Patents
Literature
1159results about "Measurement device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
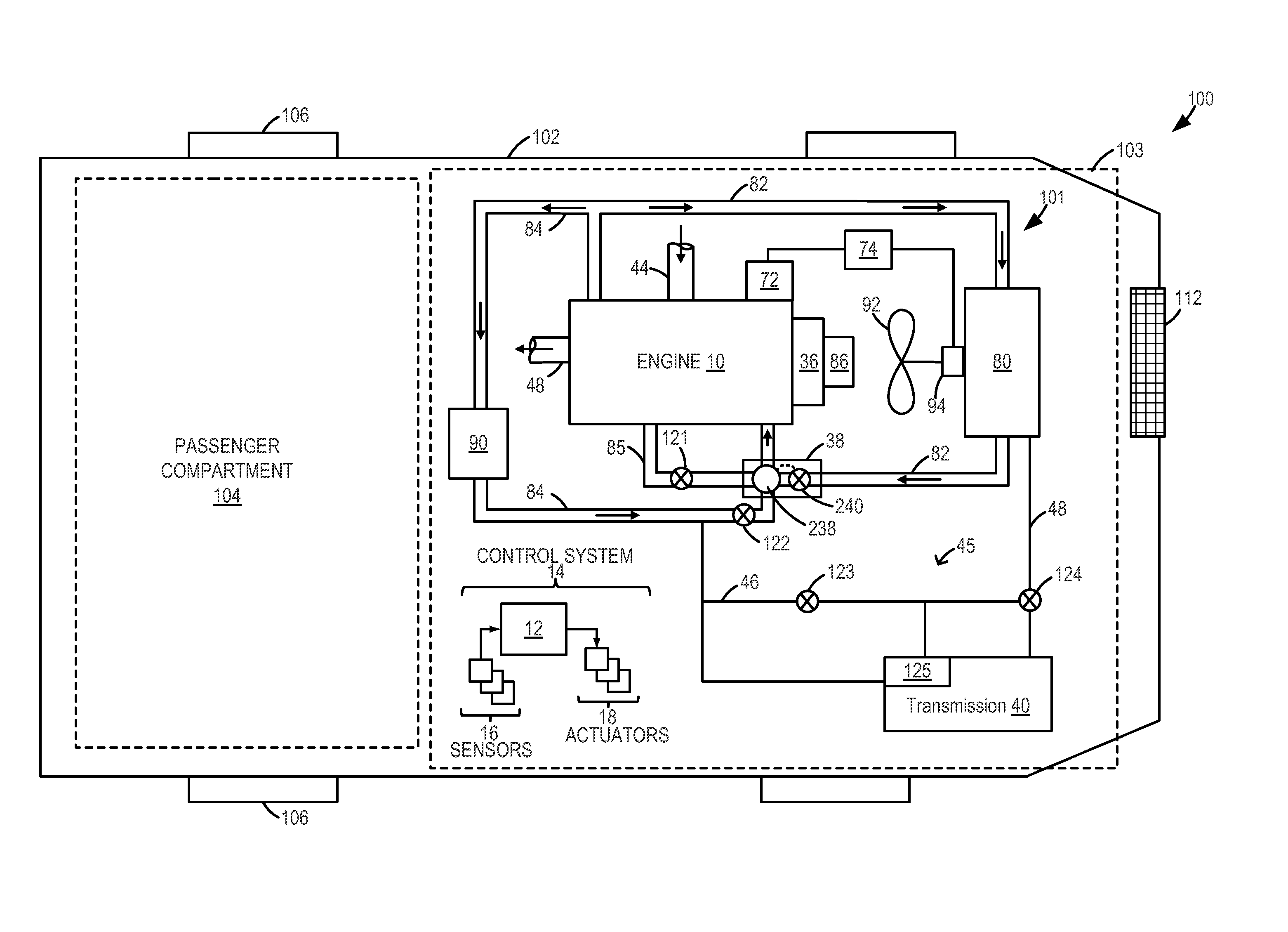
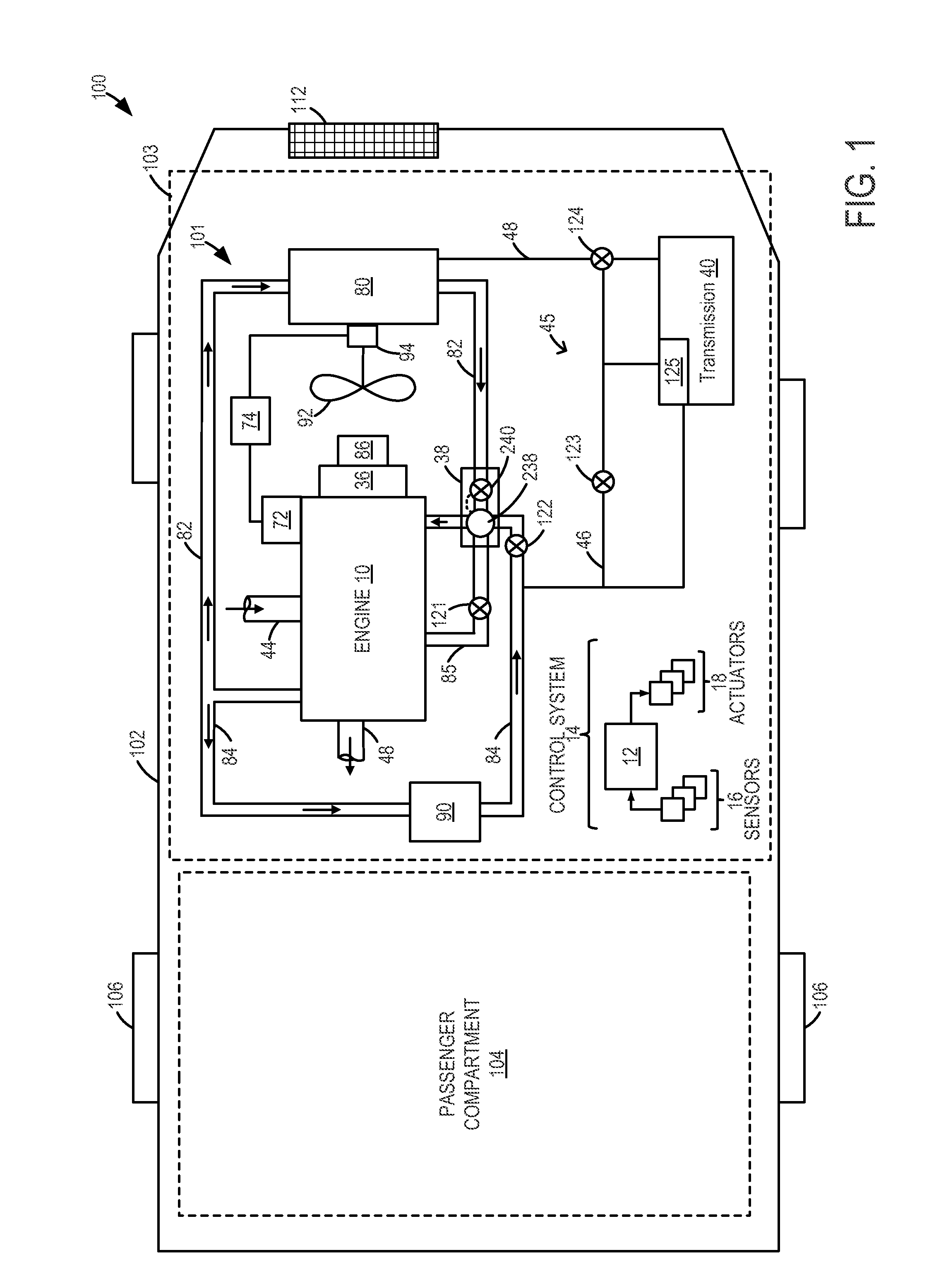
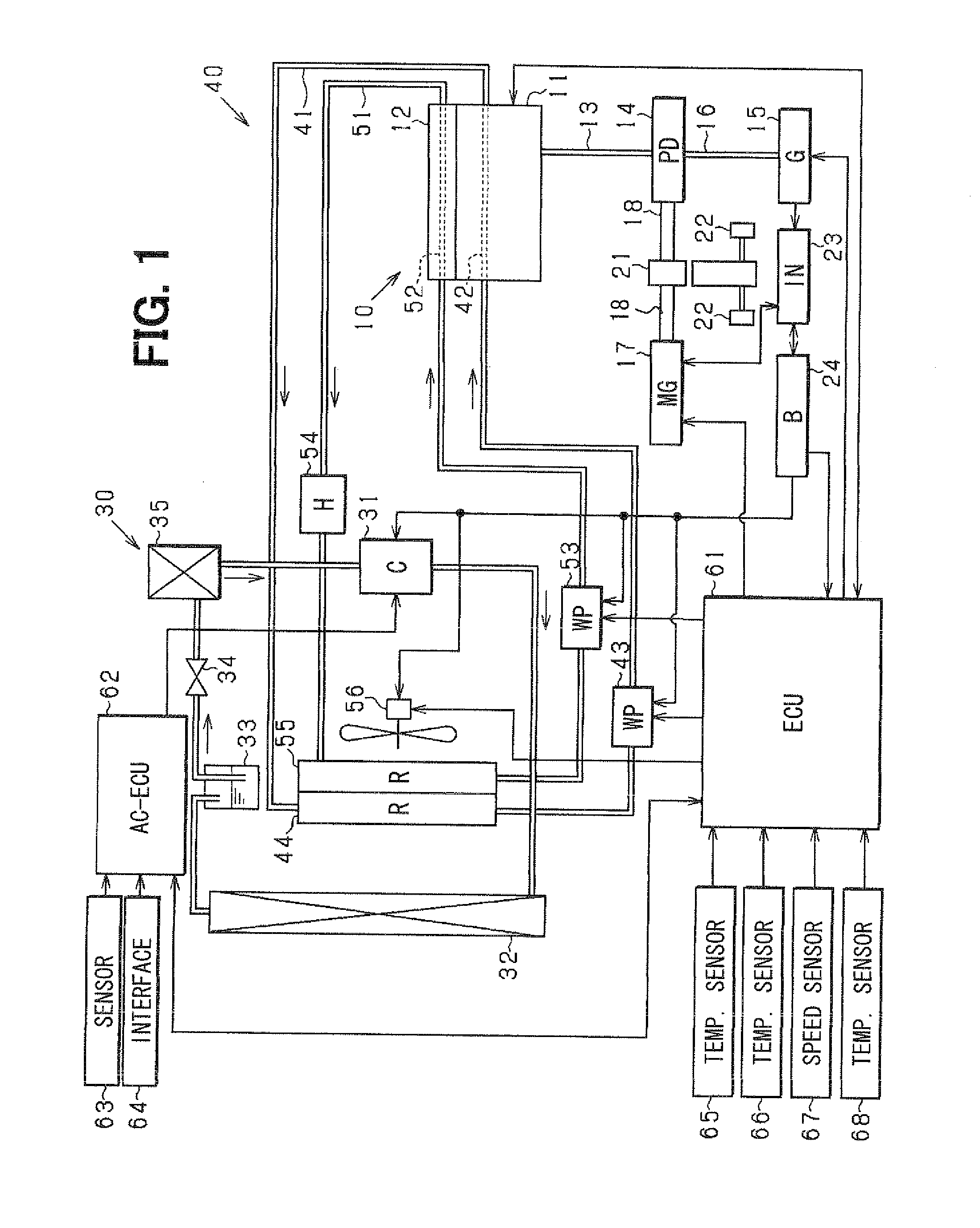
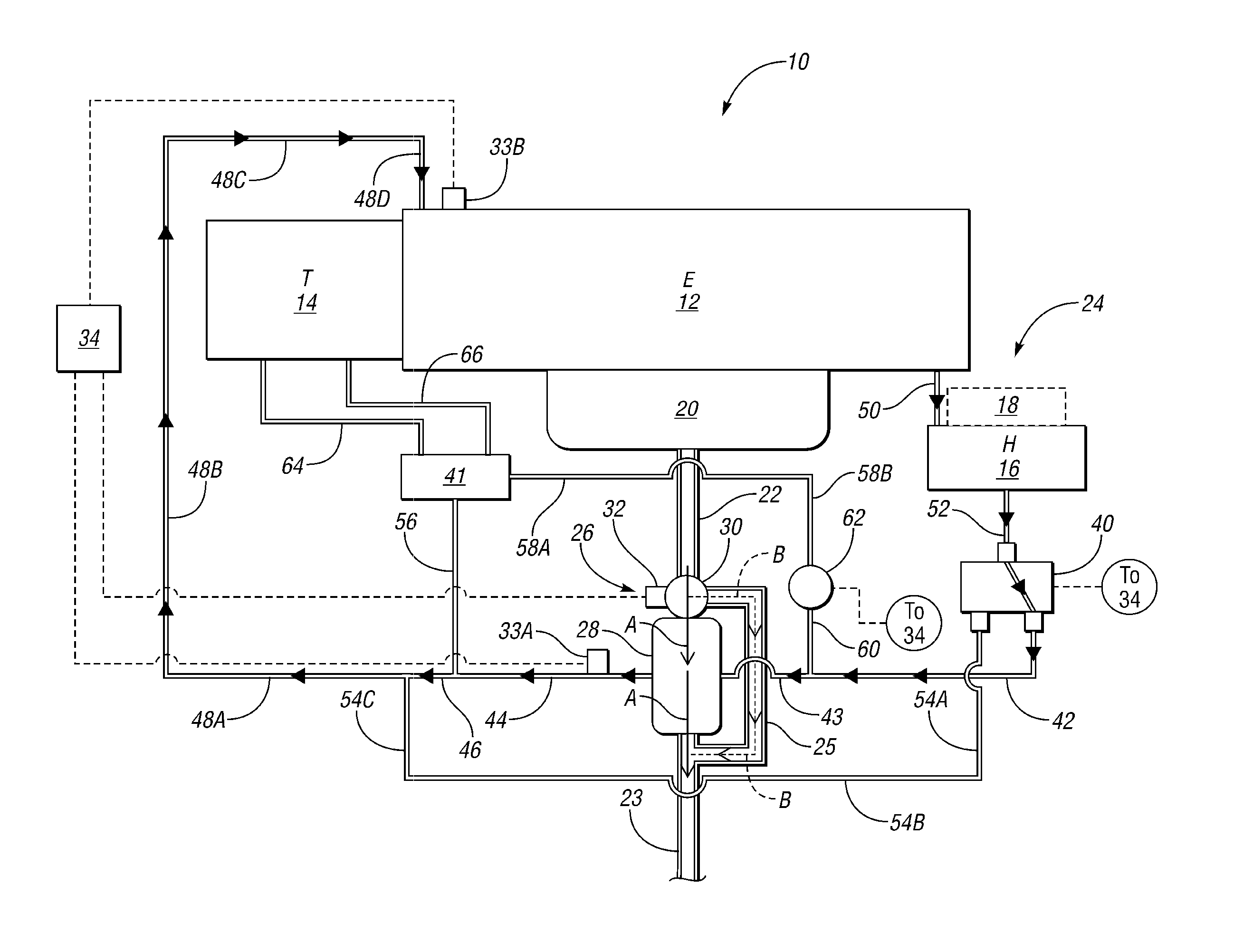
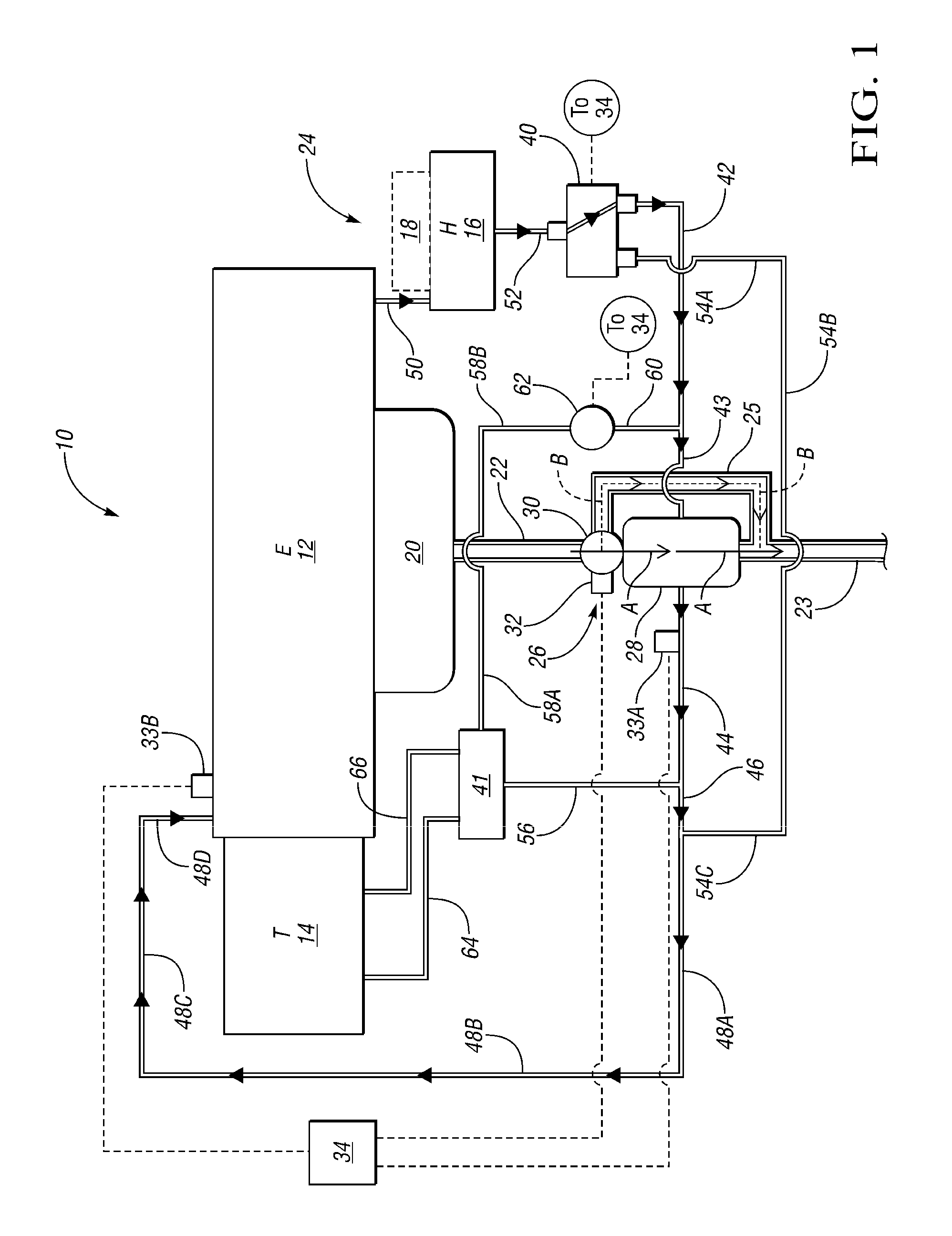
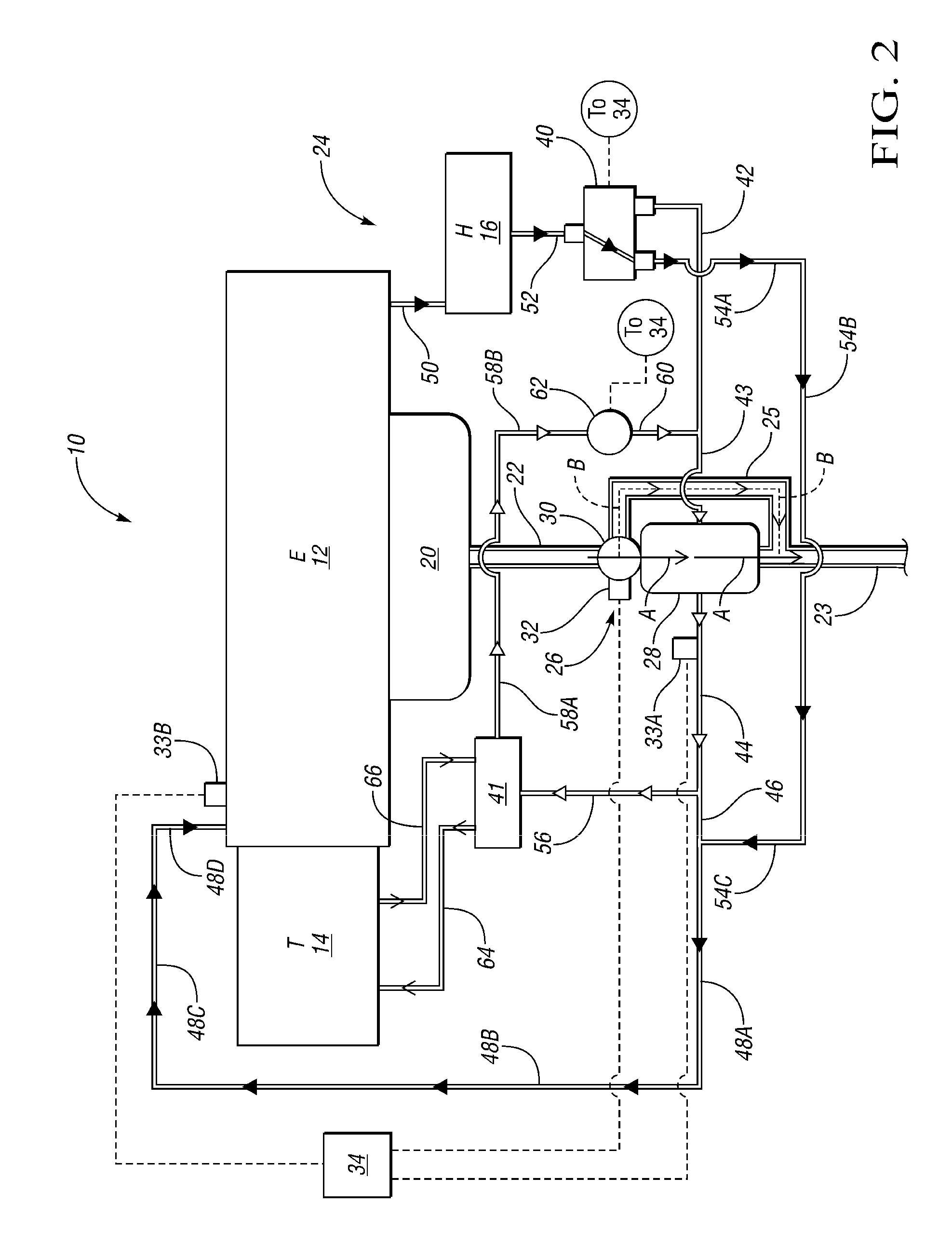
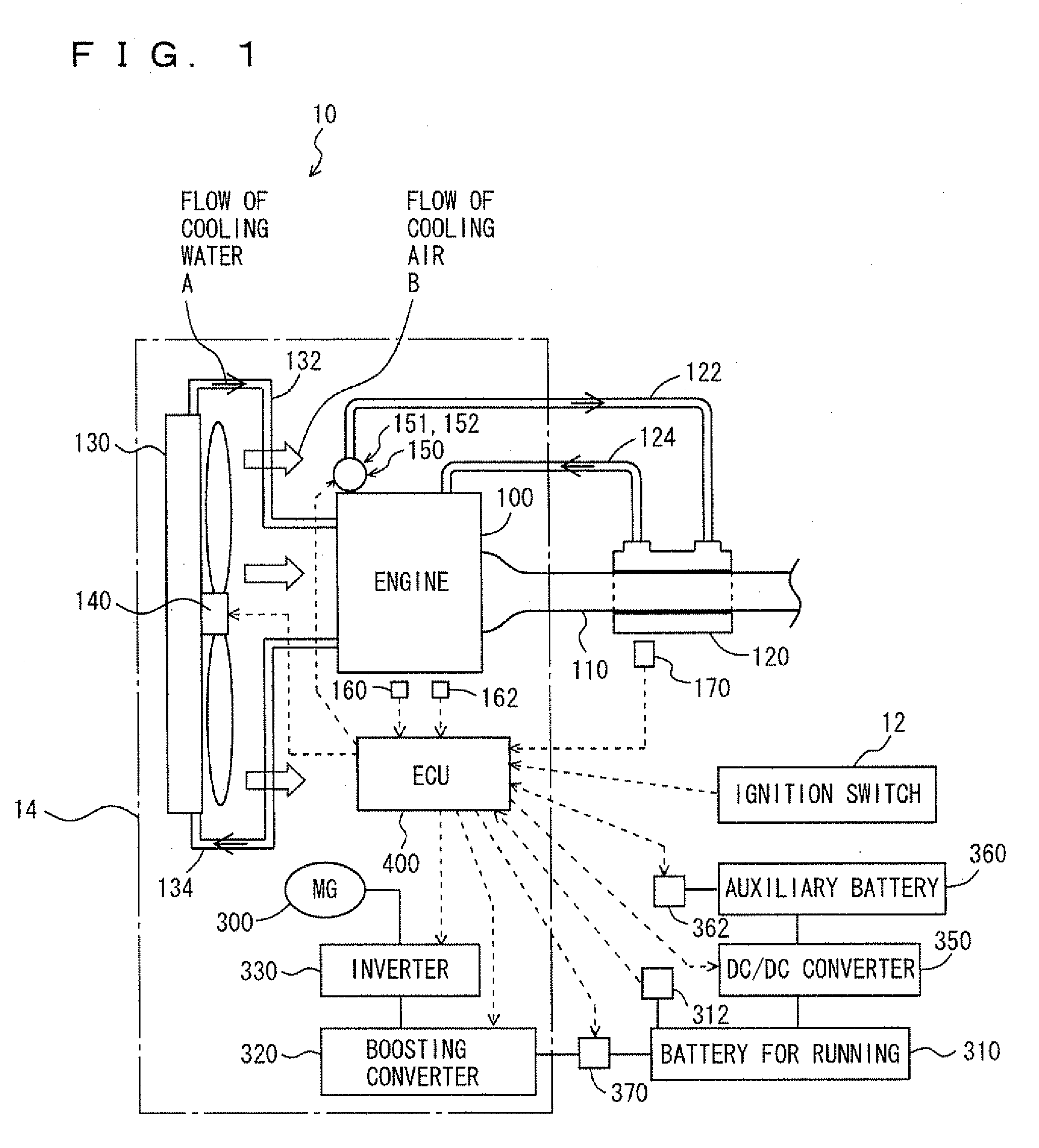
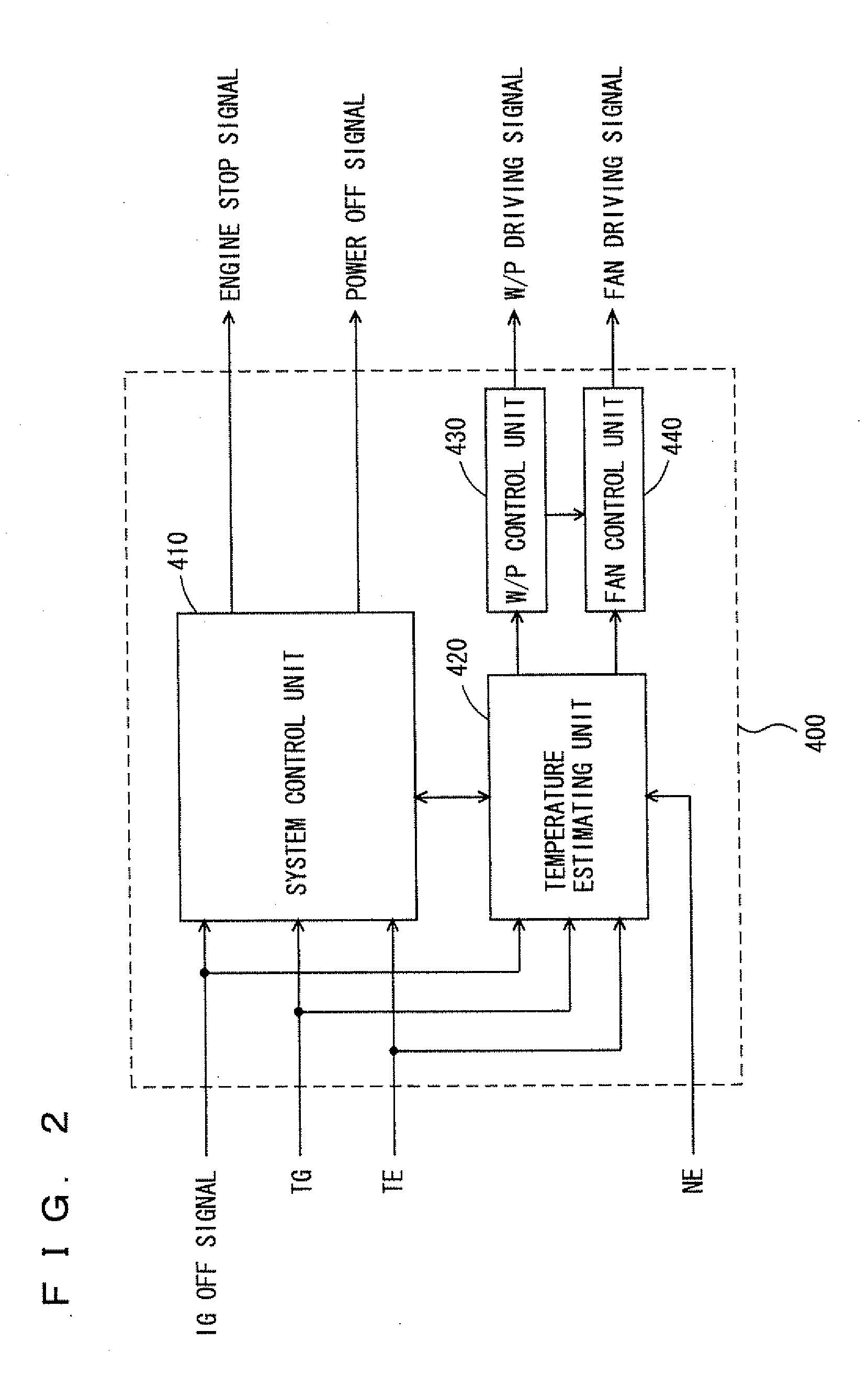
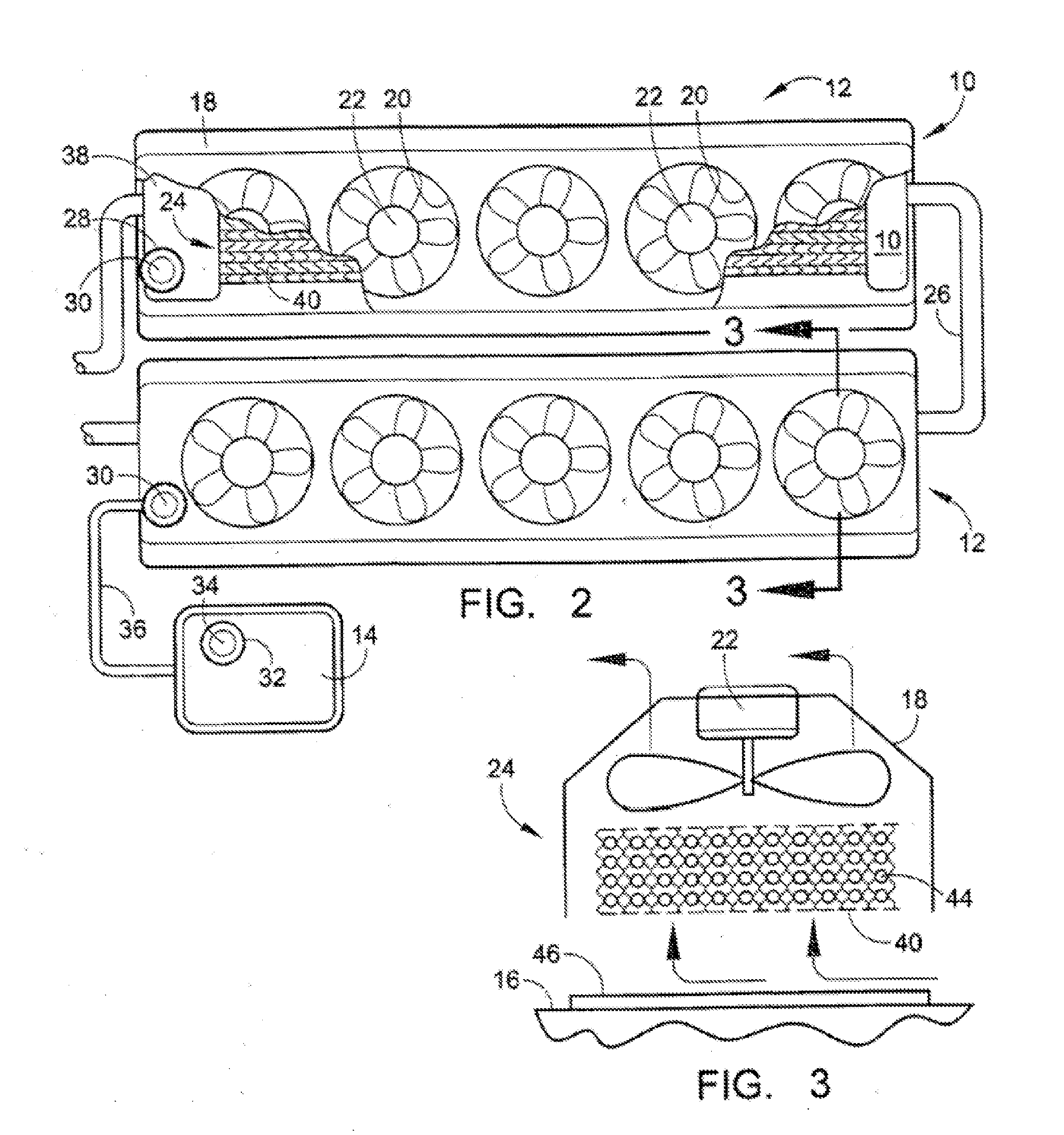
Engine cooling system
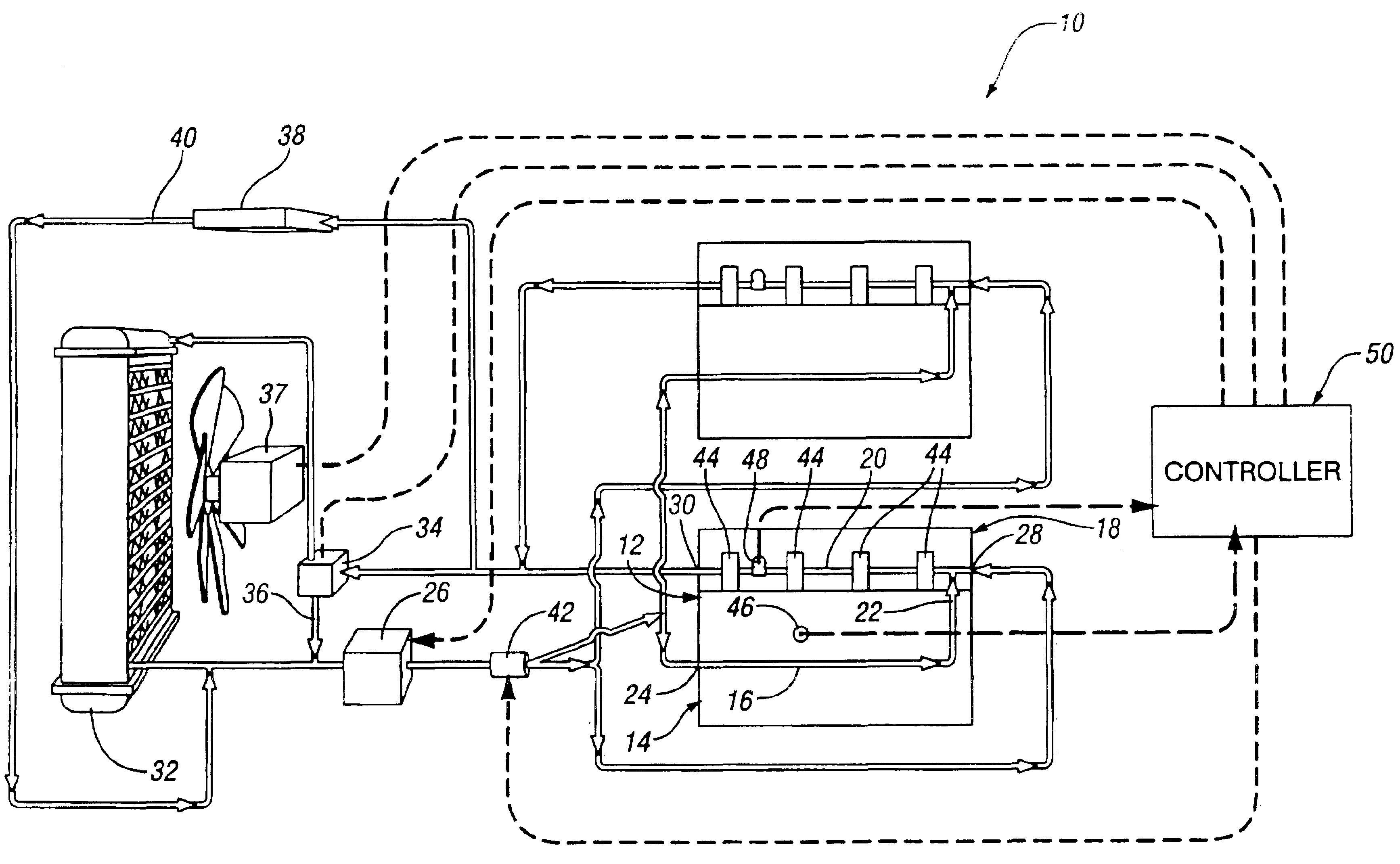
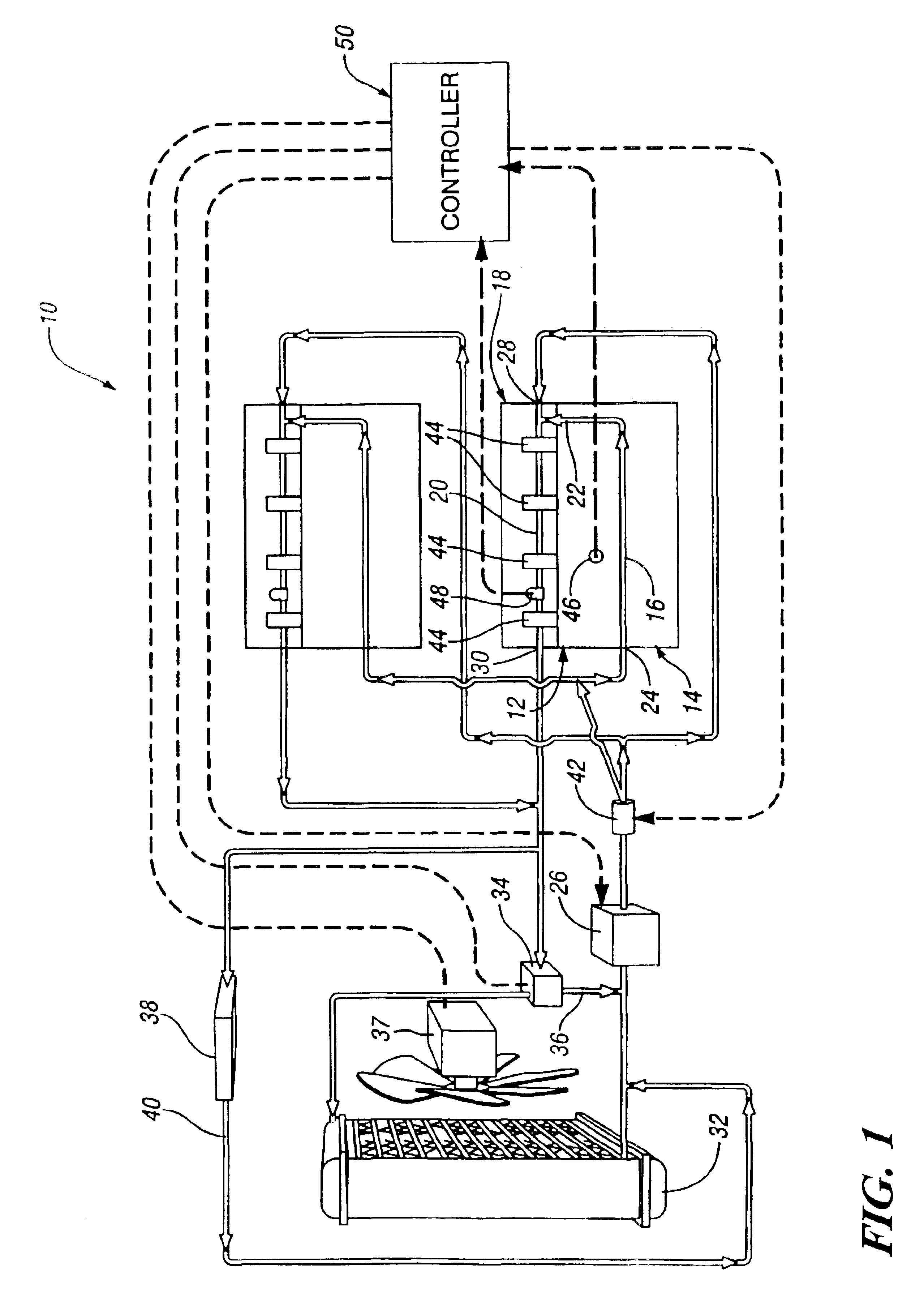
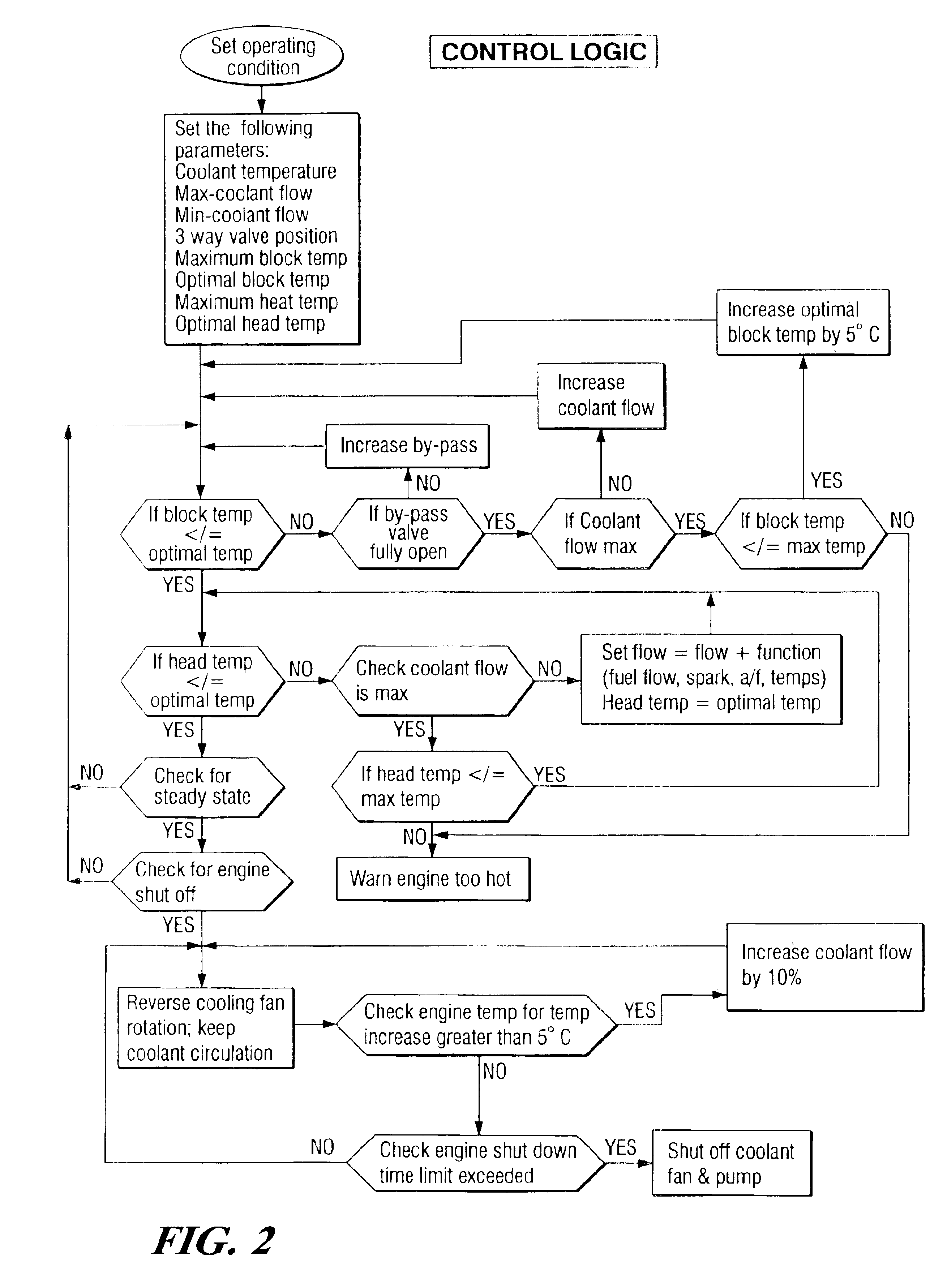
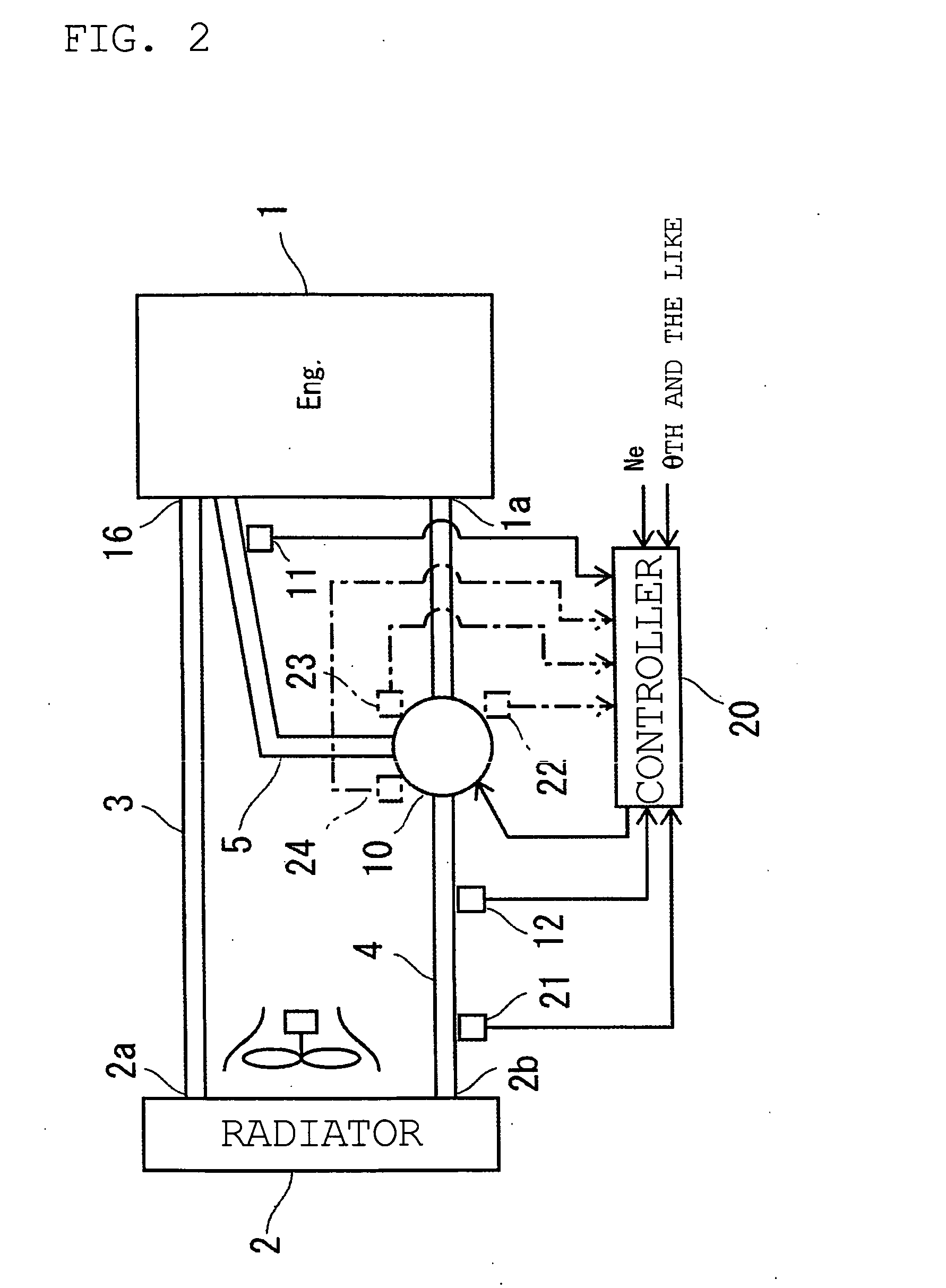
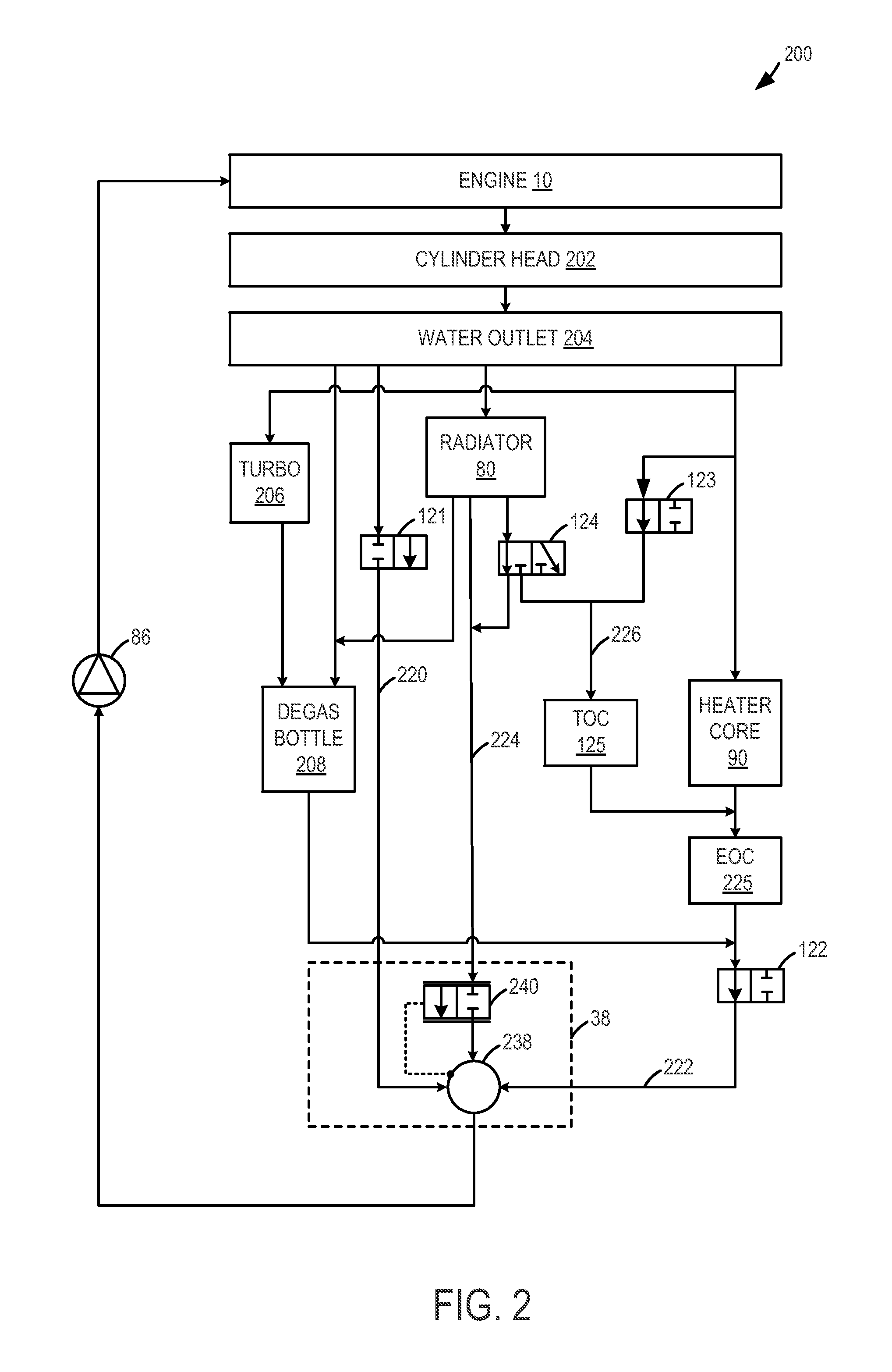
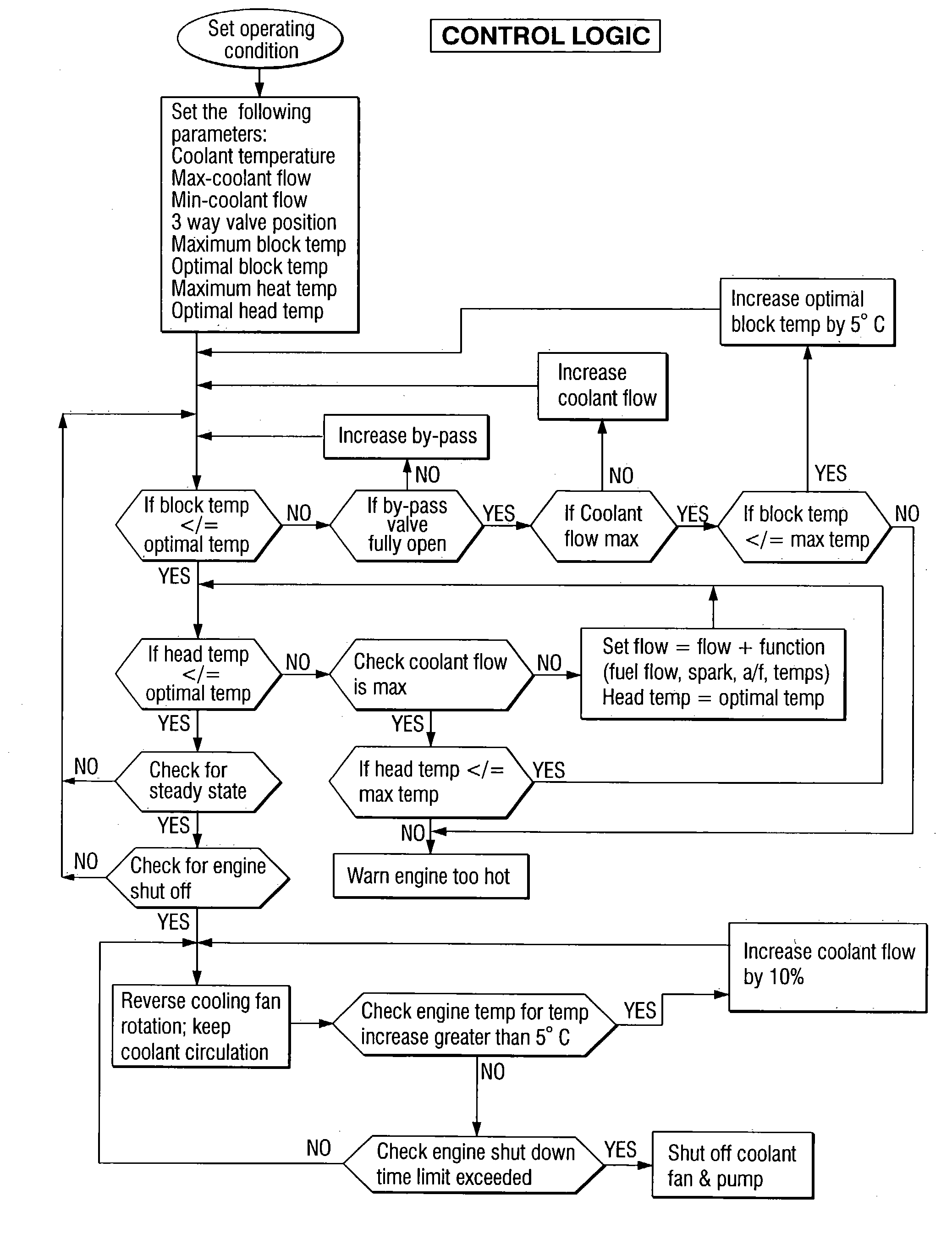
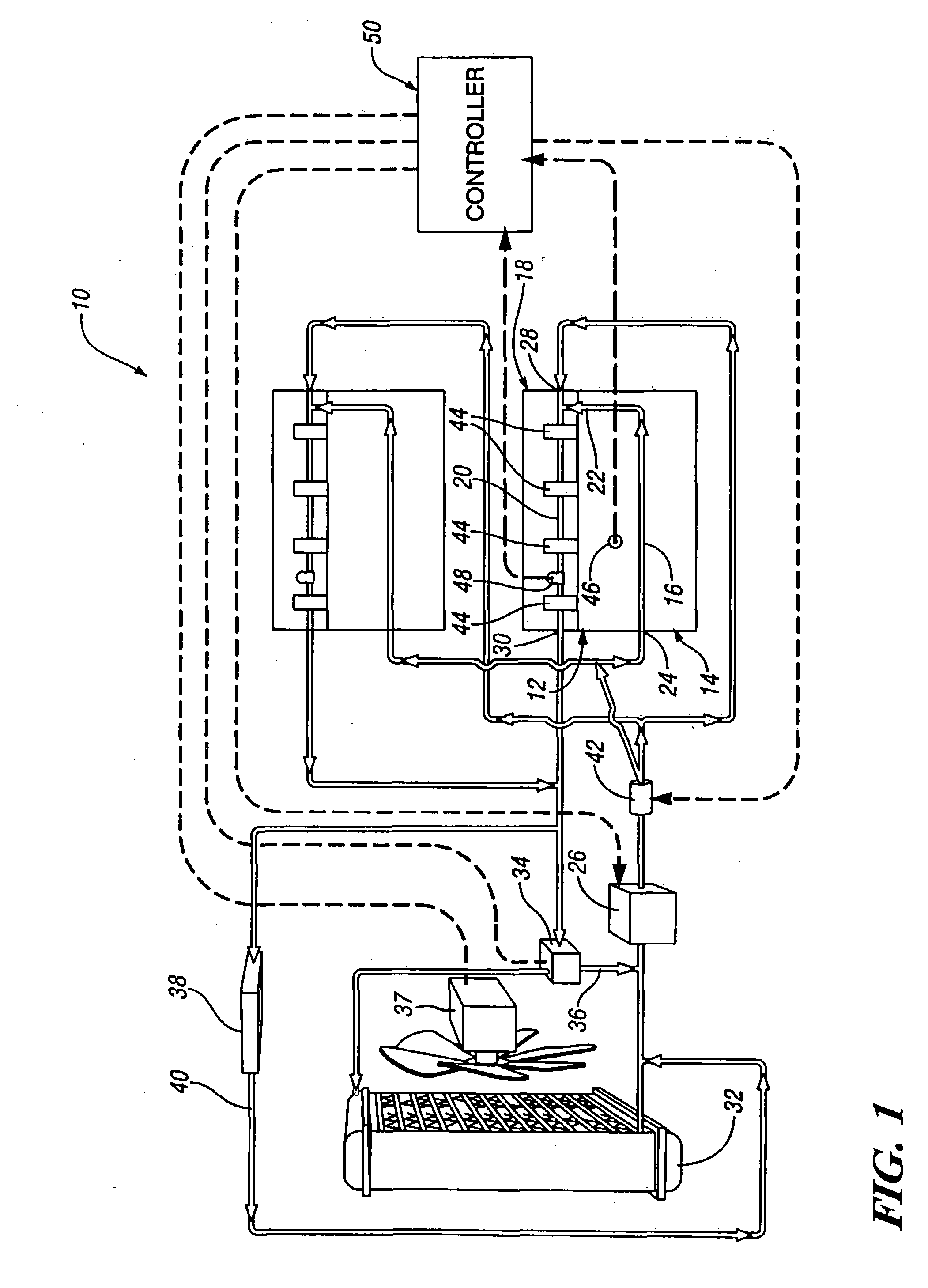
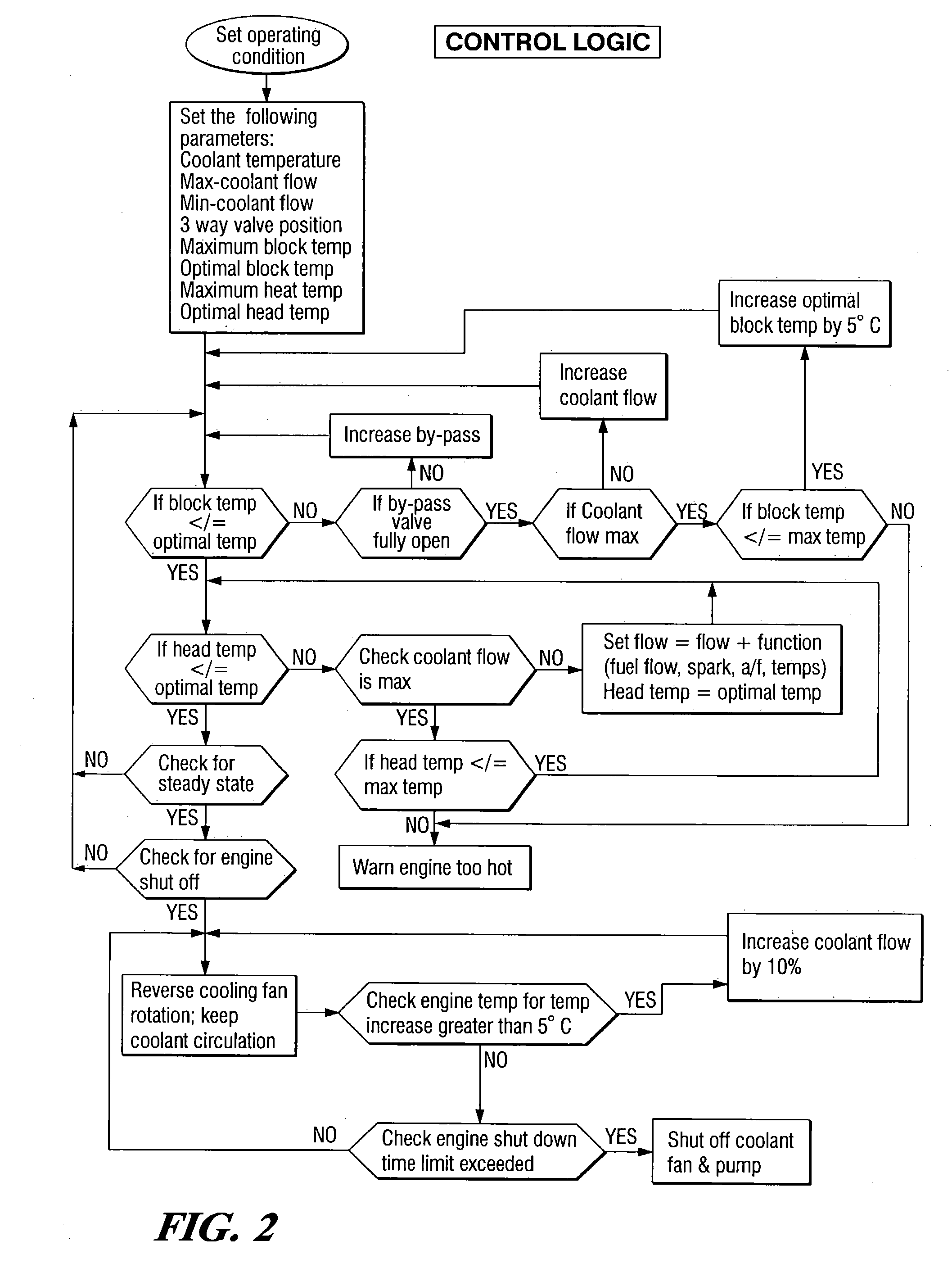
InactiveUS6955141B2Minimizes parasitic lossIncrease and decrease flow of coolantLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlCoolant flowCylinder head
A cooling system has a diverter valve to selectively control the flow of coolant through an internal combustion engine having a cylinder block with a cooling jacket and a cylinder head mounted on the block with a cooling jacket. A controller, responsive to the temperature of the block and the head, controls the diverter valve and a water pump to provide adequate coolant flow through the head and the block as needed to maintain optimal operating temperatures. After the engine is shut off, the controller continues to operate the water pump and a cooling fan to continue to cool the engine for a period of time.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
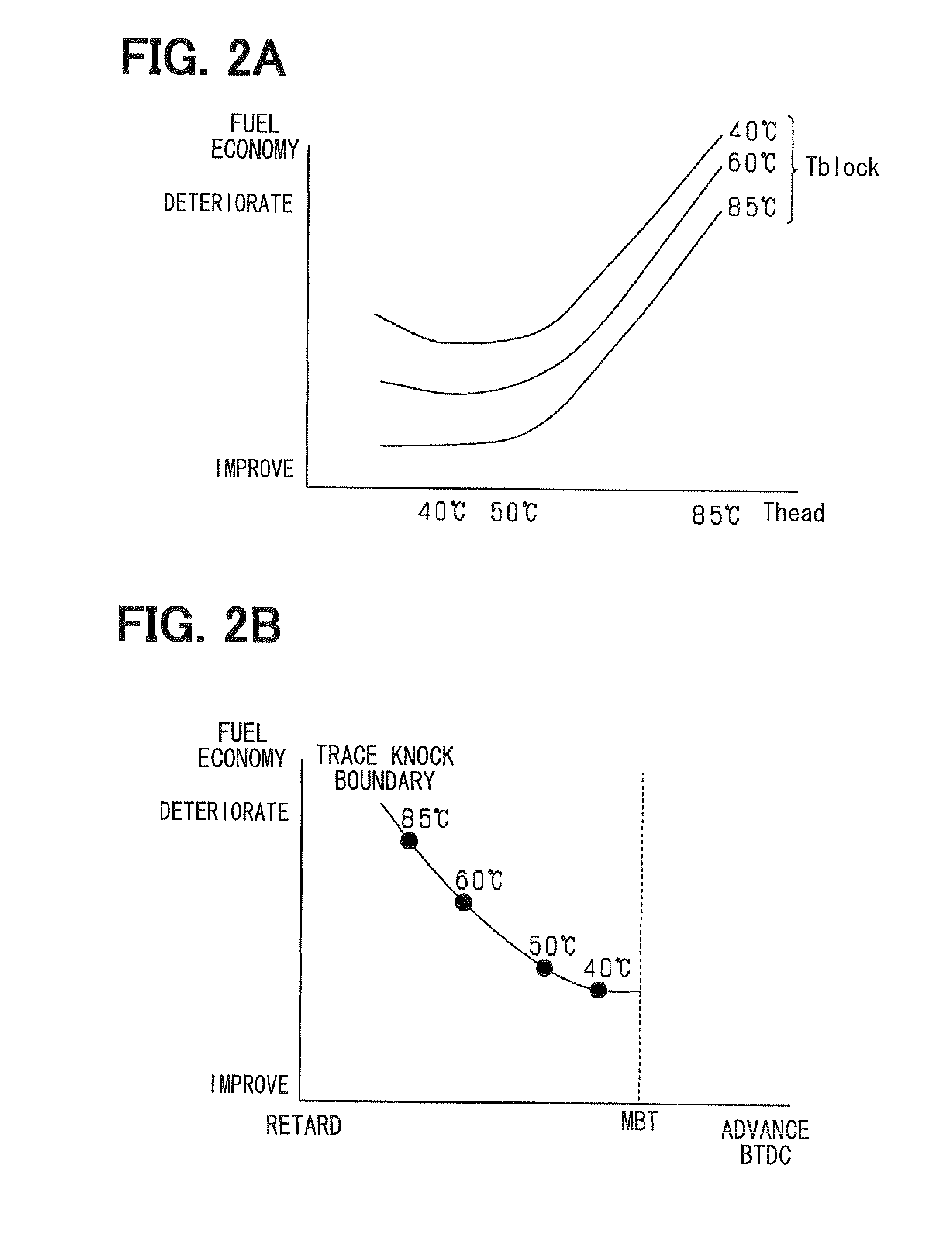
Method of controlling electronic controlled thermostat
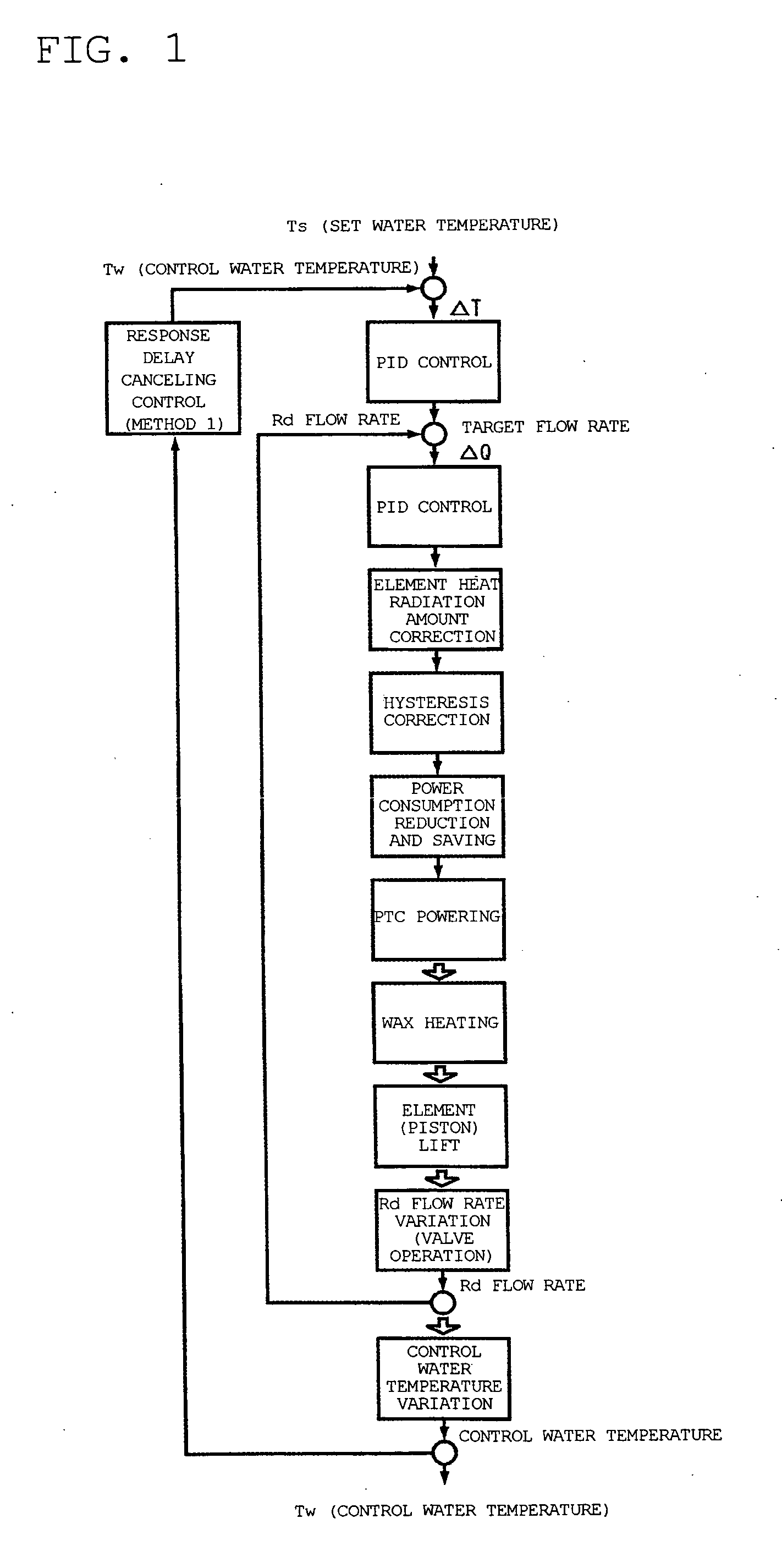
ActiveUS20050006487A1Reliable improvement in fuel consumptionPoor temperature controlTemperature control without auxillary powerElectrical controlResponse delayEngineering
An electronically controlled thermostat control method is obtained which makes it possible to eliminate the response delay from the time that the required cooling water temperature is set to the time that the actual cooling water temperature reaches the set water temperature by controlling the flow rate, and to realize high cooling water temperature tracking characteristics with a high degree