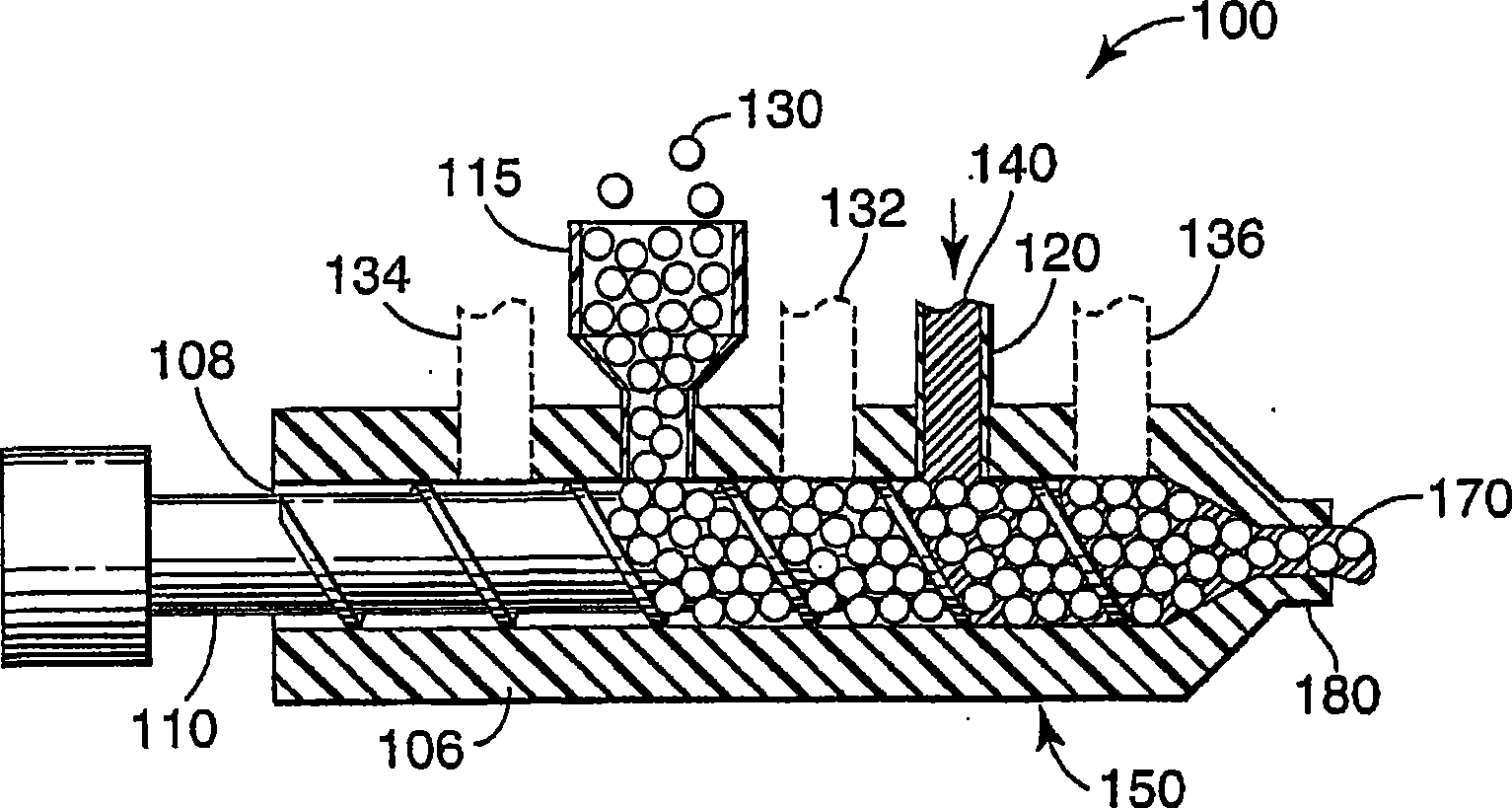
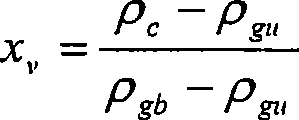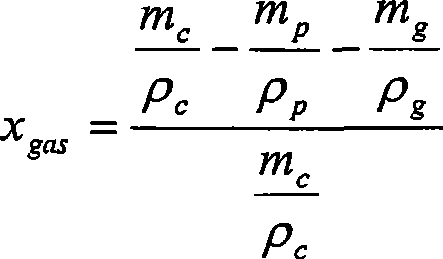Method of making composite material.
A technology of composite materials and molten polymers, which is applied in the field of preparation of composite materials, can solve the problems of high density of composite materials and rupture of trapped gas glass microbubbles, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0048] Unless otherwise specified, all parts, percentages, ratios, etc. in the examples and the rest of the specification are by weight, and all reagents in the examples are available, or from general chemical suppliers such as Sigma-Aldrich Company, Milwaukee , Wisconsin, or can be synthesized by conventional methods.
[0049] testing method
[0050] Determination of Volume Percent of Average Fractured Glass Microbubbles and Volume Percent of Trapped Gas
[0051] The furnace was heated to 600 °C and the ceramic crucible was placed in the furnace for 5 minutes. Cool the crucible in a desiccator and weigh it. The composite material sample to be tested is placed in the crucible, the sample and the crucible are weighed, and placed in a furnace heated to 600°C for 30 minutes. The crucible is removed from the furnace and weighed after cooling in a desiccator to obtain the mass of the crucible and the remaining glass. Calculate the following masses:
[0052] m c = (the quality...
Embodiment 1
[0071] Except that the vacuum port opening on the twin-screw extruder is located in zone 1 (Z1), and glass microbubbles are added using a gravimetric feeder located 38.0 cm downstream from zone 1 (Z1), and 116.0 cm downstream from zone 1 (Z1) Example 1 was prepared according to the procedure described in Comparative Example C-1, except that the molten polymer was added. The screw speed of the extruder was 75 rpm. The average collapse rate of glass microbubbles in the cooled composite was 1.2% by volume and the average entrapped gas in the composite was 3.5% by volume.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com