Microelectronic sensor device for concentration measurements
A sensor device, microelectronics technology, applied in the direction of measuring device, magnetic variable measurement, magnetic performance measurement, etc., can solve the problems of measurement signal destruction, low concentration of target substances, etc., and achieve high-precision results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0056] The same reference numbers or numbers that differ in the hundreds place refer to the same or similar parts throughout the figures.
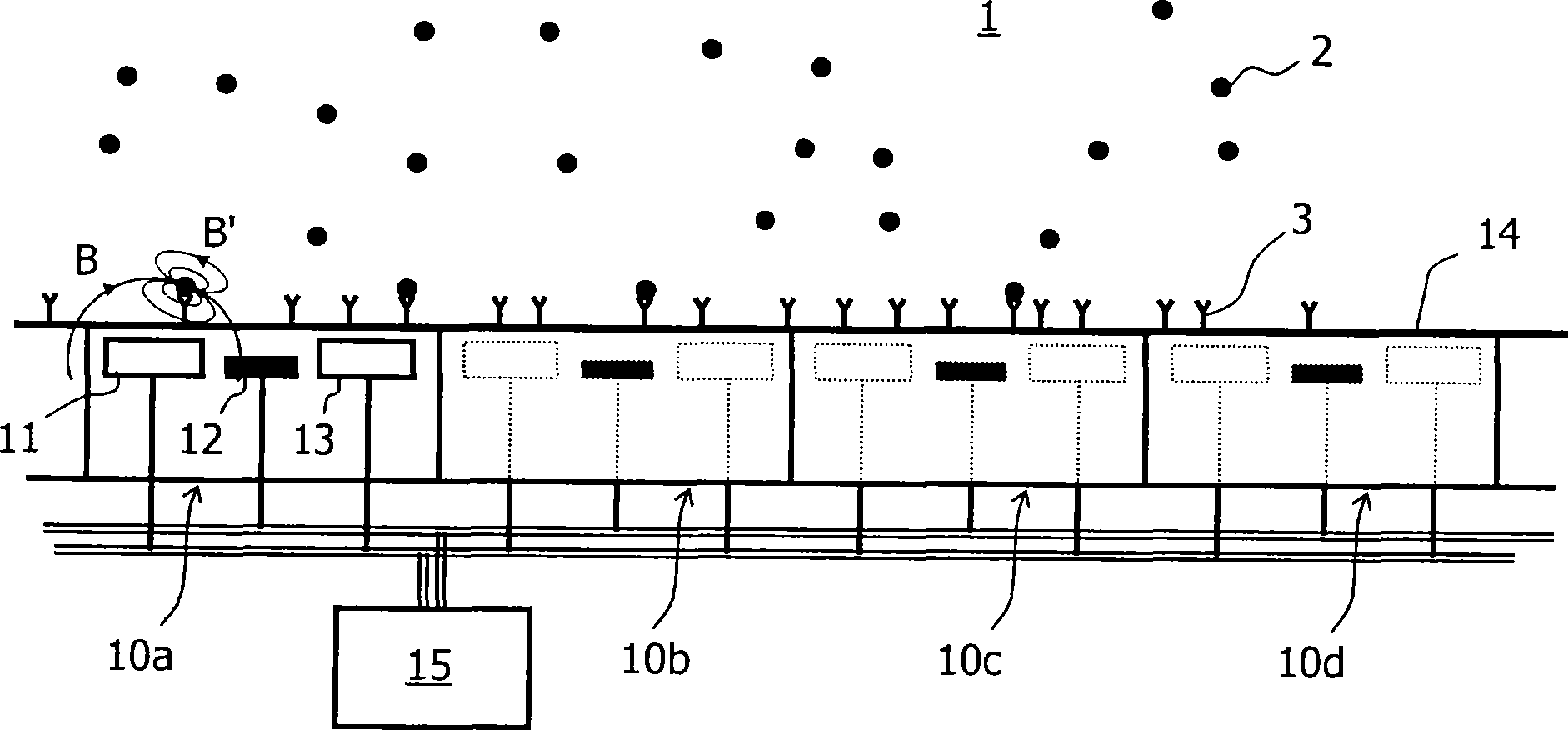
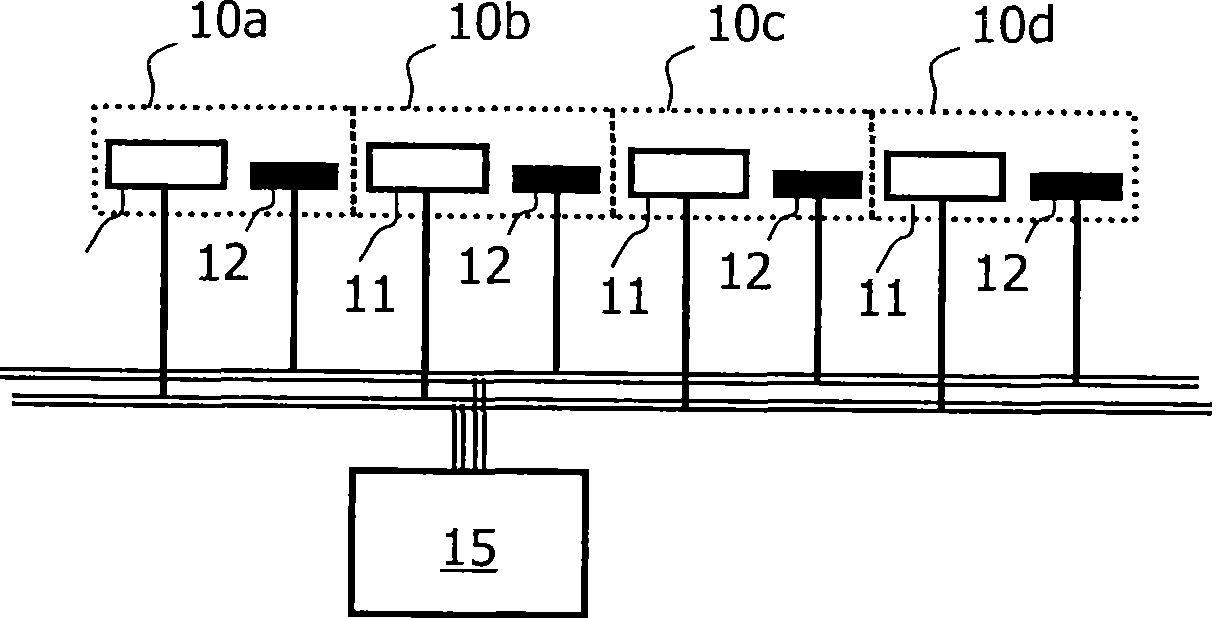
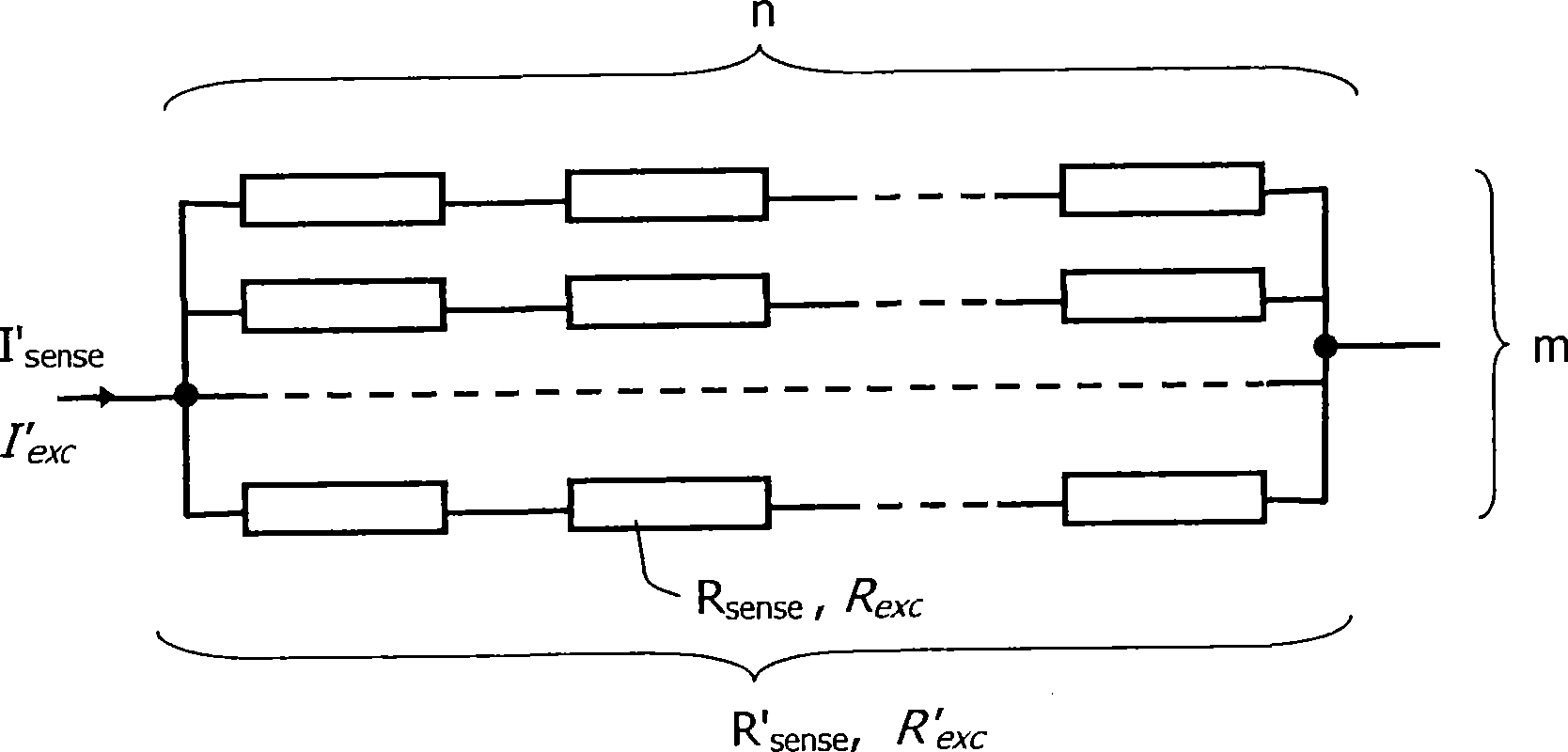
[0057] figure 1 A microelectronic biosensor according to the invention is shown, consisting of an array of (eg 100) sensor cells 10a, 10b, 10c, 10d, etc. The biosensor can eg be used to measure the concentration of target particles 2 (eg proteins, DNA, amino acids, drugs) in a sample solution (eg blood or saliva). In one possible example of a binding scheme, this is achieved by providing the sensing surface 14 with a first antibody 3 to which the target particles 2 can bind. For the sake of brevity, it is assumed here that the target particles that must be analyzed have been labeled (ie magnetic particles or beads attached) so that they can be tracked. Whether this is the case depends on the biochemical assay used. The excitation current flowing into the wires 11 and 13 of the sensor unit 10a generates a magnetic field B which magnetize...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com