of precision at a low cost. The method of the present invention is characterized in that in an electronically controlled thermostat which is used to control the cooling water temperature of an engine, and which comprises an actuator that can arbitrarily vary the degree of valve opening without depending only on the actual cooling water temperature, the actuator is controlled by the control controller, which has means for calculating the elapsed time from the powering of the actuator to the variation of the water temperature for predicting the water temperature after the elapsed time when the cooling water temperature is controlled to an arbitrarily set water temperature, and the actuator is controlled in advance in accordance with the above-described predicted water temperature.
Owner:NIPPON THERMOSTAT CO LTD
Internal combustion engine for a motor vehicle
InactiveUS20060157002A1Reduce the ratioHeating fastLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlCylinder headEngineering
In an internal combustion engine for a motor vehicle, having a cylinder head and an engine block, each with a coolant inlet port and a coolant outlet port which is common to the cylinder head the engine block, a main coolant pump having an intake side connected to the coolant outlet port and a pressure side connected to a first control valve via which coolant reaches the inlet port of the cylinder head and the inlet port of the engine block depending on the temperature of the coolant, and to a method for operating such an internal combustion engine, wherein the main coolant pump is selectively actuated to pump the coolant through at least one of the cylinder head and the engine block or is shut down depending on the engine operating state.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Thermoelectric generator
InactiveUS20060130888A1Suppressing decreaseSolve insufficient capacityLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlEngineeringTemperature difference
A thermoelectric generator has a high temperature heat source part provided on a first passage through which a first fluid for cooling an engine flows, a low temperature heat source part provided on a second passage through which a second fluid having a temperature lower than that of the first fluid flows, and a thermoelectric element for producing electric power by a