Methods and apparatus for performance verification and stabilization of radiation detection devices
A radiation detection and radiation detector technology, applied in the field of radiation sources, can solve the problems that are not suitable for testing portable monitors, scintillation detectors, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
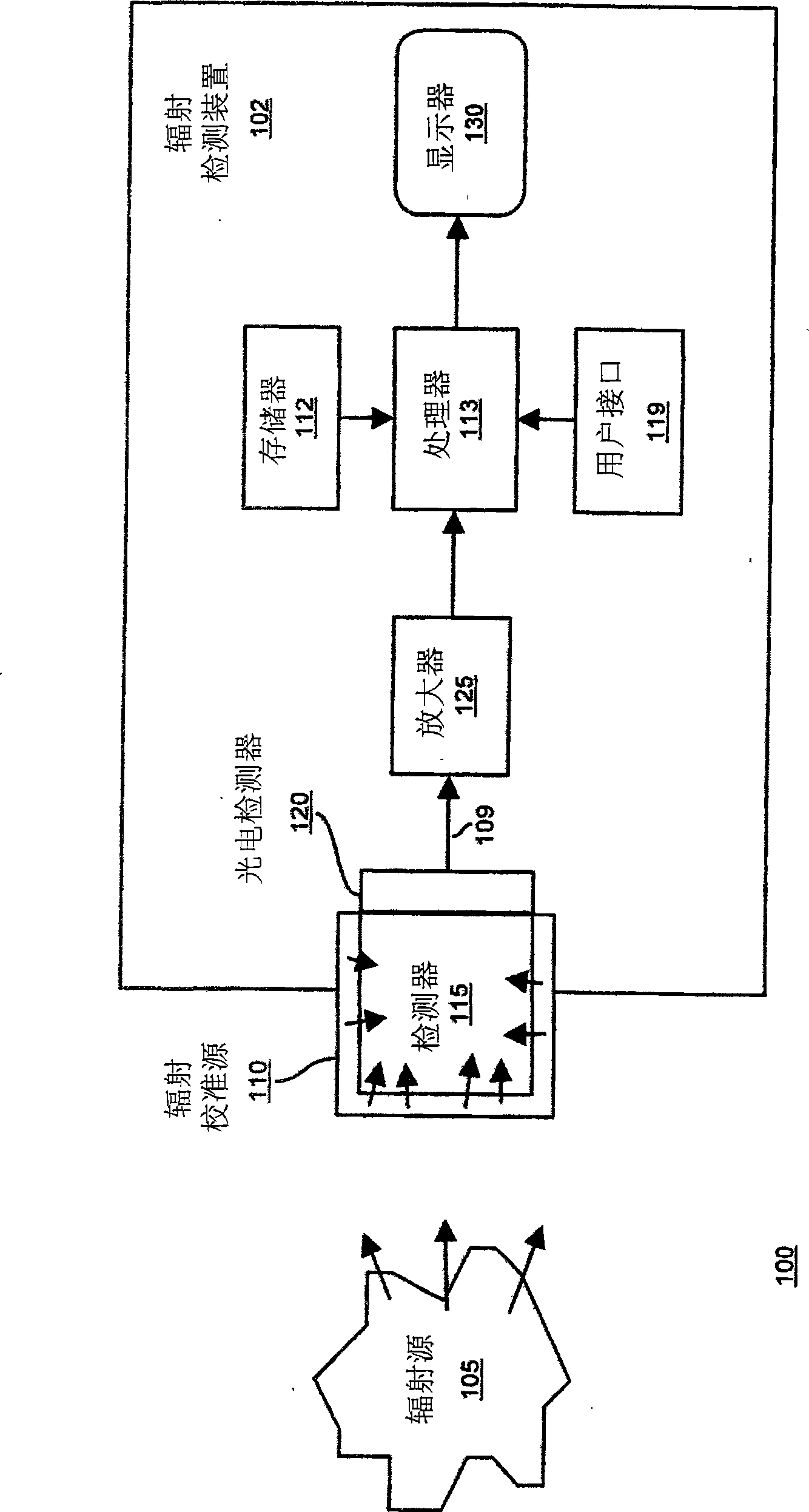
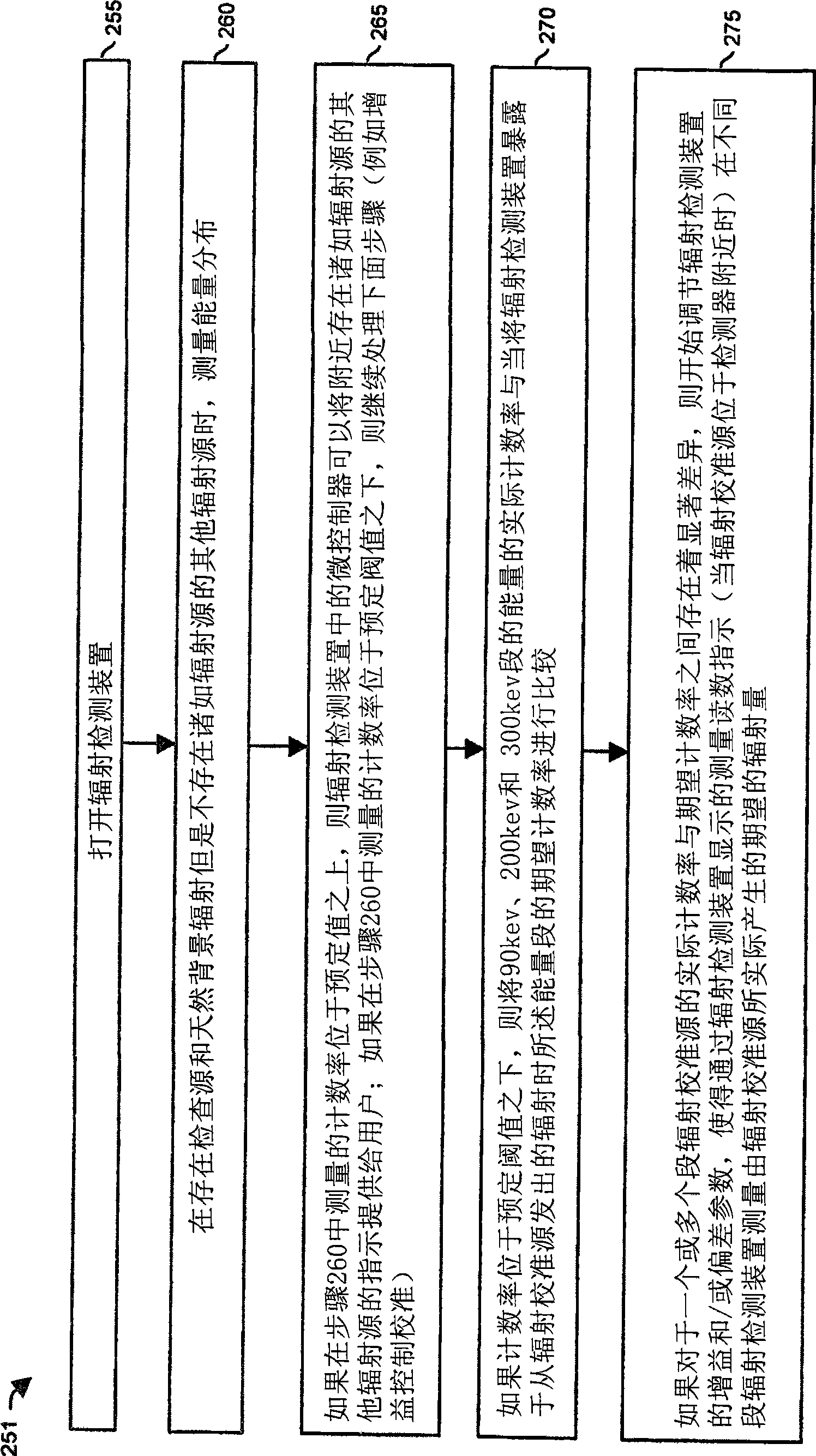
[0034] One embodiment of the invention involves the use of the rare earth element lutetium in the form of a compound for calibrating radiation detection devices. The rare earth metal contains the radioactive isotope lutetium-176 with a natural abundance of about 2.6%, producing measurable radiant energy.
[0035] Radiation lutetium-176 produces gamma energies of approximately 90, 200, and 300 keV. Such gamma energies are close to those commonly produced by so-called idiosyncratic nuclear materials such as U-235 and Pu-239 (ideal for their detection) and their respective alternatives Co-57 and Ba-133 (which are traditionally used for Calibration purposes) produced the main spectral lines. Radiation lutetium-176 has a half-life of 37 billion years. Thus, the use of lutetium in the radiometric calibration source provides the benefit that the radiometric calibration source essentially never needs to be replaced. Additionally, radiation detection devices can be precisely calibra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com