Method and system for improving encryption/decryption speed of passive optical network
A passive optical network, encryption and decryption technology, applied in the direction of transmission system, digital transmission system, multiplexing system selection device, etc., can solve the problems that it is difficult to ensure timely exchange of keys, and the speed of encryption processing cannot be guaranteed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
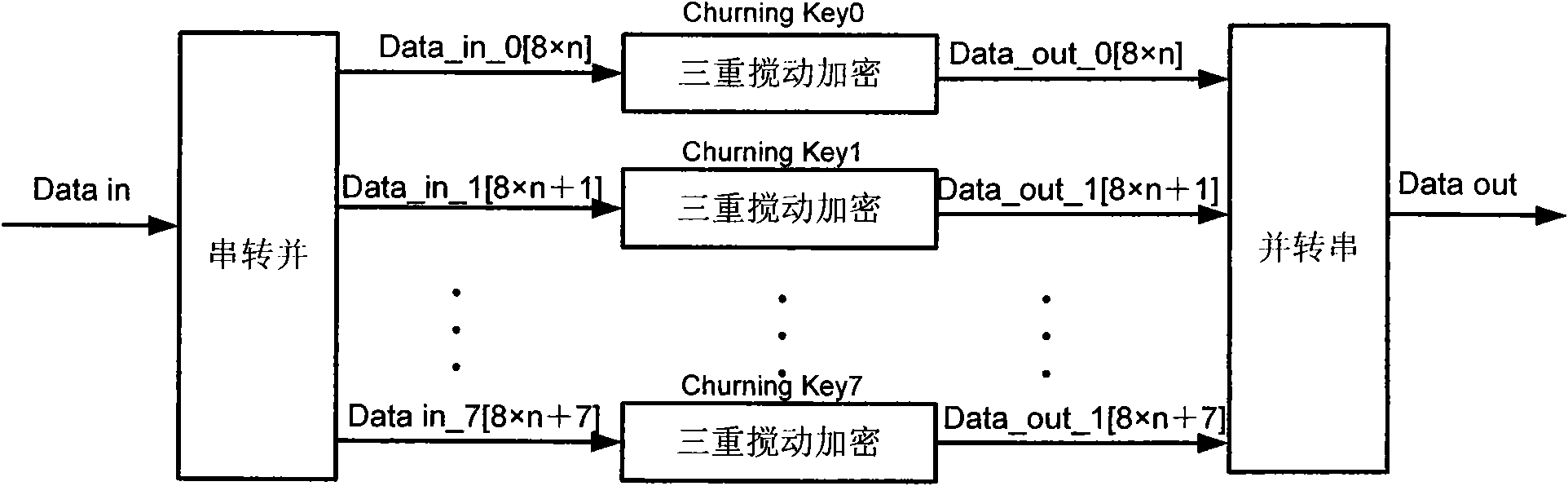
[0066] The number of stirring keys is the same as the number of seed keys, that is, m is equal to N, and the OLT and ONU directly use these m seed keys for encryption and decryption respectively. The ONU sends the seed key to the OLT through the new_churning_key message. The churning_key field in the new_churning_key message is originally 3 bytes, but is extended to 3×m bytes. In this embodiment, since N=m, only 33-3*(N-1) bytes remain in the Pad field. After receiving it, the OLT takes out the key and directly corresponds to each encrypted block.
[0067] Taking N equal to 8 as an example, combine Figure 5 Explain the corresponding steps:
[0068] Step 1: ONU generates 8 keys;
[0069] Step 2: Fill in the values of the 8 keys into the churning_key0 to churning_key7 fields of the new_churning_key message;
[0070] Step 3: ONU sends new_churning_key message to OLT, the message format is as follows image 3 shown;
[0071] Step 4: After receiving the new_churning_key m...