temperature difference produced between the high temperature heat source part and the low temperature heat source part. The first passage is included in a first circuit in which the engine and a first radiator for cooling the first fluid are connected in loop through a main passage. Further, the first passage is in parallel to the first radiator in the first circuit. The second passage is included in a second circuit that is separate from the first circuit and includes a second radiator for cooling the second fluid.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Powertrain Thermal Control with Grille Airflow Shutters
InactiveUS20110246023A1Improve vehicle fuel economyLow costCoolant flow controlAir coolingWindow shutterPowertrain
A method of powertrain thermal control in a vehicle having grille airflow shutters. The method comprises the steps of: detecting vehicle operating conditions including at least a temperature condition for an engine cooling loop and engine load; pumping engine coolant through the engine cooling loop including pumping the engine coolant through a radiator under all temperature conditions of the engine cooling loop; and adjusting the grille airflow shutters relative to a grille to selectively block a portion, none or all airflow through the grille to thereby control airflow through the radiator based upon the detected vehicle operating conditions.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and system for controlling an engine to maintain a comfortable cabin temperature within a vehicle
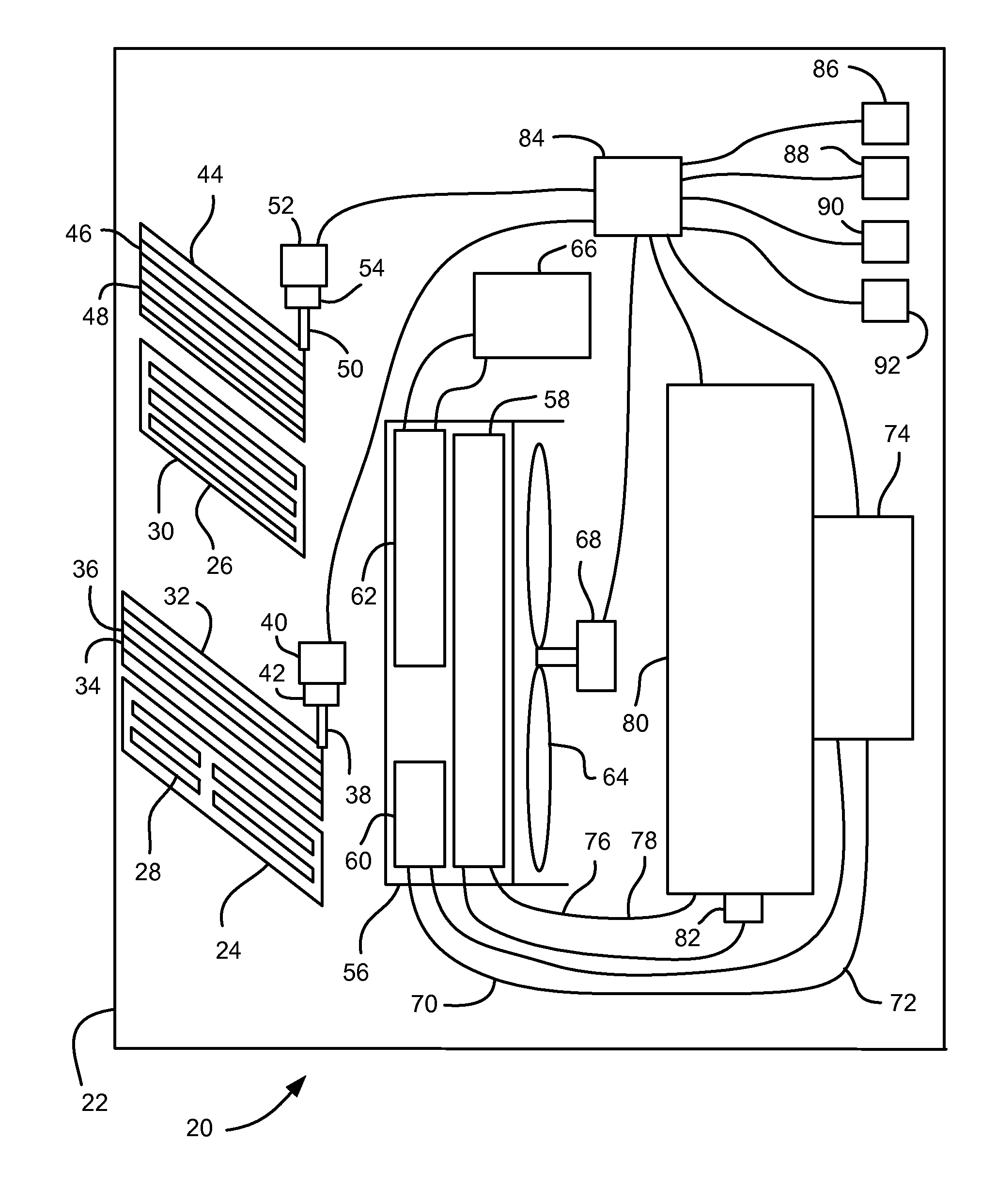
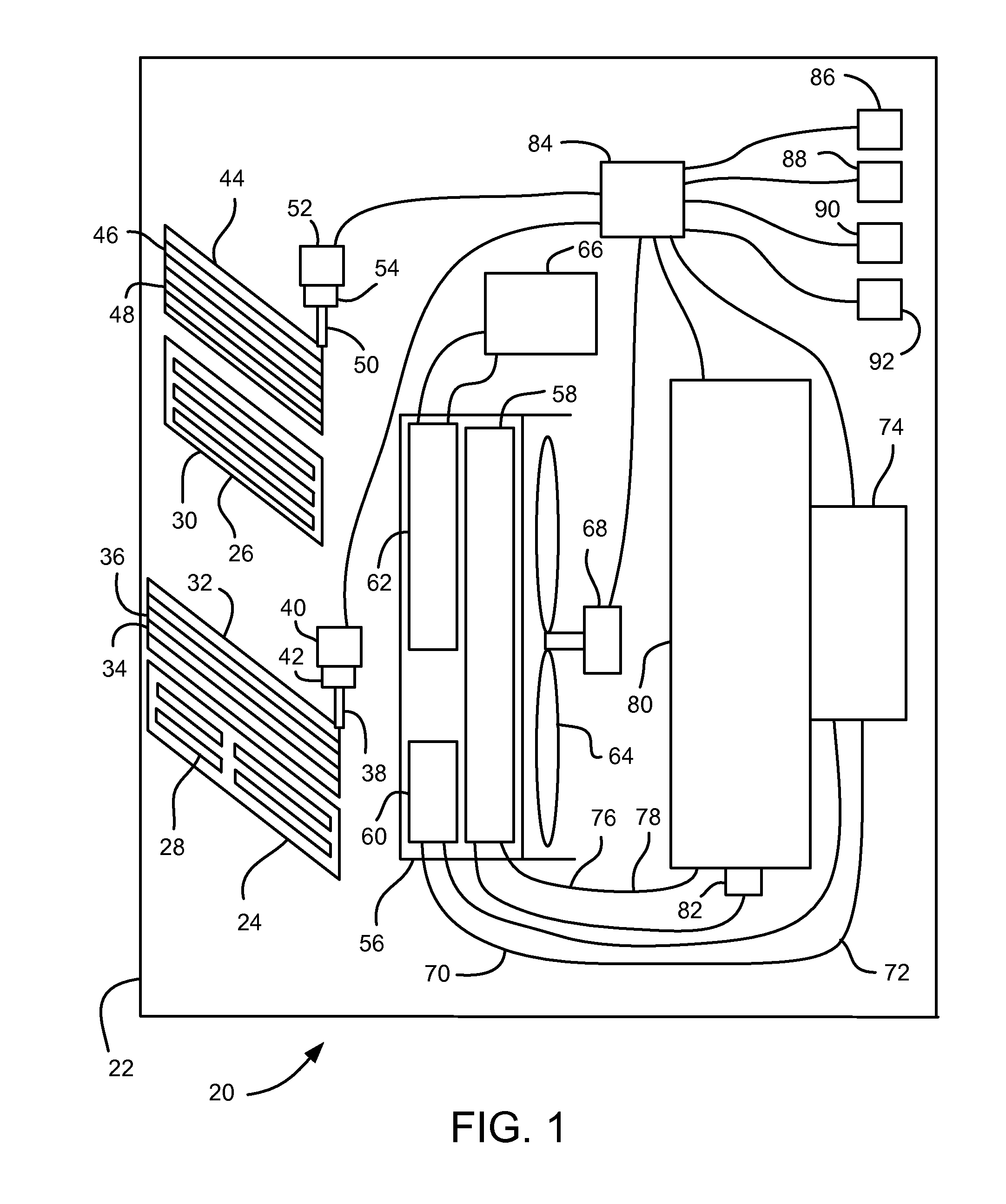
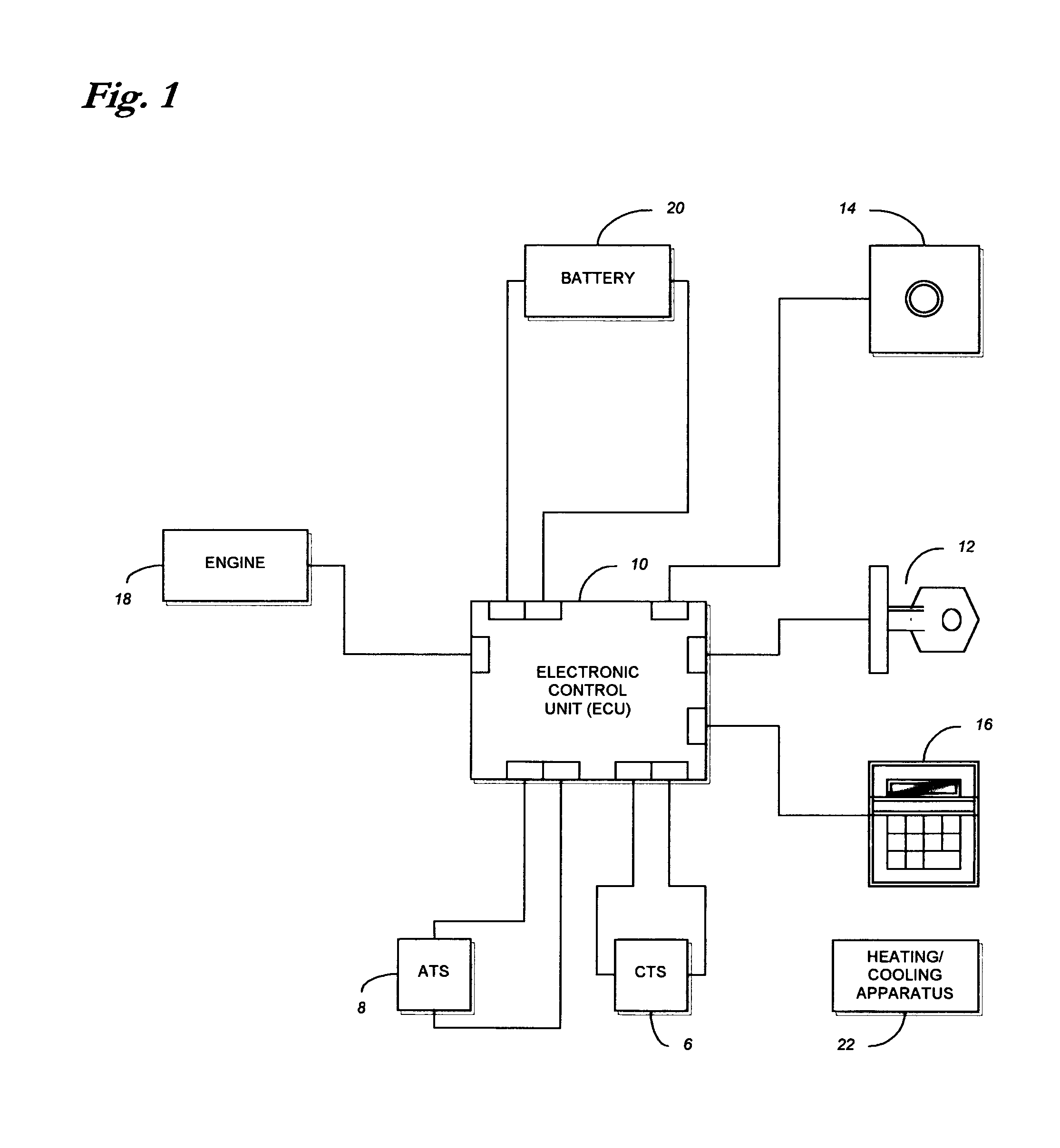
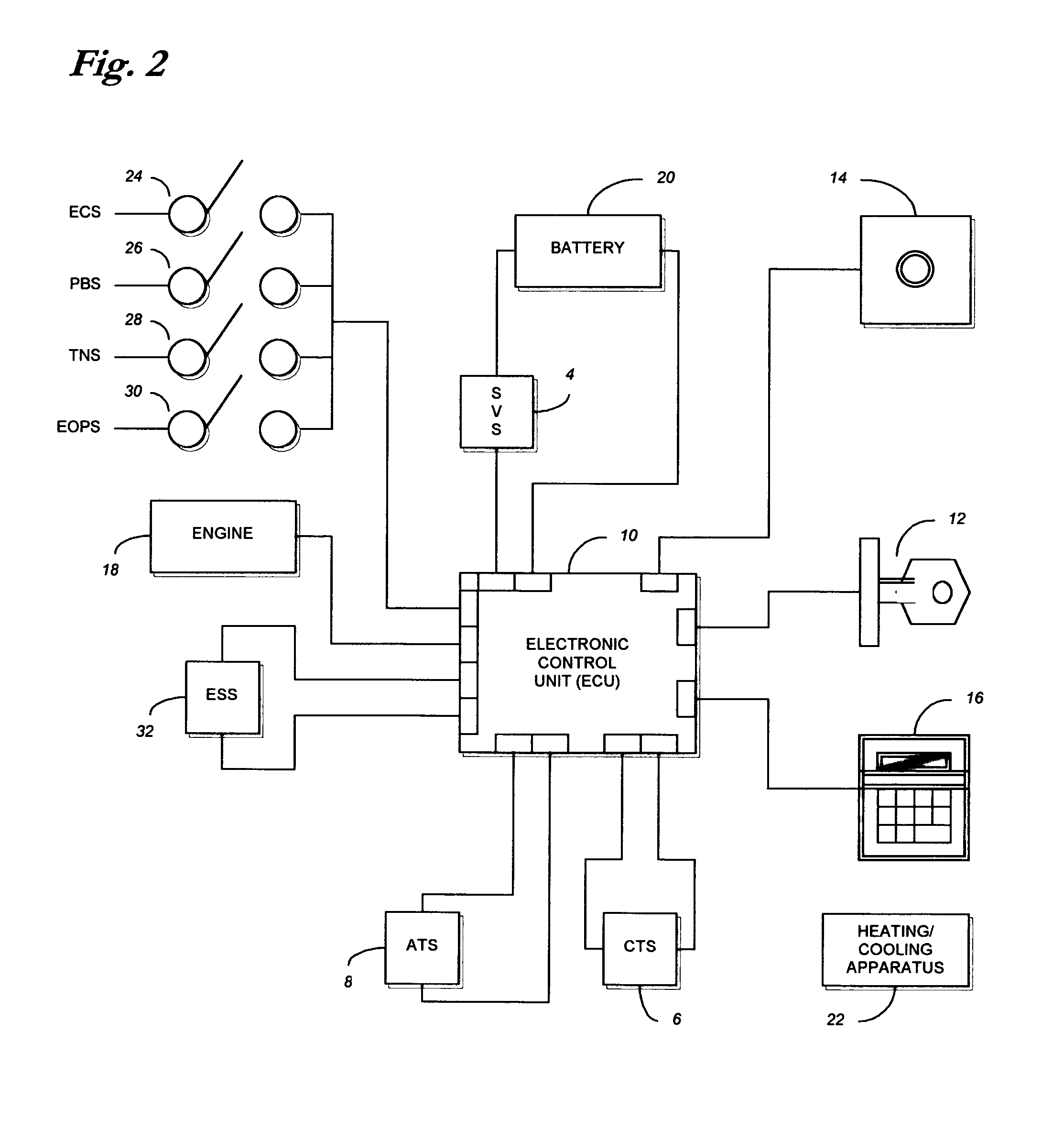
ActiveUS7027912B1Minimizing engine idlingAnalogue computers for vehiclesMeasurement deviceBody compartmentTwo temperature
A method and system for controlling an engine in order to maintain a comfortable cabin temperature within a vehicle that is equipped with an engine, a battery and a heating / cooling apparatus including determining an acceptable range of cabin temperatures, monitoring cabin and outside air temperatures, controlling automatic starting of the vehicle engine when both temperatures are outside of the acceptable range and running the engine only as is minimally necessary to maintain the cabin temperature within the acceptable range.
