Composite membrane for super straight solar cell, process for producing the composite membrane for super straight solar cell, composite membrane for substraight solar cell, and process for producing the composite membrane for substraight solar cell
A solar cell, super-straight technology, applied in the field of composite films, which can solve the problems of increased reflected light and decreased reflectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
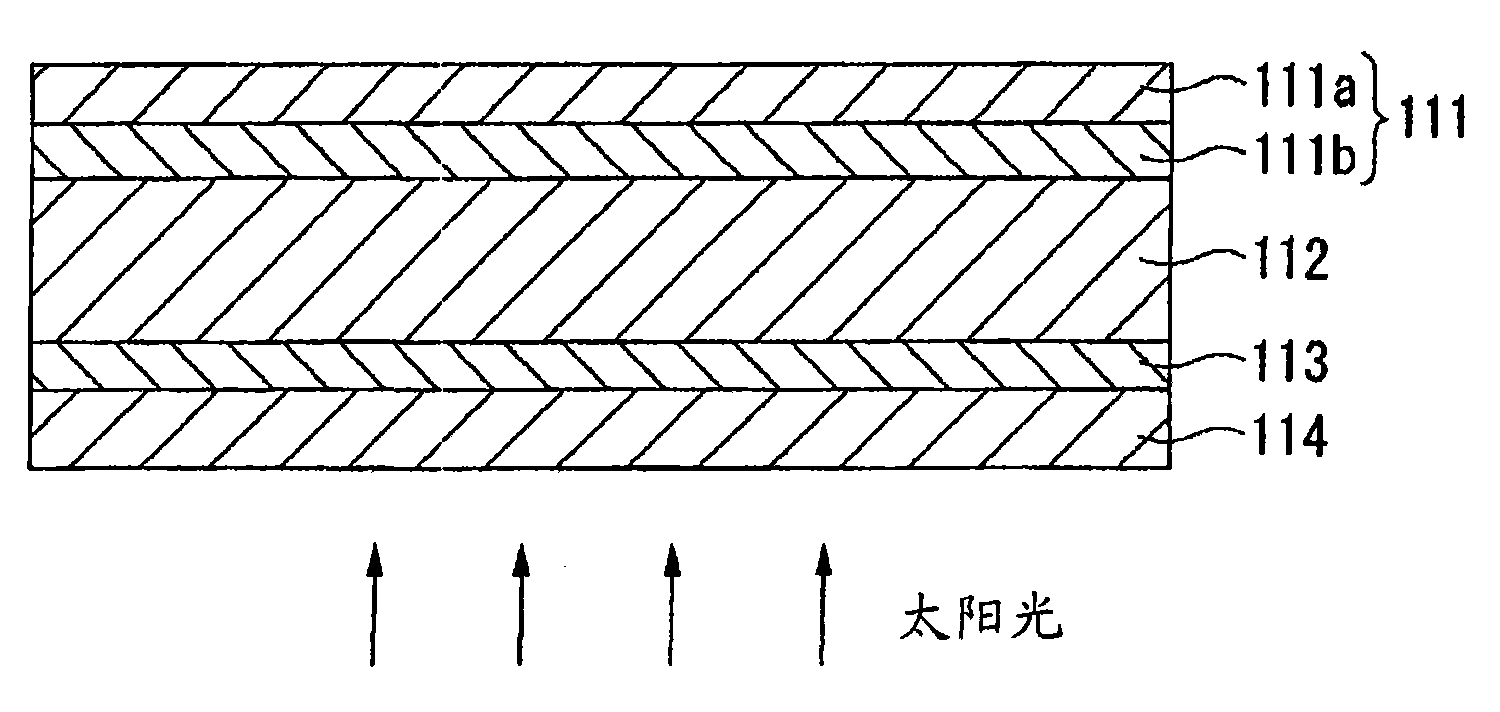
[0147] Ultra-straight thin-film solar cells are usually figure 1 As shown, a second transparent conductive film 111b is further formed on a layer formed by laminating a first transparent conductive film (transparent conductive film on the incident side of light) 113 and a photoelectric conversion layer 112 on a substrate 114 in this order, A conductive reflective film 111a is formed on the second transparent conductive film 111b.
[0148] Embodiment 1 of the present invention relates to an ultra-straight thin-film solar cell including two layers of a second transparent conductive film 111b formed on the photoelectric conversion layer 112 and a conductive reflective film 111a formed on the second transparent conductive film 111b. Composite Membrane 111.
