Indoor movable robot real-time navigation method based on visual information correction
A mobile robot and visual information technology, applied in the field of robot navigation, can solve problems such as narrow application range, large cumulative error, and poor real-time performance, and achieve the effects of improving anti-interference ability, suppressing background noise, and accelerating convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The present invention will be further described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
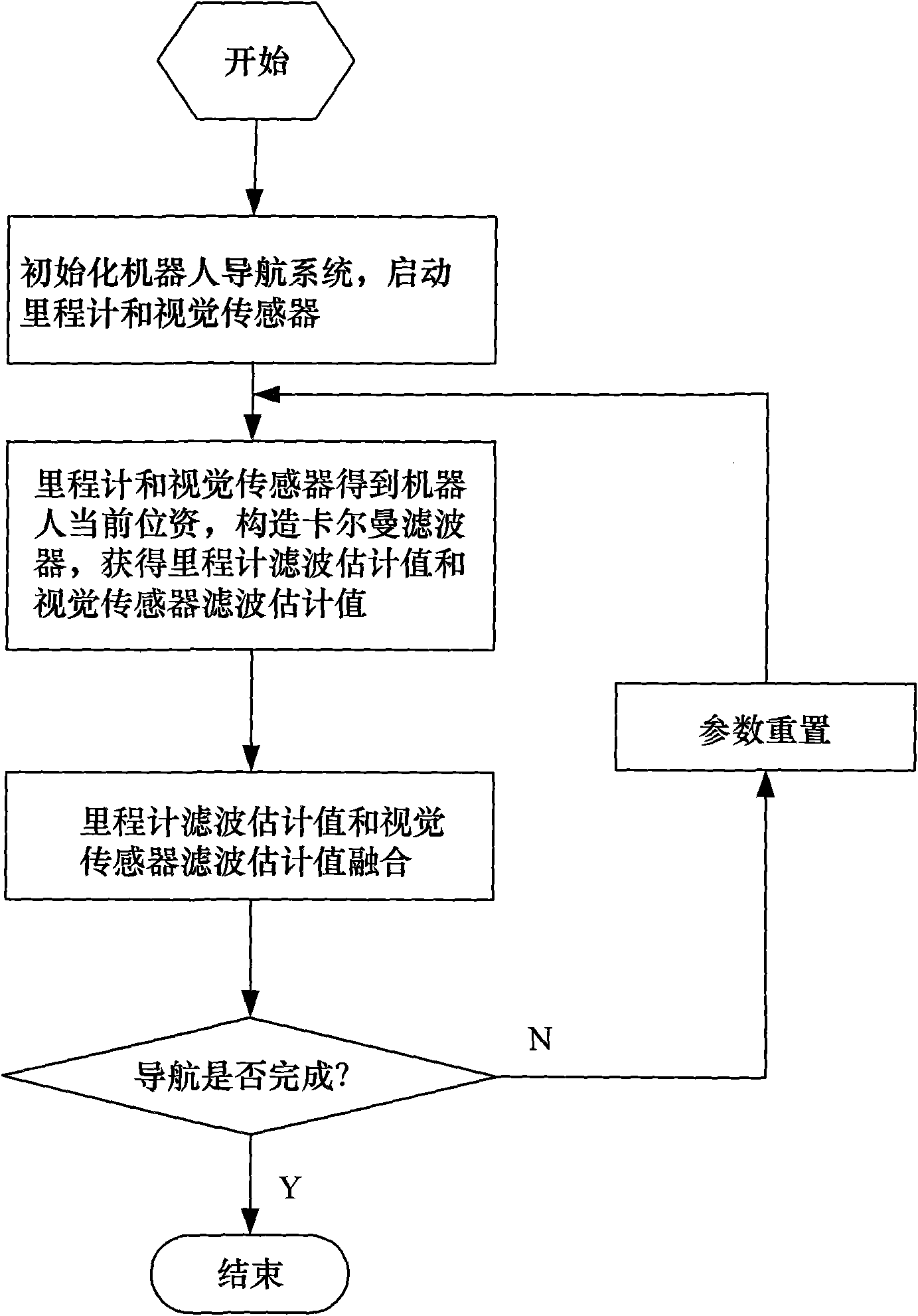
[0026] The present invention is a real-time navigation method for an indoor mobile robot based on visual information correction. The process is as follows: figure 1 As shown, it mainly includes the following steps:
[0027] Step 1: Initialize the robot navigation system, start the odometer and vision sensor;
[0028] Initialize the navigation system, including determining the initial position of the mobile robot and initializing the parameters of all filters, where the main parameters of the filter are the system noise variance matrix of the mobile robot motion model and the measurement noise variance matrix of each sensor, and start the odometer and vision sensors.