Owner:METZGER WILLIAM R
Method and device for controlling electronic water pump of water-cooling system of automobile engine
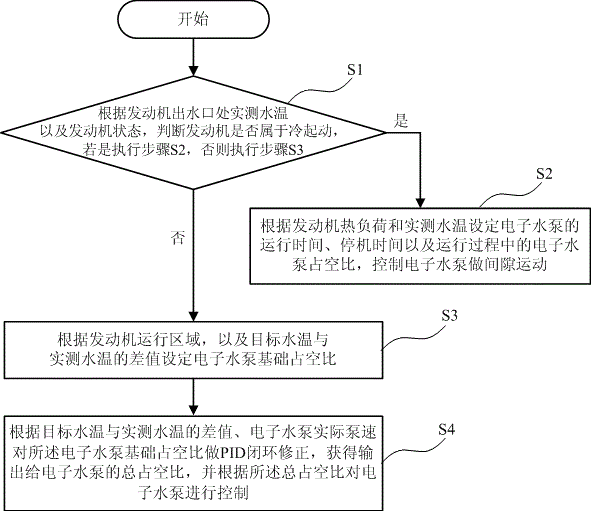
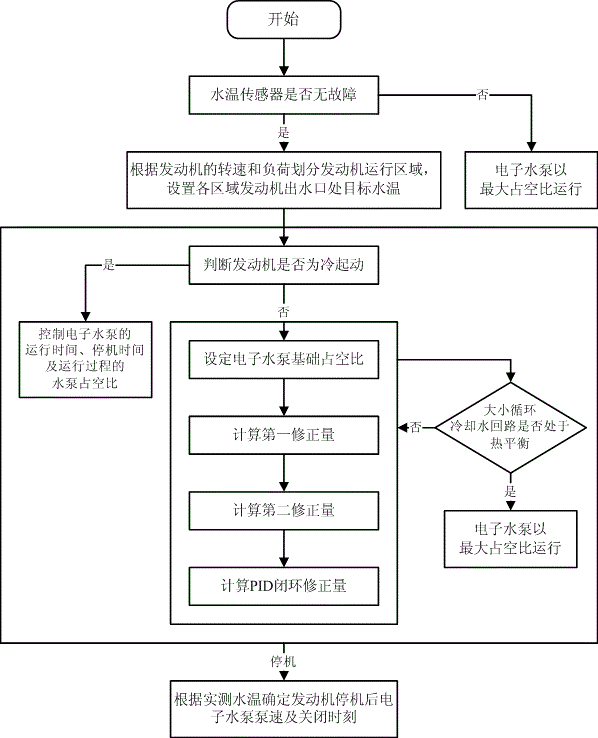
ActiveCN106246328ALower working temperatureEasy to controlCoolant flow controlMeasurement deviceIntermittent motionStop time
The invention provides a method and device for controlling an electronic water pump of a water-cooling system of an automobile engine. The method comprises the following steps: step S1, judging whether the engine is in a cold start state or not according to actually measured water temperature at a water outlet of the engine and the state of the engine, if the engine is in the cold start state, carrying out step S2, and if the engine is not in the cold start state, carrying out step S3; step S2, setting running time and stopping time of the electronic water pump according to the thermal load and the actually measured water temperature of the engine and duty ratio of the electronic water pump in a running process, and controlling the electronic water pump to carry out intermittent motion; step S3, setting a basic duty ratio of the electronic water pump according to a running region of the engine and difference between target water temperature and the actually measured water temperature; and step S4, carrying out PID closed-cycle correction on the basic duty ratio of the electronic water pump according to the difference between the target water temperature and the actually measured water temperature and actual pump speed of the electronic water pump to obtain total duty ratio output to the electronic water pump, and controlling the electronic water pump according to the total duty ratio. By the method and device for controlling the electronic water pump of the water-cooling system of the automobile engine, warming time can be shortened, and the water temperature control effect is improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU AUTOMOBILE GROUP CO LTD
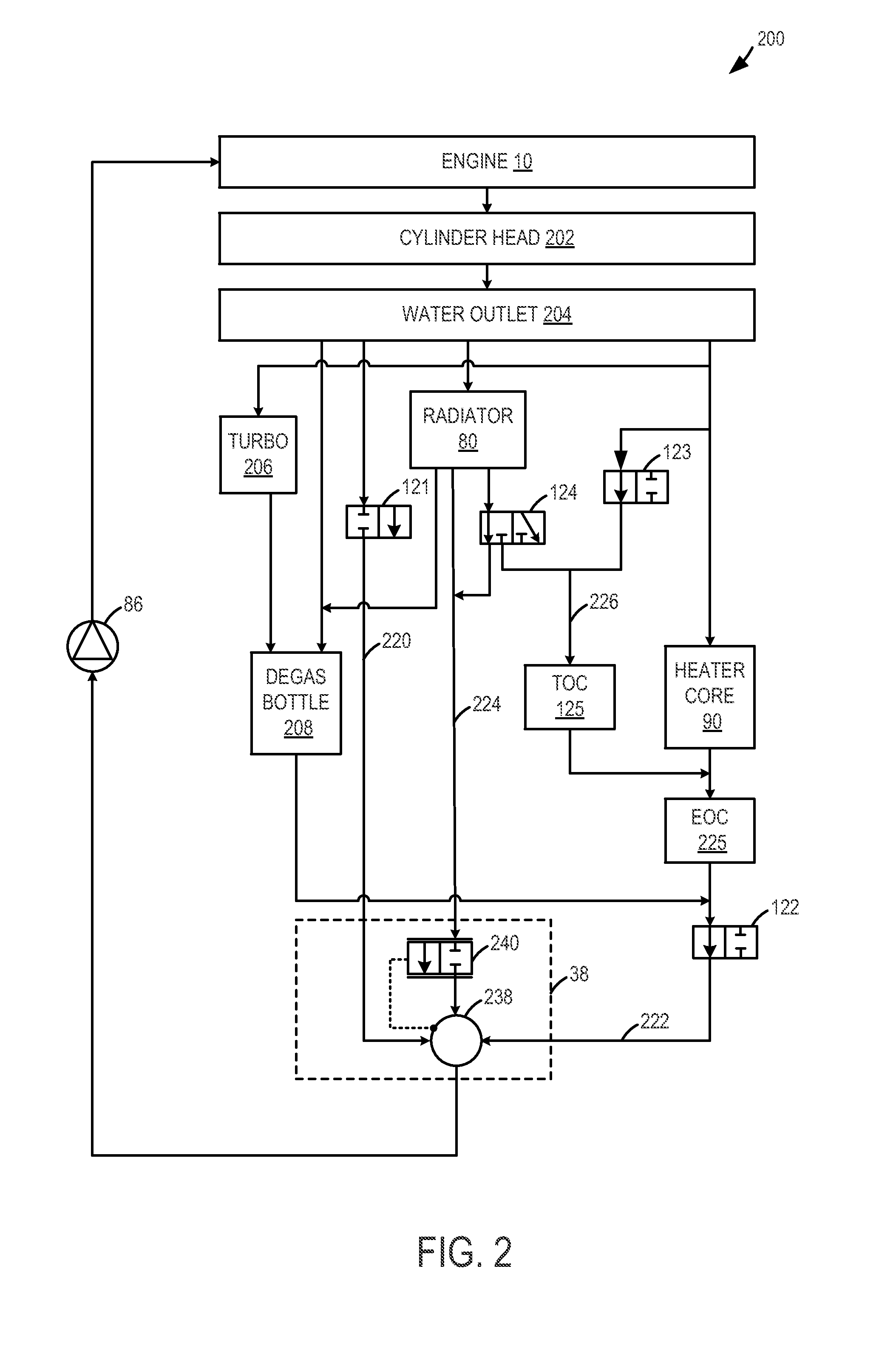
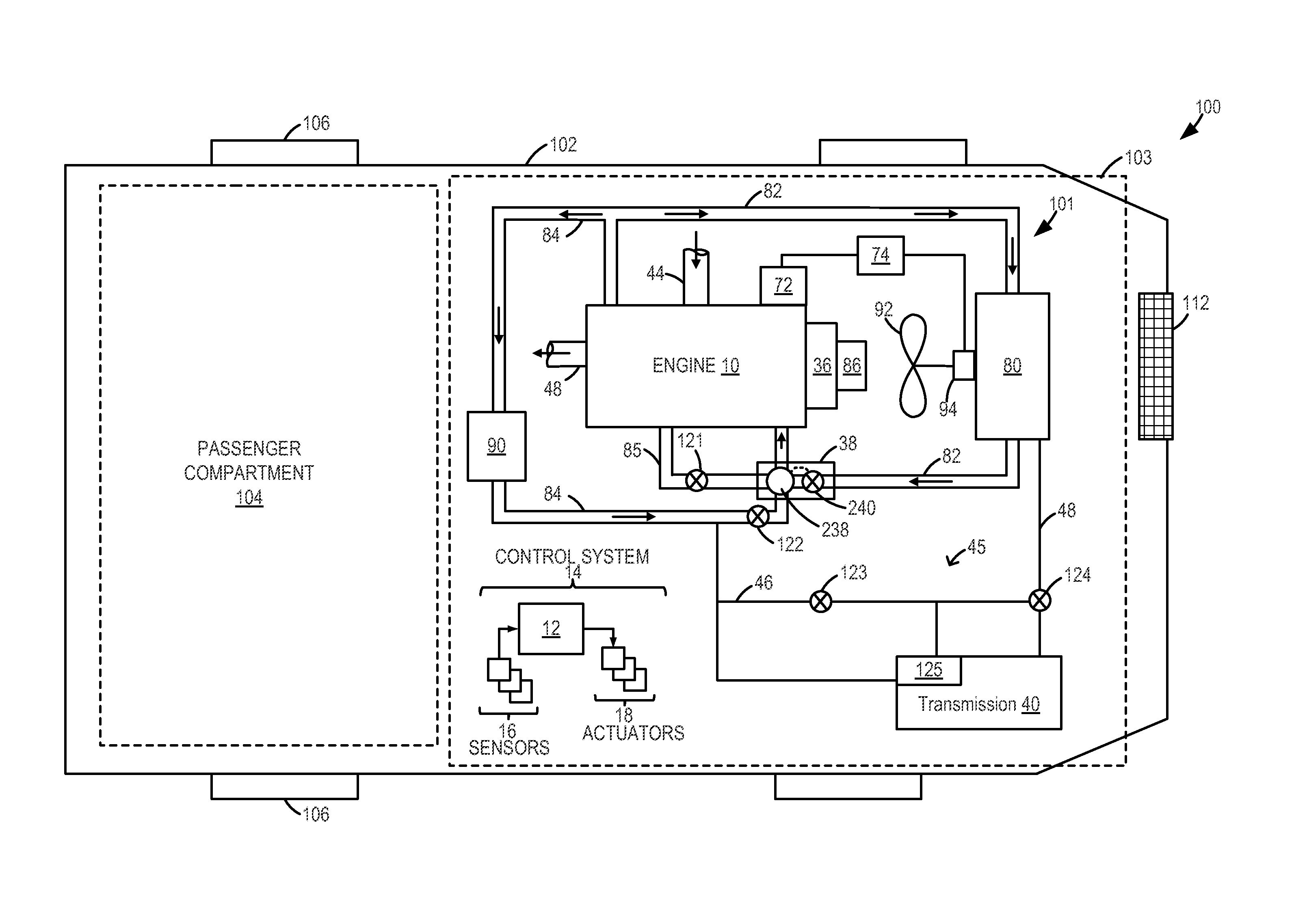
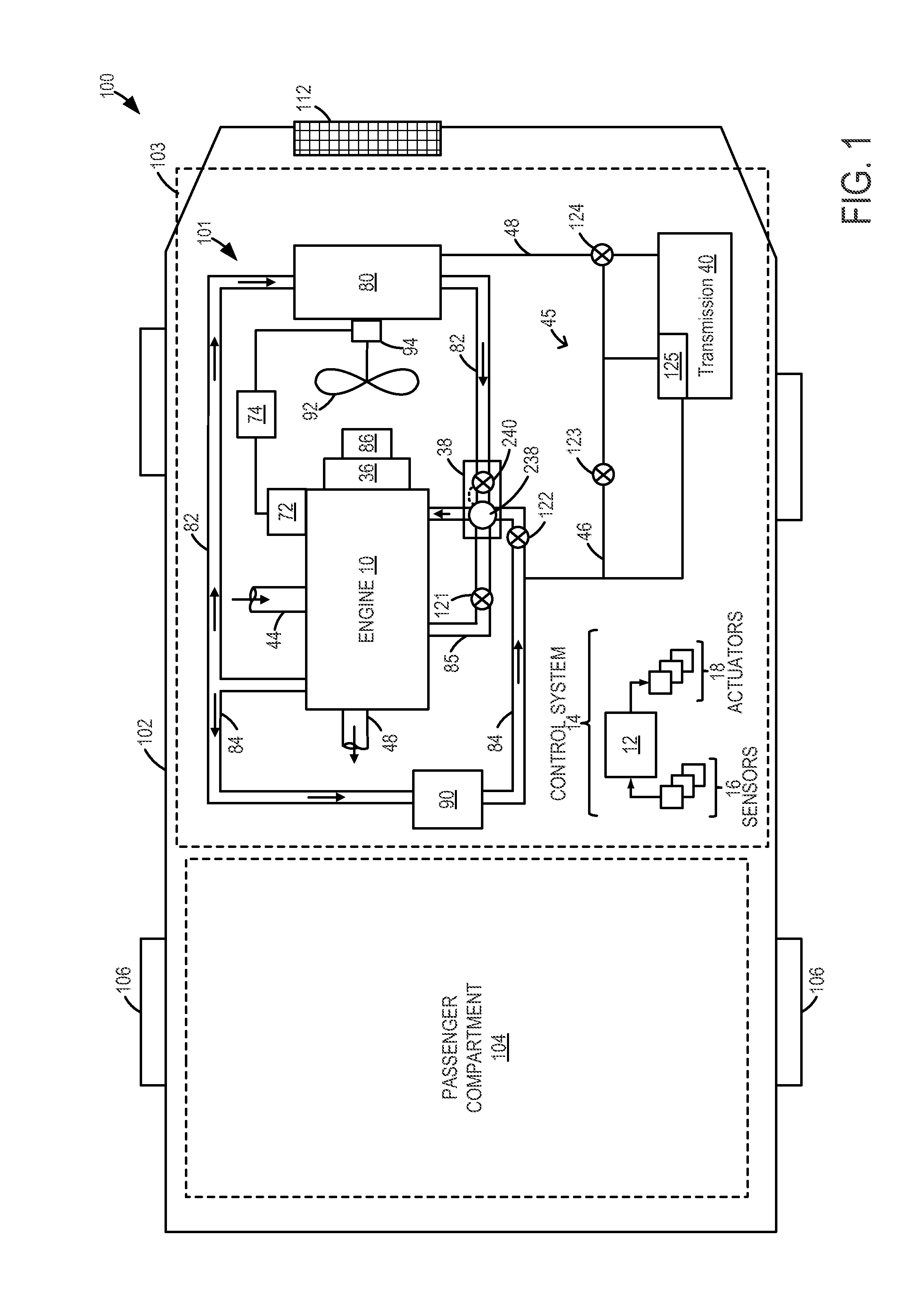
Engine cooling system control
ActiveUS20130255605A1Accurate valueReduce the possibilityLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlCoolant temperatureWarming up
Methods and systems are provided for diagnosing each of a plurality of engine cooling system components including various valves and grill shutters. Each valve may be individually closed and opened for a specified duration, and corresponding changes in coolant temperature may be monitored. If all the components are functional, the various valves may be adjusted to stagnate coolant at the engine and expedite engine warm-up during a cold-start.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Controller for engine cooling system
InactiveUS20110214627A1Avoid insufficient heatingImprove abilitiesLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlCylinder headCoolant flow
An internal combustion engine has a cylinder-head-passage through which an engine coolant flows toward a water jacket when a water pump is operated. The water pump is an electric water pump utilizing the electric power charged in the battery. A radiator is provided in the cylinder-head-passage. Even after the engine is shut off, the water pump is kept driven.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Engine cooling system control
InactiveUS20130255604A1Improve economyInternal-combustion engine testingCoolant flow controlEngineeringCoolant temperature
Methods and systems are provided for diagnosing each of a plurality of engine cooling system components including various valves and grill shutters. Each valve may be individually closed and opened for a specified duration, and corresponding changes in coolant temperature may be monitored. If all the components are functional, the various valves may be adjusted to stagnate coolant at the engine and expedite engine warm-up during a cold-start.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Cooling apparatus for liquid-cooled internal combustion engine
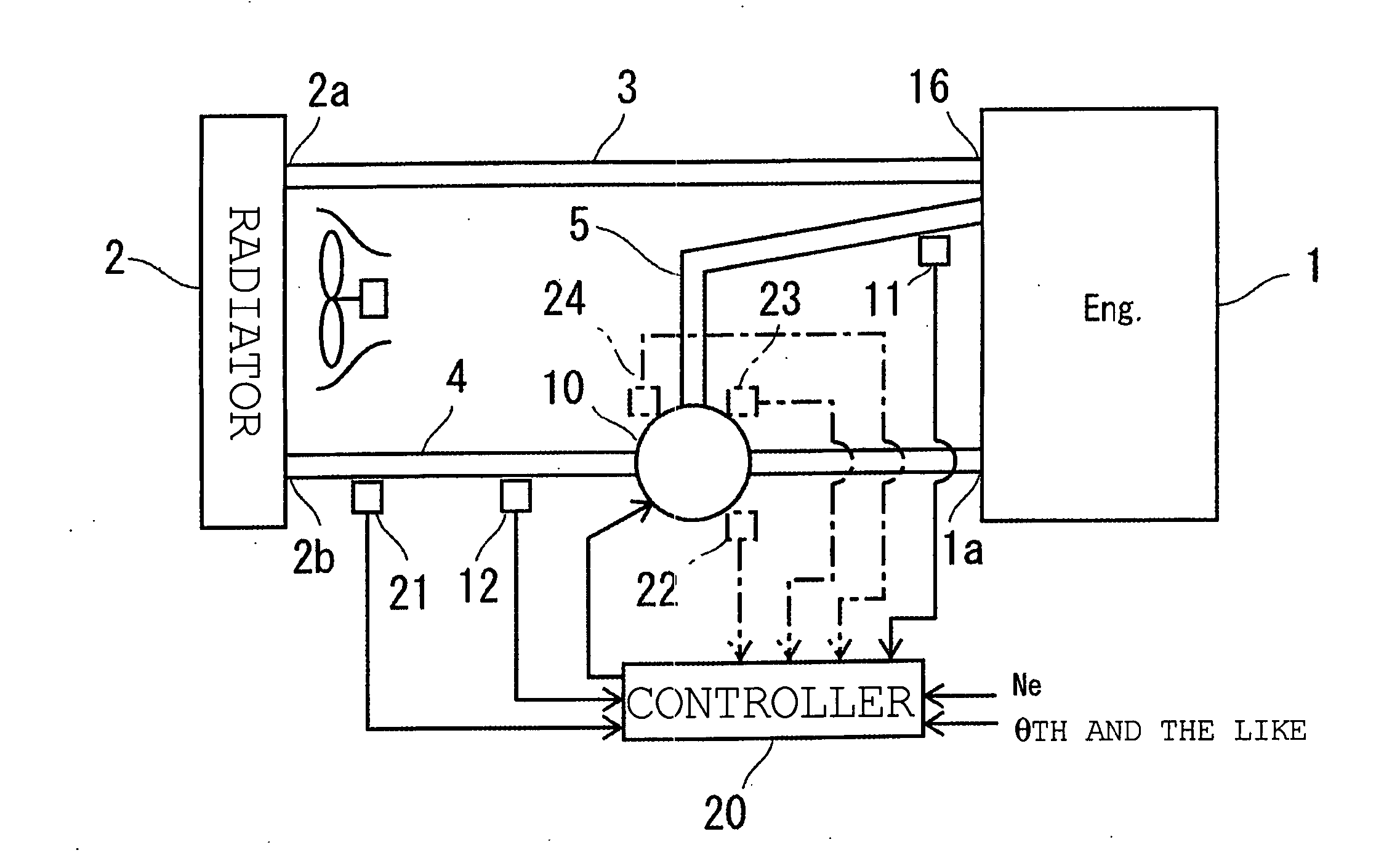
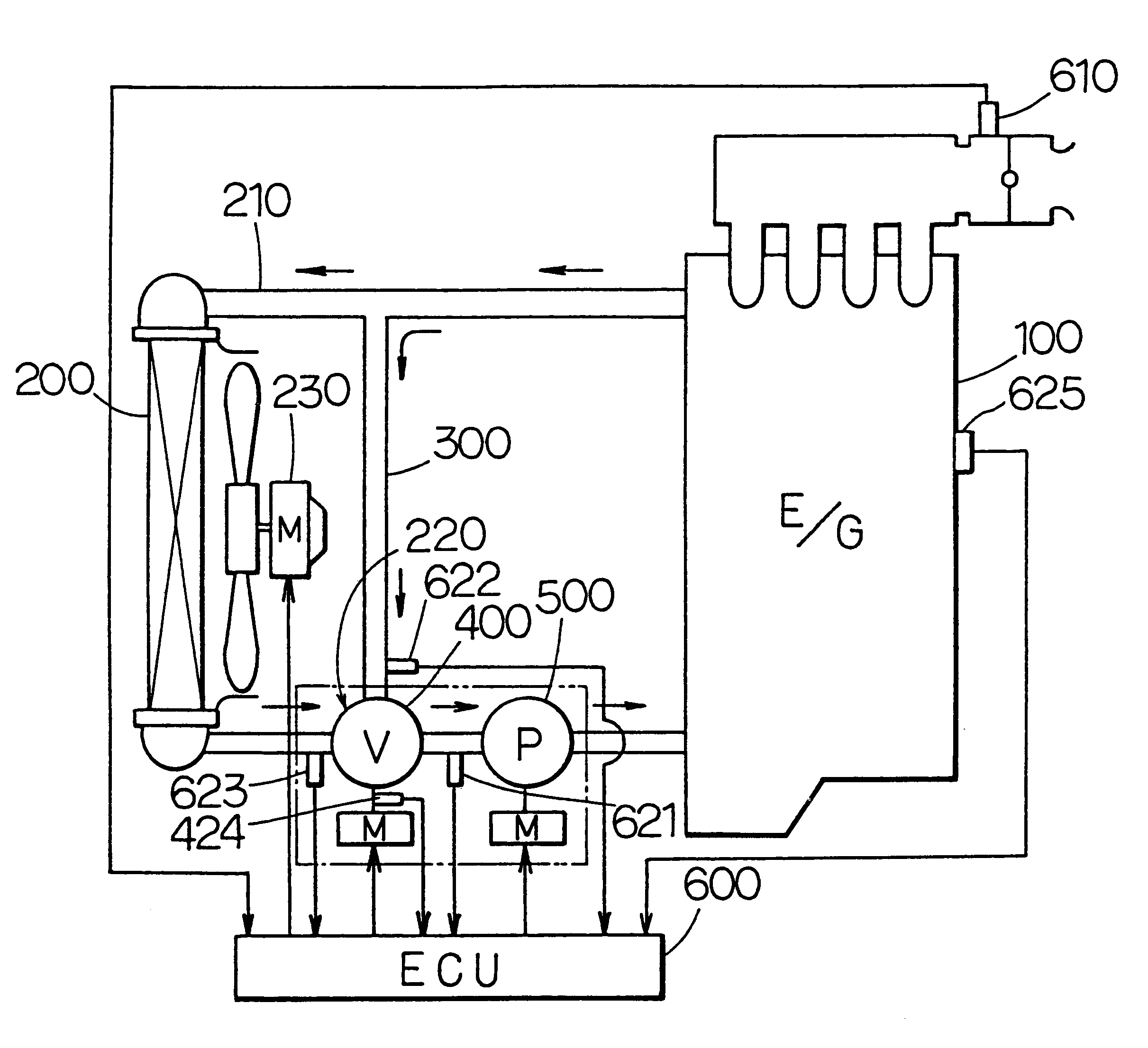
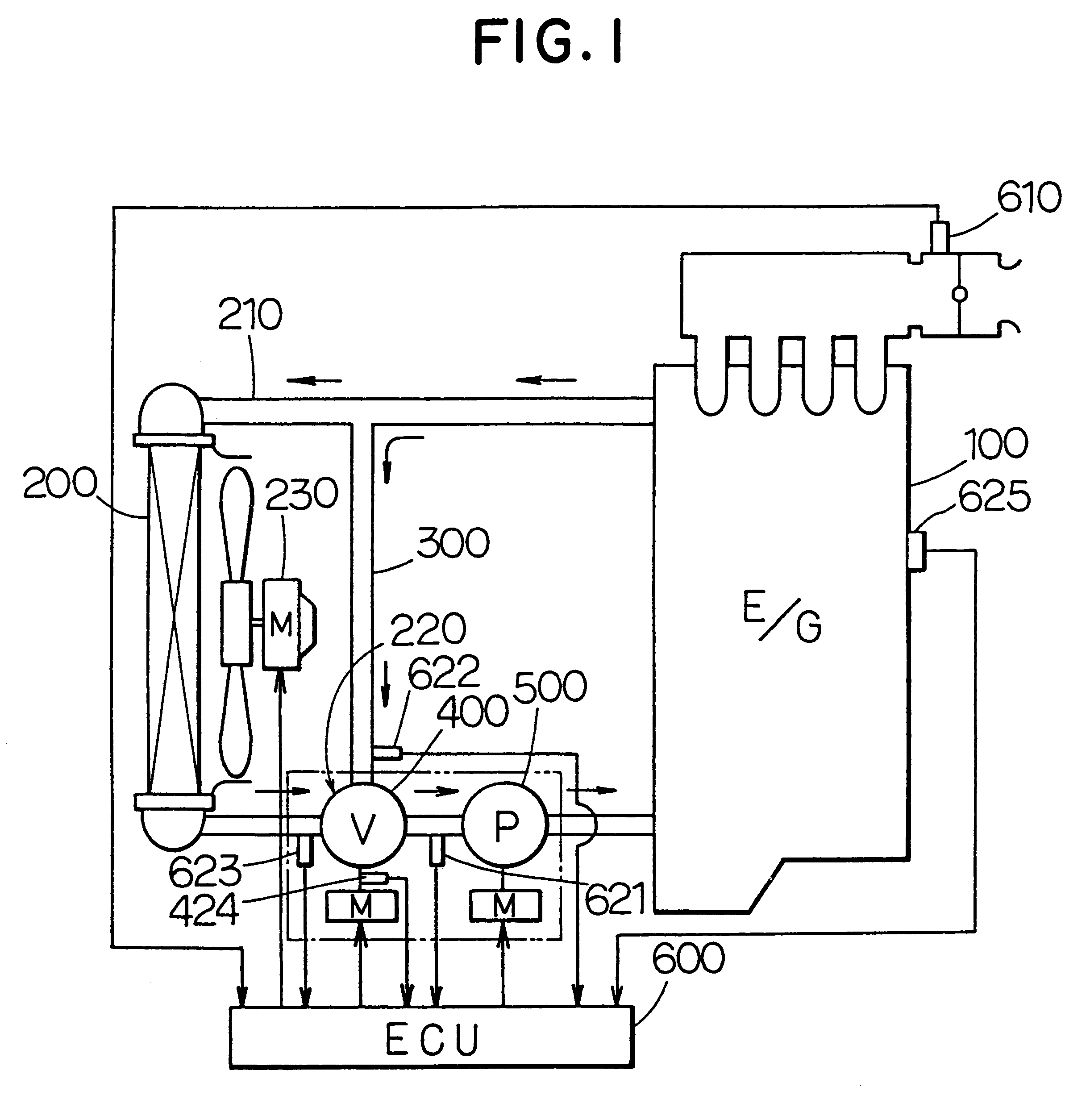
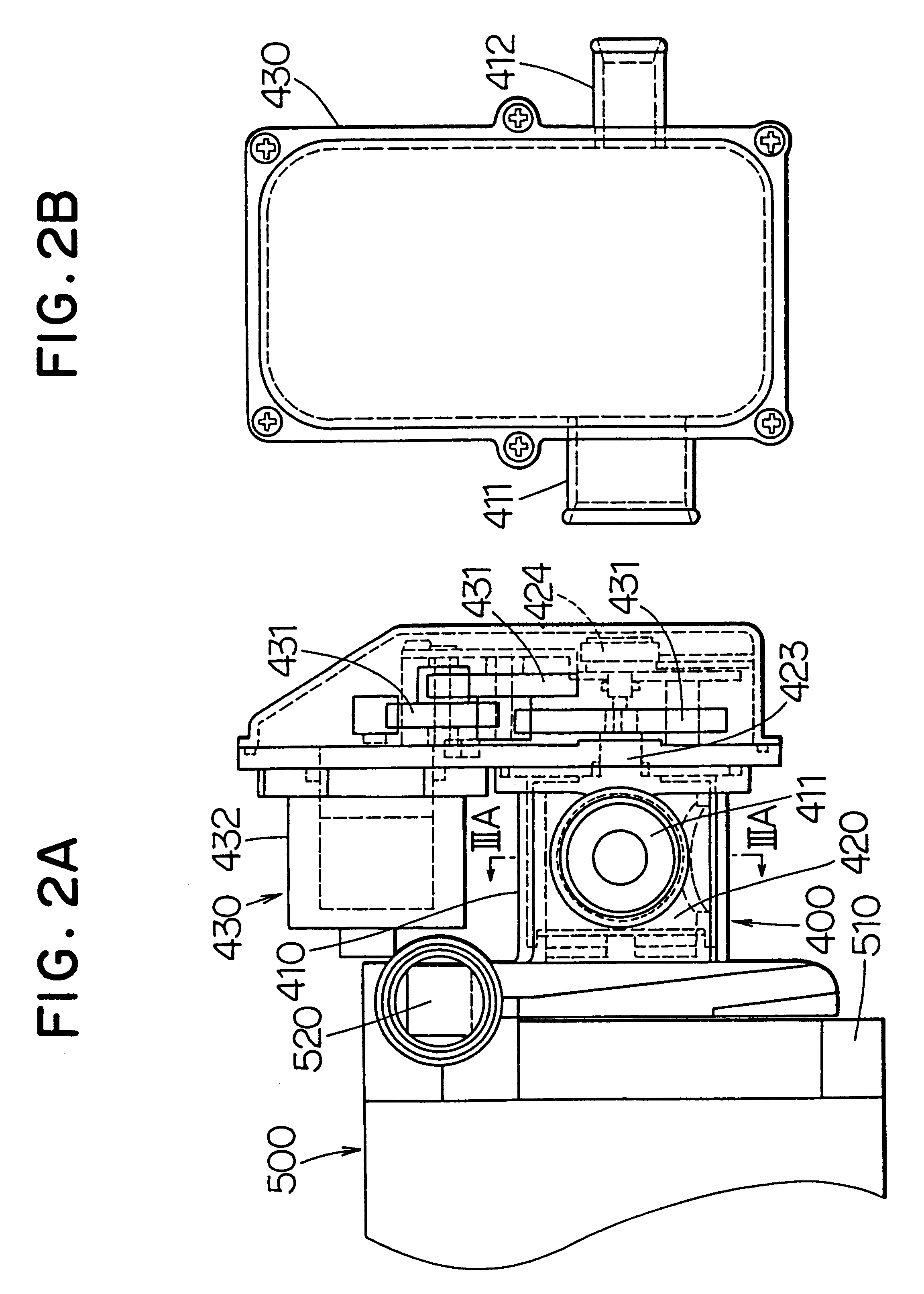
InactiveUS6390031B1Easy to controlCoolant flow controlMeasurement deviceEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A flow rate ratio of a radiator flow rate to a bypass flow rate is determined from pump water temperature, bypass water temperature and radiator water temperature. The relation between the flow rate ratio and a valve opening degree of a flow control valve is predetermined as a map. The valve opening degree is determined from the flow rate ratio and the map. Accordingly, the cooling water temperature at an inlet of a pump is accurately controlled without detecting the flow rate of the cooling water.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Cylinder head cooling structure for an internal combustion engine, including an oil temperature sensor and an oil temperature control system
ActiveUS20060065218A1Efficient use ofAvoid contactLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlTemperature controlCylinder head