Embodiment 2
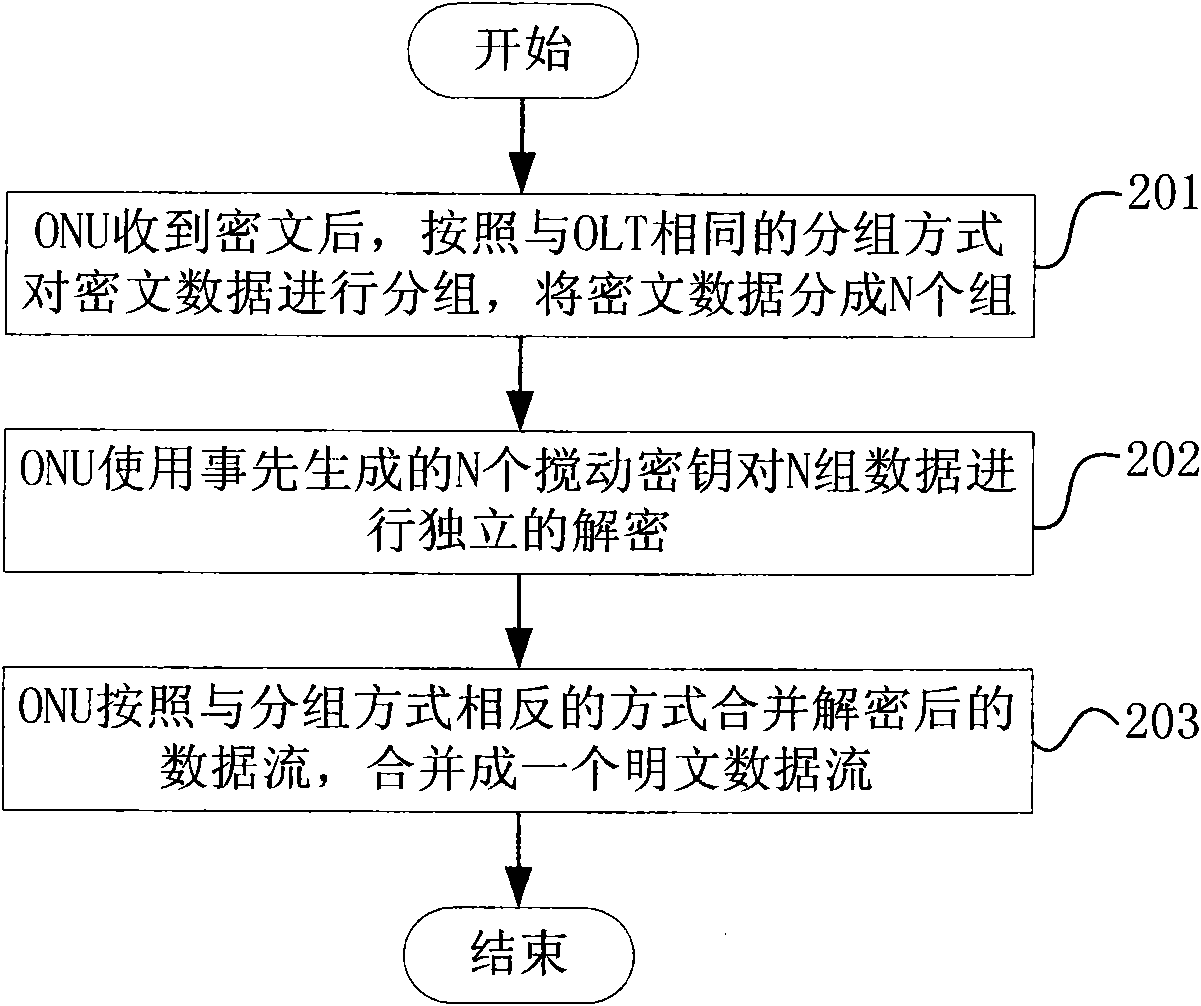
[0073] ONU and OLT use the same algorithm to generate N churning keys using m seed keys. The method for generating N keys may be through shift or bit operation, but is not limited to this method. If the number m of seed keys is less than the number N of churning keys, the ONU sends the seed key to the OLT through a new_churning_key message. The churning_key field in the new_churning_key message was originally 3 bytes, but here it is extended to 3×m bytes, so that only 33-3×(m-1) bytes remain in the Pad field. After receiving the new_churning_key, the OLT uses the same method as the ONU to use the m seed key carried in the new_churning_key to generate N seed keys, corresponding to each encrypted block.
[0074] Taking m equal to 4 and N equal to 8 as an example, combine Figure 6 Explain the corresponding steps:
[0075] as attached Figure 4 Shown:
[0076] Step 1: ONU generates 4 keys;
[0077] Step 2: Fill in the values of the four keys into the churning_key0 to chur...
Embodiment 3
[0101] Due to the limitation of the message body, for example, only t keys can be transmitted, and the m seed keys can be transmitted in multiple times. If you pass t each time, you will pass (N-1) / t+1 times in total. The key index is the same every time. The OLT obtains N keys after receiving all the messages. The churning_key field in the new_churning_key message is originally 3 bytes, which can be extended to a maximum of 24 bytes (there is also a 12-byte Pad for other functions), so that the first (N-1) / t messages can be replaced by churning_key The Pad fields used are all occupied. After receiving it, the OLT takes out the key and directly corresponds to each encrypted block.
[0102] Taking N equal to 20 and m equal to 20 as an example, combine Figure 5 and 6 Explain the corresponding steps:
[0103] Step 1: ONU generates 20 keys;
[0104] Step 2: ONU fills the values of 0-7 keys into the churning_key0 to churning_key7 fields of the new_churning_key message;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com