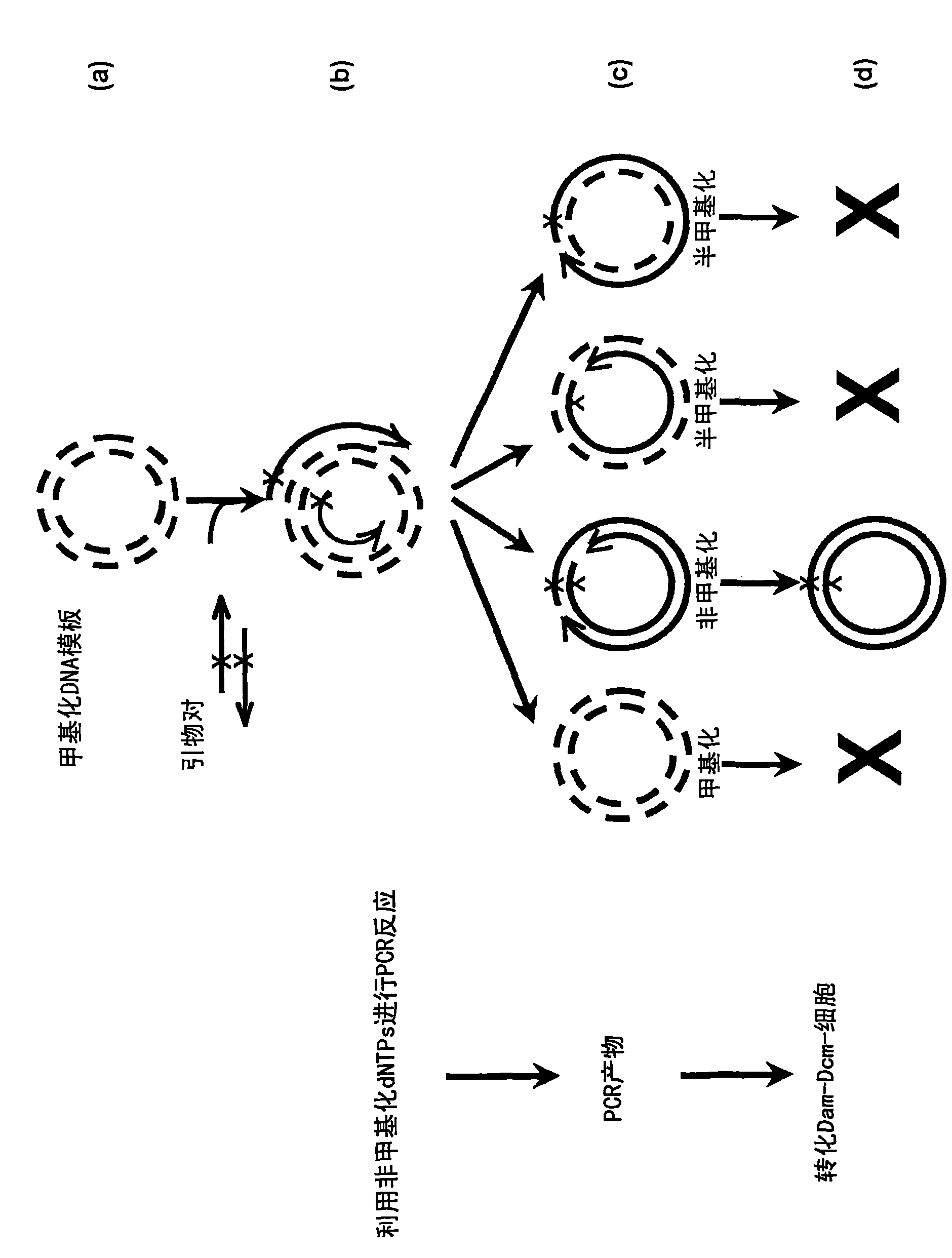
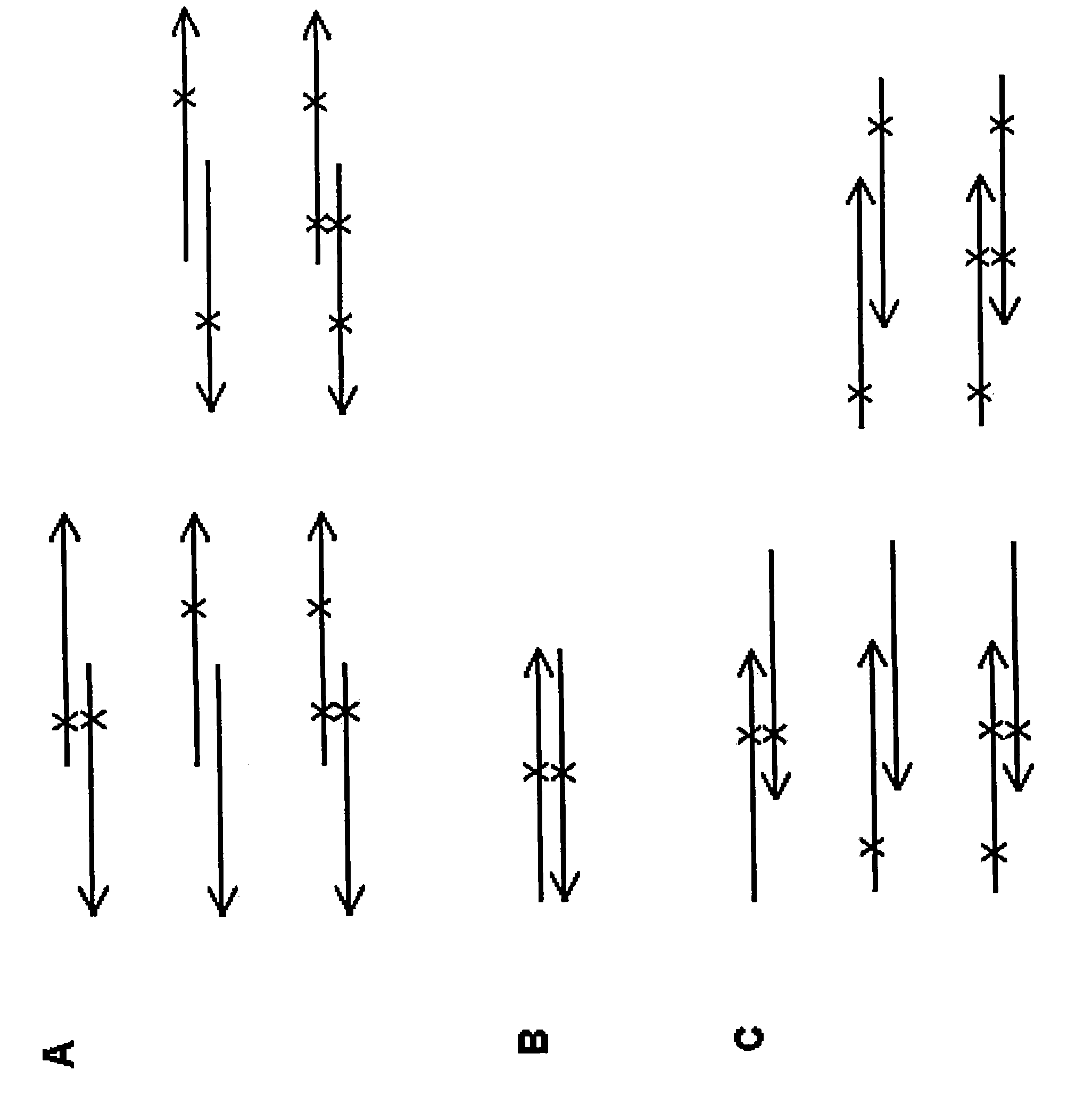
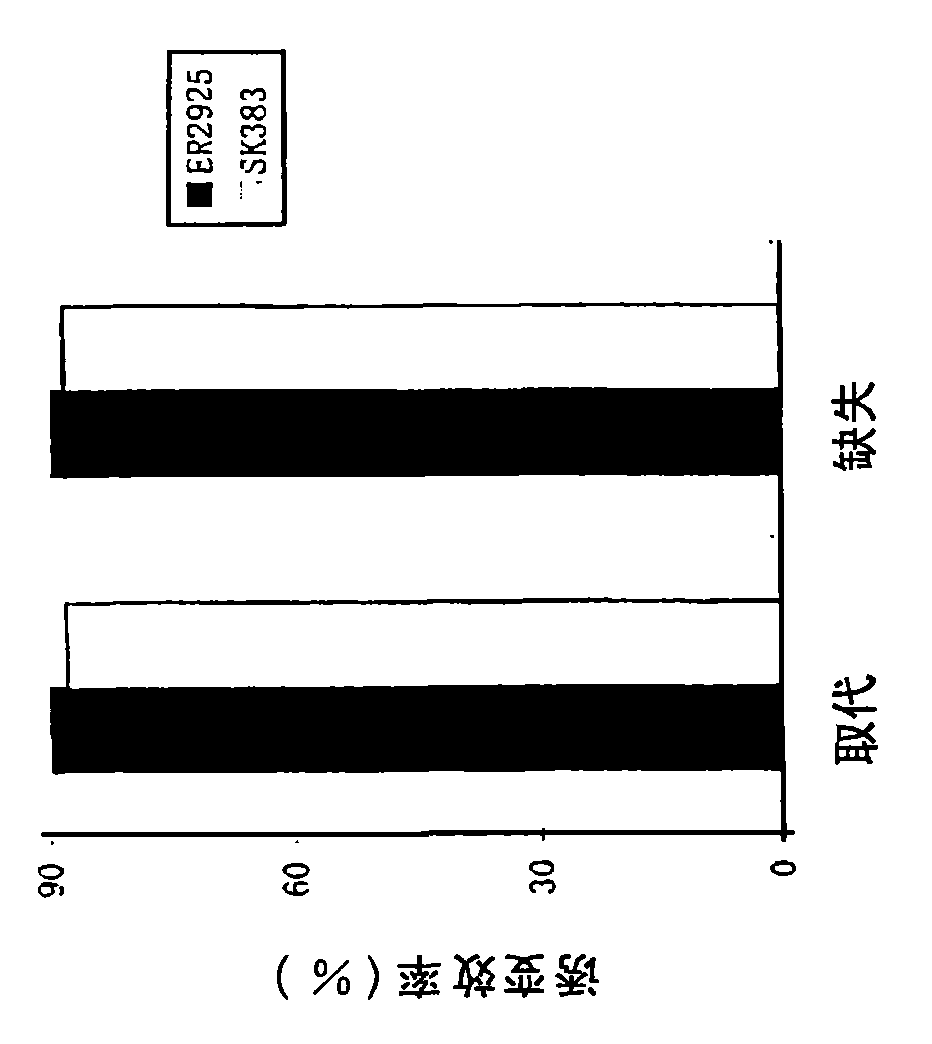
Site-directed mutagenesis in circular methylated DNA
A technology of methylation and methylase, applied in the field of molecular biology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Partially complementary primers are used in the method for Fip2 site-directed mutagenesis, wherein the mutagenesis site is located in the non-complementary region of one of the primers, and the method steps are as follows:
[0064] 1) Synthesize two partially complementary primers at the 5' end, wherein the mutation is in the non-complementary region, for the introduction of 3 nucleotide substitutions, thereby generating an EcoRV restriction site (capital letters represent 3 cores Nucleotide substitution mutations, bold represents the complementary regions of the forward and reverse primers):
[0065] Primer 1: GaTAtccatcagag-3′, and
[0066] Primer 2: cctgacacttttc-3′;
[0067] 2) Prepare the reaction solution:
[0068] 2.5 μl 10x reaction buffer (BD Biosciences)
[0069] 10ng Fip2 plasmid (GM Biosciences, Inc)