A cylinder head cooling structure and an oil temperature control system are provided for an internal combustion engine having a plurality of cylinders, each having a plurality of intake ports and a plurality of exhaust ports. The engine includes cooling oil jackets surrounding the spark plugs in the cylinder head, a thermostat attached to the front surface of the crankcase independently of an oil filter, and an oil temperature sensor disposed on a rear face of the cylinder block above the crankcase in an oil supply path formed on the cylinder rear face for supplying oil to the oil jackets. Oil passages conducting oil into the oil jacket are provided between two separate parts of a bifucated intake port and between two separate parts of a bifurcated exhaust port, and only cooling system oil reaching high temperatures is allowed to flow through the thermostat, thereby improving temperature control response.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
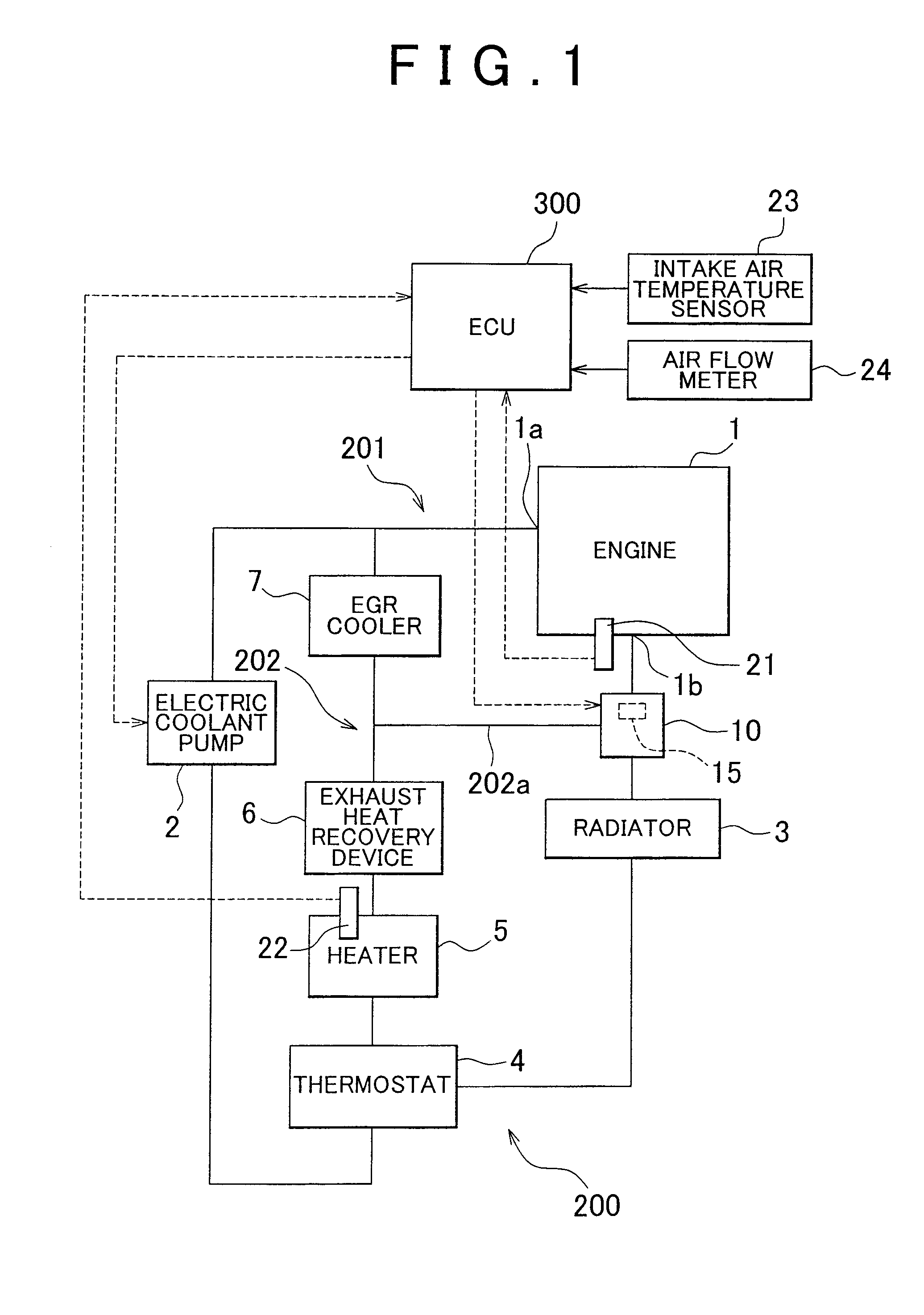
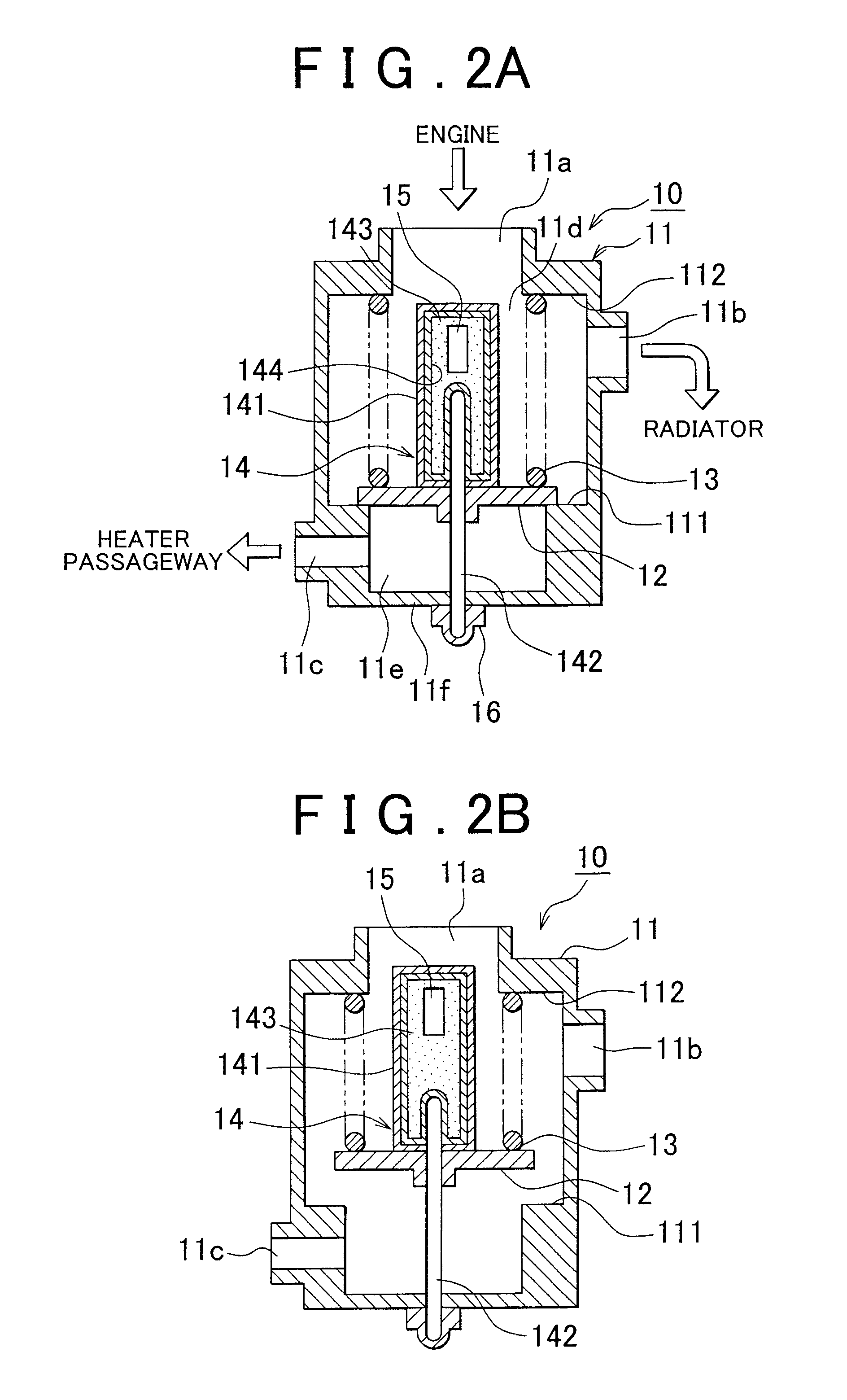
Abnormality determination apparatus and abnormality determination method for coolant temperature sensor, and engine cooling system
InactiveUS20130213600A1Increase temperatureAccurately determineAir-treating devicesCoolant flow controlCoolant temperatureChangeover
A coolant temperature sensor abnormality determination apparatus opens a changeover valve to increase the temperature of a coolant in a heater passageway if the amount of increase of the detected heater inlet coolant temperature value obtained when the intake air amount of an engine becomes equal to or greater than a predetermined value is small. Then, if the amount of increase in the detected heater inlet coolant temperature value after the changeover valve opens is greater than or equal to the predetermined value, the apparatus determines that the heater inlet coolant temperature sensor is normal. If the amount of increase in the detected heater inlet coolant temperature value is smaller than the predetermined value, the apparatus determines that the heater inlet coolant temperature sensor is abnormal.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Engine cooling system
ActiveUS20050028756A1Minimizes parasitic lossIncrease and decrease flow of coolantLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlTemperature controlCylinder head
A cooling system has a diverter valve to selectively control the flow of coolant through an internal combustion engine having a cylinder block with a cooling jacket and a cylinder head mounted on the block with a cooling jacket. A controller, responsive to the temperature of the block and the head, controls the diverter valve and a water pump to provide adequate coolant flow through the head and the block as needed to maintain optimal operating temperatures. After the engine is shut off, the controller continues to operate the water pump and a cooling fan to continue to cool the engine for a period of time.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Exhaust heat recovery for transmission warm-up
ActiveUS20110088378A1Waste heat recoveryAvoid insufficient heatingCoolant flow controlInternal combustion piston enginesOperant conditioningOperating temperature
An exhaust heat recovery system (EHRS) for a vehicle is provided that is operable to direct coolant heated by exhaust heat to a vehicle transmission under certain operating conditions after the engine is adequately heated by the exhaust heat and without further heating the engine with the exhaust heat. Thus, recovery of exhaust heat is increased as the transmission is heated to a higher operating temperature than the engine using the heated coolant. The EHRS may also operate in a bypass mode during which exhaust heat is not directed to the engine or the transmission. A method of managing exhaust heat is also provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and device for transporting heat energy that is produced in a motor vehicle
A method and an apparatus for transporting thermal energy produced in a motor vehicle provides that the waste heat of an electronic component (42), such as a pulse-controlled inverter, be utilized to heat other vehicle parts, such as the internal combustion engine (12) or the passenger compartment. To that end, preferably two coolant circuits (10, 40) are provided, which can be coupled to one another or decoupled from another in order to control the flow of heat.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
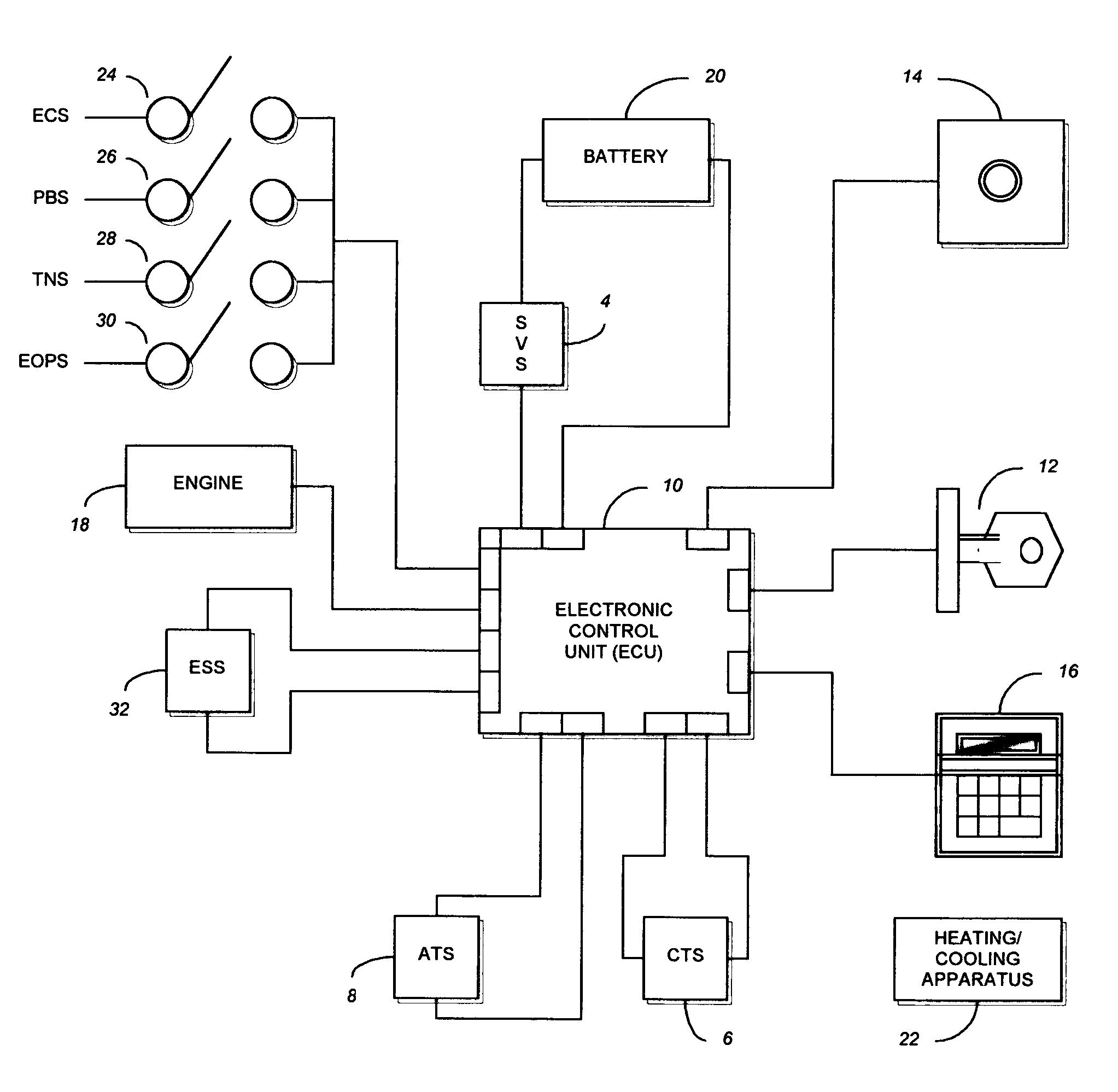
Control device for hybrid vehicles
InactiveUS6886649B2Timely maintenanceInhibition of inflowValve arrangementsElectrical controlSpool valveSolenoid valve
A control apparatus for a hybrid vehicle which includes an all cylinder deactivated operation execution flag F_ALCS for executing the all cylinders deactivated operation, when it is determined that the all cylinders deactivated operation is appropriate by the all cylinders deactivation standby flag F_ALCSSTB for determining the appropriateness of the all cylinders deactivated operation and the all cylinders deactivation release conditions realization flag F_F_ALCSSTP for determining the appropriateness of releasing the all cylinders deactivated operation, based on the all cylinders deactivation solenoid flag F_ALCSSOL for operating a spool valve, for determining an appropriateness of the operation of the solenoid valve, the all cylinder deactivation standby flag F_ALCSSTB, the all cylinder deactivation conditions realization flag F_ALCSSTP, the all cylinder deactivation solenoid flag F_ALCSSOL.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Cooling water circuit system
