Method for monitoring step profiler in measuring accuracy of chip groove depth
A groove depth and chip measurement technology, applied in measurement devices, semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurement, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not meeting the set depth requirements, time-consuming, inaccurate measurement data, etc. Guaranteed effect of accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings of the specification.
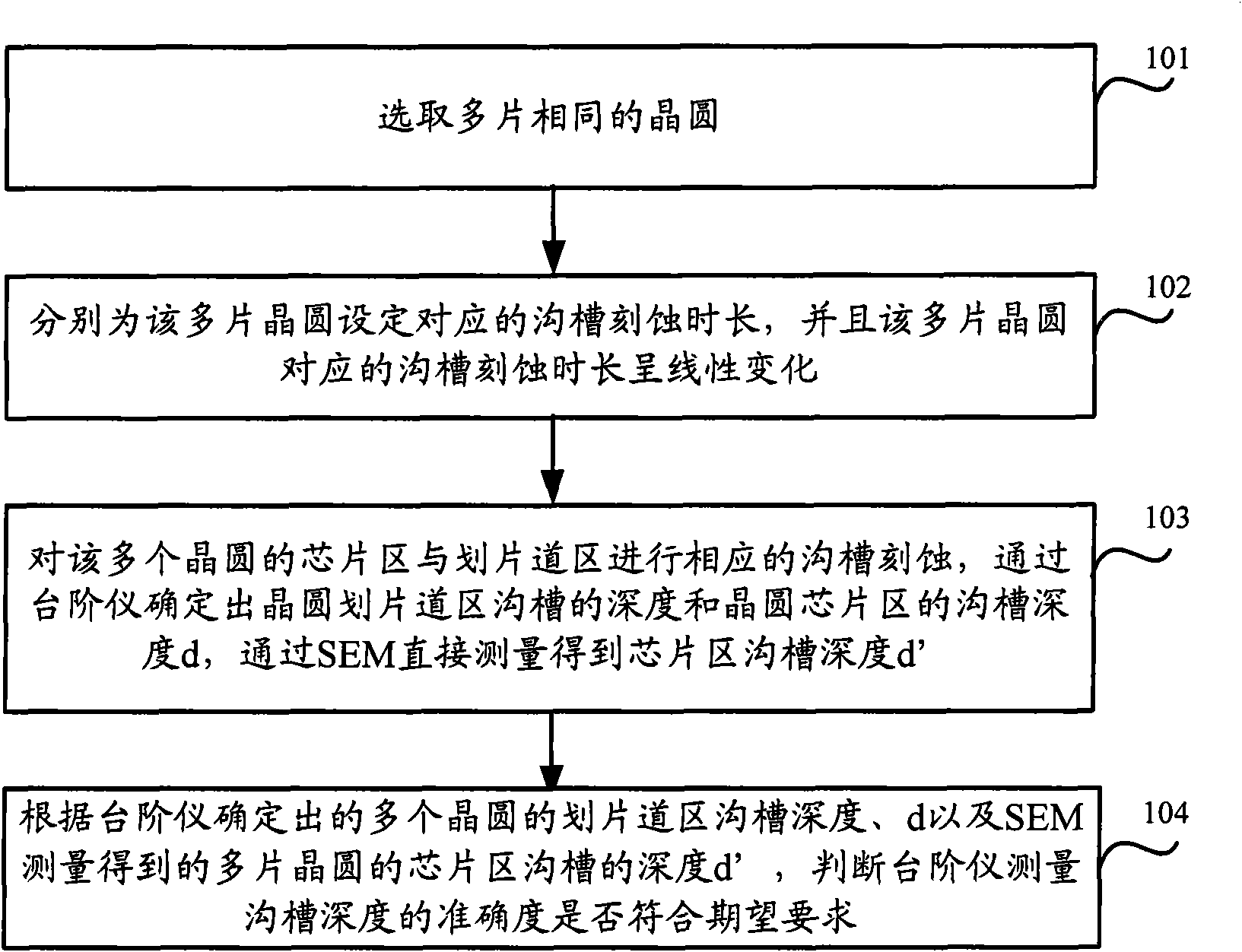
[0024] See Figure 1A , Is the method flow of the monitoring step meter measuring the accuracy of the chip groove depth in the embodiment of the present invention, and the flow includes the steps:
[0025] Step 101: Select multiple same wafers, including the same material and the same polarity.