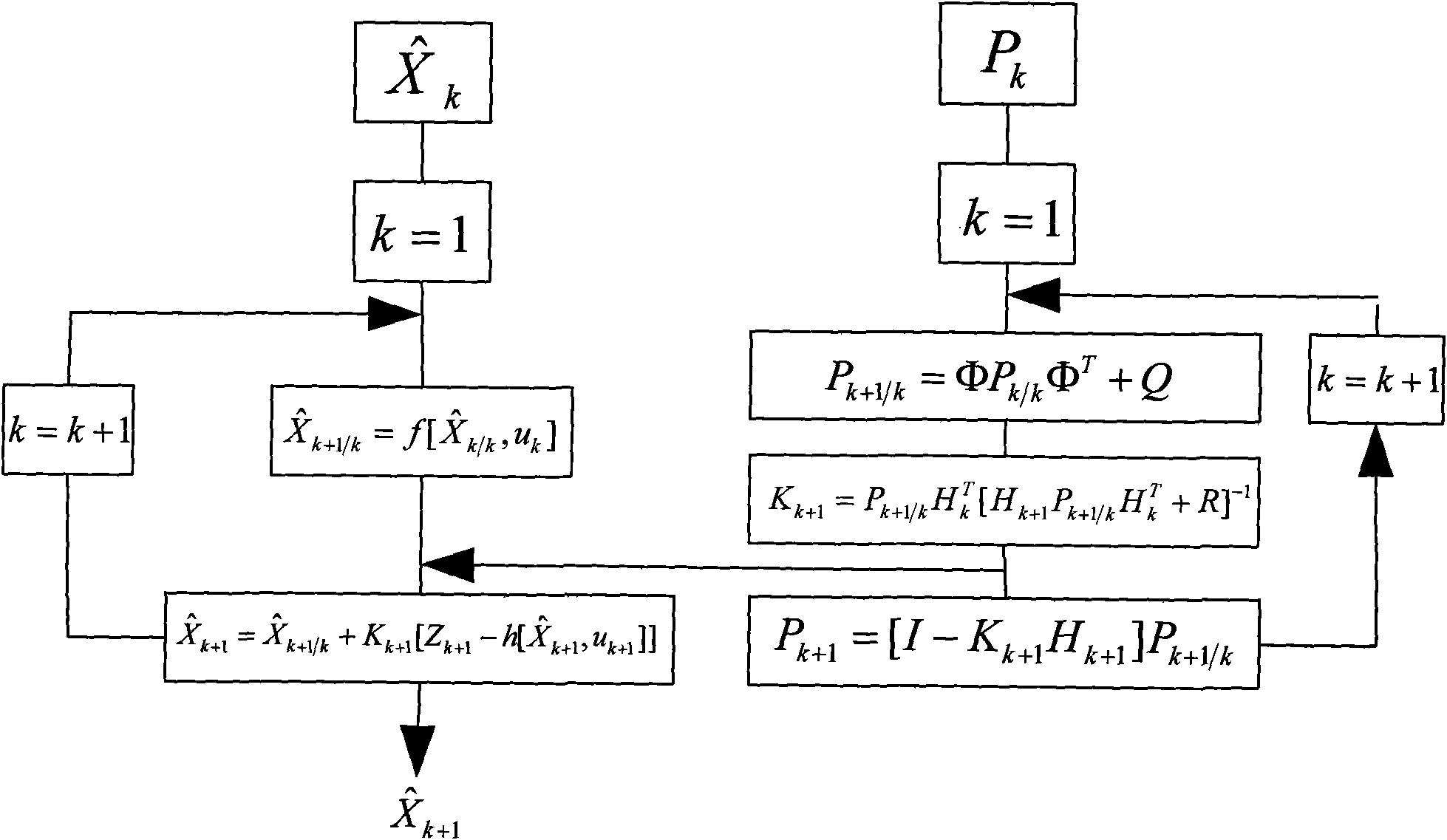
[0029] Step 2: The odometer and the visual sensor obtain the current position information of the robot, construct a Kalman filter, and obtain the estimated value of the odometer filter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com