InactiveUS6082626AImprove the heating effectGood effectAir-treating devicesCoolant flow controlWater flowEngineering
In a cooling water circuit system, cooling water pumped by a mechanically-driven first water pump circulates in a cooling water circuit, and flows through a radiator and a heater core in parallel in the cooling water circuit. An electrically-driven second water pump is disposed in the cooling water circuit at a position where cooling water to be supplied to the radiator from the first water pump and cooling water to be supplied to the heater core from the first water pump flow together. A check valve is provided in the cooling water circuit in parallel with the second water pump so that cooling water flows in one way from a water suction side of the second water pump toward a discharge side thereof. Thus, when the second water pump is operated, a total amount of cooling water pumped by the first water pump and the second water pump can flow through the radiator and the heater core. As a result, the cooling water circuit system can improve engine-cooling effect in the summer, while improving heating effect of a passenger compartment in the summer.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Engine compartment temperature sensitive louvers
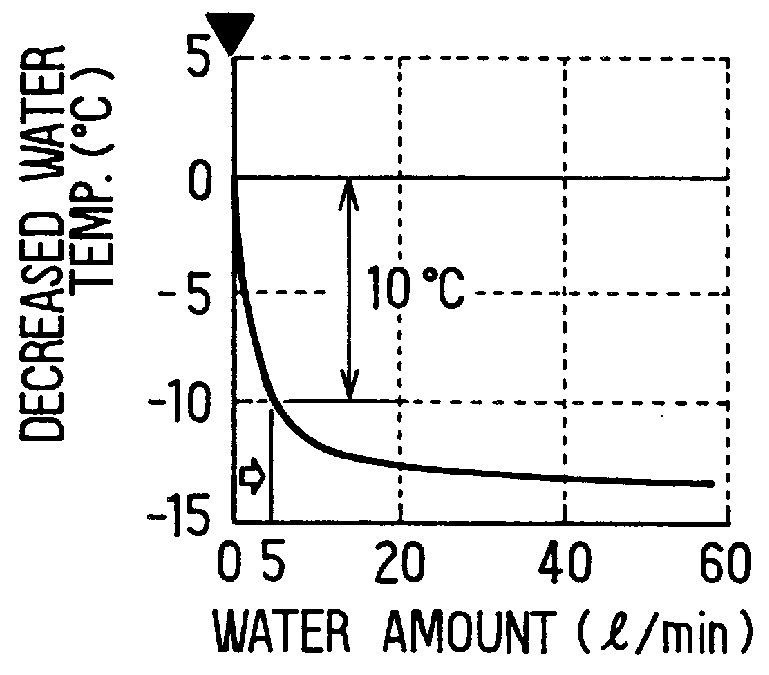
InactiveUS20070199751A1Increase magnetic susceptibilityIncrease heatCoolant flow controlAir coolingLouverTemperature sensitive
Owner:INT TRUCK INTPROP LLC
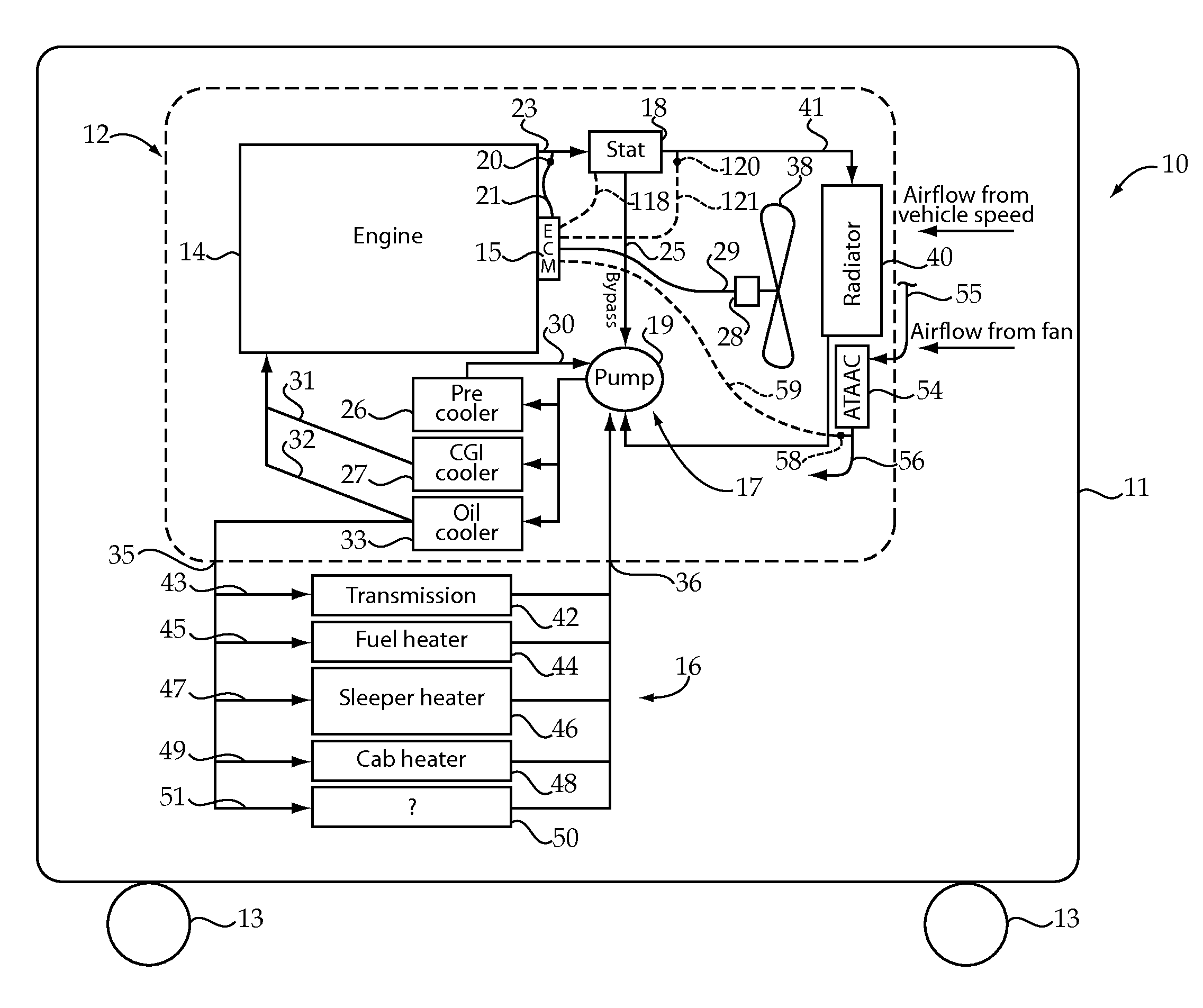
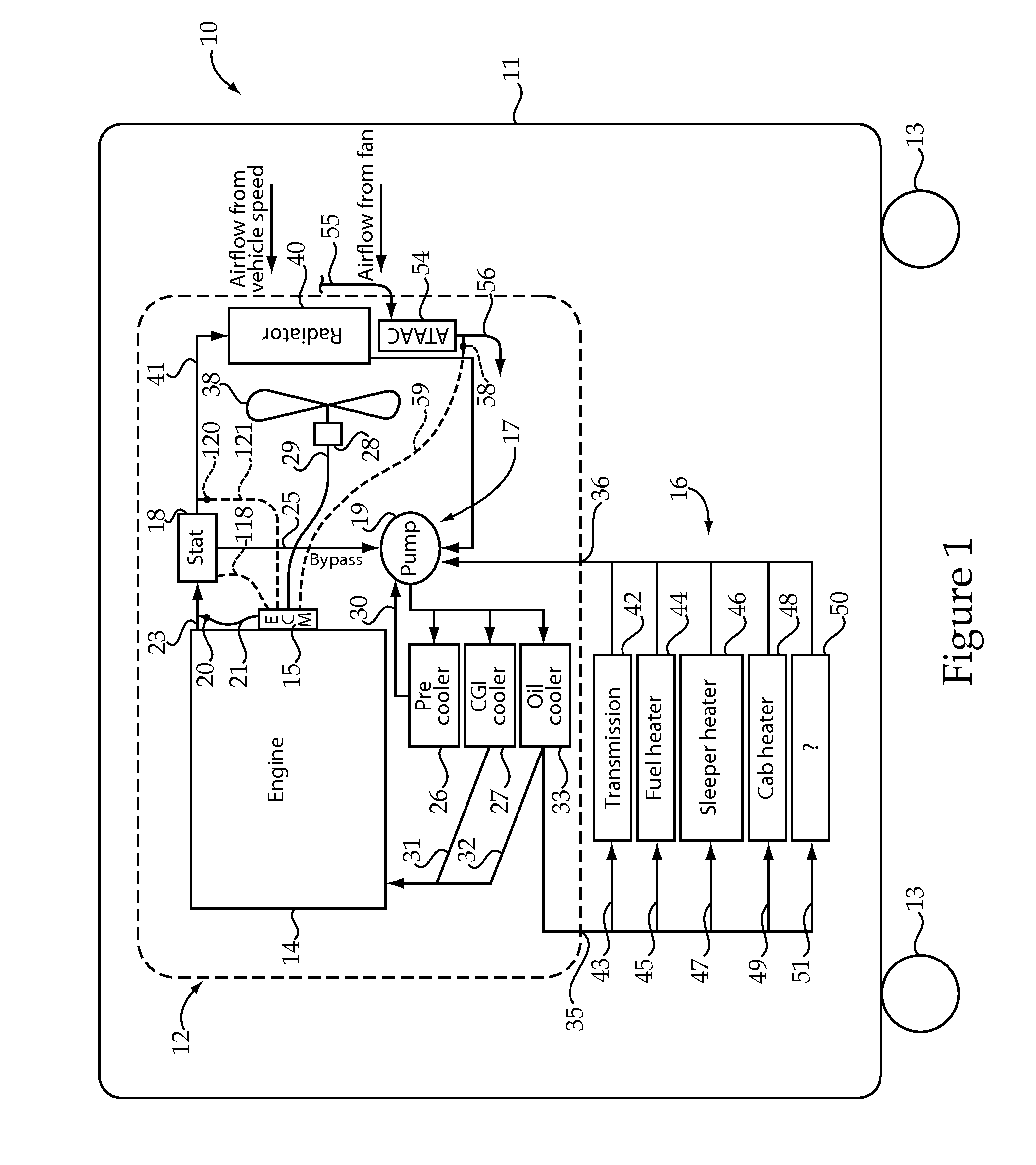
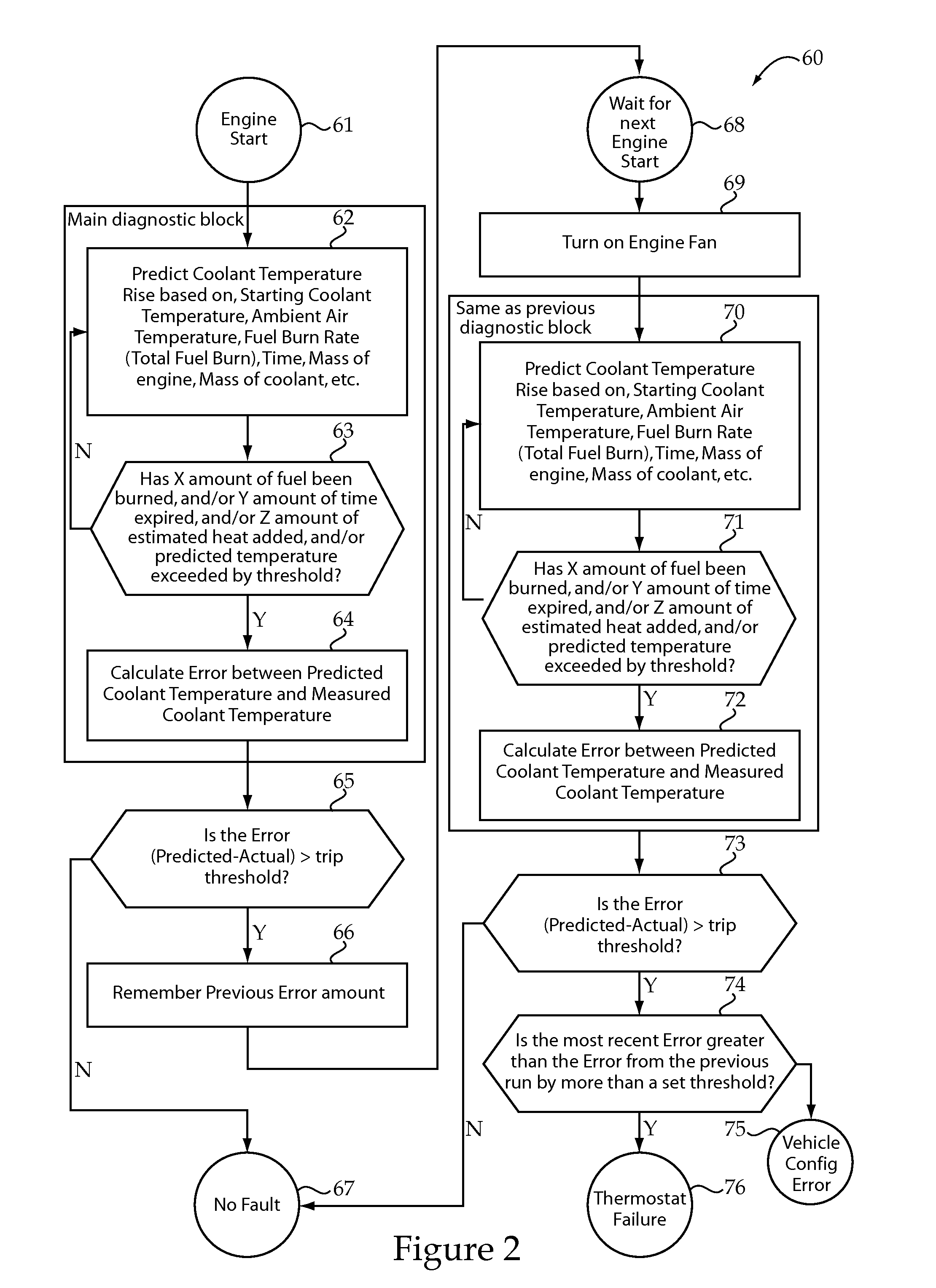
Engine cooling system onboard diagnostic strategy
An onboard cooling system diagnostic strategy utilizes at least one temperature sensor fluidly positioned between an electronically controlled engine and a thermostat. The diagnostic algorithm operates by monitoring coolant temperature during engine startup. By comparing the actual coolant temperature during engine start-up to a predicted coolant temperature that should occur if no cooling system error is present, a cooling system fault condition may be identified. If a cooling system fault is detected, the diagnostic logic may activate the engine cooling fan or intrusively open an electrically controlled thermostat while monitoring the coolant temperature response to the intrusive action. If there is a substantial change in coolant temperature responsive to the intrusive action, this phenomenon can be utilized to correctly distinguish between a thermostat failure and a vehicle configuration error corresponding to an overcooled vehicle. The present disclosure also can utilize a similar strategy to diagnose problems associated with other vehicle fluid coolers that exchange heat with ambient air moved by a circulation fan.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
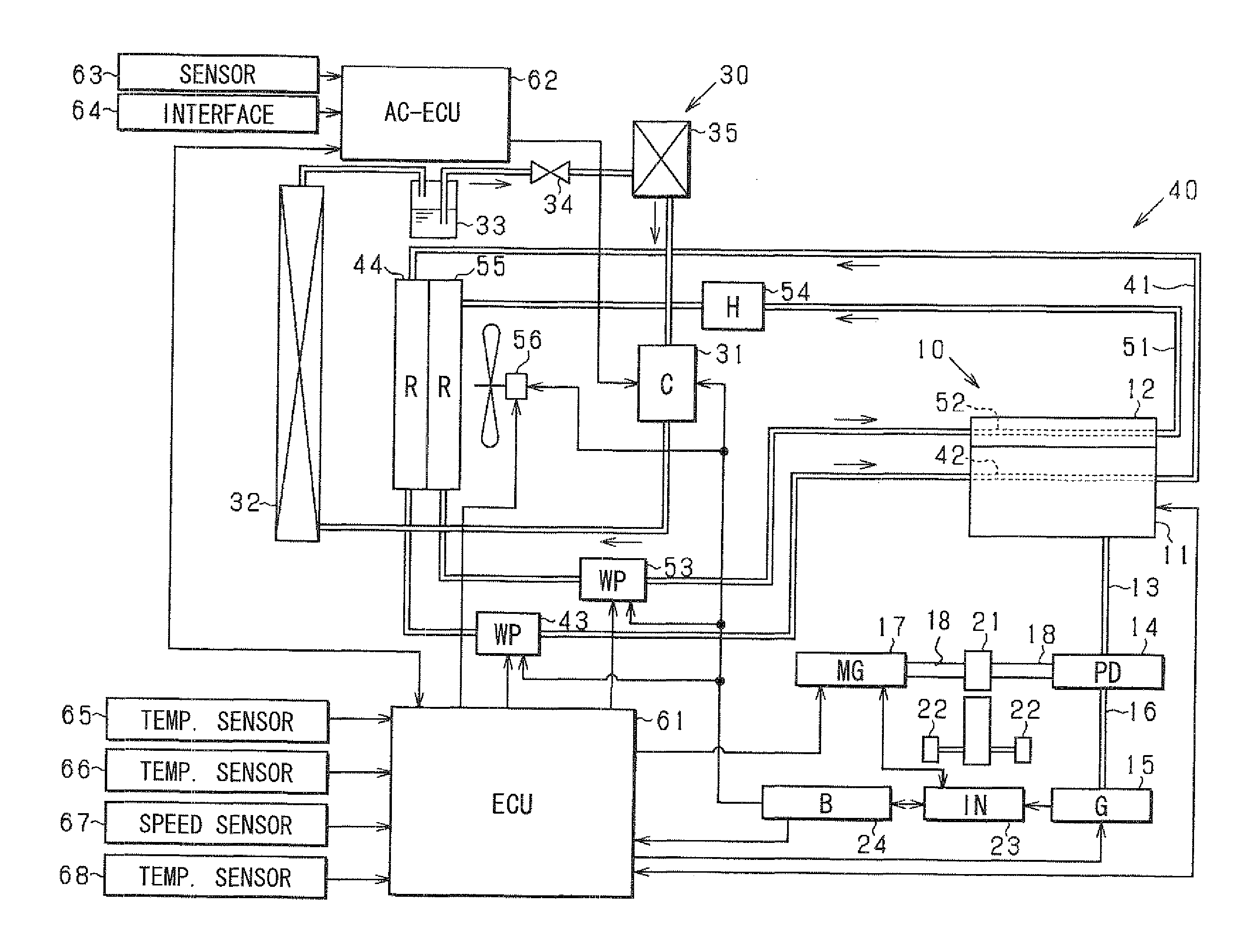
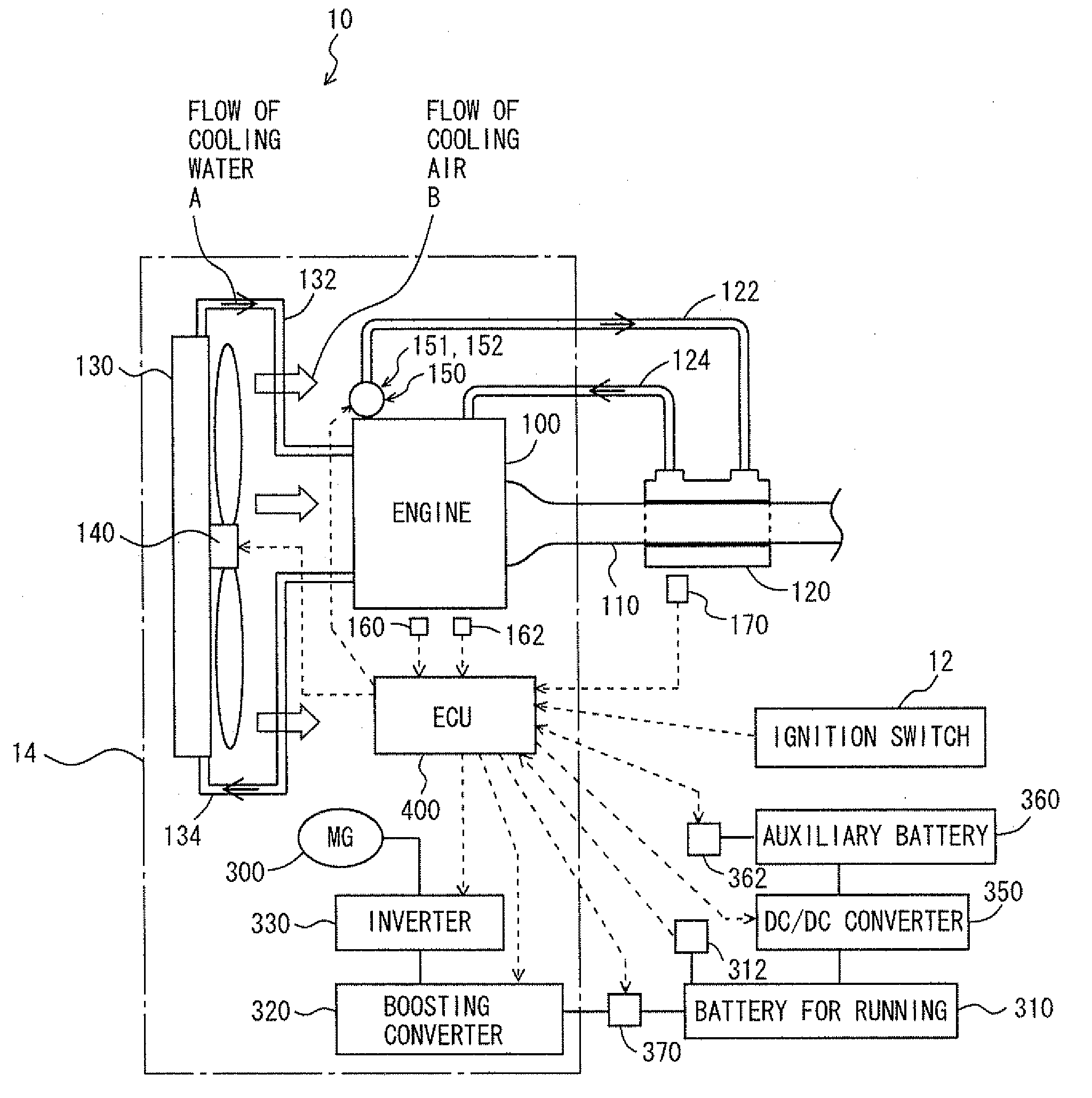
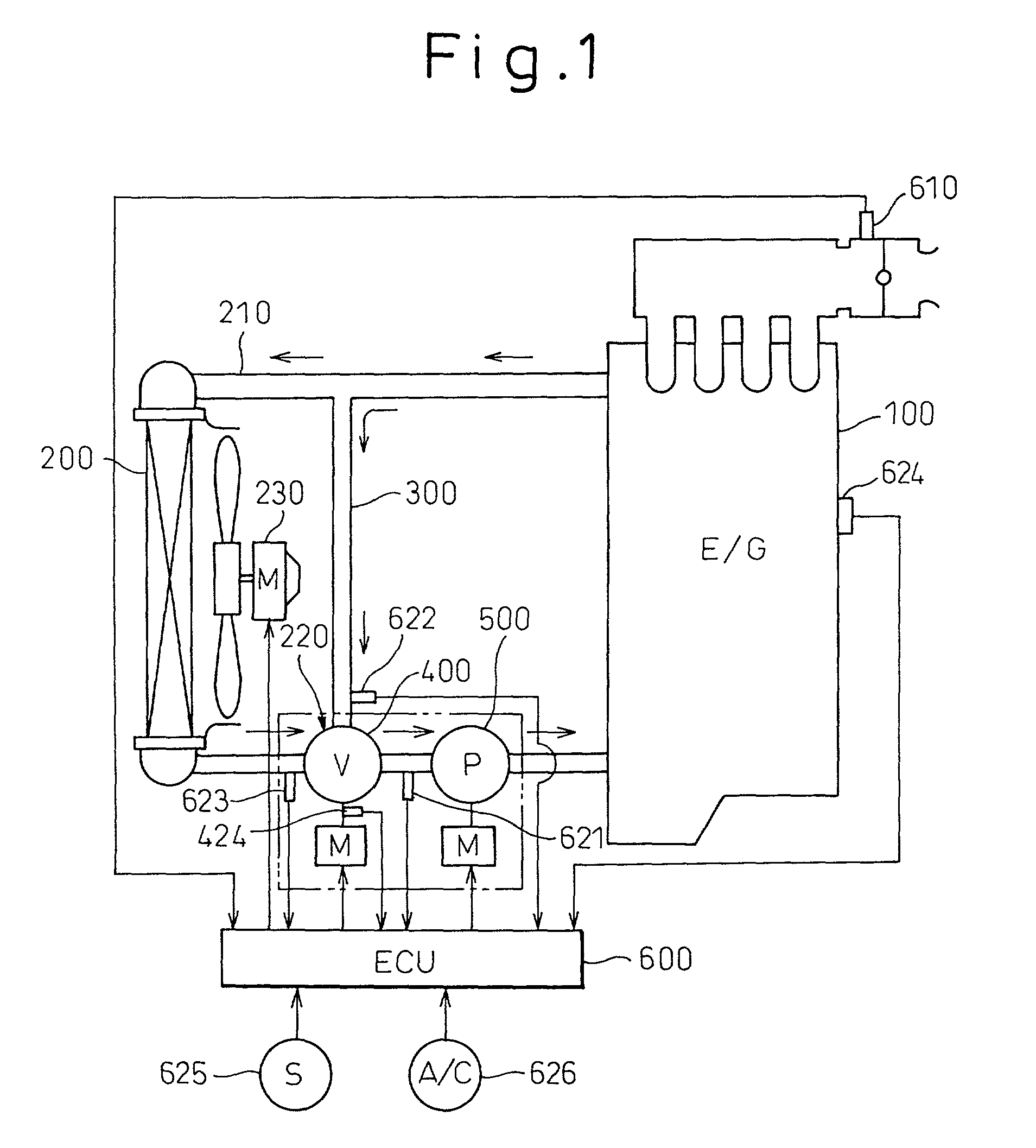
Vehicle cooling controller and cooling control method
ActiveUS20100236502A1Improve starting characteristicsFavorably warmedCoolant flow controlInternal combustion piston enginesCoolantEngine room
A drive component for driving an electric water pump for causing engine coolant to flow is mounted in an engine compartment. When the ignition is off and the temperature of a exhaust heat recovery device is above a temperature, an ECU estimates a peak temperature in the engine compartment after the stop of the engine. When the peak temperature is above a temperature, the ECU stops the engine and drives the electric water pump and an electric fan for cooling the drive component for driving the electric water pump.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
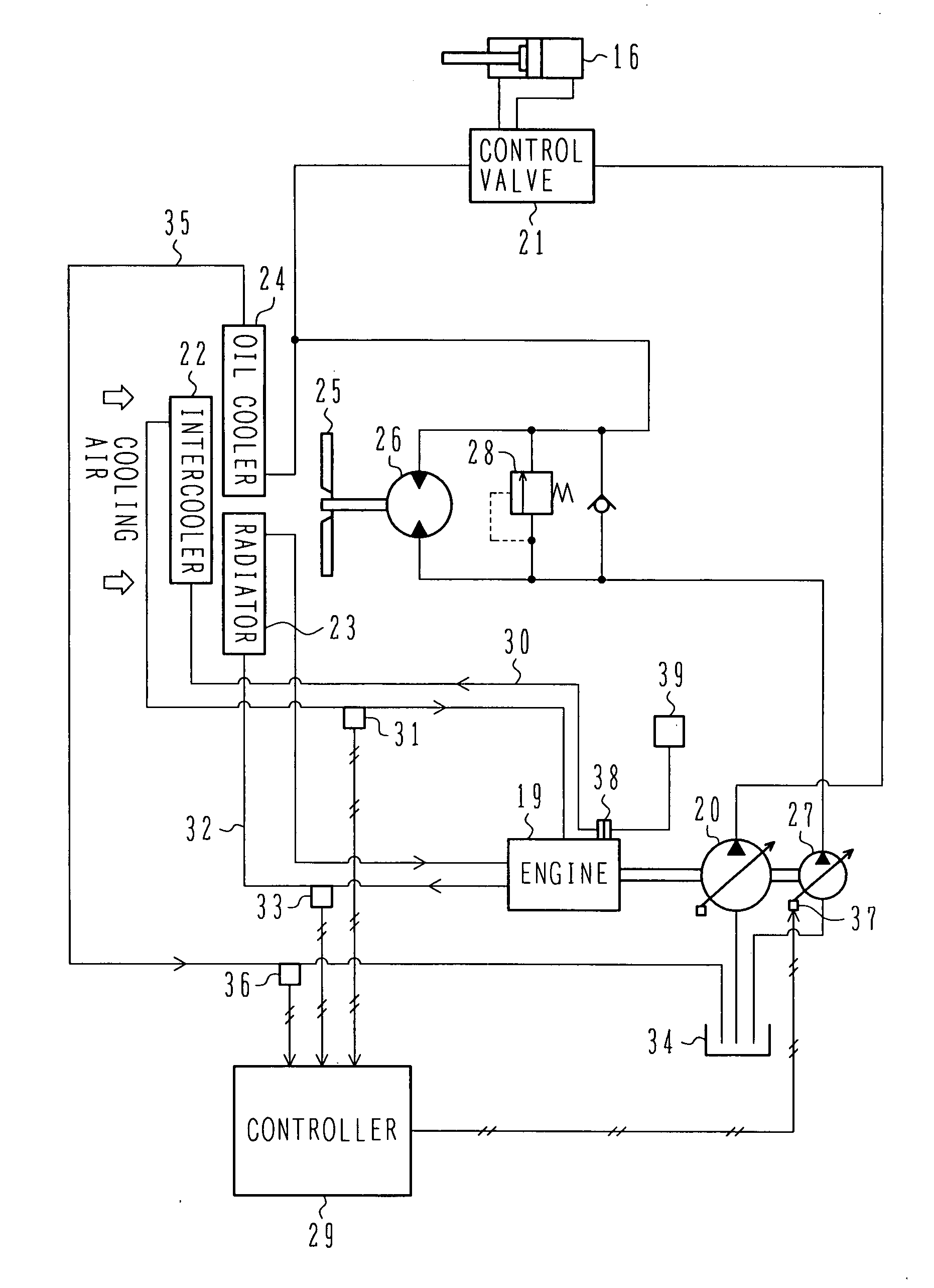
Cooling System for Construction Machine
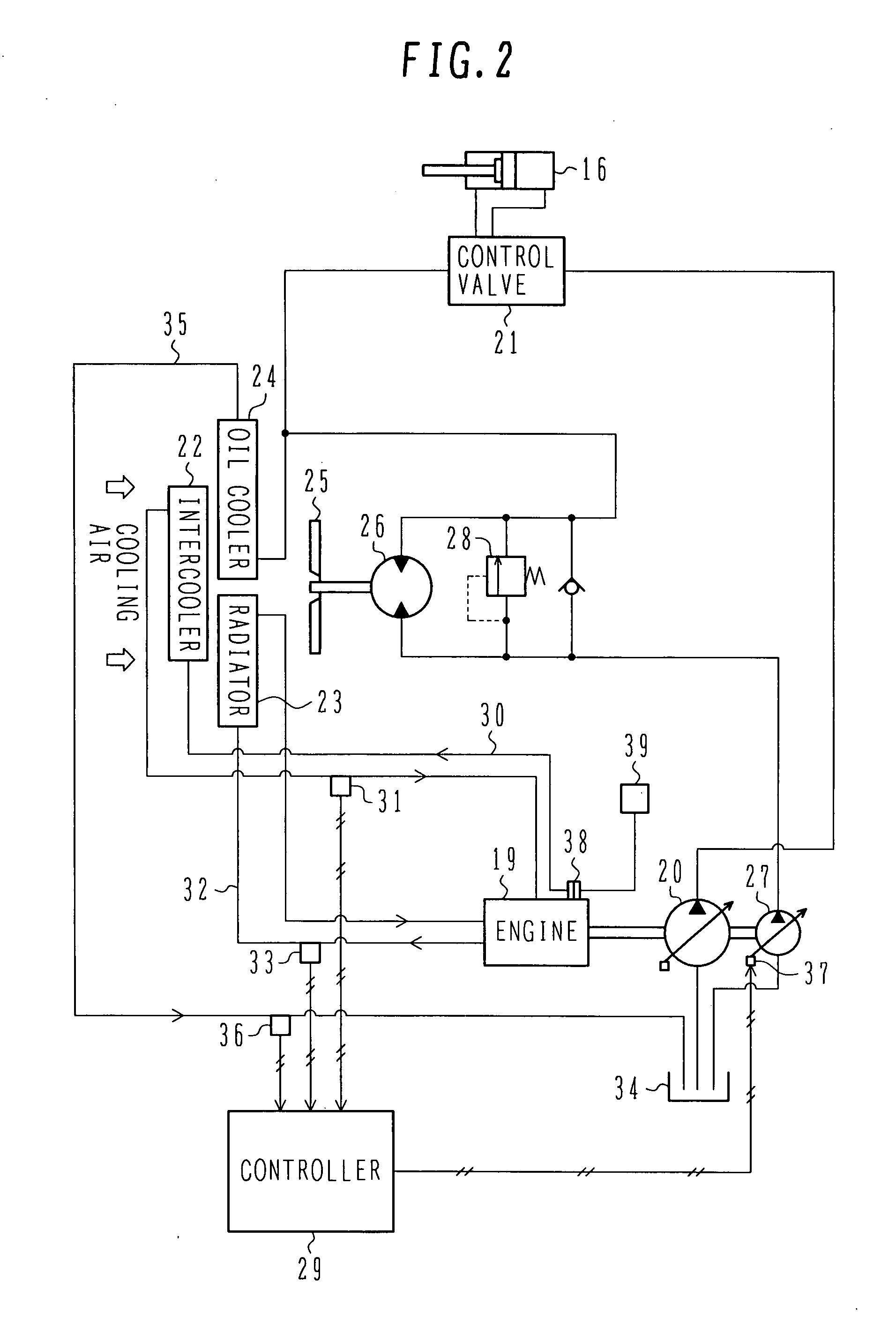
ActiveUS20090217655A1Reduce noiseReliably producedFluid couplingsCoolant flow controlHydraulic motorControl signal
A cooling system for a construction machine, which can reduce noise of a cooling fan and can reliably produce cooling air at a required flow rate.The cooling system comprises a cooling fan 25 for producing cooling air introduced to an intercooler 22, a radiator 23 and an oil cooler 24, a fan hydraulic motor 26 for driving the cooling fan 25, a fan hydraulic pump 27 for delivering a hydraulic fluid to the fan hydraulic motor 26, an air temperature sensor 31 for detecting an air temperature T1 at an outlet of the intercooler 22, a cooling water temperature sensor 33 for detecting a temperature T2 of cooling water for the radiator 23, a working oil temperature sensor 36 for detecting a temperature T3 of working oil for the oil cooler 24, and a controller 29 for outputting a control signal corresponding to a maximum value among calculation values N1, N2 and N3 of cooling fan rotation speed, which correspond respectively to detected values T1, T2 and T3 from the air temperature sensor 31, the cooling water temperature sensor 33 and the working oil temperature sensor 36.
