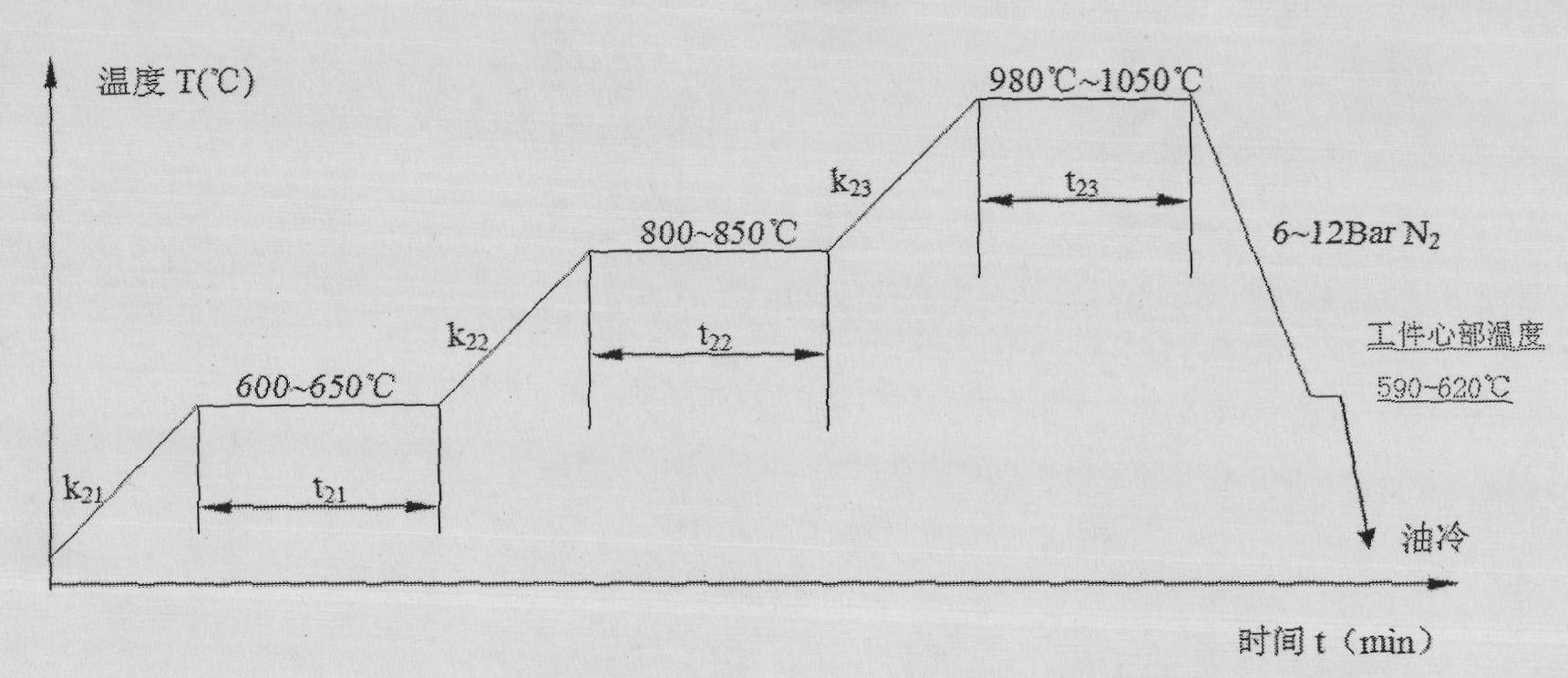
Quenching process of H13 steel for compression molds
A die-casting mold and process technology, applied in the field of quenching technology, can solve the problems of affecting the service life of the mold, reducing the comprehensive performance of the workpiece, and low cooling speed, so as to reduce the probability of occurrence, ensure the quality of quenching, and control the amount of deformation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Vacuum the vacuum high-pressure gas quenching furnace until the pressure in the furnace is 0.8X10 -1 Pa, after filling high-purity N with a pressure of 100Pa 2 Protect; heat up at a heating rate of 5°C / min, and keep warm when the furnace temperature reaches 600°C until the temperature difference between the surface of the treated piece and the core is less than 50°C; continue heating at a heating rate of 5°C / min, when the furnace When the temperature reaches 800°C, heat preservation is carried out until the temperature difference between the surface of the treatment piece and the core is less than 50°C; then continue to heat up at a heating rate of 10°C / min. When the furnace temperature reaches 980°C, heat preservation is carried out until the treatment piece is completely heated. Continue to keep warm for 30 minutes. Fill the vacuum high-pressure gas quenching furnace with N2, and cool the treated piece to a core temperature of 590°C; then take the resulting treated p...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Vacuum the vacuum high-pressure gas quenching furnace until the pressure in the furnace is 1.0X10 -1 Pa, after filling high-purity N with a pressure of 1000Pa 2 Protect; heat up at a heating rate of 8°C / min, and keep warm when the furnace temperature reaches 650°C until the temperature difference between the surface of the treated piece and the core is less than 50°C; continue heating at a heating rate of 8°C / min, when the furnace When the temperature reaches 850°C, heat preservation is carried out until the temperature difference between the surface of the treatment piece and the core is less than 50°C; then continue to heat up at a heating rate of 8°C / min. When the furnace temperature reaches 1050°C, heat preservation is carried out until the treatment piece is completely heated. Continue to keep warm for 15 minutes. Fill N into the vacuum high-pressure gas quenching furnace 2 , cooling the treated piece to a core temperature of 620°C, and keeping it warm in a vacuu...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Vacuum the vacuum high-pressure gas quenching furnace until the pressure in the furnace is 0.9X10 -1 Pa, after filling with high-purity N with a pressure of 10Pa 2 Protect; heat up at a heating rate of 6°C / min, and keep warm when the furnace temperature reaches 625°C until the temperature difference between the surface of the treated piece and the core is less than 50°C; continue heating at a heating rate of 6°C / min, when the furnace When the temperature reaches 840°C, heat preservation is carried out until the temperature difference between the surface of the treatment piece and the core is less than 50°C; then continue to heat up at a heating rate of 9°C / min. When the furnace temperature reaches 1000°C, heat preservation is carried out until the treatment piece is completely heated. Continue to keep warm for 20 minutes. Fill N into the vacuum high-pressure gas quenching furnace 2 , cool the treated piece to a core temperature of 600°C, then take the treated piece ou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com