Solid-state imaging device
一种固体摄像装置、分光的技术,应用在高灵敏度化及包含红外光的彩色化领域,能够解决彩色化欠缺灵活性等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
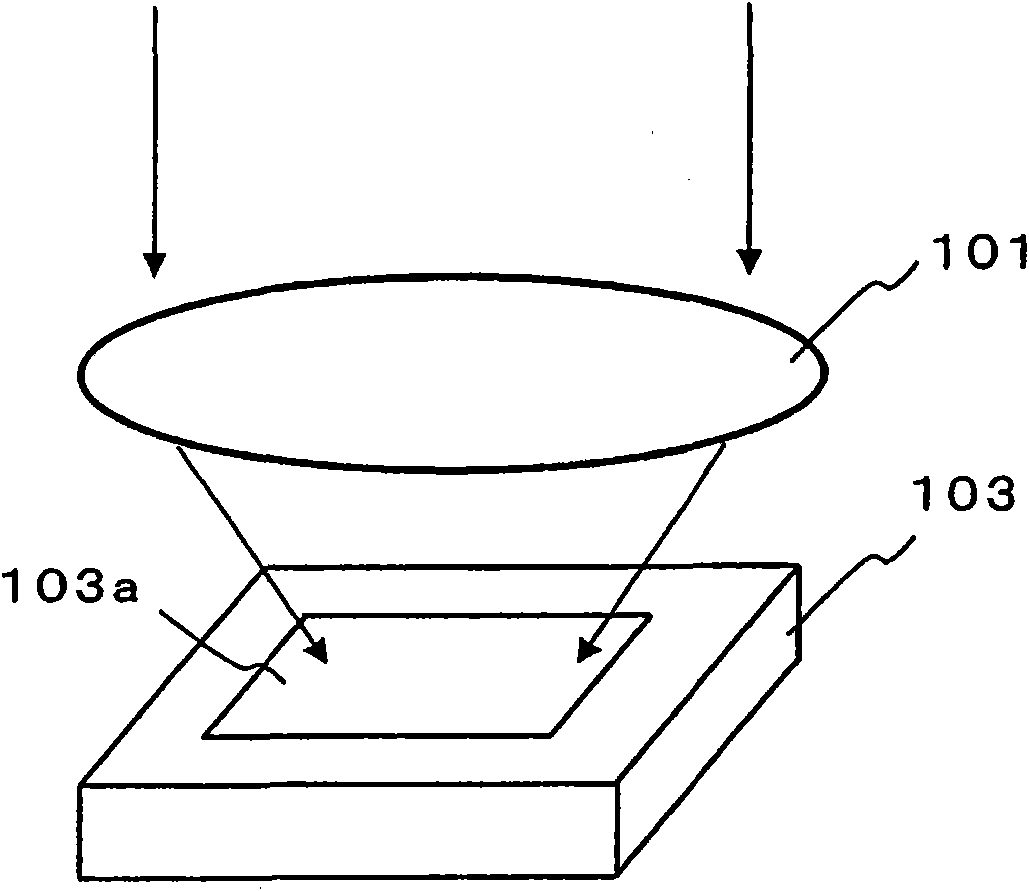
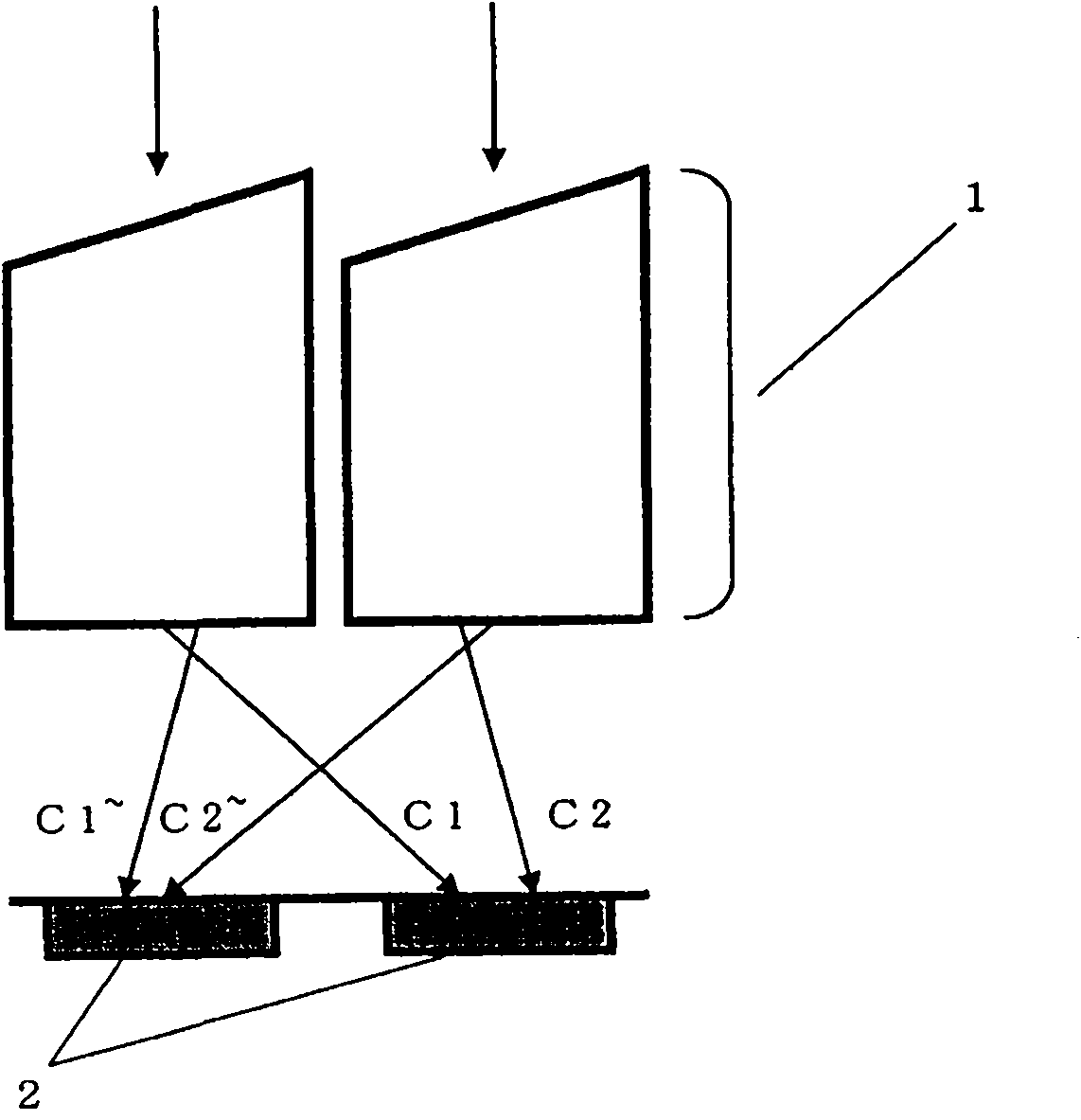
[0131] Figure 1A It is a perspective view schematically showing how light transmitted through the lens 101 enters the solid-state imaging device 103 . On the imaging surface 103 a of the solid-state imaging device 103 , a plurality of photosensitive cells are arranged two-dimensionally. As a result of imaging achieved by the lens 101 , the amount of light incident on the imaging surface 103 a (incident light amount) varies depending on the incident position. Typically, each photosensitive unit is a photodiode, and outputs an electrical signal (photoelectric conversion signal) corresponding to the amount of incident light through photoelectric conversion. Typically, the solid-state imaging element 103 is a CCD or a CMOS sensor, and is manufactured by known semiconductor manufacturing techniques. An array of optical elements having a spectroscopic function is provided at a position facing the surface on which the photosensitive cell array is formed in the solid-state imaging ...