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
Internal combustion engine for a motor vehicle
InactiveUS7237513B2Heating fastLow viscosityLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlMobile vehicleExternal combustion engine
In an internal combustion engine for a motor vehicle, having a cylinder head and an engine block, each with a coolant inlet port and a coolant outlet port which is common to the cylinder head the engine block, a main coolant pump having an intake side connected to the coolant outlet port and a pressure side connected to a first control valve via which coolant reaches the inlet port of the cylinder head and the inlet port of the engine block depending on the temperature of the coolant, and to a method for operating such an internal combustion engine, wherein the main coolant pump is selectively actuated to pump the coolant through at least one of the cylinder head and the engine block or is shut down depending on the engine operating state.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
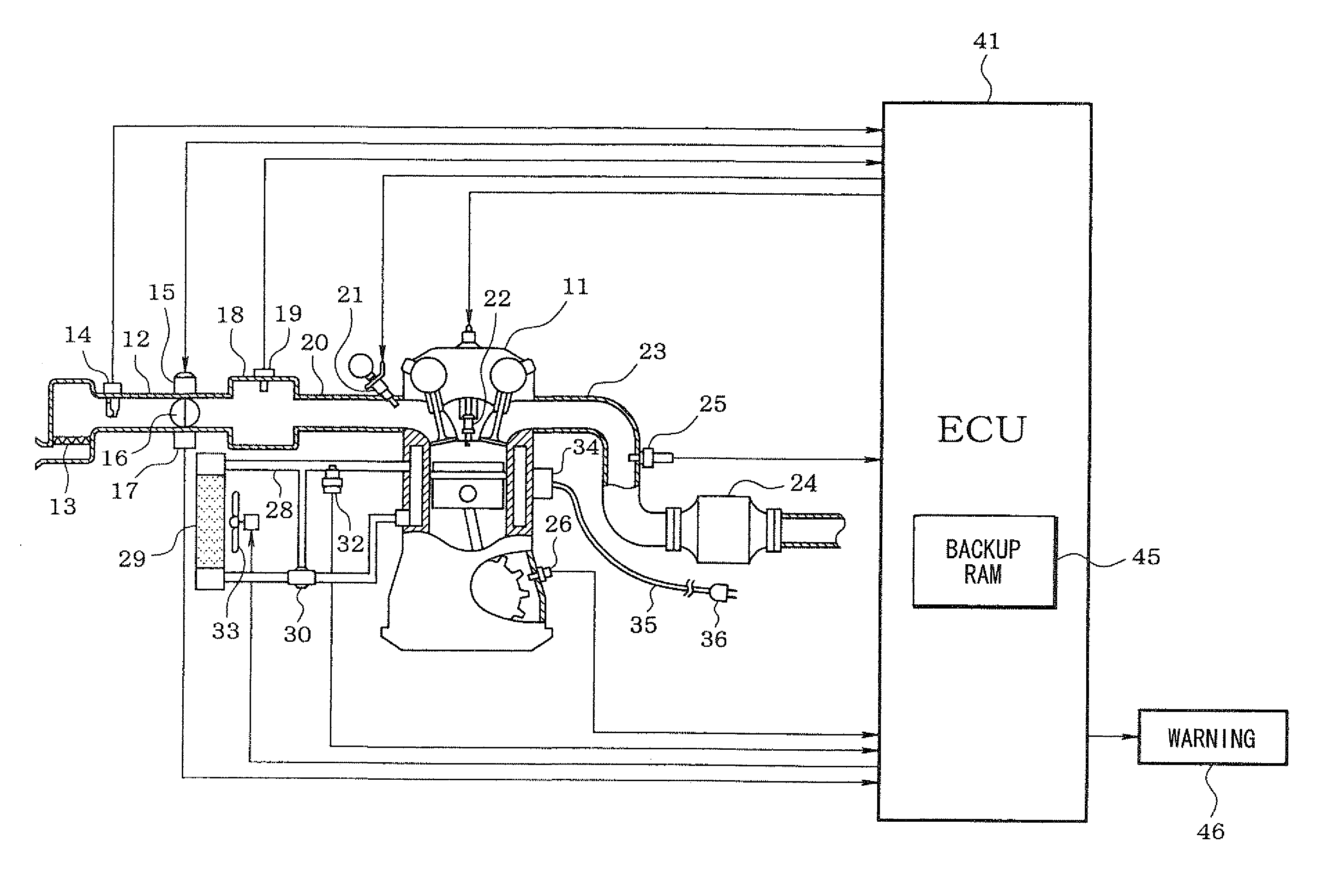
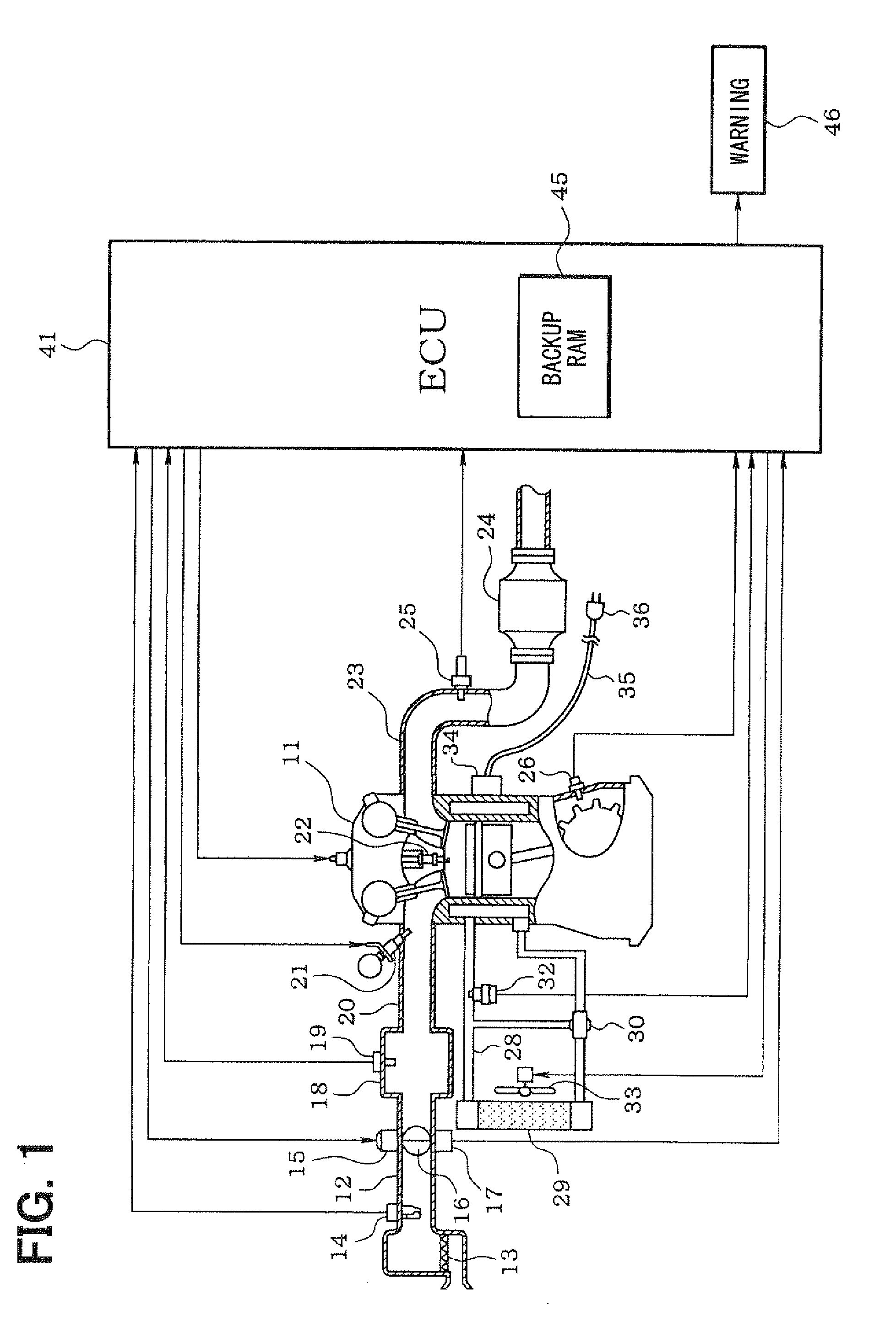
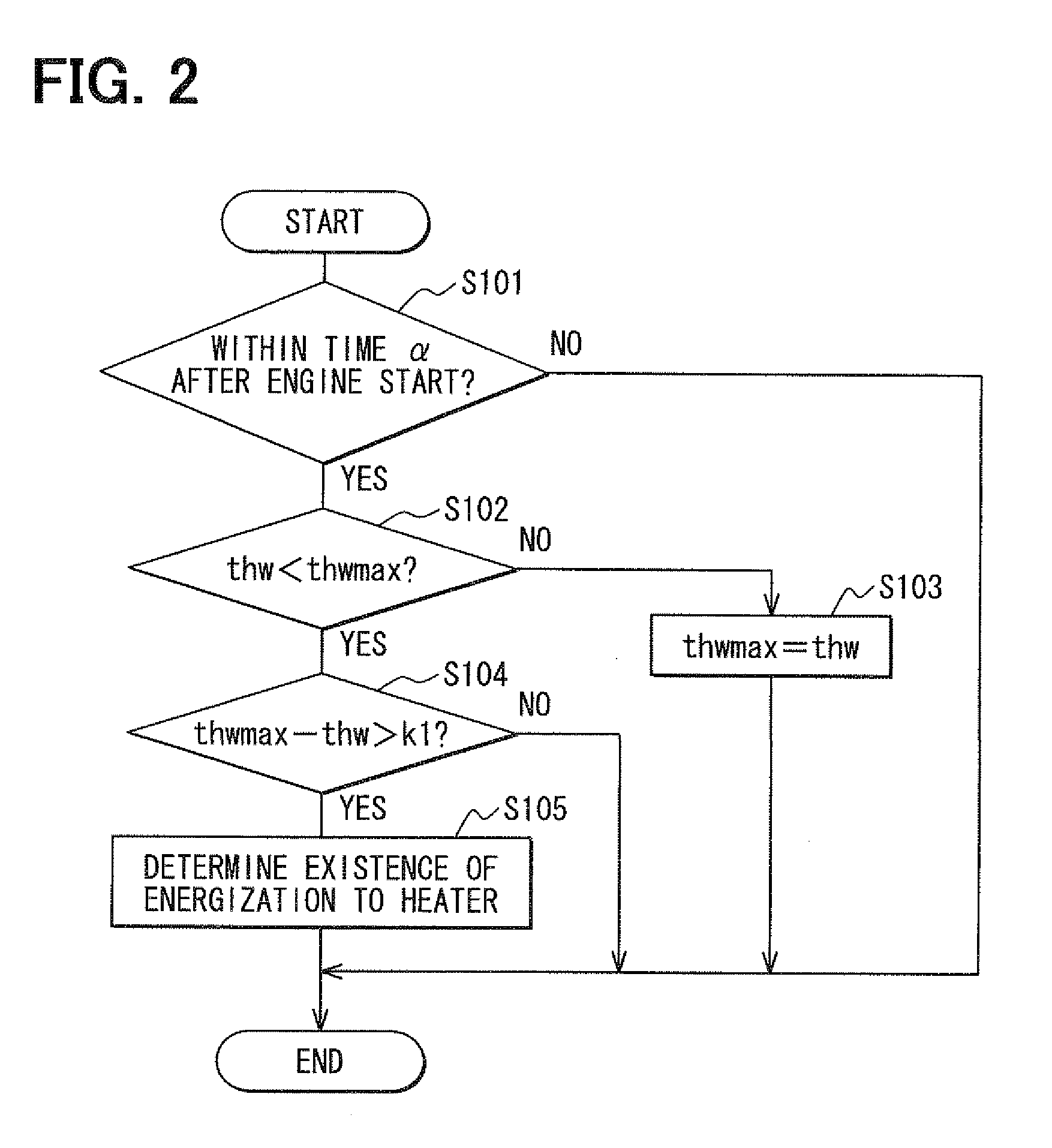
Controller, cooling system abnormality diagnosis device and block heater determination device of internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20080300774A1Improve accuracyEasy to adaptAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A plug of a power cord of a block heater which is mounted to a cylinder block of an engine, is connected to a household power receptacle to energize the block heater during an engine stoppage in cold climate. Thus, an engine coolant is kept warm to prevent freeze. Existence / nonexistence of the energization to the block heater during the engine stoppage is determined based on a behavior of coolant temperature or a behavior of engine rotation speed immediately after an engine start. If it is determined that the energization to the block heater exists, abnormality diagnosis of a cooling system is prohibited or a condition for the abnormality diagnosis is corrected and estimation coolant temperature is corrected.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Cooling device for liquid-cooled type internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20010020452A1Coolant flow controlMeasurement deviceExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
In a cooling device for an engine, having a motor-driven pump and a flow rate control valve, to obtain a predetermined discharge flow rate (circulating coolant amount) from the pump 500, a pump duty is minimized while maintaining a water flow resistance as low as possible (maintaining a valve opening degree theta as large as possible). Thereby, a value of an electric current flowing through the pump 500 becomes smaller to decrease the energy consumption (power consumption).
Owner:DENSO CORP
System for monitoring the coolant level and the temperature of an internal combustion engine
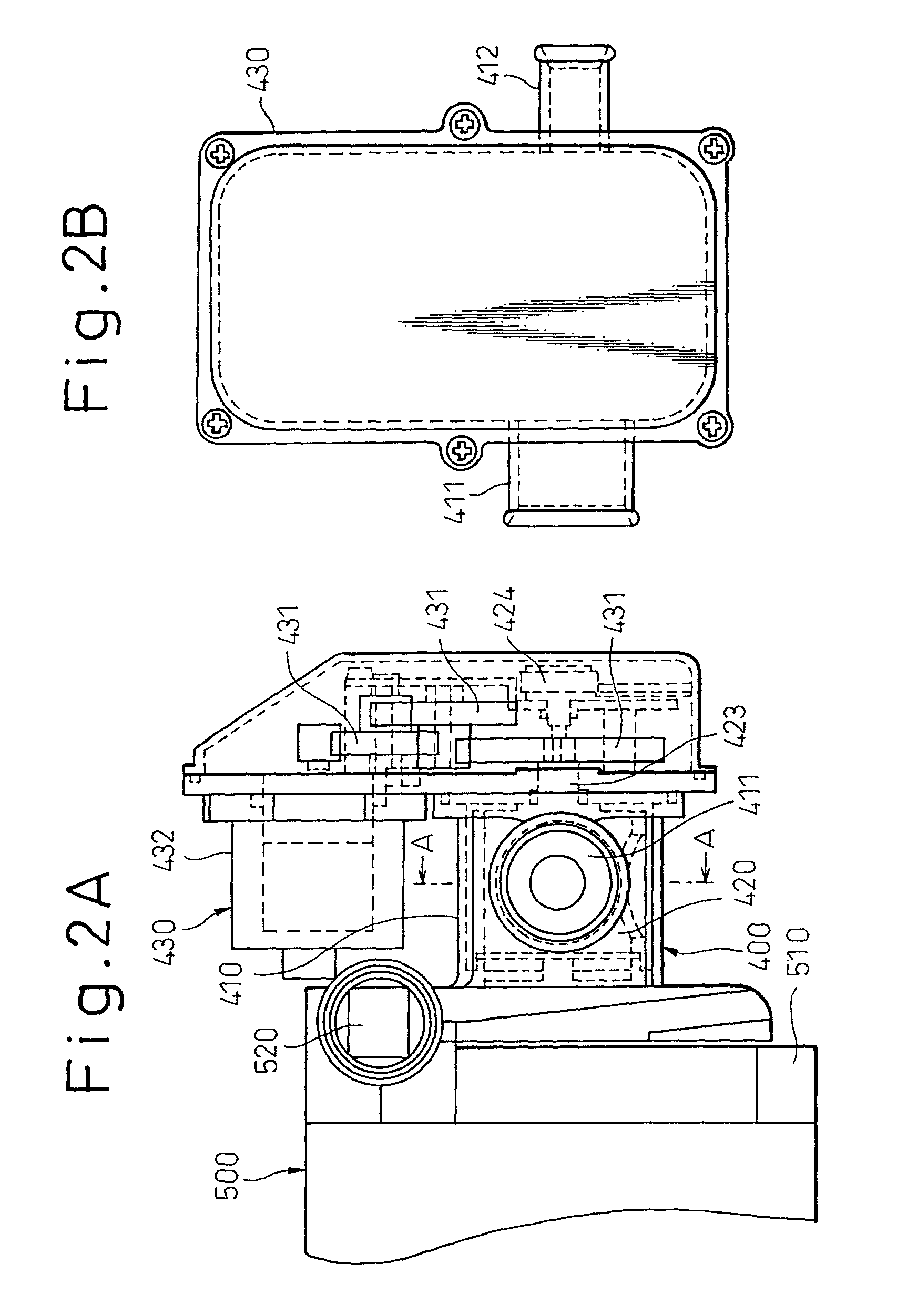
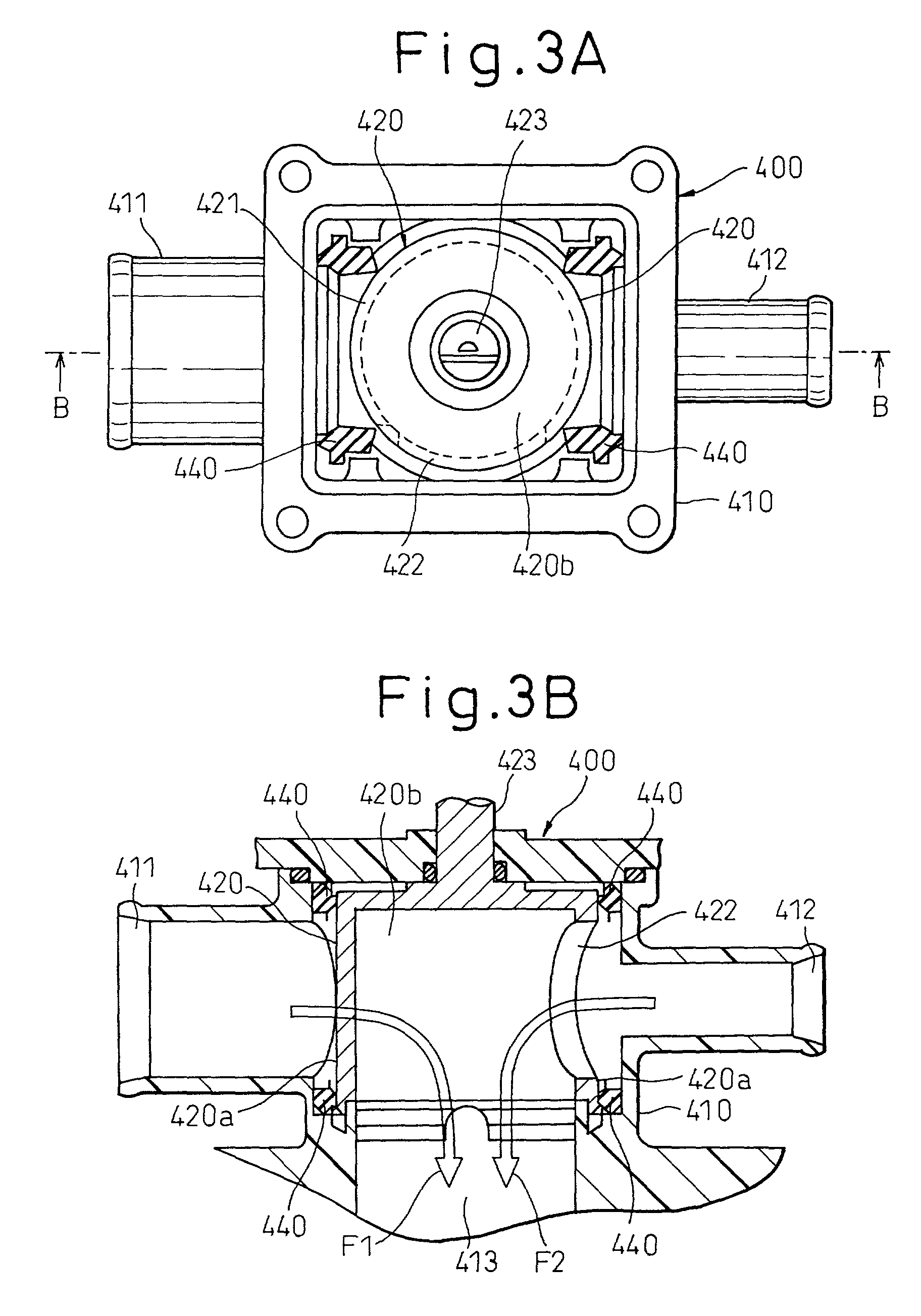
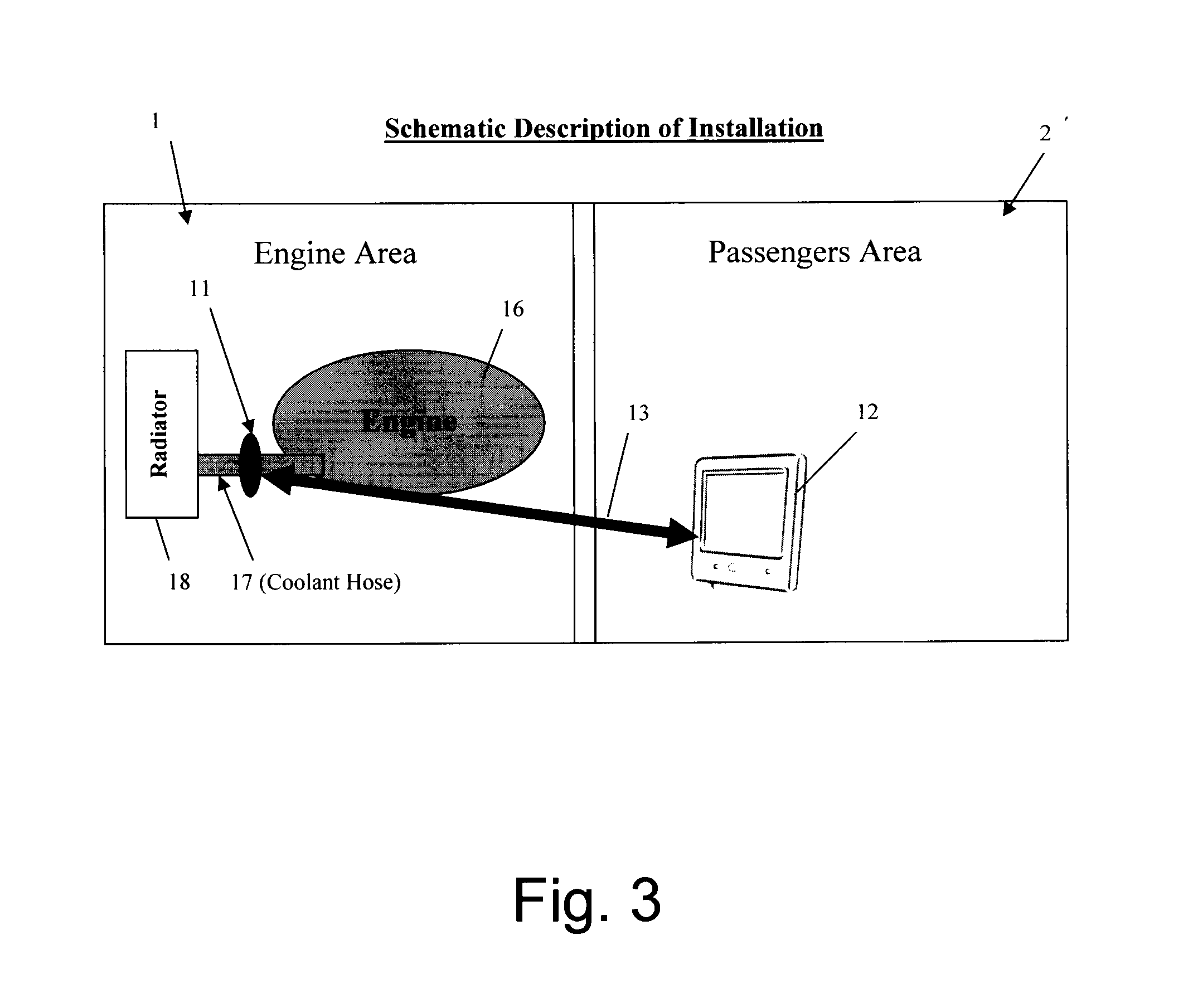
InactiveUS20130103284A1Analogue computers for vehiclesFail safeUltrasonic sensorInternal combustion engine
The present invention relates to a non-invasive engine guard system, which comprises: a) at least one ultrasonic sensor for providing data representing the cooling fluid level in a coolant hose, wherein said coolant hose connects between said engine and a radiator; b) a temperature sensor for monitoring” whether the temperature of said engine or said coolant hose is not above a predetermined level; c) attaching means for externally attaching said ultrasonic sensor and said temperature sensor on top of said coolant hose; d) an electronic unit for controlling said system, processing said data, and for generating information related to the temperature and the cooling fluid level in said coolant hose.
