Image prediction/encoding device, image prediction/encoding method, image prediction/encoding program, image prediction/decoding device, image prediction/decoding method, and image prediction decoding
A technology of predictive coding and predictive decoding, which is applied in image communication, television, electrical components, etc., and can solve the problems of degradation of reproduced image quality, increase of information amount, and decrease of coding efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
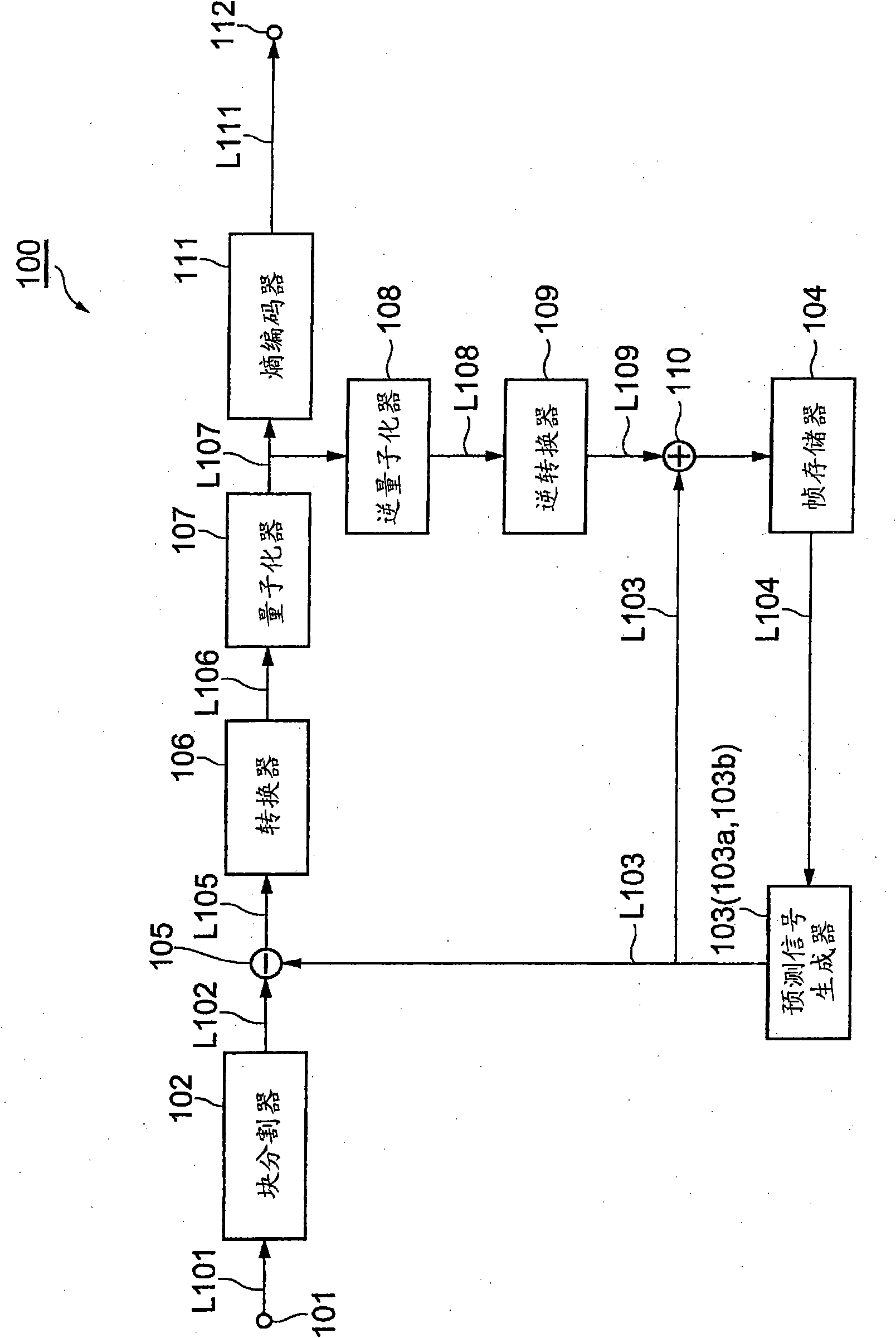
[0185] figure 1 It is a block diagram showing an image predictive encoding device 100 capable of executing an image predictive encoding method according to an embodiment of the present invention. The image predictive coding device 100 is configured to include an input terminal 101, a block divider 102 (area dividing unit), a prediction signal generator 103 (predicted signal generating unit), a frame memory 104, and a subtractor 105 (residual signal generating unit) , A converter 106 (encoding unit), a quantizer 107 (encoding unit), an inverse quantizer 108, an inverse converter 109, an adder 110, an entropy encoder 111, and an output terminal 112. The converter 106 and the quantizer 107 function as an encoding unit.