Embodiment approach 2
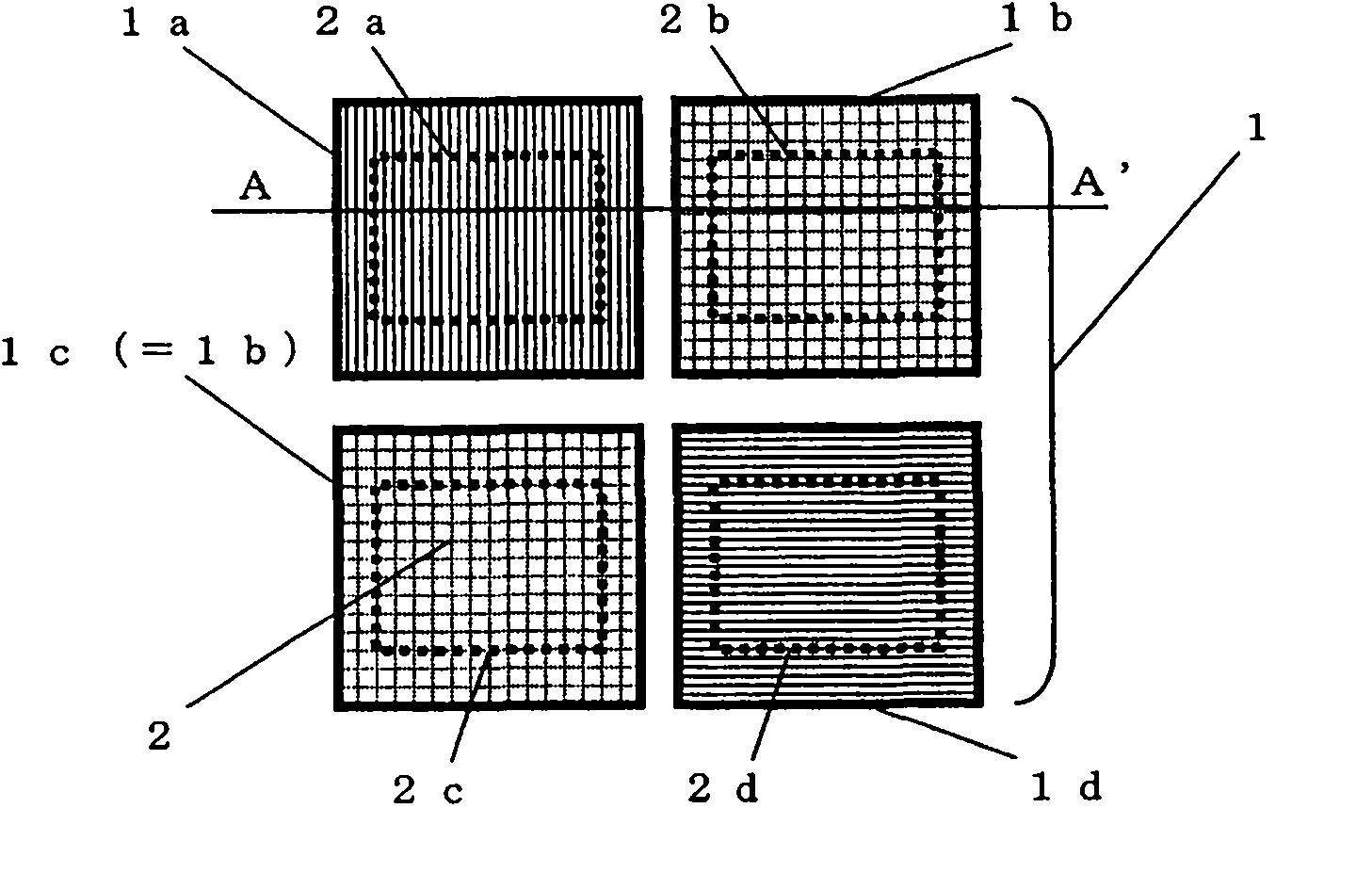
[0161] Next, a second embodiment will be described with reference to the drawings. Figure 2A It is a diagram showing the arrangement of an optical element array in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, and is a plan view of an imaging element basically composed of photosensitive cells in 2 rows and 2 columns. Figure 2B It is a plan view showing the type of light incident on the photosensitive cell.
[0162] The basic configuration of the present embodiment is similar to that of the first embodiment, except that the elements corresponding to the light-splitting elements 1d of the optical element array 1 are replaced with transparent elements 1e.
[0163] The spectroscopic elements 1a and 1b in this embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment. Therefore, the amount of light received by the photosensitive units 2a, 2b directly below them is also the same as Figure 2B As shown, it is the same as the case of Embodiment 1. Therefore, the color signal 2C2 and the ...
Embodiment approach 3
[0169] Next, a third embodiment will be described with reference to the drawings. 3 is a diagram showing the arrangement of an optical element array in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, and is a plan view of an imaging element basically composed of photosensitive cells in 2 rows and 2 columns. Figure 3B It is a plan view showing the type of light incident on the photosensitive cell.
[0170] The basic configuration of the optical element array is similar to that of Embodiment 1, except that the elements corresponding to the light-splitting element 1b and the elements corresponding to the light-splitting element 1c of the optical element array 1 are replaced with simple transparent elements 1e, Also exactly the same. That is, in the basic unit of 2 rows and 2 columns, one transparent element is used in Embodiment 2, and two transparent elements are used in this embodiment.
[0171] In this embodiment, there are two transparent elements 1e, and the light receiving units ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com