Solid-state imaging device, manufacturing method of the same, and imaging apparatus
By forming a thin film gate electrode on a semiconductor substrate, the problem of difficulty in installing planar CMOSFETs and vertical transistors at the same time in the existing technology is solved, higher refinement and density packaging are achieved, and image processing speed and accuracy are improved.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
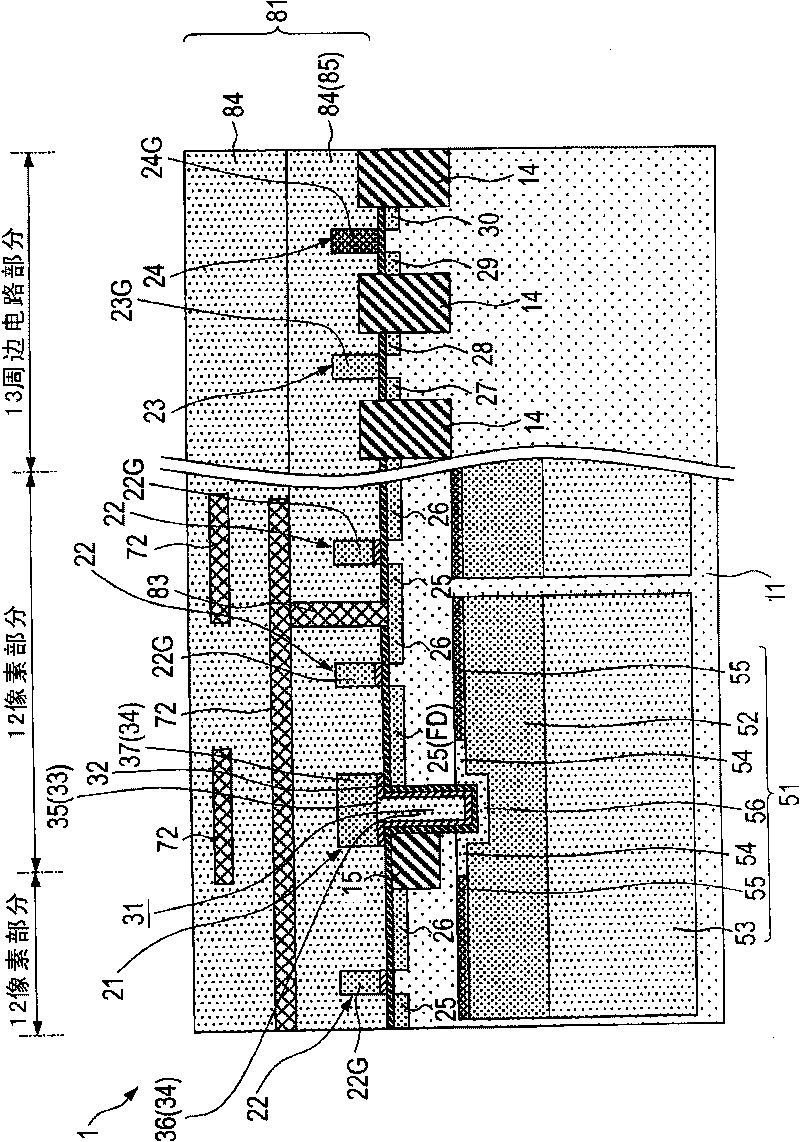
[0102] [First Example of Configuration of Solid-State Imaging Device]
[0103] will use figure 1 A schematic configuration sectional view of FIG. 1 illustrates an example (first example) of the configuration of the solid-state imaging device according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0104] Such as figure 1 As shown, in the semiconductor substrate 11, a photoelectric conversion portion 51 that photoelectrically converts incident light to obtain an electric signal is formed. Further, in the semiconductor substrate 11 , the pixel portion 12 is formed including a vertical transistor 21 that reads signal charges from the photoelectric conversion portion 51 and a planar transistor 22 that processes the read signal charges. In addition, a peripheral circuit portion 13 is formed on the periphery of the pixel portion 12 . The peripheral circuit section 13 has a first conductivity type (hereinafter, eg N type) channel transistor (hereinafter referred to as NFET) 2...
