Relay zero crossing disconnection arc extinguishing method
A relay and zero-crossing technology, applied in the direction of relays, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as easy breakdown of air, high cost, and impact on the life of relay contacts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
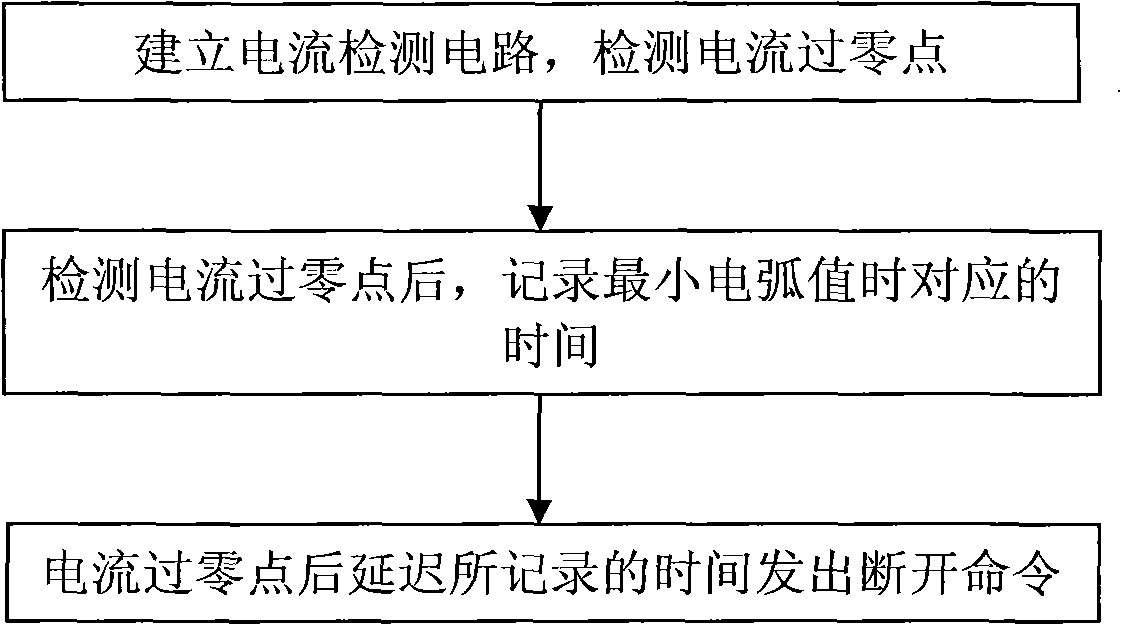
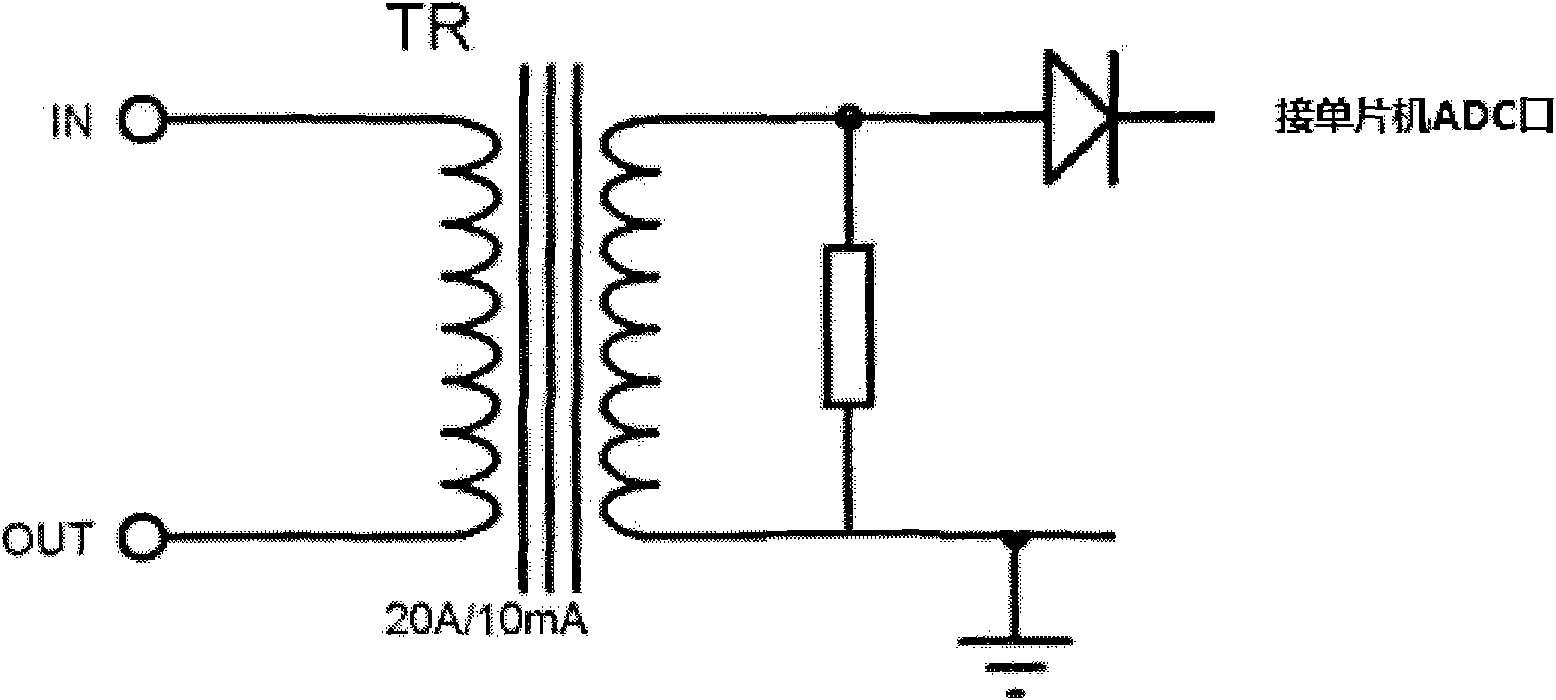
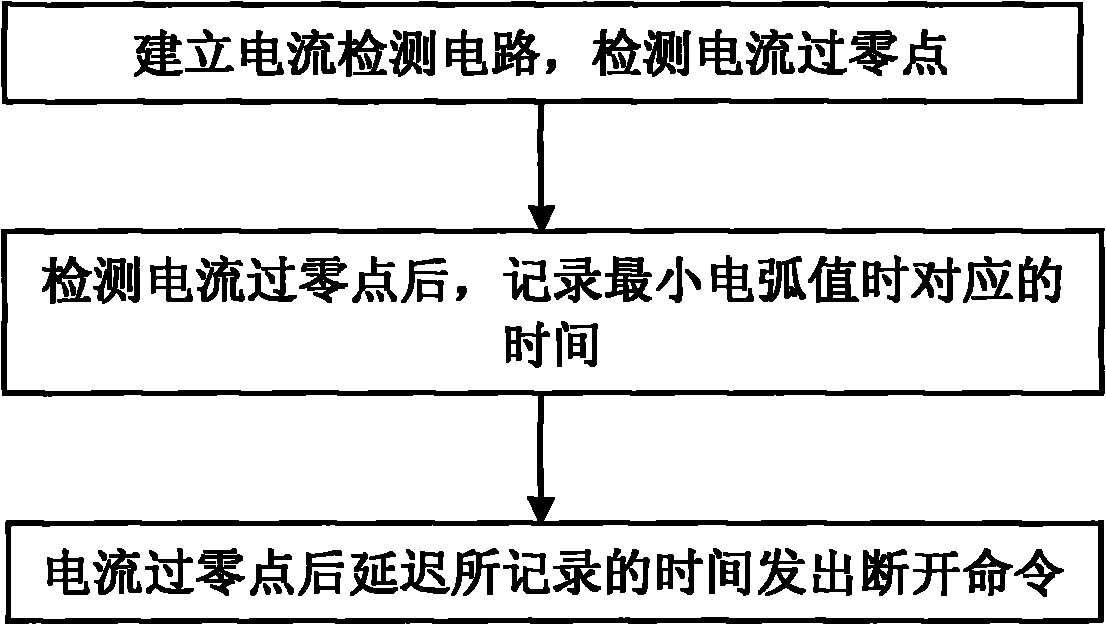
[0017] Connect the mechanical relay to a 2000W lighting load, use the Hall current sensor to convert the AC current value with a voltage of 220V and a frequency of 50Hz into a low-voltage signal of 0-5V, and then measure it through the ADC port of the ATMEGA16 microcontroller to identify the current within 15ms after detecting the zero-crossing point of the current, at an interval of 0.01ms, the ATMEGA16 microcontroller sends a disconnection command to the mechanical relay, observes the relay contacts, and records the arc value; take the time corresponding to the minimum arc is the delay time t, and store the delay time t into the EEPROM of the ATMEGA16 single-chip microcomputer. In the future, each time a command needs to be sent to the relay to be disconnected, the zero-crossing point of the current is first detected, and then the delay time t is controlled by the ATMEGA16 single-chip microcomputer to disconnect. The last delay time set in this embodiment is 9.6ms.
Embodiment 2
[0019] Connect the mechanical relay to a 1000W lighting load, use the Hall current sensor to convert the 220V AC current value into a 0-5V low-voltage signal, and then measure it through the ADC port of the ATMEGA16 microcontroller to identify the zero-crossing point