[0149] In the composite film 111 according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, the second transparent conductive film 111b is formed by applying a composition for a transparent conductive film containing conductive oxid...
Embodiment approach 2
[0201] Ultra-straight thin-film solar cells usually have a first transparent conductive film (transparent conductive film on the incident side of light) and a photoelectric conversion layer stacked on the substrate in this order, and then a second transparent conductive film is formed on the photoelectric conversion layer. A structure in which a conductive reflective film is formed on the second transparent conductive film.
[0202] Embodiment 2 of the present invention relates to a composite film for an ultra-straight solar cell, which has a second transparent conductive film formed on a photoelectric conversion layer of an ultra-straight solar cell, and a conductive film formed on the second transparent conductive film. Sexual reflective film.
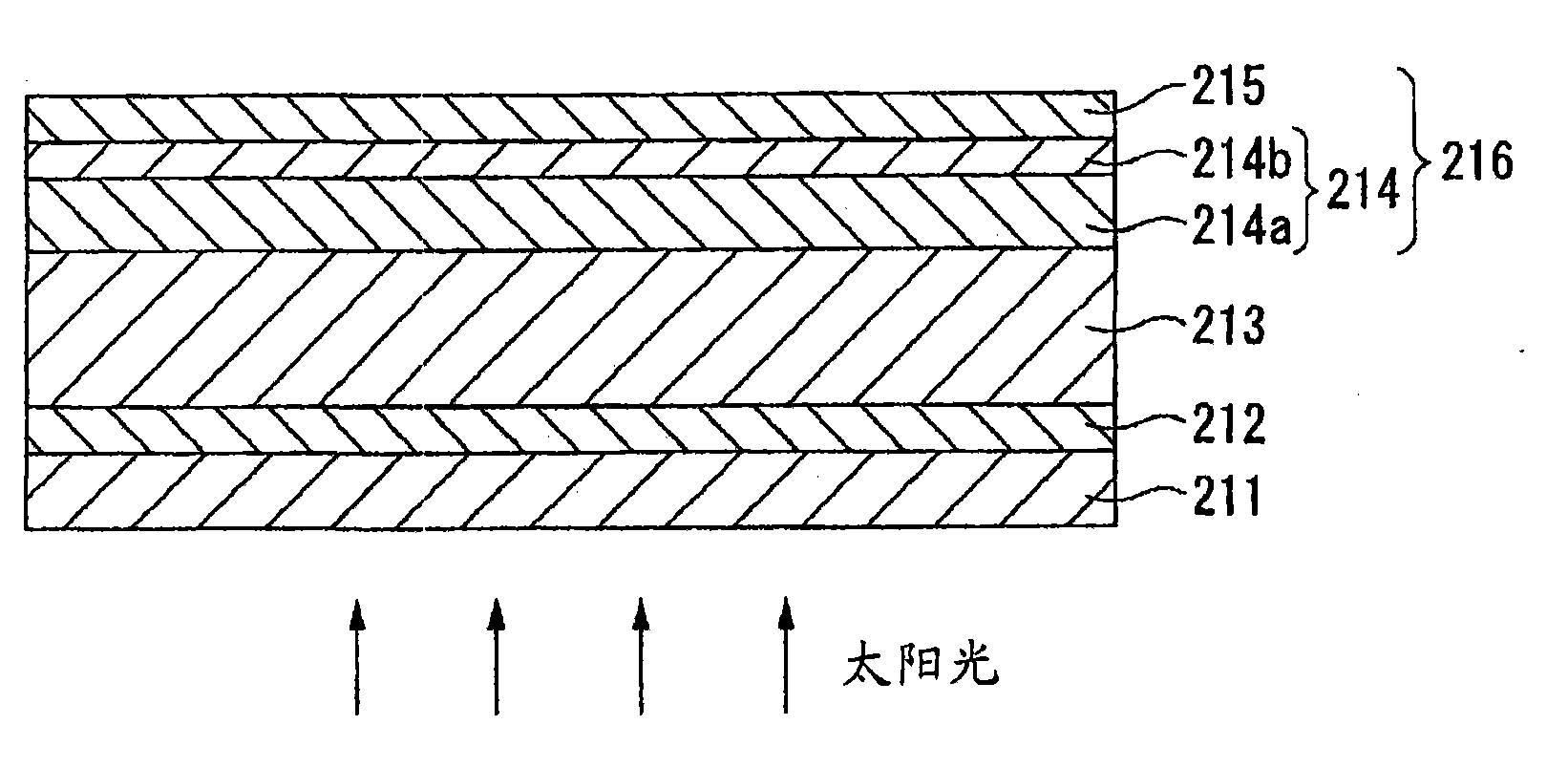
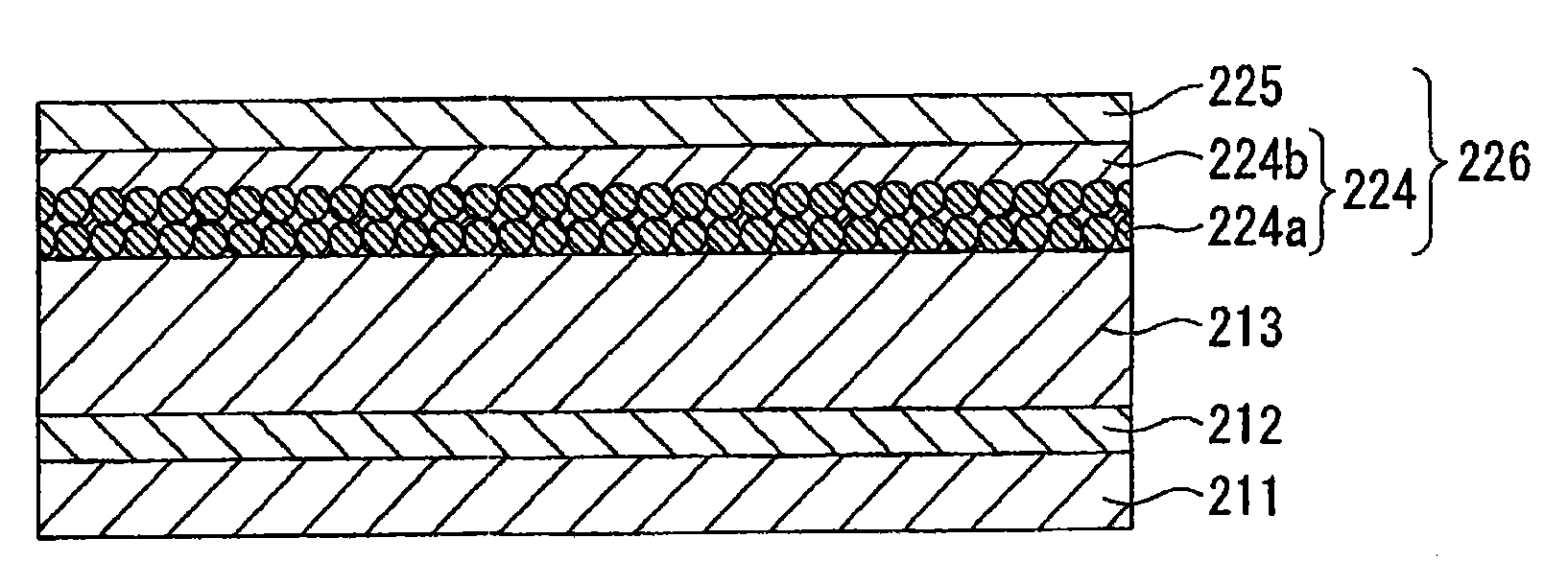
[0203] figure 2 It is a figure which schematically shows the cross section of the composite membrane which concerns on Embodiment 2 of this invention. The characteristic structure of the composite membrane 216 according to Embodim...
Embodiment approach 3
[0259] Substraight solar cells are usually as Figure 4 As shown, it has a structure in which a composite film 312 is formed on a substrate 311, and a photoelectric conversion layer 313 and a first transparent conductive film (transparent conductive film on the incident side of light) 314 are arranged on the composite film 312. A structure formed by stacking layers in sequence. The composite film 312 has a conductive reflective film 312a formed on the base material 311, and a second transparent conductive film 312b formed on the conductive reflective film 312a.
[0260] Embodiment 3 of the present invention relates to a composite film 312 for a substraight solar cell, which has a conductive reflective film 312a formed on a substrate 311 and a second transparent conductive film 312b formed on the conductive reflective film 312a. Floor.
[0261] In the composite film 312 according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention, the conductive reflective film 312a is formed by coatin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com