no. 3 example
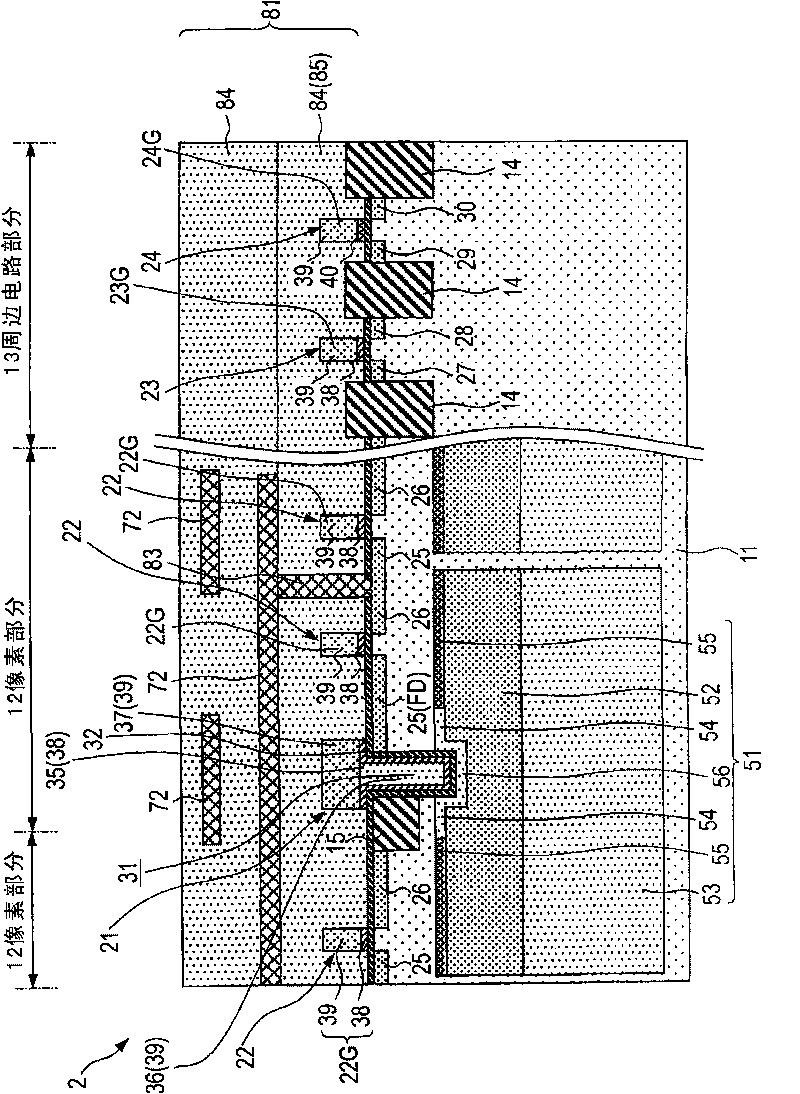
[0174] [Third Example of Configuration of Solid-State Imaging Device]
[0175] will use image 3 The schematic configuration cross-sectional view of is an illustration of an example of the configuration of a solid-state imaging device according to a third embodiment of the present invention (third example).
[0176] Such as image 3 As shown, in the semiconductor substrate 11, a photoelectric conversion portion 51 that photoelectrically converts incident light to obtain an electrical signal is formed. Further, in the semiconductor substrate 11 , the pixel portion 12 is formed including a vertical transistor 21 that reads signal charges from the photoelectric conversion portion 51 and a planar transistor that processes the read signal charges. In addition, a peripheral circuit portion 13 is formed on the periphery of the pixel portion 12 . The pixel circuit section 13 has a first conductivity type (hereinafter, eg N type) channel transistor (hereinafter referred to as NFET) ...
