Pest-control compositions and methods having high target and low non-target activity
A technology for controlling pests and compositions, applied in the directions of botanical equipment and methods, animal repellents, plant growth regulators, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0163] Compositions for controlling insects were prepared according to the following table:
[0164] Element
CAS
W / W
white thyme oil
8007-46-3
20.6
Isopropyl myristate
110-27-0
34.3
[0165] oil of wintergreen
45.1
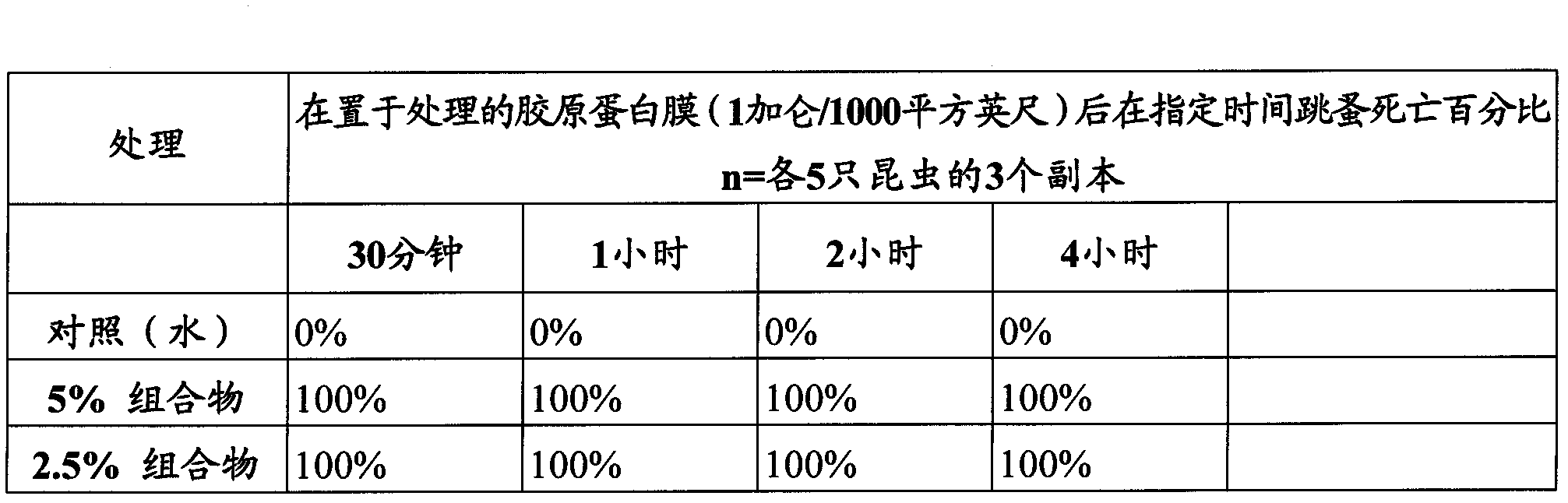
[0166] Compositions were tested against fleas by adding various concentrations of the composition to a collagen membrane (1 gallon per 1000 square feet) and then placing fleas (n=3, replicas of 5 fleas each) on the membrane ability to control insects. 跳蚤死亡率在附 figure 2 Measured at the time points indicated in .
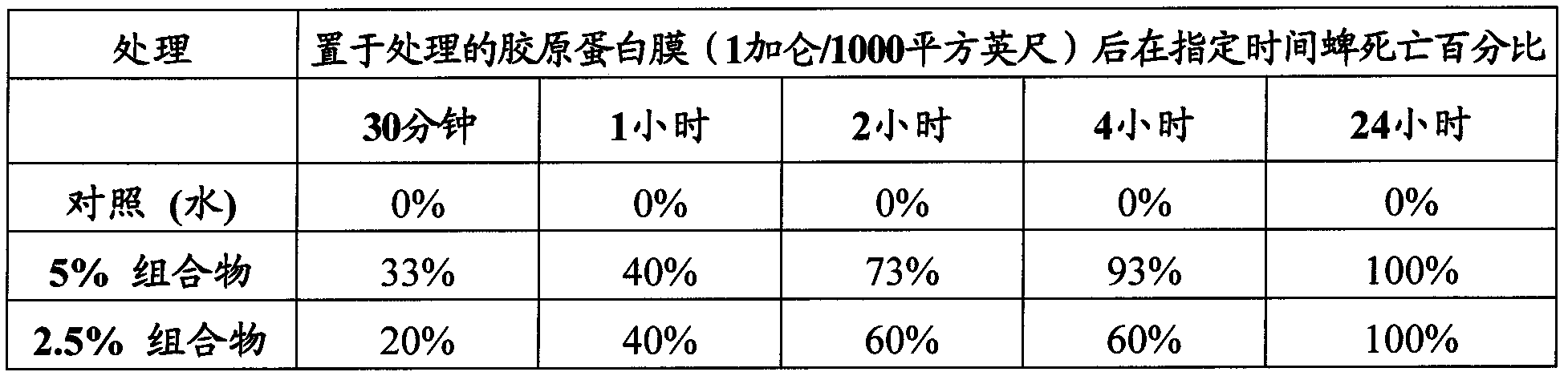
[0167]The compositions were then tested by adding various concentrations of the compositions to the collagen membrane (1 gallon per 1000 square feet) and then placing fleas (n=3, 5 tick replicas each) on the membrane Insect control against ticks. Tick mortality in the image 3 Measured at the time points indicated in .
[0168] The data reflect the selectivity of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0170] LD of chemicals that will be tested 50 Values (determined for wild-type flies) apply locally to wild-type and tyramine receptor mutant (TyrRneo30) lines. Mortality was determined 24 hours after treatment. Data are the average of three replicates with 5 flies per replicate. This experiment was repeated five times.
[0171] data (attached Figure 4 ) shows the selectivity of the thymol and carvacrol test chemicals, which do not affect flies expressing mutant forms of the tyramine receptor.
Embodiment 3
[0173] Test compositions for controlling parasites were prepared according to Table 1.
[0174] Mice were treated with various dose levels of the test composition for different periods of time (see appendix Figure 5 ). Briefly, the test composition was administered to mice in varying amounts (1 mg / kg body weight, 10 mg / kg body weight, or 100 mg / kg body weight) over a period of three or three weeks, after which 200 hatchable eggs of H. nana Infect every animal. During the incubation period of 2 weeks post-infection, the animals continued to be treated with the different test amounts of the blend composition. During the third week post-infection, the feces of the treated and infected mice were examined, and then the mice were sacrificed at the end of the third week to determine the cure rate. Background infection numbers were established by infecting untreated animals with 200 hatchable eggs of H. nana.
[0175] The results obtained show that, although the composition is ef...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com