[0026] Step 102: Set corresponding trench etching durations for the multiple wafers respectively, and the trench etching durations corresponding to the multiple wafers vary linearly.
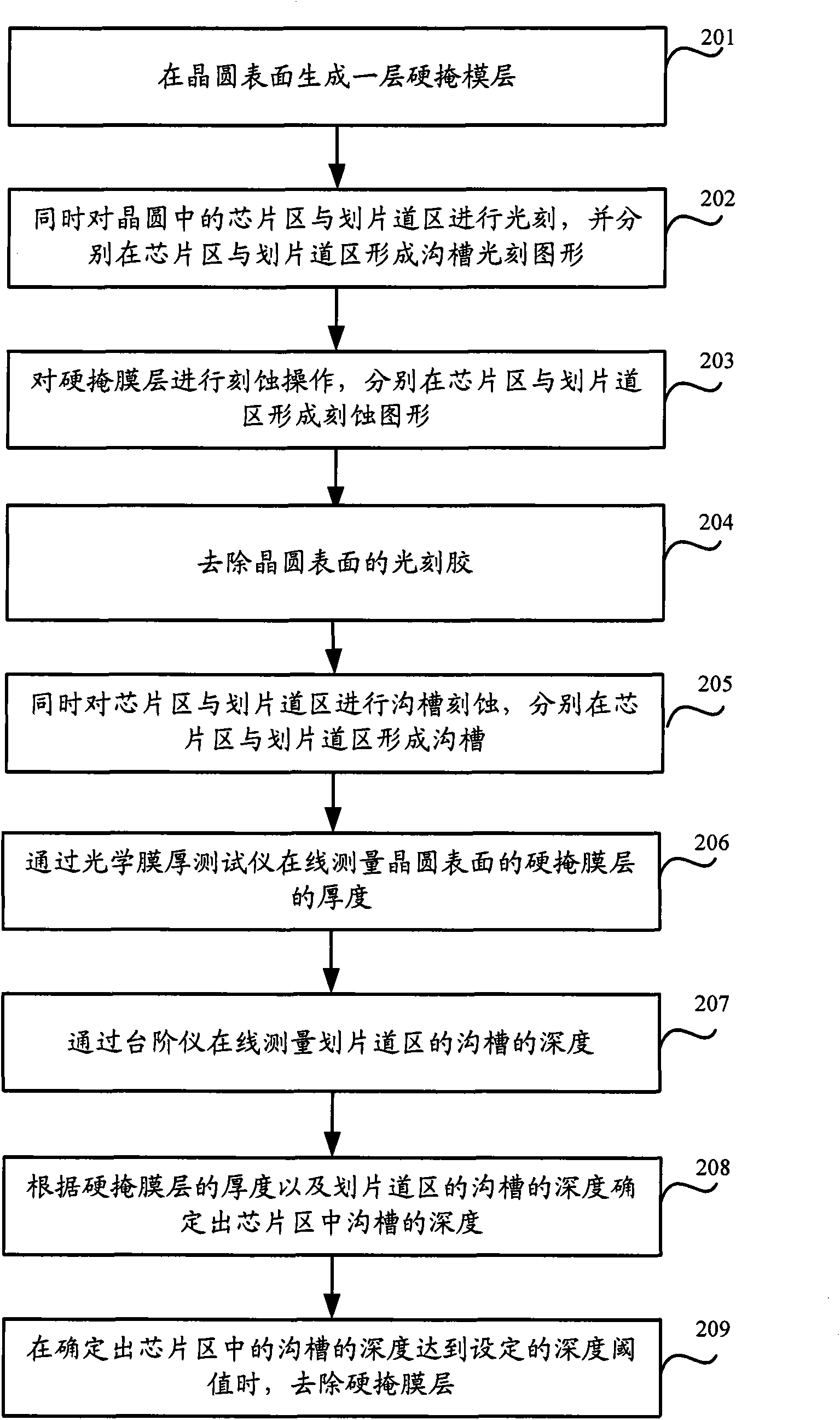
[0027] Step 103: For each wafer, trench etching is performed in the chip area and scribing track area of the wafer, and the trench etching time is the same as the set etching time corresponding to the wafer. A groove is formed in the scribing track area; and the depth of the groove in the scribing track area of the wafer is measured by a step meter, and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com