[0186] The structure of the image predictive encoding device 100 configured as described above will be described below.
[0187] The input terminal 101 is a terminal for inputting a signal of a moving image composed of a plurality of images.
[0188] The block divide...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
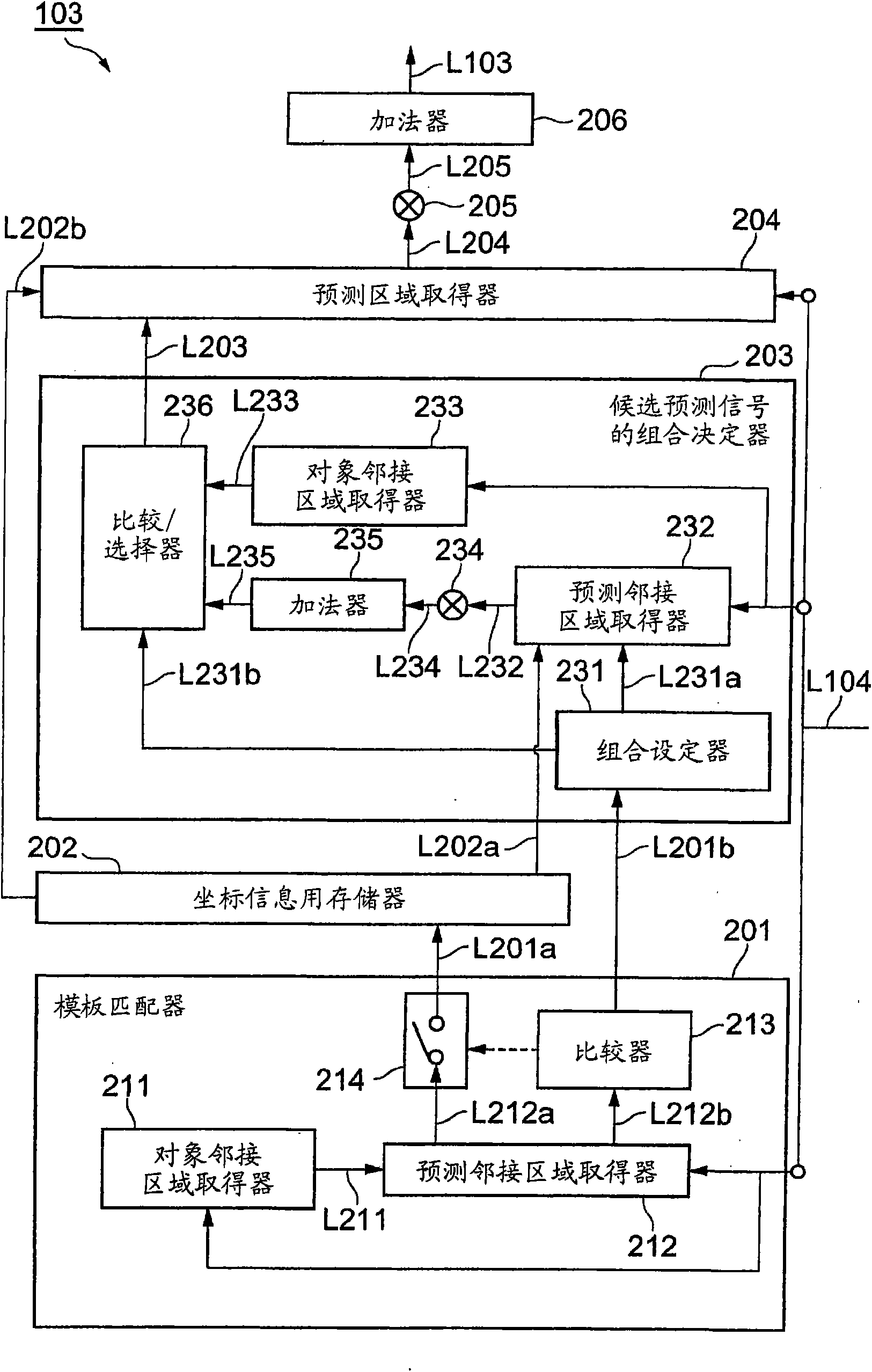
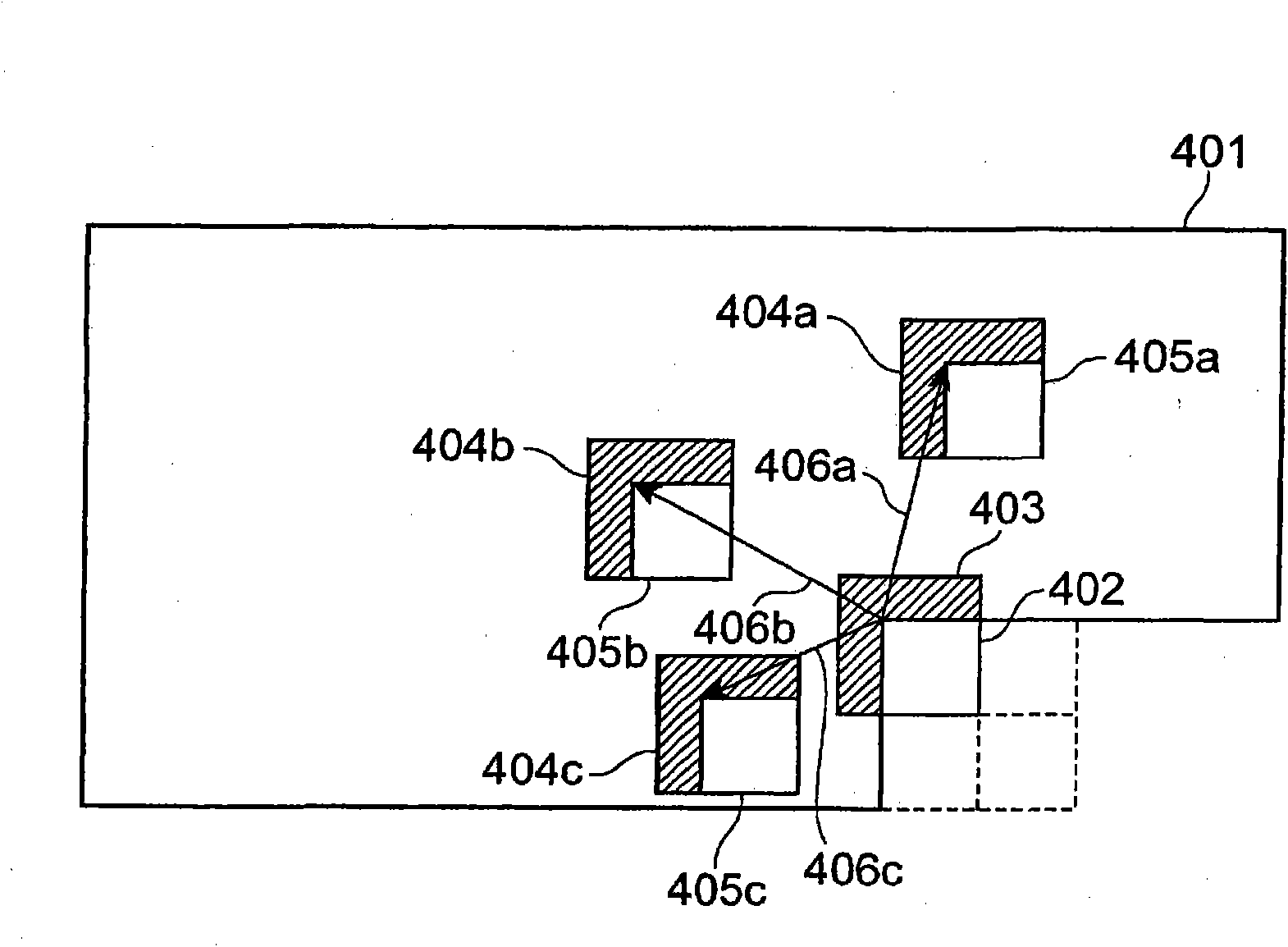
[0263] In the first embodiment, a method is shown in which the correlation between the prediction adjacent region and the target adjacent region is used to determine the candidate prediction signal (the pixel signal of the prediction region) for generating the prediction signal of the target region from a plurality of candidates. )The combination. In the second embodiment, a prediction signal generator 103a is shown that uses correlation between a plurality of candidate prediction signals to determine a combination of candidate prediction signals for generating the prediction signal of the target region from the plurality of candidates. In addition, in the second embodiment, the method of determining the combination of candidate prediction signals is not described, but the method of determining the number of candidate prediction signals is described. This embodiment shows a case where the combination of candidate prediction signals is uniquely determined based on the number of ...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0305] In the first and second embodiments, the description has been made on the premise that the weighted average when generating the prediction signal of the target region from a plurality of candidate prediction signals is a predetermined technique. However, if the candidate prediction signal combination selection method in the first embodiment of the present invention is used, it is possible to select from a plurality of prepared weight coefficients for each appropriate target region without additional information. This embodiment can be understood in consideration of the deformation of the drawings used in the previous description and the following description. Next, a third embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the deformed drawings. The drawings and descriptions overlapping with the first embodiment are omitted.
[0306] The processing of the prediction signal generator 103b of the third embodiment will be described. In addition, the pre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com