Porous carbon electrode with conductive polymer coating
A porous carbon material, porous conductive carbon technology, applied in the field of porous carbon materials, anode electrodes, direct methanol fuel cells, lithium ion batteries or fuel cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
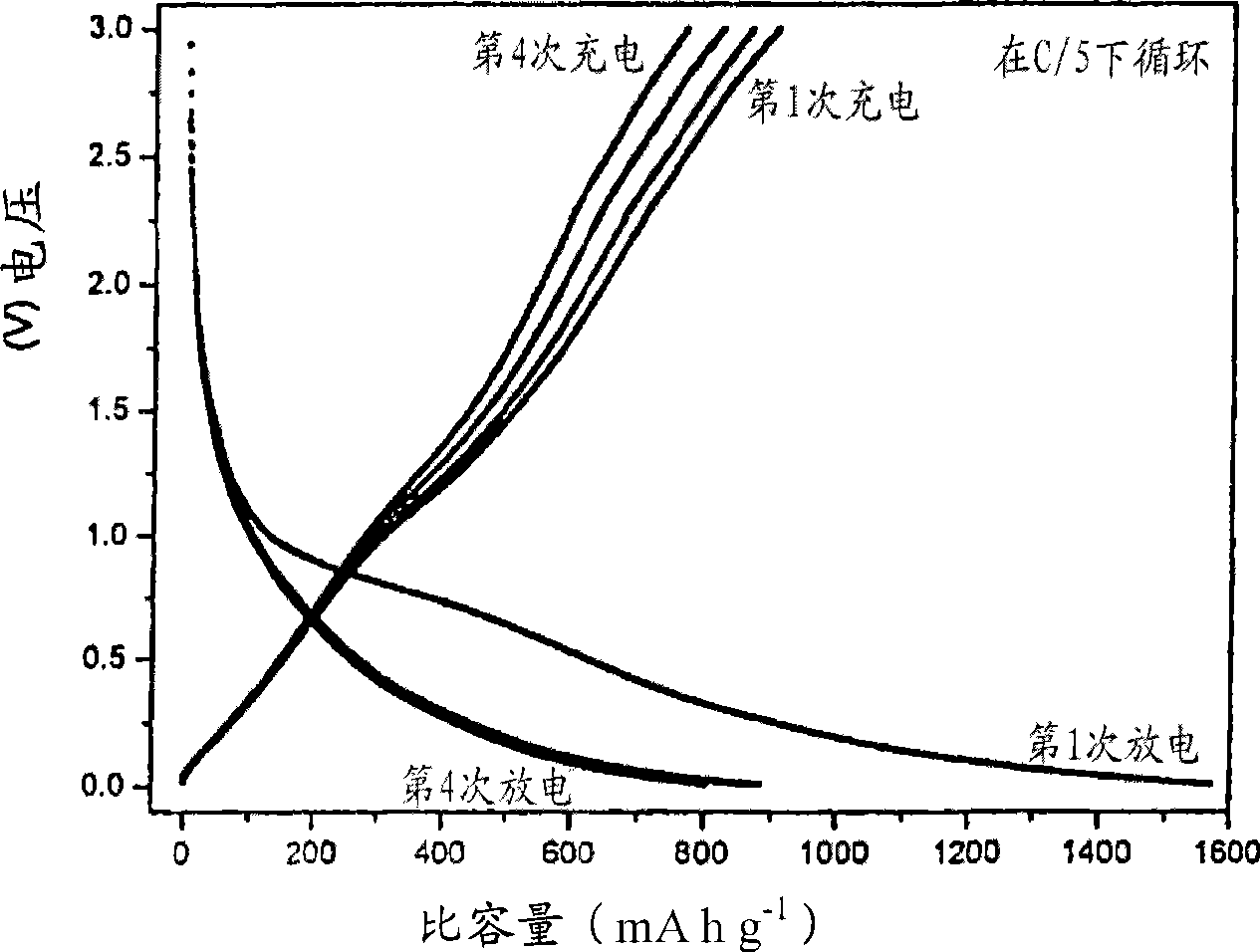
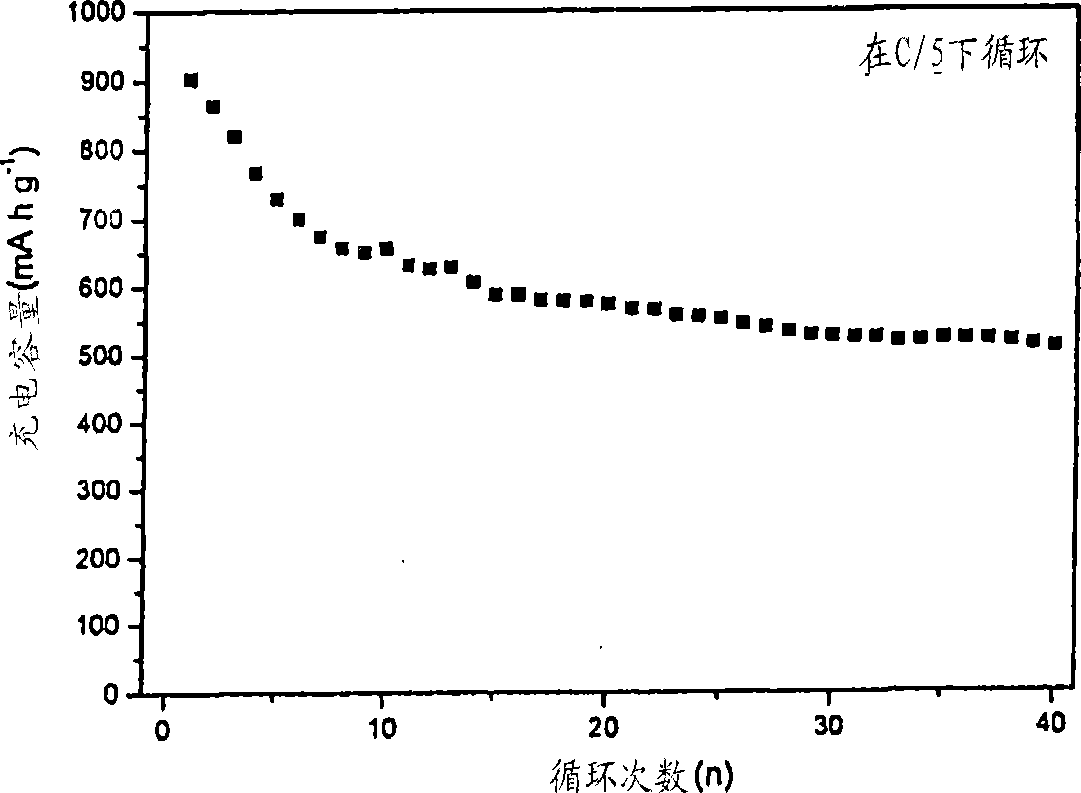
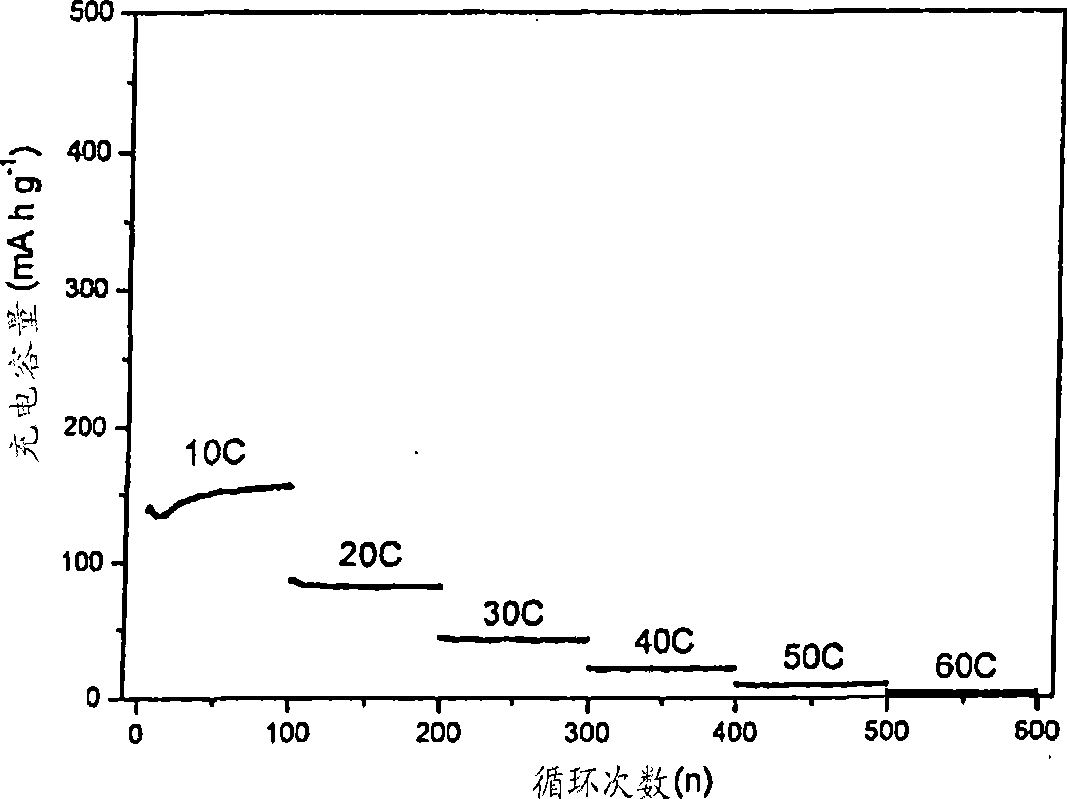
[0071] Turning first to Figures 17A and 17B, the preferred non-graphitic carbon materials of the present invention will first be described. As shown in Figure 17A, it is indicated in the upper left of the figure how the non-graphitic carbon structure changes as it undergoes heat treatment (pyrolysis) at different temperatures. It can be seen from this figure that within the temperature range of 600°C to 1000°C involved in the present invention, that is, 873 to 1273°F, the structure includes a plurality of small graphite stacks 2 in random orientations. The stack itself comprises sheets of carbon atoms 4 arranged generally in a hexagonal arrangement. The sheet 4 shown as a rectangle in FIG. 17B is called graphene. There is no positional correlation of the carbon atoms within each graphene with the position of the carbon atoms in the graphene below or above.
[0072] As the heat treatment temperature increases, the non-graphitic carbon gradually becomes more ordered, transform...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com