of the current; detect Within 15ms after the zero-crossing point of the current, at an interval of 0.1ms, the ATMEGA16 microcontroller sends a disconnection command to the mechanical relay, observes the relay contacts, and records the arc value; take the time corresponding to the minimum arc as the delay time t and The delay time t is stored in the EEPROM of the ATMEGA16 single-chip microcomputer. In the future, when a command needs to be sent to the relay to be disconnected, the zero-crossing point of the current is first detected, and then the delay time t is controlled by the ATMEGA16 single-chip microcomputer. The last setting in this embodiment The latency is 9.6ms.
Embodiment 3
[0021] Connect the mechanical relay to a 500W lighting load, use the mutual induction coil to convert the 220V AC current value into a low-voltage signal of 0-5V, and then measure it through the ADC port of the ATMEGA64 microcontroller to identify the zero-crossing point of the current; detect the current Within 15ms after the zero point, at an interval of 0.2ms, the ATMEGA64 MCU sends a disconnection command to the mechanical relay, observes the relay contacts, and records the arc value; the time corresponding to the minimum arc is taken as the delay time t and the delay time t is stored in the EEPROM of the ATMEGA64 single-chip microcomputer. When it is necessary to send a command to the relay to be disconnected every time in the future, the zero-crossing point of the current is first detected, and then the delay time t is controlled by the ATMEGA64 single-chip microcomputer. The delay time is the last setting in this embodiment is 9.6ms.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com