Controlled release oral dosage formulations comprising a core and one or more barrier layers
An oral preparation and barrier layer technology, which is applied in the field of controlled release preparations of pharmaceutically active agents, can solve the problems of reduced surface area of dosage forms, reduced release rate, reduced drug concentration, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] Example 1. Three-layer tablet containing 40 mg of nisoldipine
[0096] Three different formulations were prepared, each containing 40 mg of nisoldipine. These formulations are referred to as Formulation A, Formulation B, and Formulation C, as described in Tables 1-3. Formulation C was coated with an enteric coating (5% weight gain) containing S100 (methacrylic acid copolymer type B) and Combination of L100 (methacrylic acid copolymer type A). Formulations A and B from Colorcon, West Point, PA II seal coat for coating.
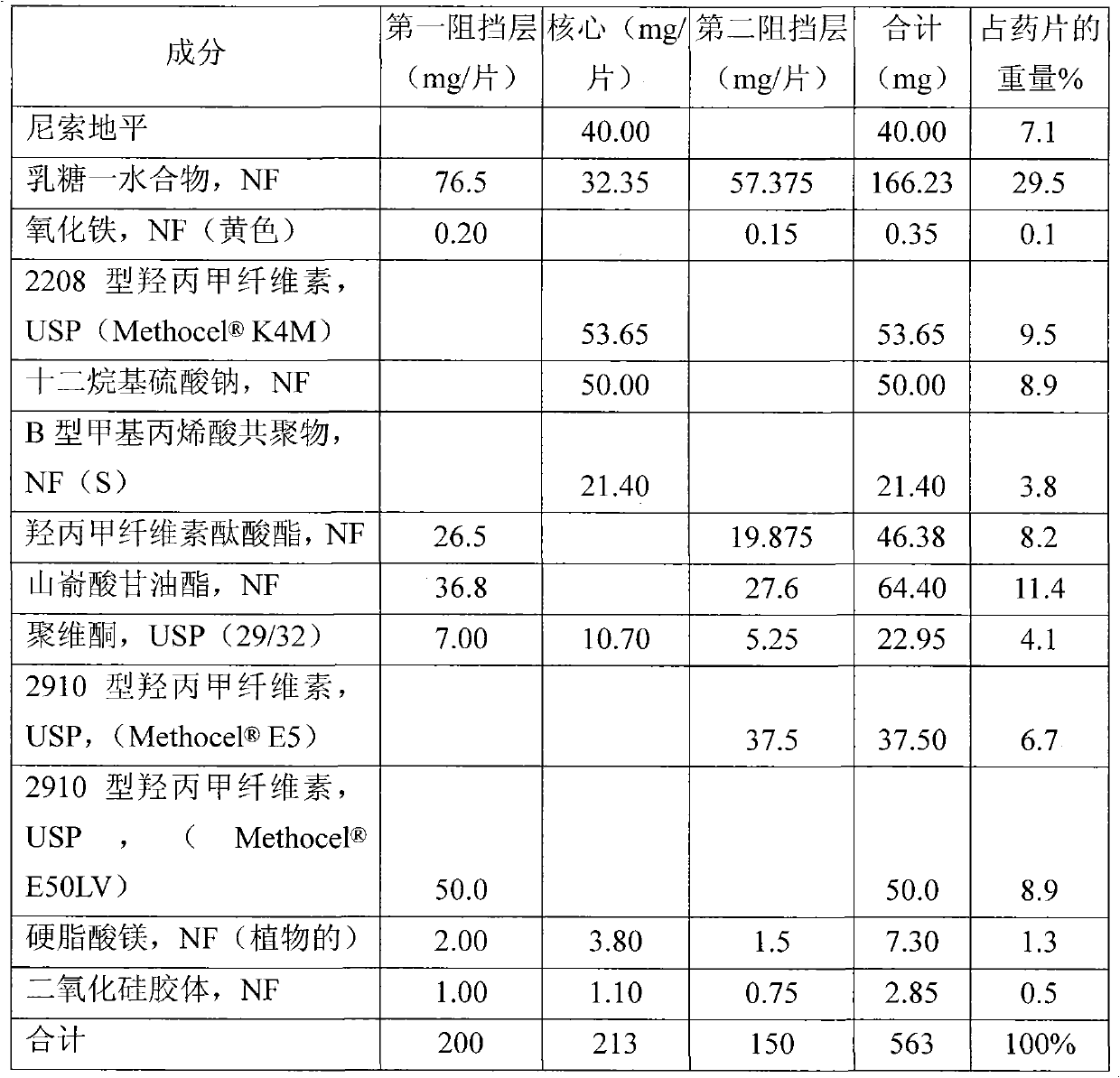
[0097] Table 1 Components of Formulation A
[0098]
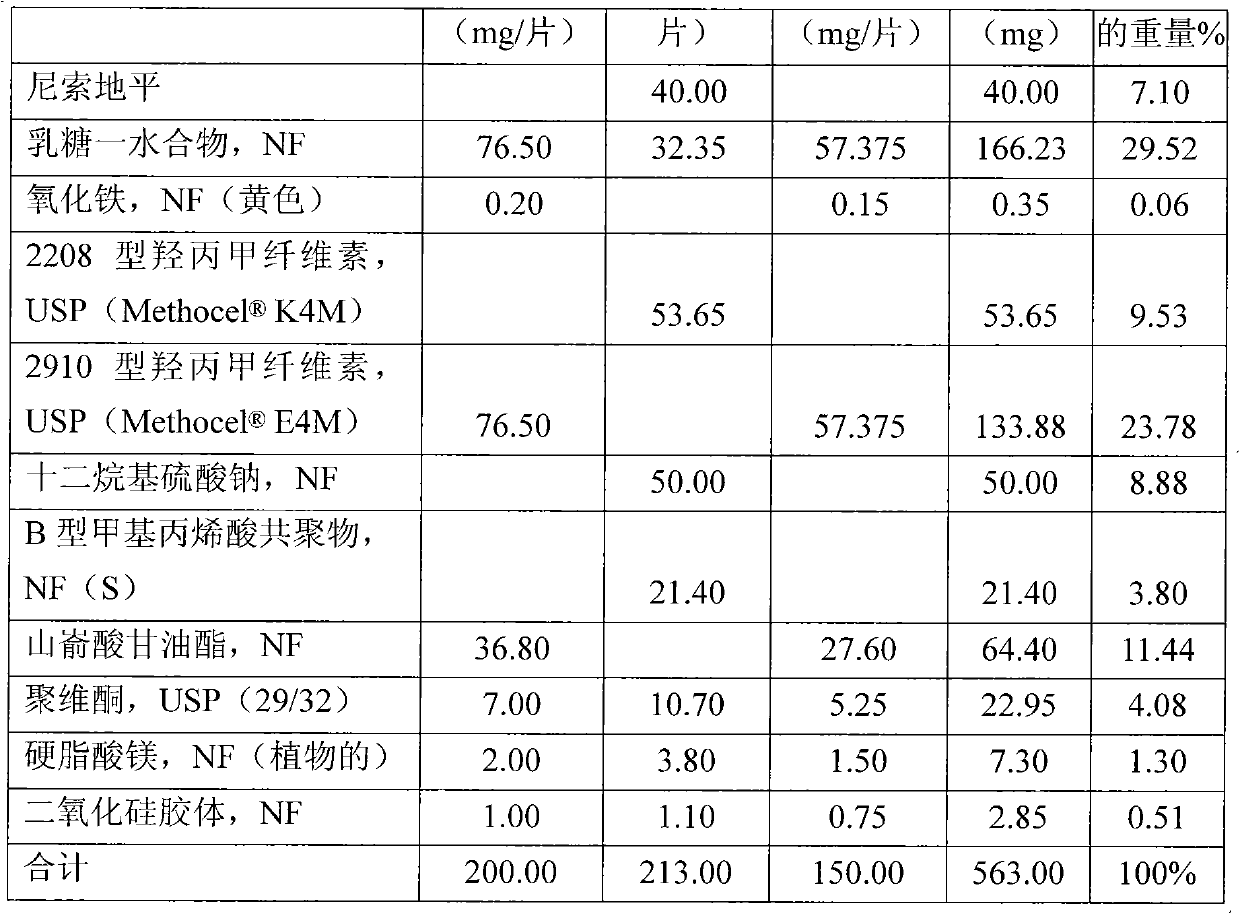
[0099] Table 2 Components of Formulation B
[0100]
[0101]
[0102] Table 3 Components of Formulation C
[0103]
[0104]
[0105] The formulations described above were prepared as follows:
[0106] core or central layer
[0107] 1. Stir nisoldipine and sodium lauryl sulfate in a high shear mixer for two minutes. Lactose monohydrate, povidone, methacrylic acid copolymer ...
Embodiment 2
[0130] Embodiment 2. The study of relative bioavailability of Nisoldipine 40mg extended-release tablet under fasting condition
