Method for controlling an internal combustion engine
A technology for internal combustion engines and regulators, which is applied to the cooling of internal combustion piston engines, combustion engines, and engines. It can solve problems such as high temperature rise of charge air coolers, increased loads of internal combustion engine components, and reduced life expectancy. Stabilize the regulating circuit Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
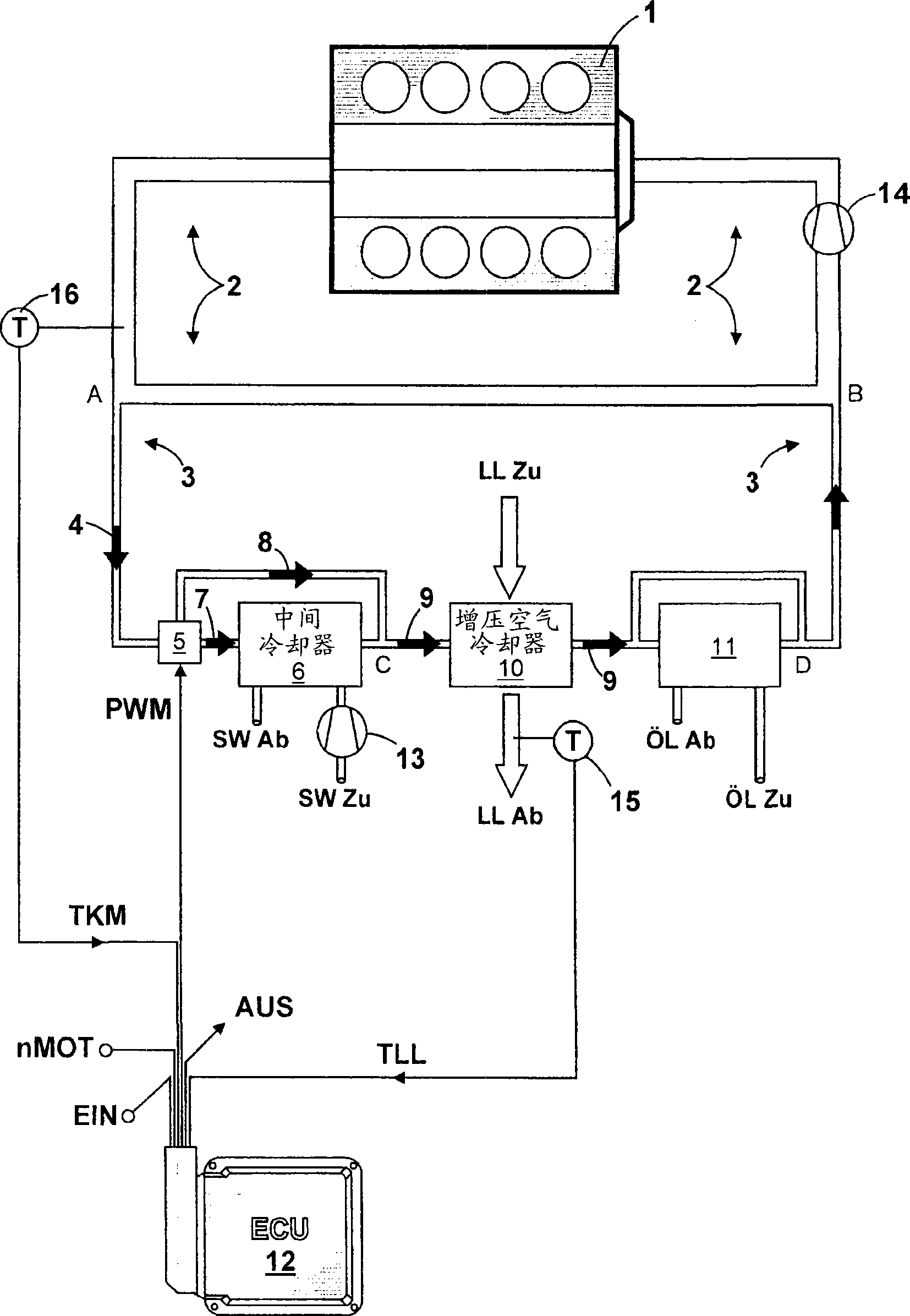
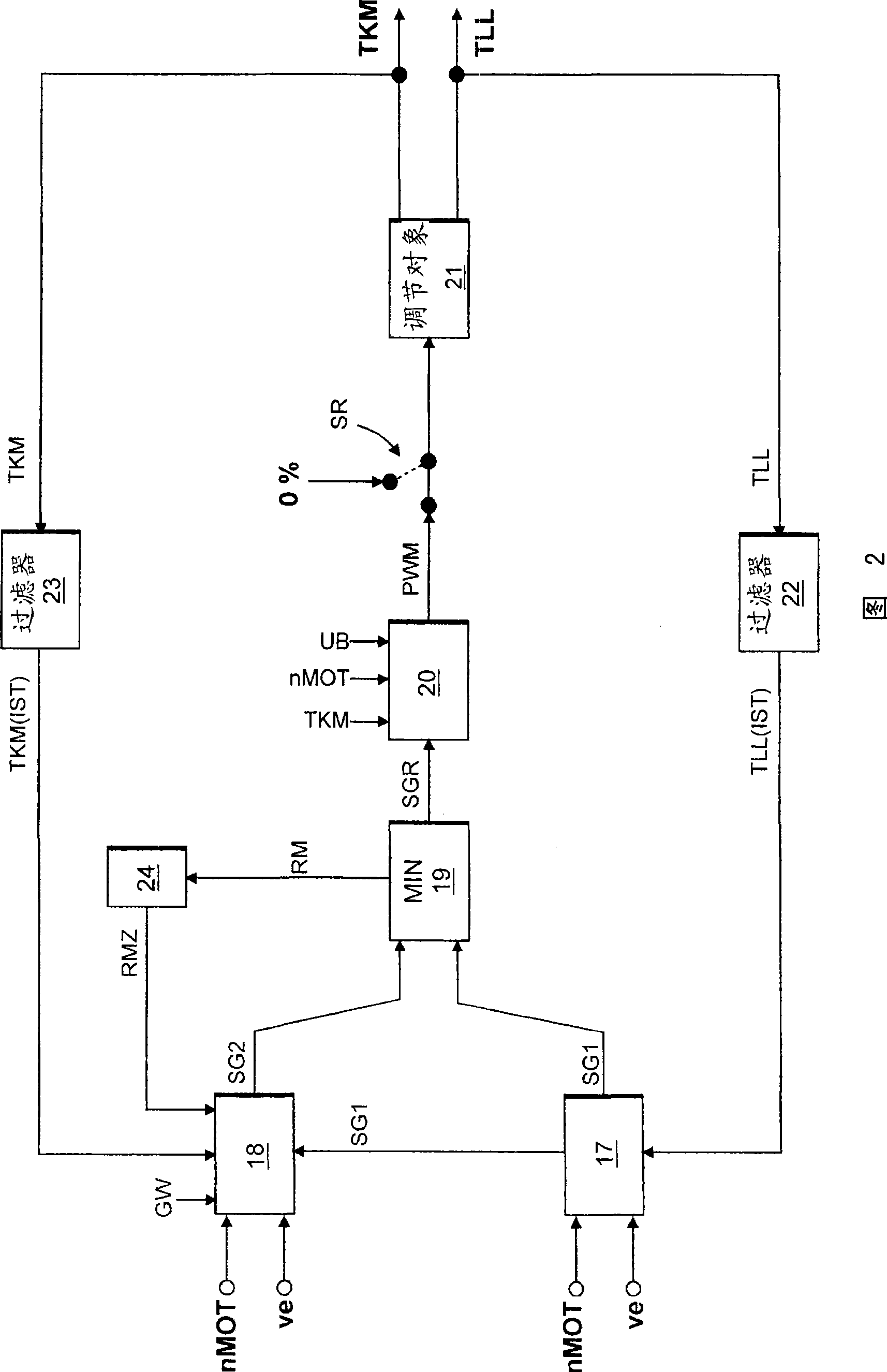
