Liquid crystal display drive circuit
A liquid crystal drive circuit and circuit technology, which can be used in instruments, static indicators, etc., to solve problems such as liquid crystal LC afterimages.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
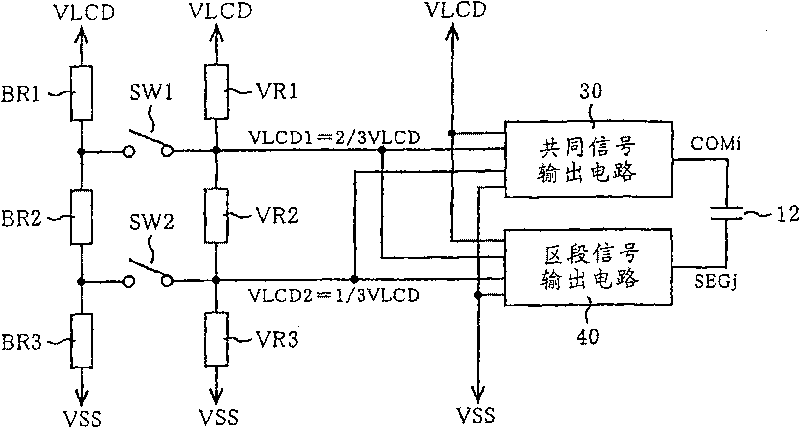
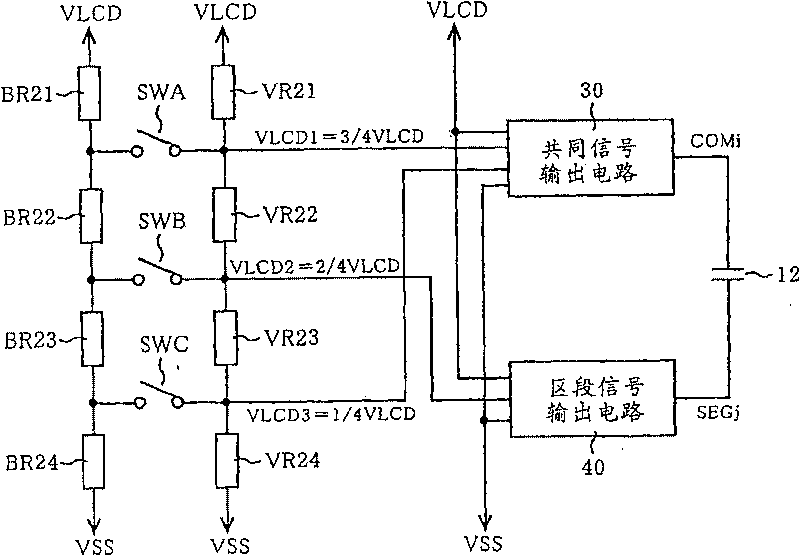
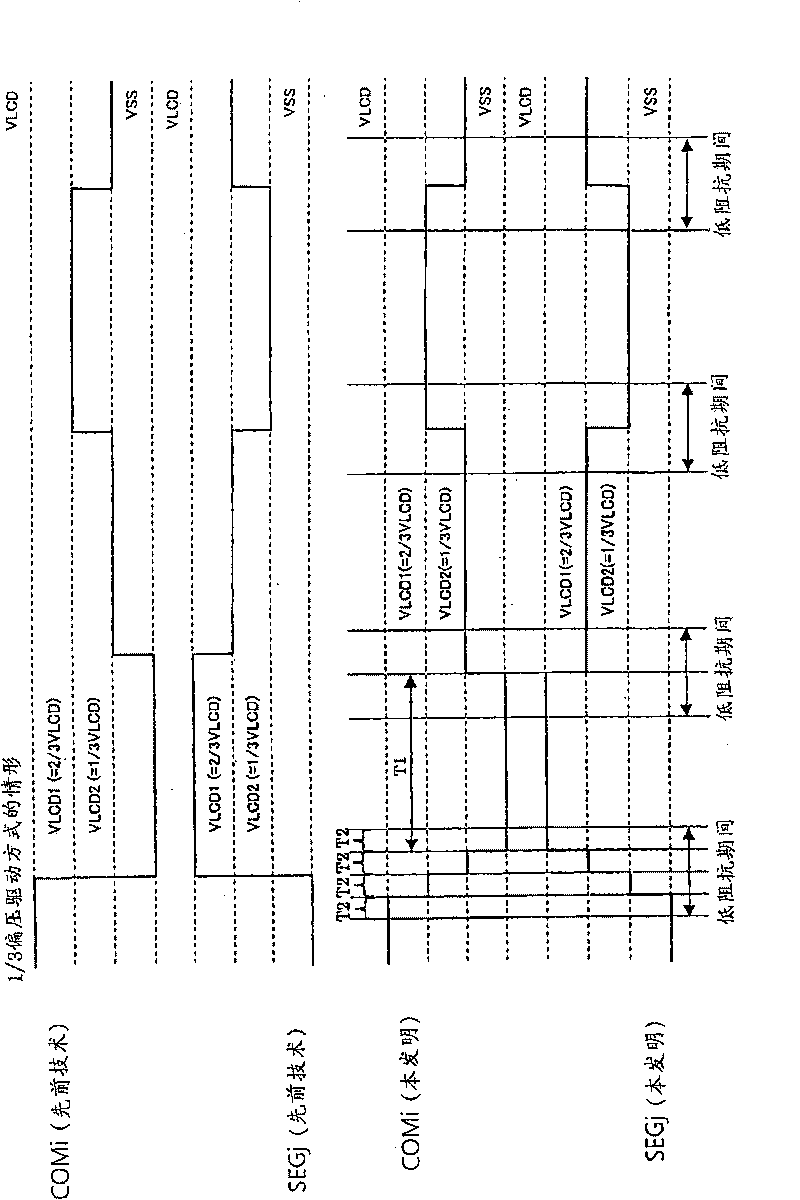
[0063] Before describing the embodiment of the present invention, firstly, the 1 / 3 bias driving method is taken as an example to examine the situation where the impulse noise of the liquid crystal panel 12 is likely to be generated. For example, imagine output as Figure 13 The common signal COM1, COM2, and the segment signal SEG1 to the liquid crystal panel 12 are shown. In this case, during the period TA, the common signal COM1 changes from a high potential VLCD to a low potential VSS (=ground potential 0V), and the segment signal SEG1 changes from a low potential VSS to a high potential VLCD in turn. Therefore, the potential difference between the corresponding electrodes reaches VLCD, and the segment SEG1 corresponding to the common COM1 is lit.
[0064] In this period TA, although the common signal COM2 changes from the second intermediate potential VLCD2 to VLCD1, since the segment signal SEG1 rises from the low potential VSS to the high potential VLCD at this time, impulse...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com