Owner:EL SOL TECH
Control system for internal combustion engine with catalyst for purifying exhaust gas
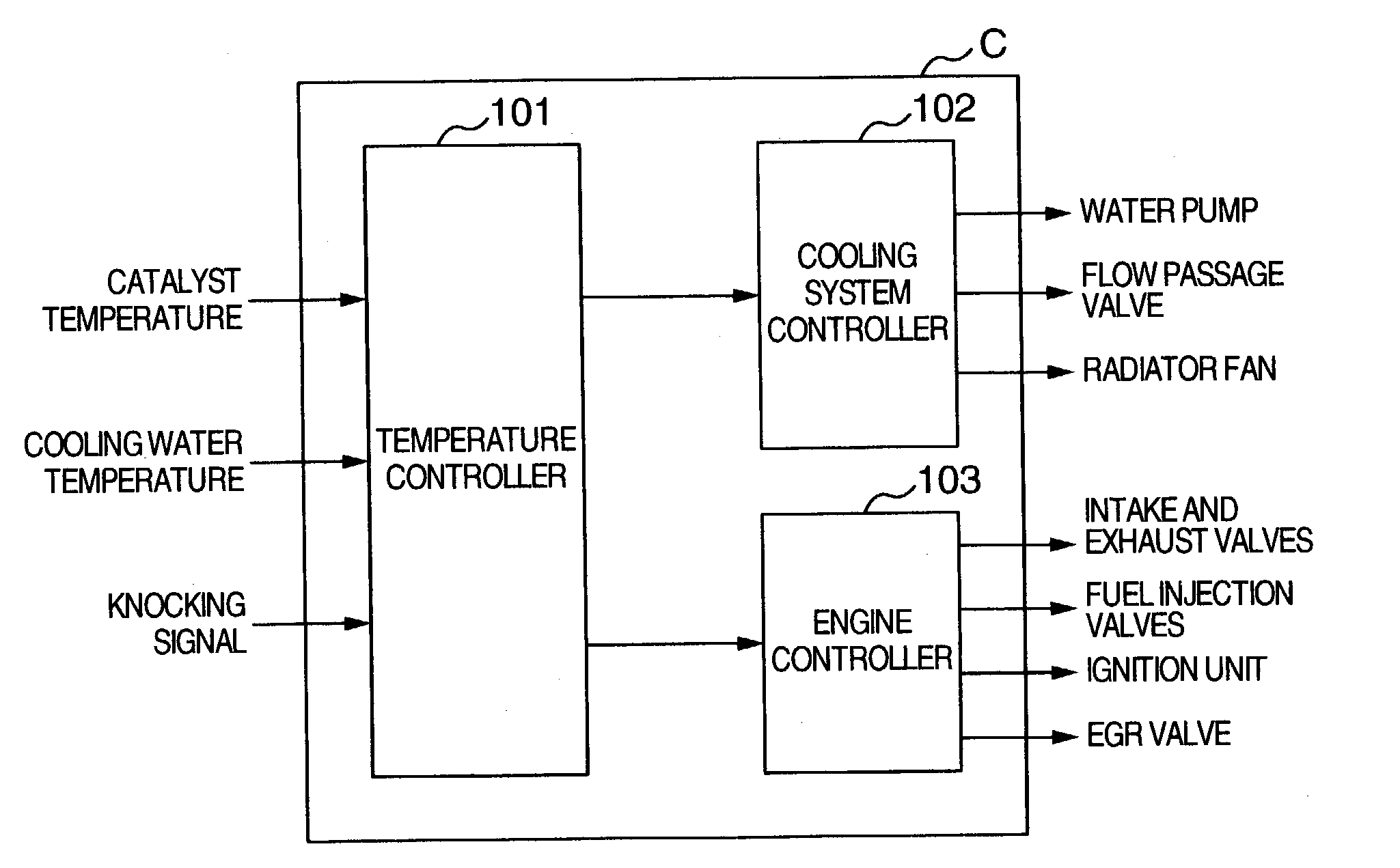
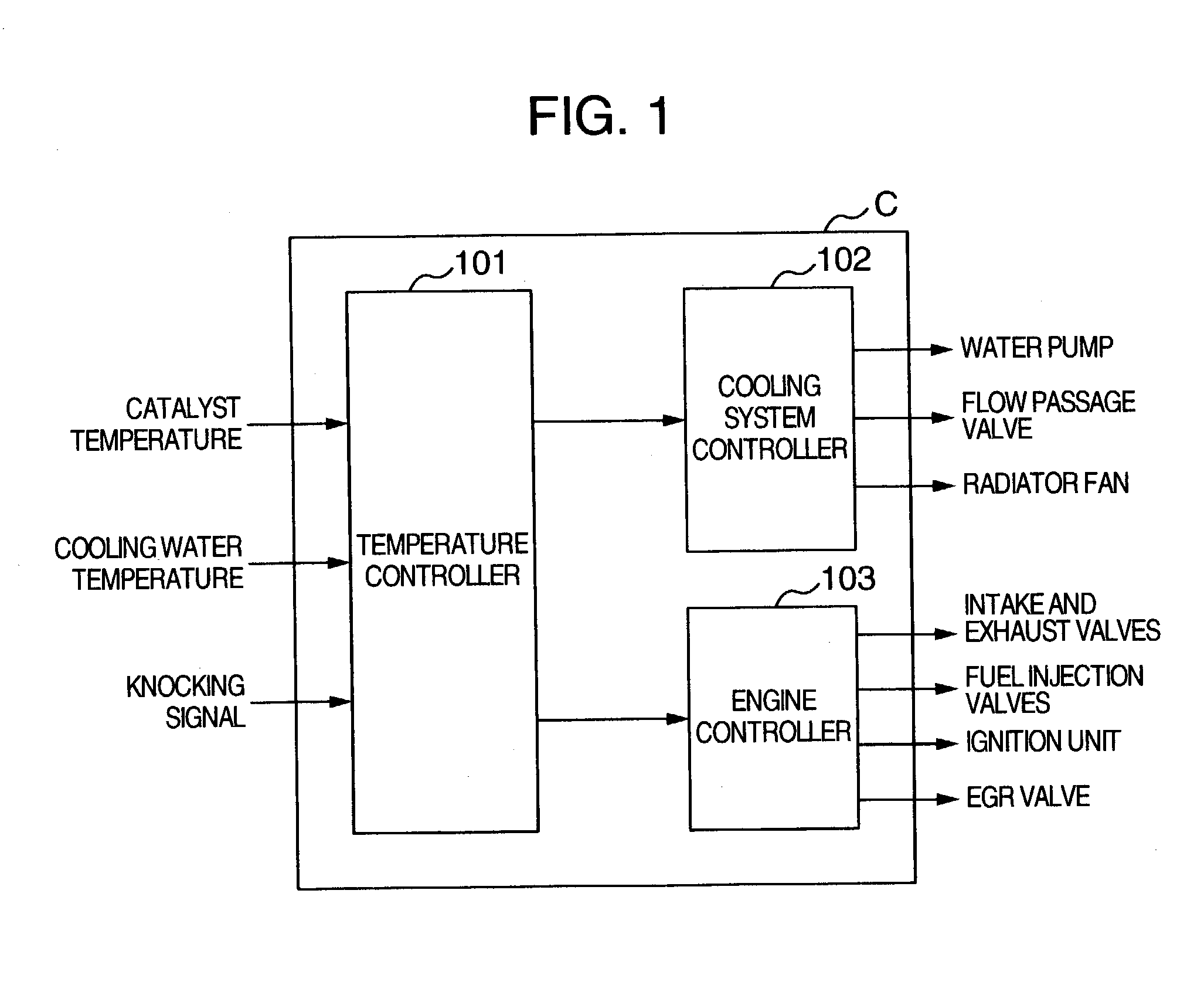
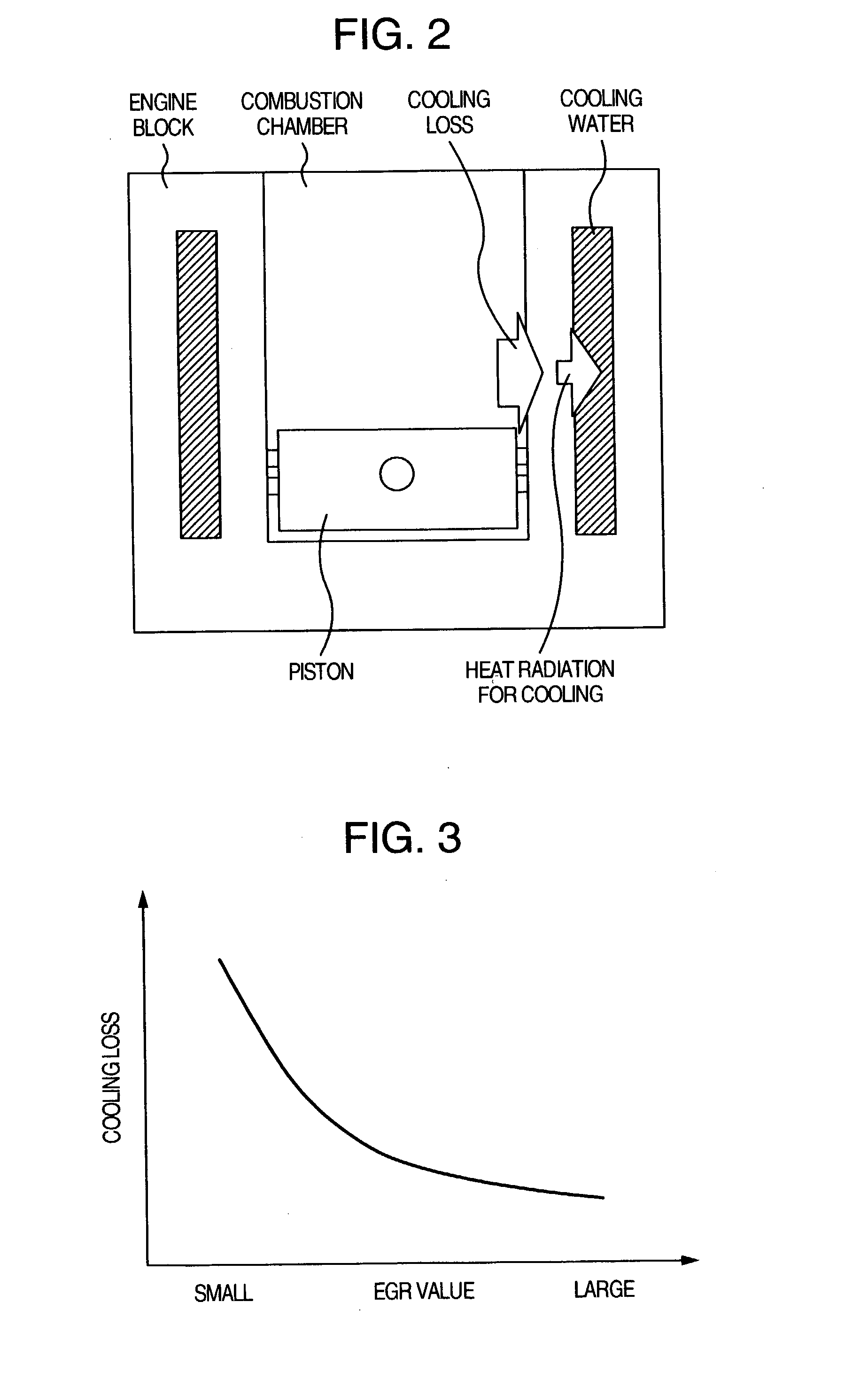
There is provided a control system for an internal combustion engine, which aim for early warm-up of catalyst and the engine in order to control a cooling loss and a heat radiation for cooling in such a way that the warm-up of the catalyst is carried out prior to the warm-up of the engine. That is, if the temperature of the catalyst is not greater than an activation temperature, there is carried out at least one of (1) retardation control of the ignition timing, (2) stopping control of a water pump for engine cooling water, (3) lowering control of the flow rate of the cooling water, but if the temperature of the catalyst is higher than the activation temperature, there is carried out at least one of control of the water pump in accordance with a temperature of the cooling water and control of retardation of the ignition timing, until the temperature of the cooling water reaches a warm-up temperature which is a normal operation temperature of the engine.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Bi-directional automotive cooling fan
InactiveUS7121368B2Adequate engine coolingMaximize air flow dynamicCoolant flow controlPump componentsCylinder blockTraffic conditions
The instant invention pertains to a road vehicle's axial flow cooling fan which normally draws cooling air from in front of the vehicle and blows it into the engine bay. The instant invention includes a control circuit for the fan motor that provides variable speed and bi-directional, or reverse and normal, fan operation. Reverse fan operation blows air from the engine bay through the radiator and out the front of the vehicle, and normal fan operation blows into the engine bay. Two input sensors feed the control circuit, one for road speed of the vehicle and other for engine temperature. When the engine is below its operating temperature and the vehicle is moving, the fan is made to blows in reverse at a speed proportional to road speed so as to block cold ram air from entering and blasting onto a warming engine. This speeds engine warm-up to reduce emissions, improve fuel economy, and speed windshield defogging. The fan may also be made to blow in reverse when the engine is cold and the vehicle is stopped, in order that exhaust-heated air from the exhaust manifold behind the engine, may be drawn forward over the engine block to speed its warming. When the engine is above its operating temperature and the vehicle is idling or moving slowly, as in traffic, then the control circuit causes the fan to again blow in reverse cooling both the radiator and the engine bay components and preventing hot, noxious fumes from vehicles in front from being drawn into the vehicle. Blowing in reverse in traffic conditions also eliminates hot air looping back to the front of the car and drawn in through the radiator. As vehicle speed increases, the fan is made to revert to normal operation augmenting ram air flow through the radiator.
Owner:MACKELVIE WINSTON
Vehicle Rooftop Engine Cooling System and Method
InactiveUS20080053129A1Improve efficiencyReduce electricity loadAir-treating devicesCoolant flow controlArea networkControl signal
An vehicle rooftop cooling system includes a radiator located outside of the engine compartment of a vehicle, the radiator having a liquid coolant inside the radiator; a fan coupled to the radiator and configured to extract hot air from the radiator; a first sensor proximate to the radiator configured to measure coolant temperature of the coolant in the radiator; and a controller communicably coupled to the first sensor, the controller configured to receive inputs from the first sensor, to make determinations based on the received inputs, and to communicate control signals across a controller area network (CAN) in response to said determinations, wherein the controller is further configured to communicate a first control signal to cool the liquid coolant upon determining that the first sensor has measured temperature above a threshold.
Owner:SHEPPARD MULLIN RICHTER & HAMPTON
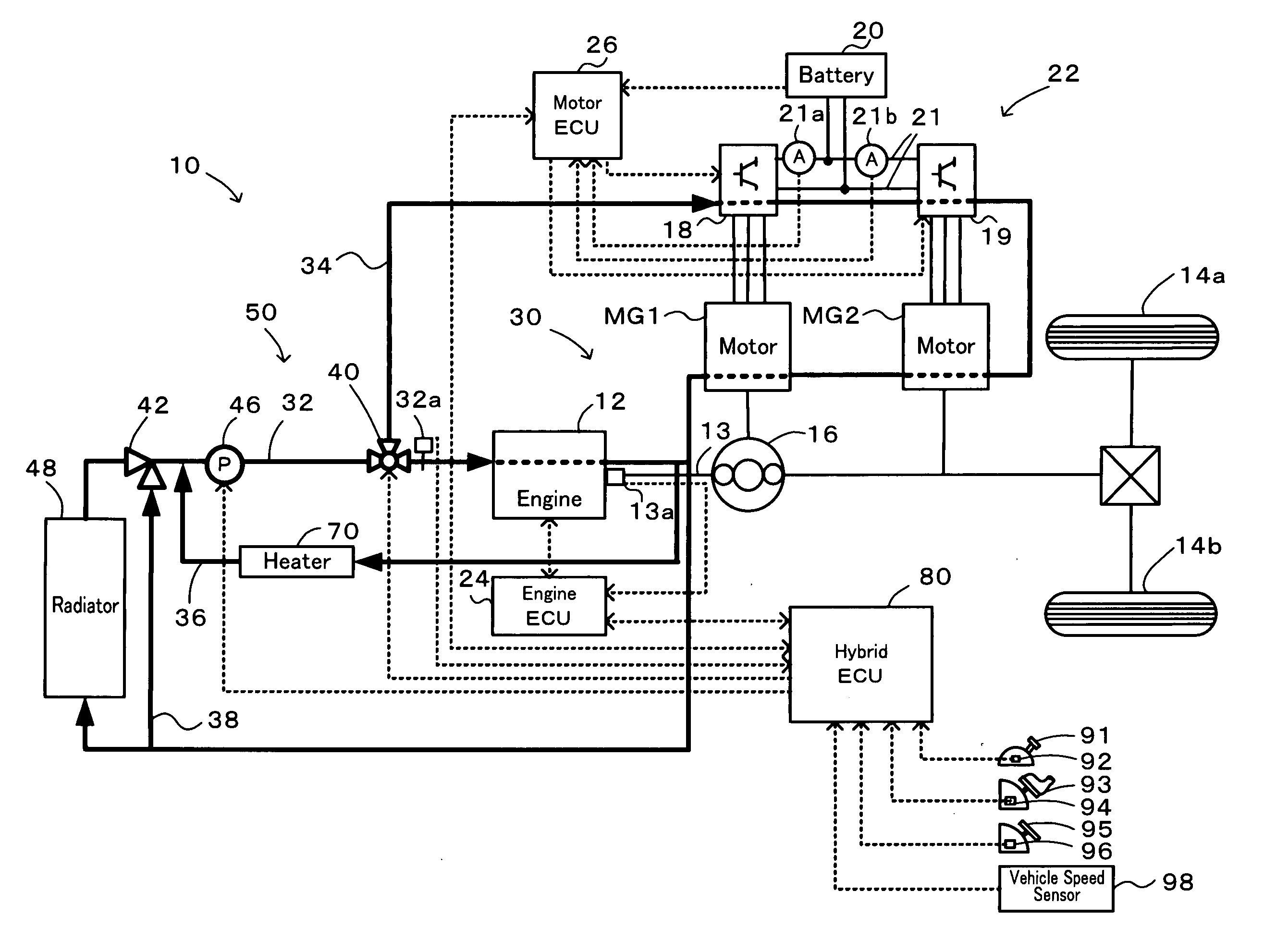
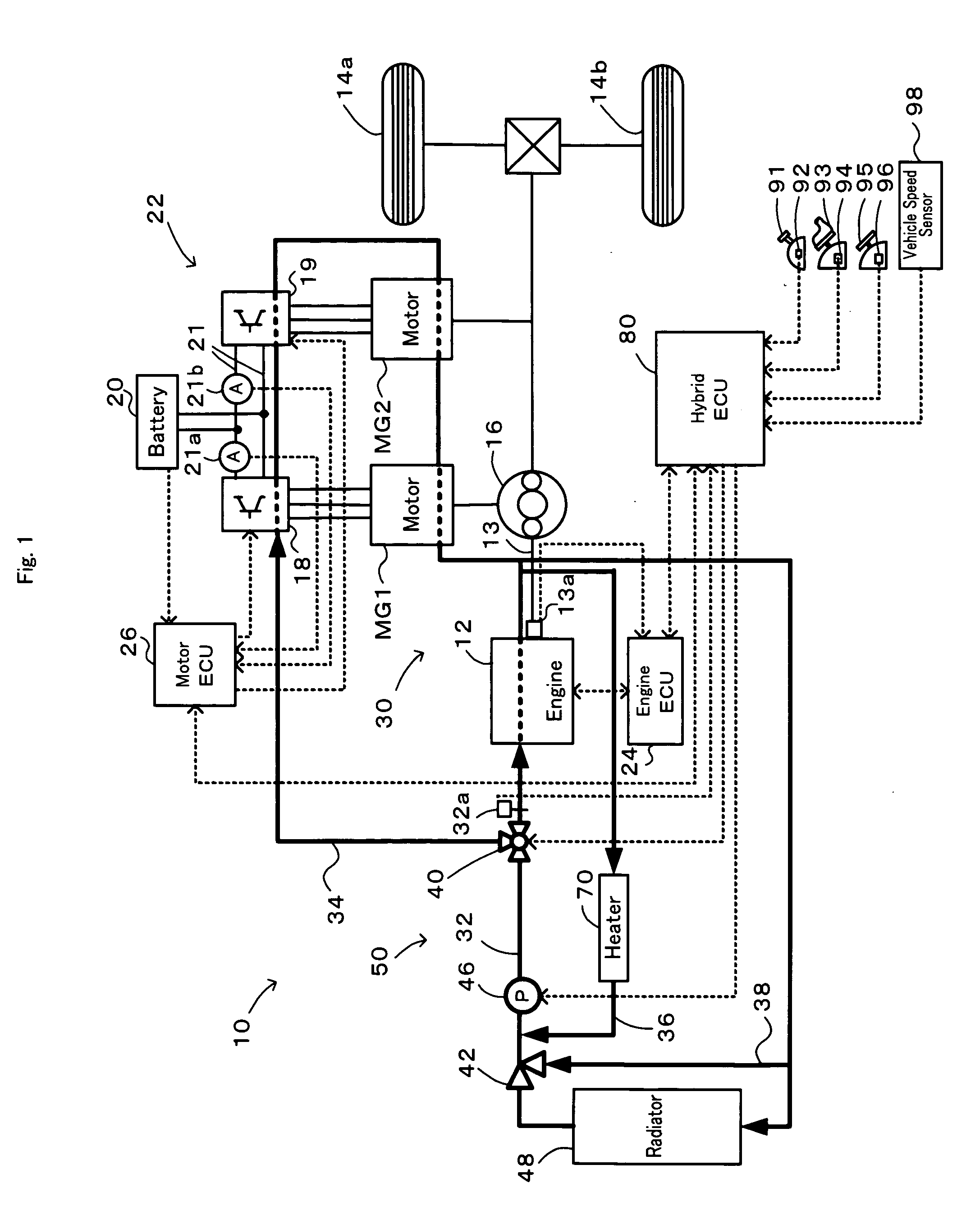
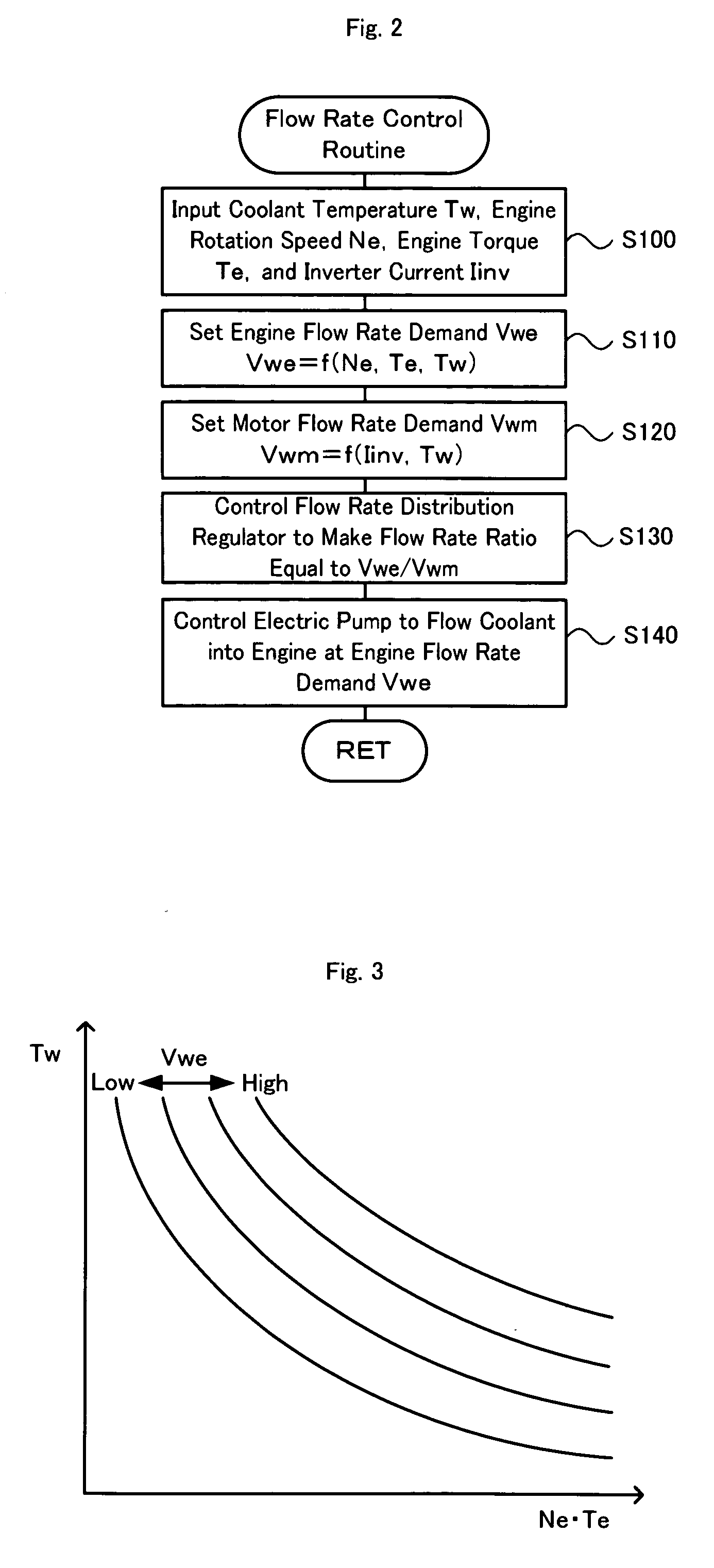
Cooling System, Control Method of Cooling System, and Vehicle Equipped With Cooling System
InactiveUS20090139686A1Reduce power consumptionIncrease heat radiationHybrid vehiclesAir-treating devicesCoolant flowEngineering
A cooling system is equipped with a circulation flow path arranged to flow a coolant into an engine, a motor drive system flow path branched off from the circulation flow path and arranged to flow the coolant into a motor drive system, a flow rate distribution regulator provided at a junction of the circulation flow path and the motor drive system flow path, and an electric pump configured to pressure-feed the coolant through the circulation flow path. In the cooling system, the procedure of flow rate control sets an engine flow rate demand Vwe based on a rotation speed Ne and a torque te of the engine and a coolant temperature Te (step S110), while setting a motor flow rate demand Vwm based on an inverter current Iinv of the motor drive system and the coolant temperature Te (step S120). The flow rate distribution regulator and the electric pump are then controlled to make a flow rate of the coolant flowed into the engine and a flow rate of the coolant flowed into motors and inverters included in the motor drive system respectively equal to the set engine flow rate demand Vwe and the set motor flow rate demand Vwm (steps S130 and S140).
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com