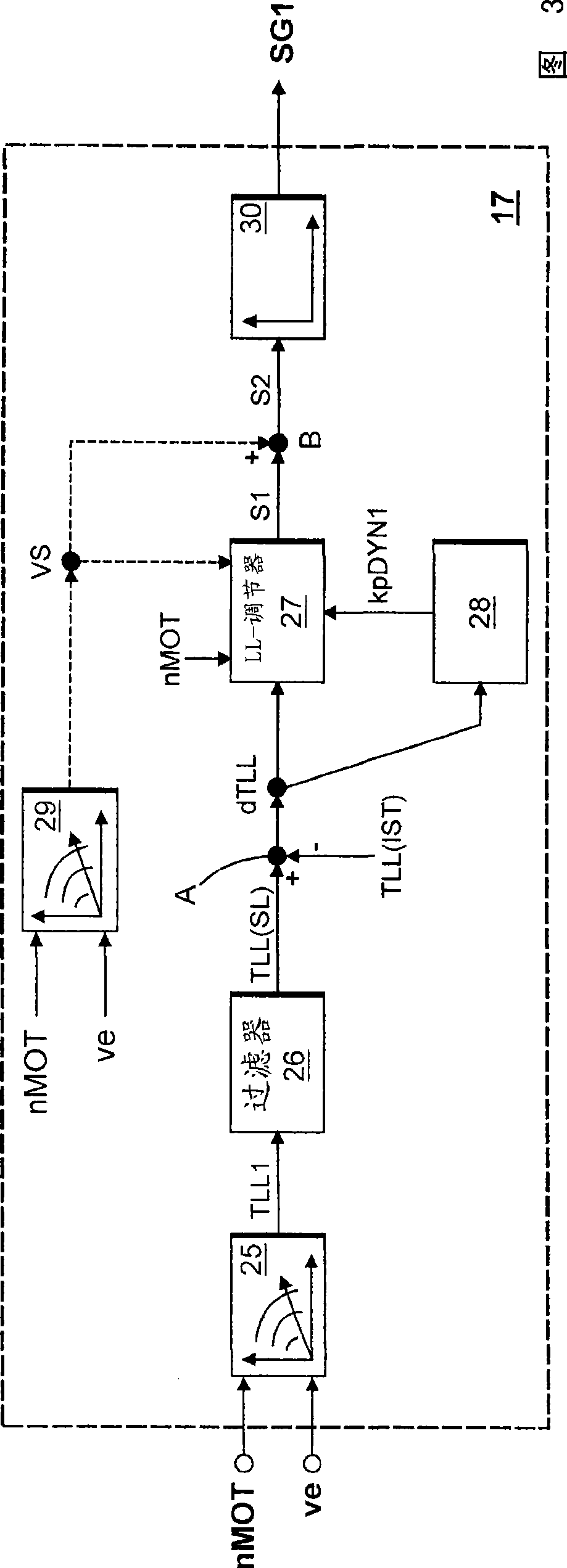
[0018] figure 1 A system diagram is shown. The cooling circuit for cooling internal combustion engine 1 comprises a high-temperature circuit 2 with a coolant pump 14 and a low-temperature circuit 3 . The low-temperature circuit 3 branches off from the high-temperature circuit 2 at point A and joins again at point B into the high-temperature circuit 2 . The coolant flows in the high-temperature circuit 2 and in the low-temperature circuit 3 are regulated via throttling points (not shown) in the high-temperature circuit 2 . The coolant flow in the low-temperature circuit 3 after the branching point (position A) out of the high-temperature circuit 2 is designated as coolant flow 4 in the figure. A combined characteristic curve thermostat valve 5 , an intercooler 6 with a bypass line, a charge air cooler 10 and a lubricating oil heat exchanger 11 with a bypass line are arranged in series in the low-temperature circuit 3 . The coolant flow 4 is divided into an intercooler coolan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com