Method for determining a switching time of an electrical switching device
A technology of electrical switches and switching times, applied in the direction of electrical switches, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of expensive, undeterminable switching times, etc., and achieve the effect of cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
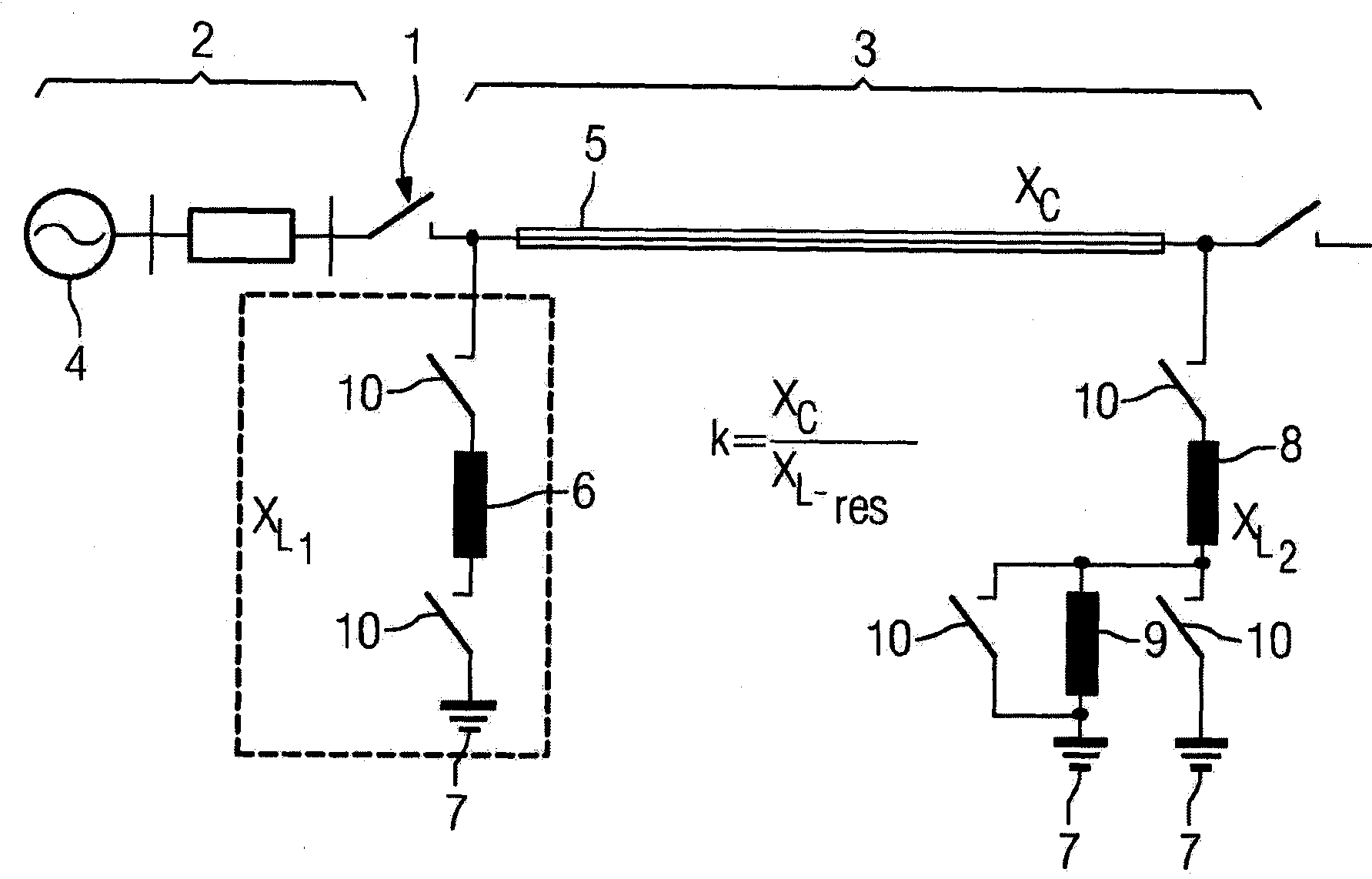
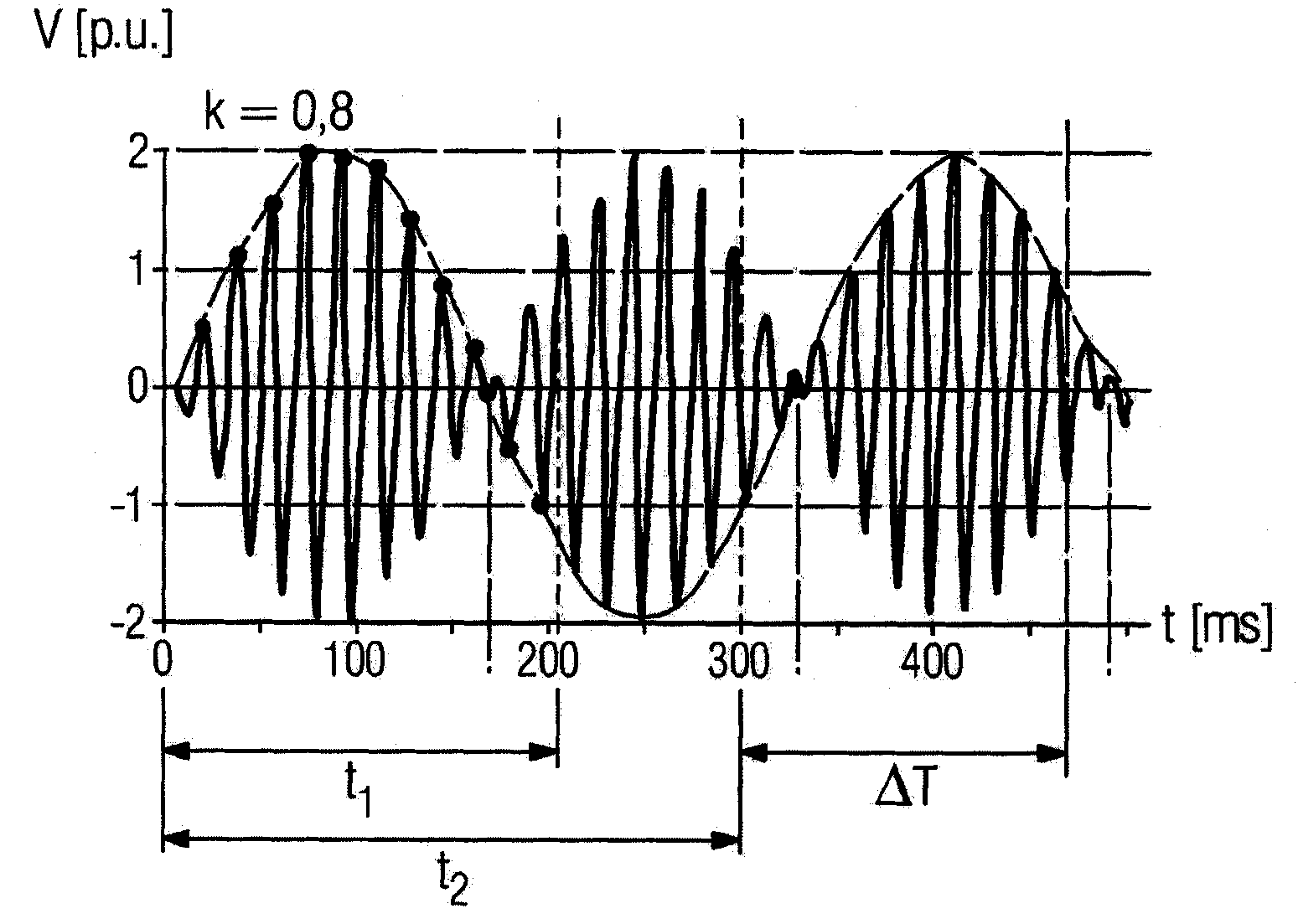
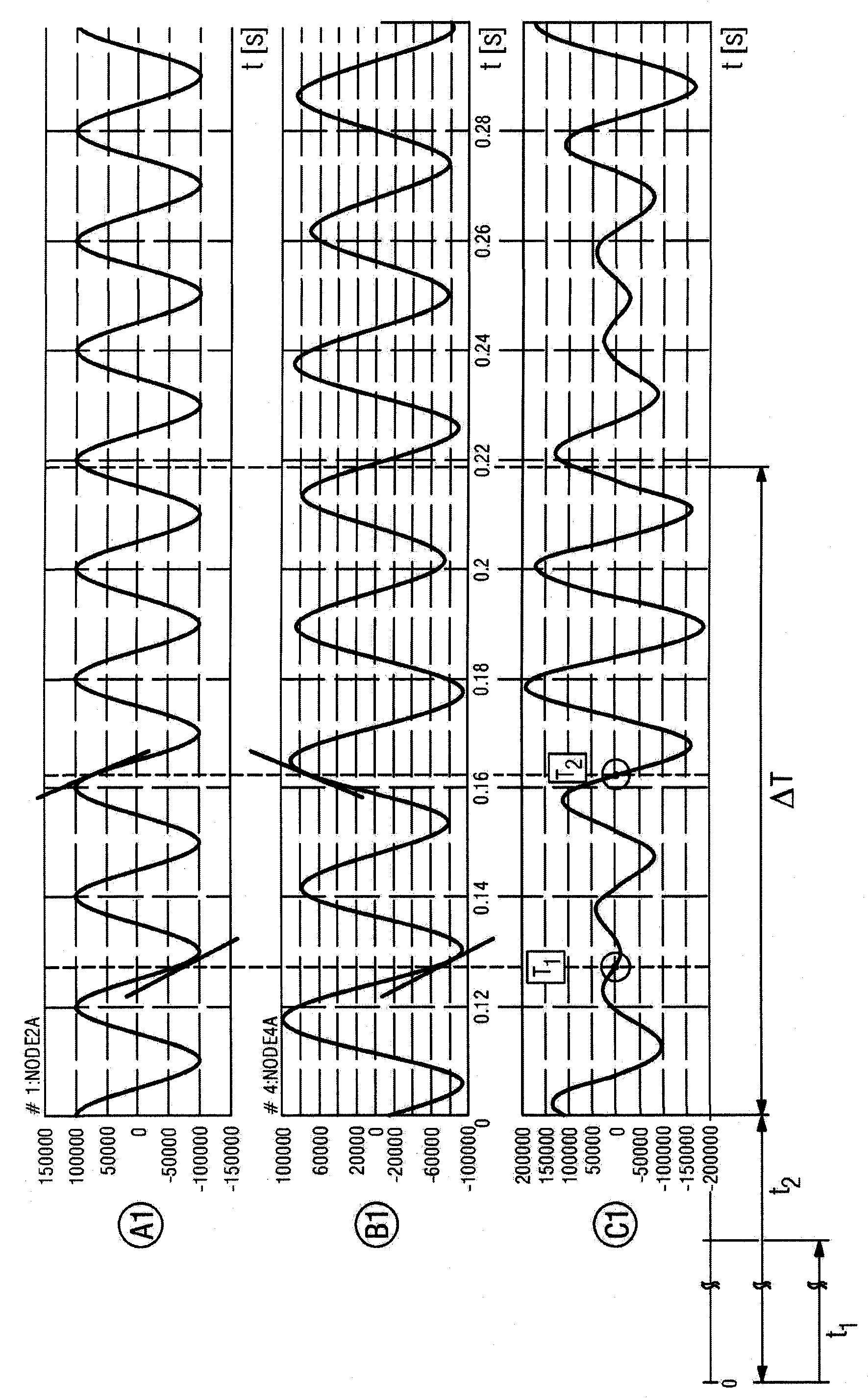
[0020] figure 1 The schematic structure of a line section within a power transmission network is shown. The electrical switch has a breaker gap 1 which is formed, for example, by two contact elements which are movable relative to one another. The first line part 2 and the second line part 3 can be connected to each other or separated from each other through the circuit breaker gap 1 . The first line part 2 has a generator 4 which supplies a driving voltage, for example a 50 Hz alternating voltage of a polyphase alternating current system. The second line part 3 has an overhead wire 5 which is connectable at its first end to ground potential 7 via a first choke coil 6 and at its second end to ground potential via a second choke coil 8 7 connections. Furthermore, it can additionally also be proposed to connect a further choke coil 9 to the second choke coil 8 . Via different switching devices 10 , the inductor coils 6 , 8 , 9 can be connected to ground potential in different...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com