[0131] The pharmacokinetic parameters of Formulations A-C described in Example 1 were compared with those of the reference formulation (Formulation D). The reference preparation is Delayed-release nisoldipine (40 mg). is a core-wrapped formulation consisting of a core containing nisoldipine coated with an immediate release coat also containing nisoldipine. given in Table 4 components and their concentrations.
[0132] The goal of this single-dose, open-label, randomized study was to compare the performance of the test formulation (nisoldipine 40 mg extended-release tablet) described in Example 1 with an equivalent oral dose under fasting conditions when administered to healthy individuals. Commercially available reference products ( 40mg extended-release tablet) absorption rate and oral bioavailability.
[0133] Table 4 Components (Formul...
Embodiment 3
[0156] Embodiment 3. The study of the relative bioavailability of Nisoldipine 40mg extended-release tablet under feeding condition (fed condition)
[0157] The goal of this study was to compare formulation A described in the examples with the market formulation food effect. In order to determine the food effect of formulations A and Sular, the pharmacokinetic data of these two formulations under fasted conditions in Example 2 were used as reference. The same 32 individuals from Example 2 were recruited for the food effect study.
[0158] Twenty-six (26) individuals completed the study. According to the randomization schedule, individuals receive their assigned treatment in the first period and additional treatment in subsequent periods. Dosing days were separated by a washout period of at least 7 days. An equal number of individuals were randomly assigned to each possible treatment order. Blood samples were collected and analyzed as described in Example 2. Table 9 shows...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com