no. 4 example
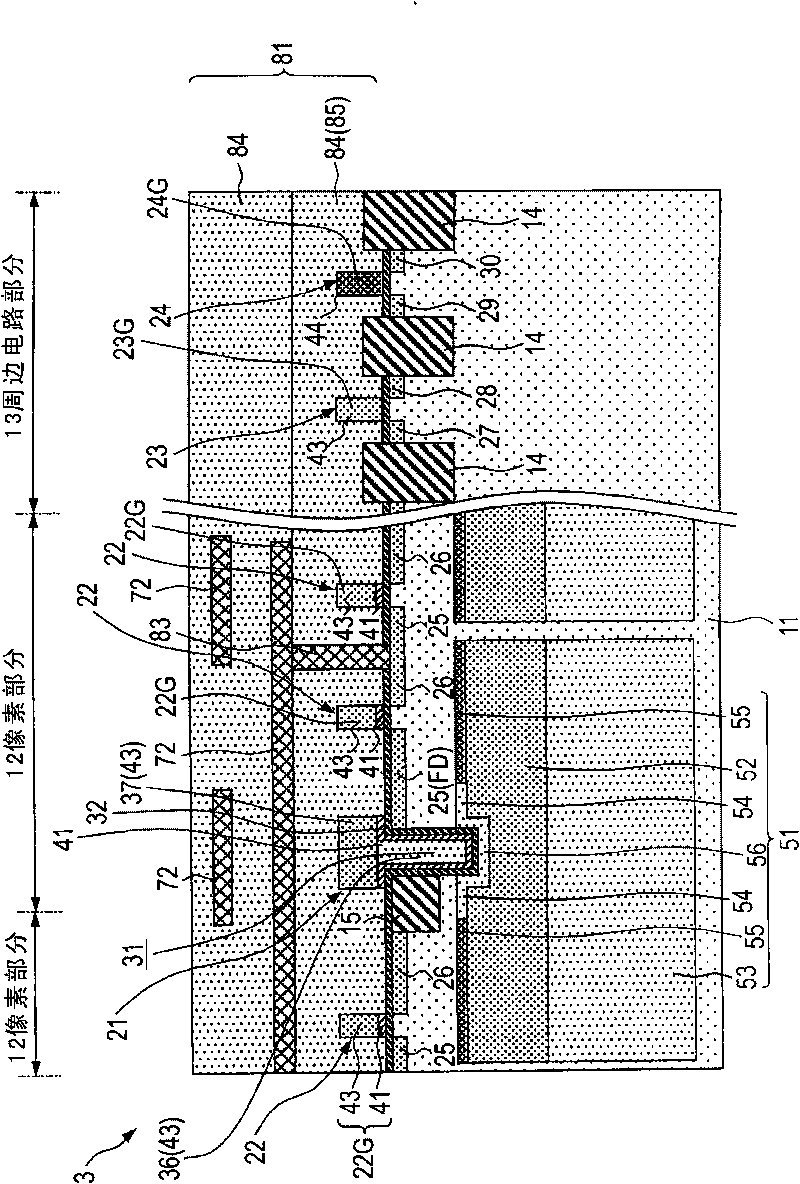
[0216] [Fourth Example of Configuration of Solid-State Imaging Device]
[0217] will use Figure 4 The schematic configuration cross-sectional view of is an illustration of an example of the configuration of a solid-state imaging device according to a fourth embodiment of the present invention (fourth example).
[0218] Such as Figure 4 As shown, in the semiconductor substrate 11, a photoelectric conversion portion 51 that photoelectrically converts incident light to obtain an electrical signal is formed. Further, in the semiconductor substrate 11 , the pixel portion 12 is formed including a vertical transistor 21 that reads signal charges from the photoelectric conversion portion 51 and a planar transistor that processes the read signal charges. In addition, a peripheral circuit portion 13 is formed on the periphery of the pixel portion 12 . The pixel circuit section 13 has a first conductivity type (hereinafter, eg N type) channel transistor (hereinafter referred to as N...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com