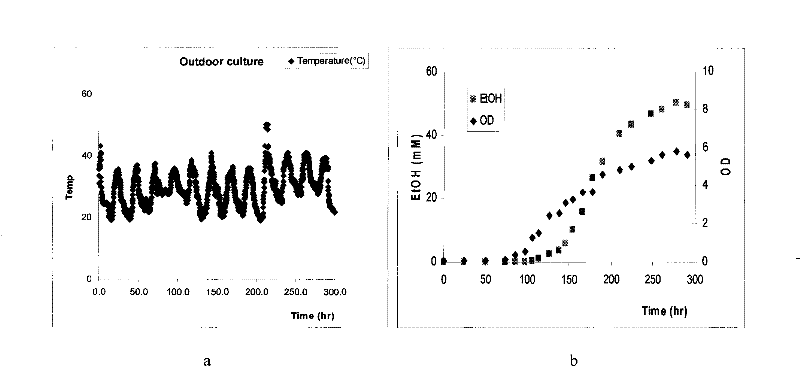
[0050] Specific operation: the wild Synechocystis sp. 6803 was inoculated in the photosynthetic bioreactor group (consisting of six 150ML shake flasks built in a modified shaker, and the working solution was 50ML), and it was cultured by BG-11 culture medium, and the shaker had a built-in light source , the light intensity on the surface of the reactor is about 200Einstein / m 2 / s. The temperature of the shaker was regulated below 30 °C and the speed was 200 RPM. After 5 days, put them into a hot water bath box to heat and heat shock. Then put it back into the photosynthetic bioreactor at 30°C, and after the complete "whitening" phenomenon occurs (about 3 days), centrifuge the Synechocystis 6803 cells, discard the supernatant, and use fresh BG-11 culture medium to cultivate " albino" of Synechocystis 6803 cells. Synechocystis cells adapted to the heat shock will regenerate chlorophyll, thereby restoring photosynthesis and growth. At the same time, the metabolic mechanism of...
Embodiment 2
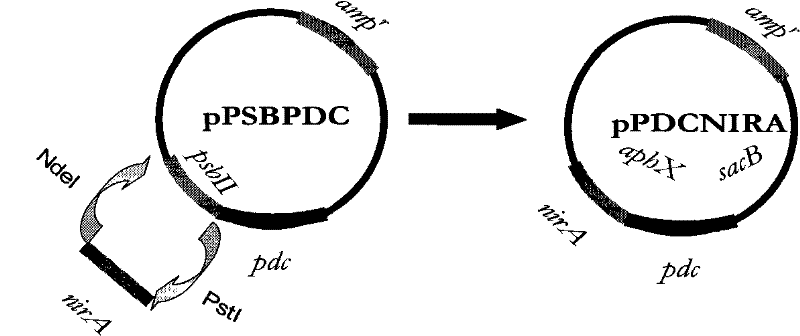
[0051] Embodiment 2: pyruvate decarboxylase gene pdc and nirA promoter design
[0052] By the method of bioinformatics, be easy to obtain the sequence of pyruvate decarboxylase gene pdc and nirA promoter (the inventor of the present invention uses the search engine http: / / www.kegg.com / that Japanese Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes provides The sequences of the pyruvate decarboxylase gene pdc and the nirA promoter were obtained). Pdc (sequence number: 1) and nirA (sequence number: 2) can be obtained by artificial synthesis in turn (Roy, et al. European Journal of Biochemistry.191 (3): 647-652, 1990; Shabalina, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 34: 2428-2437, 2006; Satya et al. Proc IEEE Comput Soc Bioinform Conf. 2: 294-305, 2003; Kim, et al. Gene. 199: 293-301, 1997). The sequence obtained above was analyzed by the Sanger method (F. Sanger, Science, 214, 1215, 1981) to confirm the base sequence.
Embodiment 3
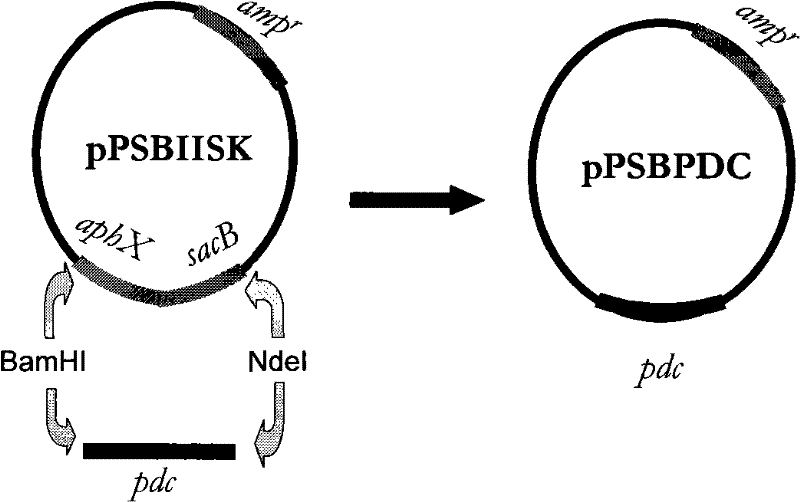
[0053] Embodiment 3: Transformation of Synechocystis mutant strain S.strictus with pdc gene
[0054] A pair of PCR primers P1 (sequence number: 4) and P2 (serial number: 5):
[0055] P1 (5-terminal primer): 5'-GGAGTAAG CATATG AGTTATACTG-3'
[0056] Nd
[0057] P2 (3' end primer): 5'-GGATCTCGACTCTAGA GGATCC -3'
[0058] BamHI
[0059] Among them, a NdeI restriction site was designed for primer P1, and its sequence was CA↓TATG, and a BamHI restriction site was designed for primer P2, and its sequence was GGATC↓C. A pdc DNA fragment P of 1410 bp was amplified by conventional PCR amplification method. PCR reaction: add in 0.5mL sterile centrifuge tube successively: deionized water 36μl; 10XTaq enzyme buffer 5μl; 4XdNTP (2.5mmol / L) 5μl; P1 primer 1μl; P2 primer 1μl; ) 1 μl; Taq enzyme (3U / μl) 1 μl. A total of 50 μl.
[0060] Thermal cycle parameters of PCR reaction: first, 94°C pre-denaturation for 5 minutes; ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com