Vacuum brazing technique of stainless steel plate fin structure
A technology of stainless steel plate and brazing process, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, welding equipment, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of many structural defects and low strength, improve reliability, ensure brazing quality, and optimize vacuum brazing The effect of craft
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
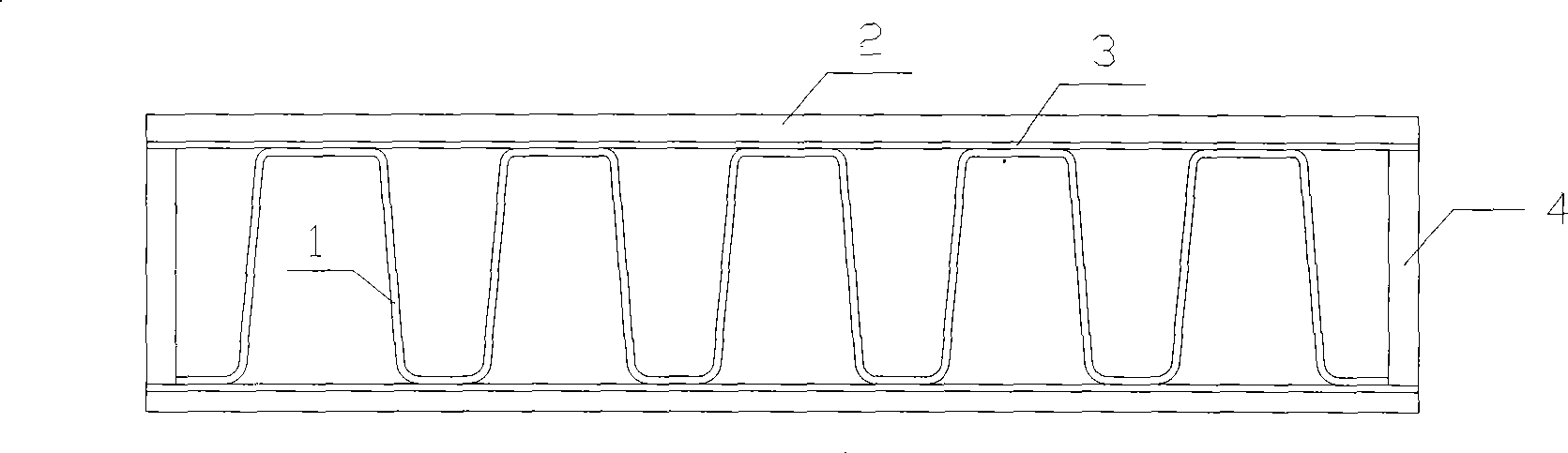
[0018] Embodiment 1: A stainless steel plate-fin structure is composed of fins (1), partitions (2), and seals (3). The material of the fins and the partitions are 304 stainless steel, the thickness of the fins is 0.2mm, and the thickness of the partitions is 0.4mm. The solder is nickel-based solder BNi2, and the thickness of the solder is 105 μm. First put a fin on the partition (metal flat plate), and then put a partition on it. The solder foil is preset between the fin and the partition, and then the two sides are sealed with edge seals to form a basic unit (such as figure 1 shown). Stack many basic units layer by layer, clamp firmly with the special brazing fixture designed by the inventor, apply a pressure of 5 MPa, put them into a vacuum brazing furnace, and use vacuum brazing to make a stainless steel plate-fin structure.
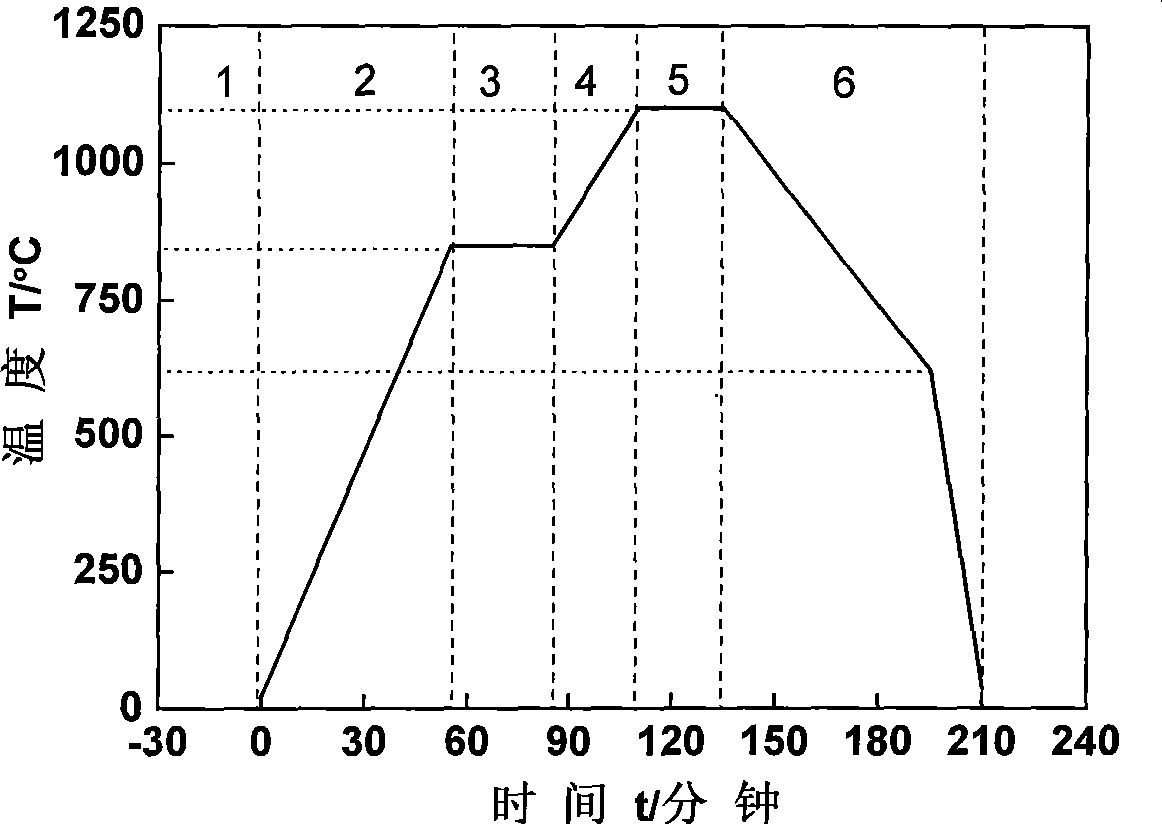
[0019] The vacuum brazing heating process consists of the following six steps:
[0020] The first step is the vacuum stage: the degree of vacuum ...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2: A stainless steel plate-fin structure, consisting of fins (1), partitions (2), and seals (3). The material of the fins and the partitions are 304 stainless steel, the thickness of the fins is 0.2mm, and the thickness of the partitions is 0.4mm. The solder is nickel-based solder BNi2, and the thickness of the solder is 110 μm. First put a fin on the partition (metal flat plate), and then put a partition on it. The solder foil is preset between the fin and the partition, and then the two sides are sealed with edge seals to form a basic unit (such as figure 1 shown). Stack many basic units layer by layer, clamp firmly with the special brazing fixture designed by the inventor, apply a pressure of 5 MPa, put them into a vacuum brazing furnace, and use vacuum brazing to make a stainless steel plate-fin structure.
[0028] The vacuum brazing heating process consists of the following six steps:
[0029] The first step is the vacuum stage: the degree of vacuum ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com