System for realizing life cycle model of plate blank in basic automation
A basic automation and life cycle technology, which is applied in the system field of realizing the slab life cycle model, can solve the problems that the actual pulling speed in the cooling area cannot be accurately obtained by the frequency converter, the target flow rate in the cooling area is inaccurate, and the speed is reduced to achieve the solution goal The problem of accurate flow control, improving the accuracy of target flow control, and avoiding the effect of time lag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
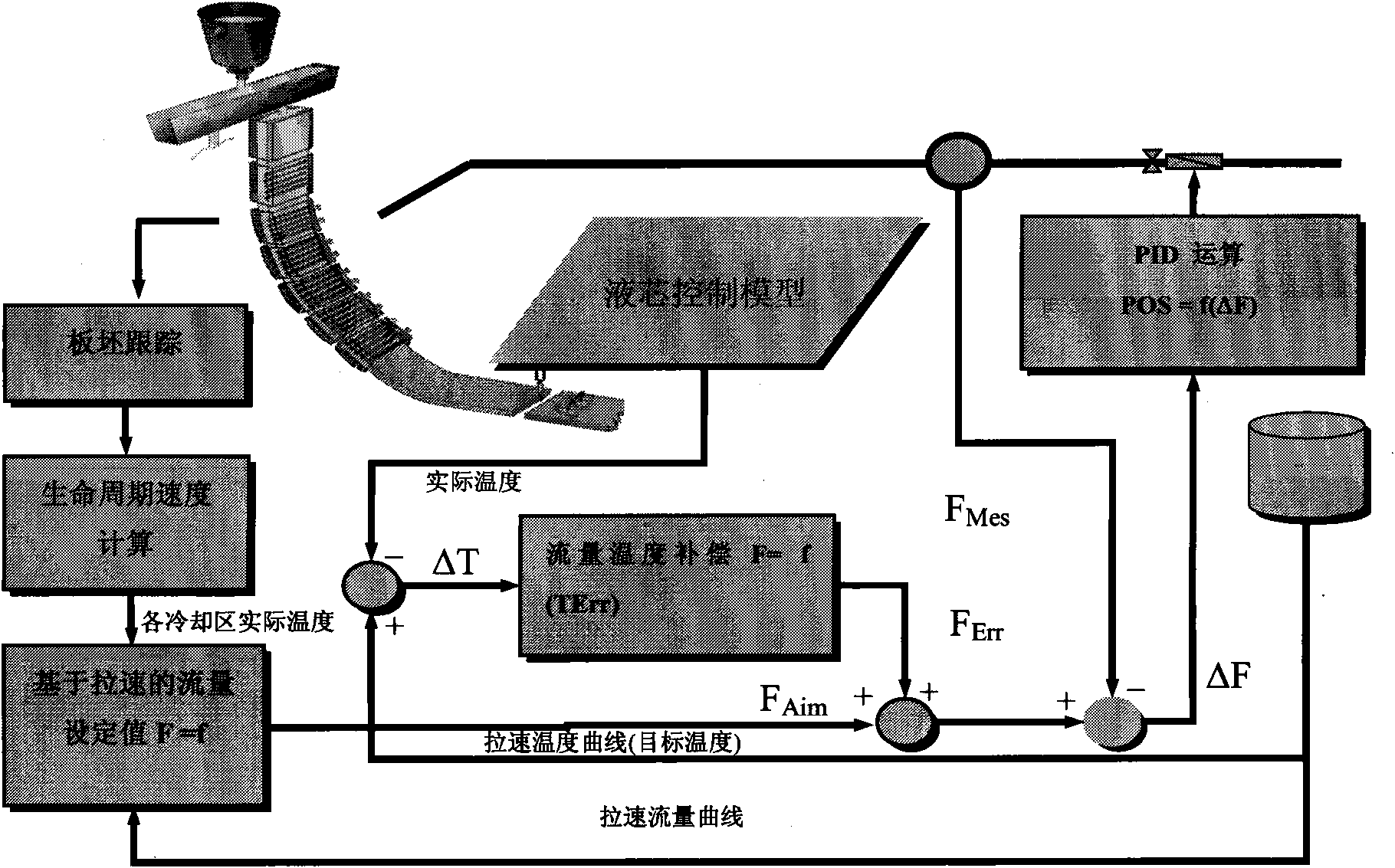
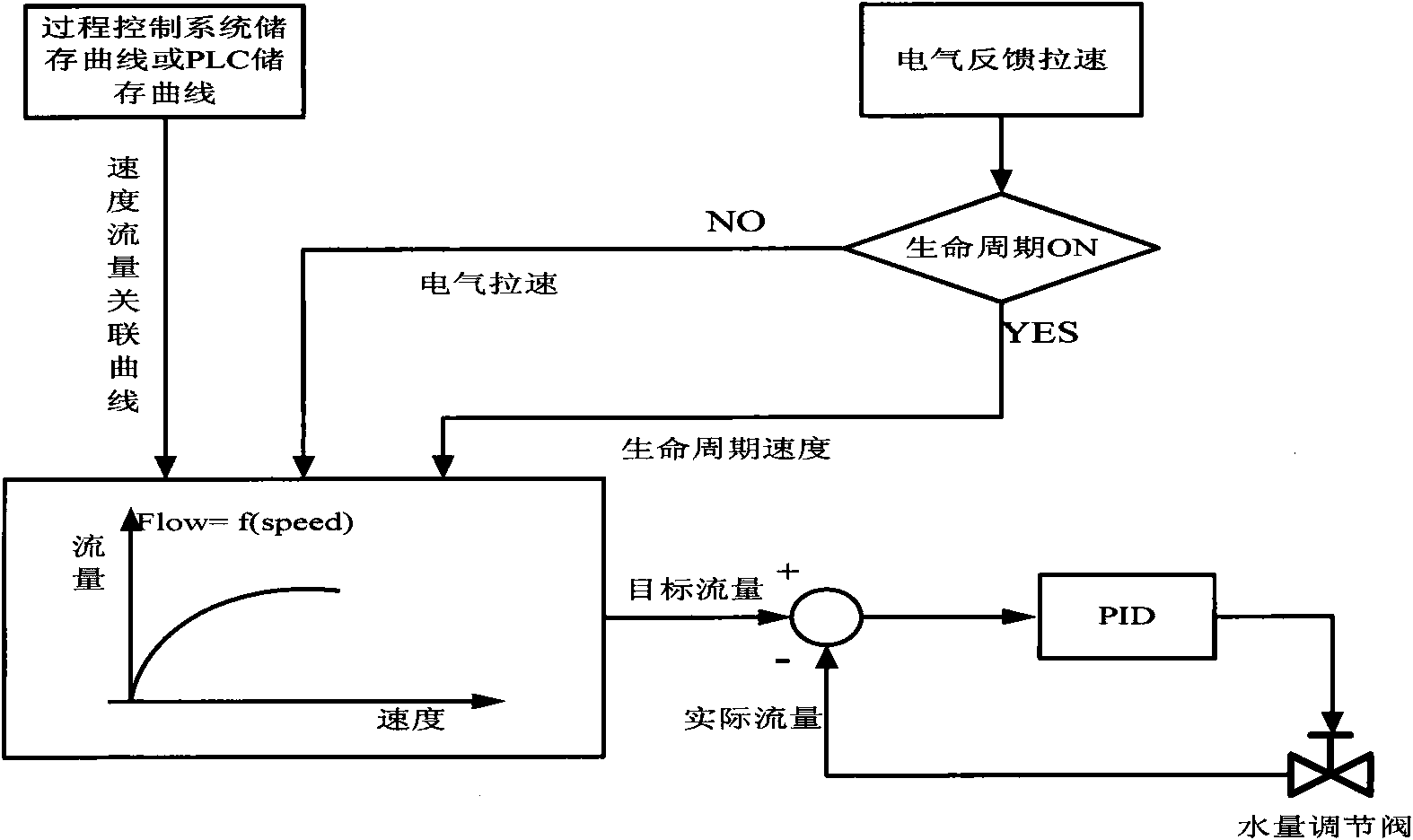
[0029] see figure 1 As shown, in an embodiment of the present invention, the system for implementing the slab life cycle model in basic automation includes:
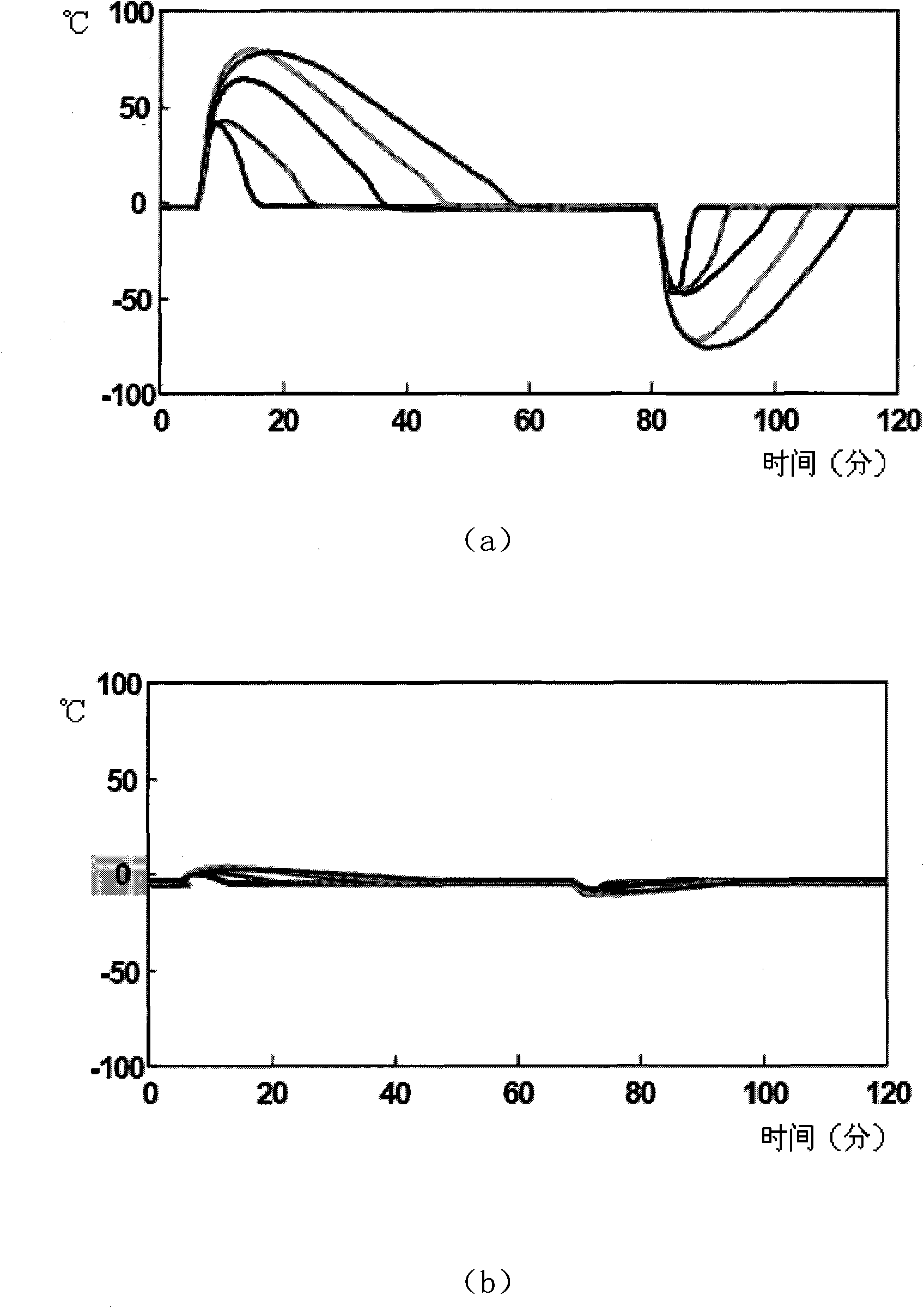
[0030] The slab tracking module dynamically tracks the heat flow slices, and divides the heat flow into N (N is an integer greater than 1) cooling zones (or cooling loops) according to mechanical and process design, and each cooling zone is further divided into M (M is an integer greater than 1) slices with a length of 100mm, and the time when each slice is poured out of the crystallizer is stored in the time queue data block (combined with Figure 4 shown) and move forward with the slice (because of pouring), until the slice is out of the casting machine.
[0031] The time queue structure for each cooling circuit PLC to track slices is as follows: Figure 4 as shown ( Figure 4 Middle V 1 , V 2 , Vn respectively represent the actual speed of cooling circuit 1, the actual speed of cooling circuit 2, and the actual s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com