Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose hard capsules and process of manufacture
A technology of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and hard capsules, which is applied in the field of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose hard capsules and its preparation, and can solve problems such as poor appearance quality and solubility properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0099] Example 1: Aqueous composition for the manufacture of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose hard capsules
[0100] 5 kg of a composition of 18.8% HPMC type 2906 (28.7% methoxyl content, 5.4% hydroxypropoxyl content) with a viscosity of 4.4 cPs at 2% strength (w / w) was prepared as follows:
[0101] Under stirring, the HPMC powder was dispersed into hot water at 75 °C. Foam formation was observed. After powder dispersion was complete, the temperature was maintained at 75°C with very gentle stirring to defoam the dispersion. The dispersion was then cooled to 10° C. with gentle stirring to achieve dissolution of the HPMC. Holding the composition at 10° C. for more than 30 minutes, a ready dipping composition for capsule manufacture was obtained.
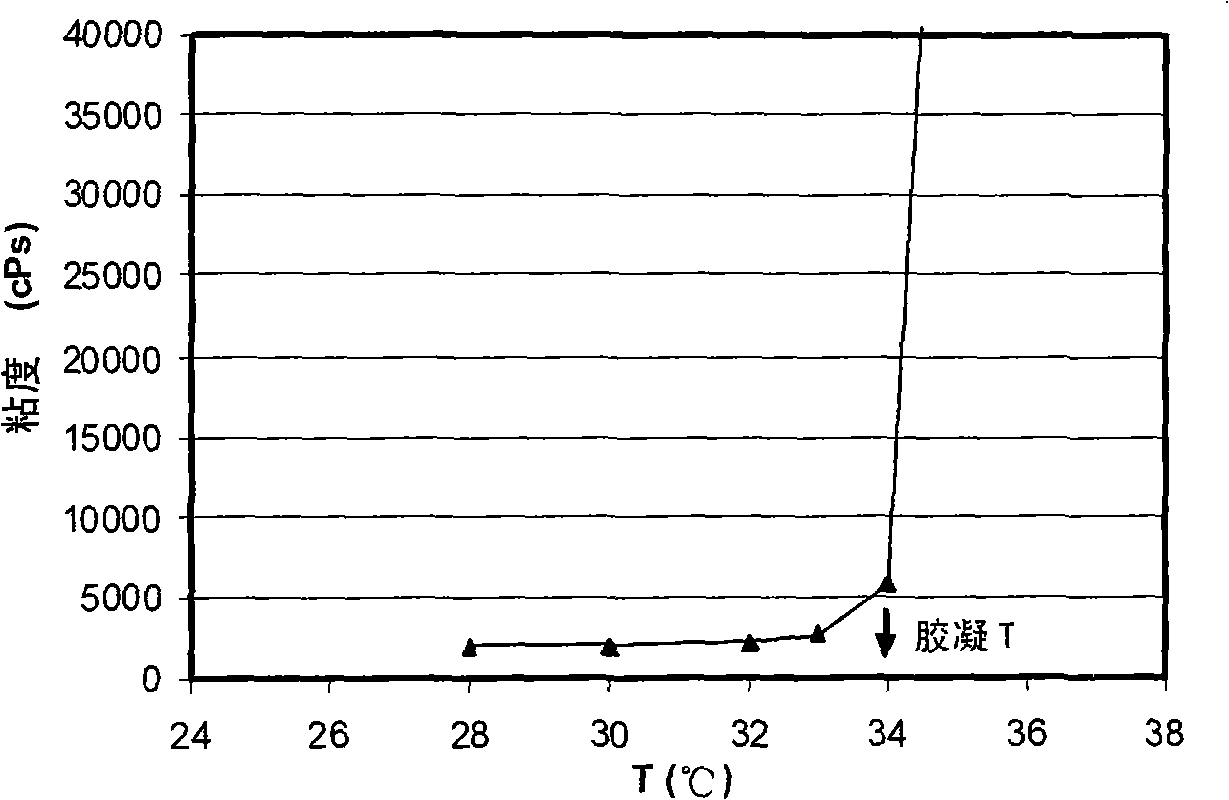
[0102] The gel temperature of the HPMC composition was determined by gradually heating the composition for viscosity measurement. The gelling temperature was found to be 34°C.
Embodiment 2
[0103] Embodiment 2: the manufacture of hard capsule
[0104] The composition prepared in Example 1 was poured into the dip pan of a pilot plant for hard capsule manufacture. Dip pins of size 0 were preheated at 75°C while maintaining the dipping composition at 32°C. At this temperature, the viscosity of the dipping composition is 2000 cPs. Size 0 capsules were made via the conventional dipping method but using preheated pins. After impregnation, the capsules were dried in an oven with hot air at 60°C and 40% RH for 3 minutes, followed by hot air at 40°C and 40% RH.
[0105] The obtained capsules are of high quality: good and standard size (top wall thickness > 140 μm), high transparency (similar to gelatin hard capsules), excellent dissolution and mechanical properties.
Embodiment 3
[0106] Example 3: Optimum preheating temperature for pins
[0107] Example 2 was repeated, but preheating the dipped pins at 60°C instead of 75°C. It should be noted that pin size 0 is considered a medium-large size.
[0108] After dipping, gelation on the pins is suboptimal to obtain commercially usable capsules. During drying, the solution partly flowed down the pin, resulting in a top wall thickness of less than 50 μm.
[0109] Conclusion: For the manufacture of size 0 capsules, 60°C is less preferable than 75°C as the pin preheating temperature.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| transmittivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com