Data syncretizing method for urban traffic circulation indexes
A technology of data fusion and smoothness, which is applied in the direction of traffic flow detection, traffic control system, traffic signal control, etc., and can solve problems such as queue length and parking rate that cannot meet urban road traffic control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
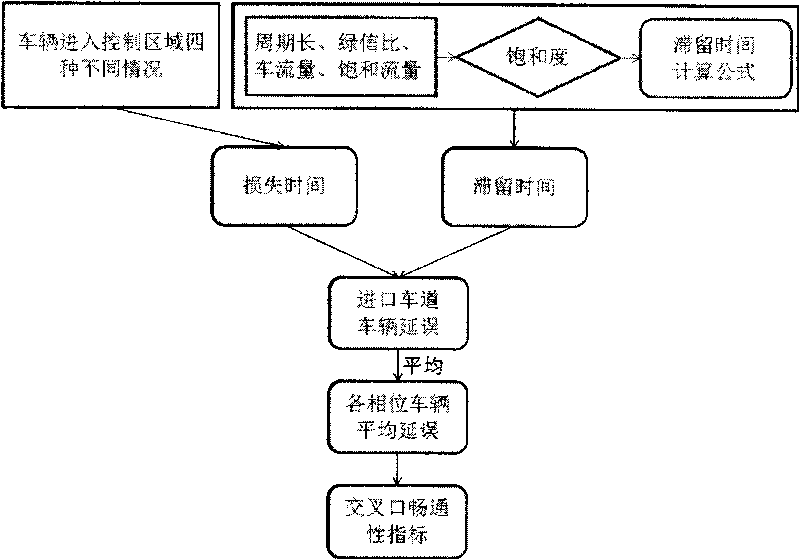
[0044] Embodiment 1: The data fusion method of the smoothness index of the intersection, such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of the data fusion method of the traffic flow index of the intersection according to the present invention, and the traffic flow index of the intersection is determined by the average delay time of vehicles in each phase in the intersection. The average delay time of a vehicle includes: dwell time and lost time, where the dwell time refers to the queuing waiting time at an intersection, which is calculated from the dwell time determined by the vehicle saturation, which is determined by the cycle of traffic lights It is determined by the length, green signal ratio, traffic flow and saturated flow; the lost time refers to the time delayed due to the phase conversion of the intersection and the driver's reflection, which is determined by four different situations when the vehicle enters the control area of the signal light at the lion intersectio...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Embodiment 2 The Fusion Method of the Unimpededness Index at Multiple Intersections on Arterial Lines
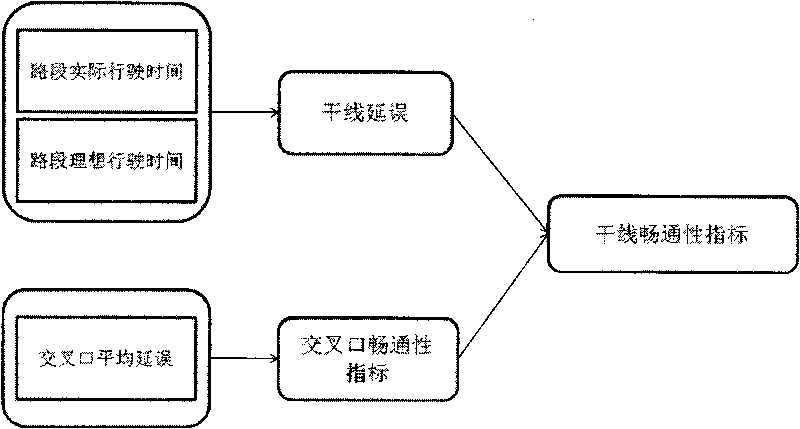
[0087] Such as figure 2 A schematic diagram of the data fusion method for the flowability index of multiple arterial intersections according to the present invention is shown. In multi-arterial intersections, the smoothness index is reflected by the average travel time delay of vehicles passing through the intersections of the arterial line. The average travel time delay of each intersection of the arterial line is composed of two parts, one is the estimated travel time and the ideal travel time The difference; the second is the average delay time of vehicles at each intersection. Among them, the data fusion steps of each smoothness index include:
[0088] Step 1: Estimation of Mainline Travel Time
[0089] The trunk line travel time refers to the time it takes for a vehicle to enter the trunk line, pass through all the intersections of the trunk line, and leave t...
Embodiment 3
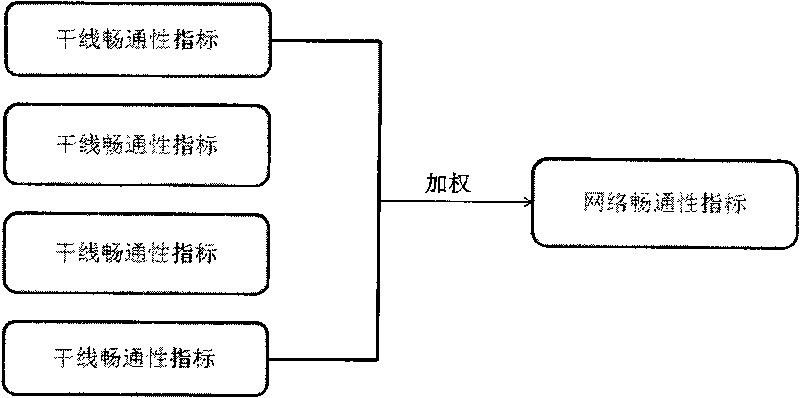
[0108] Embodiment 3 The data fusion method of the smoothness index of multi-trunk and multi-intersection in the road network, such as image 3 As shown, the road network multi-artery multi-intersection smoothness index is reflected by the average travel time delay weighted expectation value of several arterials in the region. Similar to the idea of single-point control intersection smoothness index, weighted expectation is also an improvement, considering the relationship between primary and secondary arterial roads, that is, the weight assigned to major arterial roads is relatively large while the weight of secondary arterial roads is relatively small.
[0109] Taking a traffic network with four main lines as an example, the north-to-south main line on the left is represented by LNS, the north-to-south main line on the right is represented by RNS, the west-to-east main line below is represented by DWE, the west-east main line above is represented by UWE, and the cross The p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com