[0070] 0.5 μl Primer 1 (20 μM)
[0071] 0.5 μl Primer 2 (20 μM)
[0072] 1 μl of 10 mM dNTPs (2.5 mM of each dNTP) (BD Biosciences)
[0073] Add do...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Partially complementary mutagenesis primers are used in the method for site-directed mutagenesis of Fip2, and the mutagenesis site is located in the complementary region of the two primers. The steps of the method are as follows:
[0086] 1) Synthesize two partially complementary primers at the 5' end, wherein the mutation is used to introduce a substitution of 3 nucleotides in the complementary region, thereby generating an EcoRV restriction site (capital letters represent 3 nucleotides Substitution mutations, bold represents the complementary regions of the forward and reverse primers) Substitution substitutions:
[0087] Primer 3: ttgaatgaaaag-3′, and
[0088] Primer 4: tttcaagggc-3';
[0089] 2) Prepare the reaction solution:
[0090] 2.5 μl 10x reaction buffer (BD Biosciences)
[0091] 10ng Fip2 plasmid (GM Biosciences, Inc)
[0092] 0.5 μl Primer 1 (20 μM)
[0093] 0.5 μl Primer 2 (20 μM)
[0094] 1 μl of 10 mM dNTPs (2.5 mM of each dNTP) (BD Biosciences...
Embodiment 3
[0107] According to the method steps of the present invention, Fip2 is mutagenized with two completely complementary primers, and the steps are as follows:
[0108] 1) Synthesize two fully complementary primers, where the mutation is used to introduce a 1 nucleotide substitution (capital letters):
[0109] Primer 5: 5′-gagctcctgaccgCgaaccaccagctgaaag-3′, and
[0110] Primer 6: 5′-ctttcagctggtggttcGcggtcaggagctc-3′;
[0111] 2) Prepare the reaction solution:
[0112] 2.5 μl 10x reaction buffer (BD Biosciences)
[0113] 10ng Fip2 plasmid (GM Biosciences, Inc)
[0114] 0.5 μl Primer 1 (20 μM)
[0115] 0.5 μl Primer 2 (20 μM)
[0116] 1 μl of 10 mM dNTPs (2.5 mM of each dNTP) (BD Biosciences)
[0117] Add double distilled water to make the final reaction volume reach 25 μl;
[0118] 3) Incubate the reaction solution prepared in step 2) at 98° C. in a PCR instrument (PTC-200thermocycler, Bio-Rad,) for 30 minutes, and incubate at 95° C. for 5 minutes to denature the template....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com