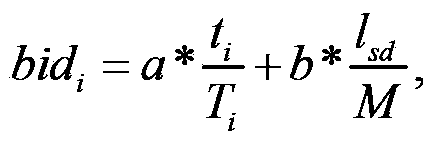Lightest carrying optical track resource allocation system for optical track network
A technology for light rail network and resource allocation, which is applied in transmission systems, digital transmission systems, data exchange networks, etc., and can solve the problems that cannot meet the real-time requirements of light rail network services, the utilization rate of light rail resources is low, and it is impossible to realize light rail network. Light rail resource allocation and other issues to achieve the effect of reducing the number of setup and teardown, improving latency requirements, and reducing network congestion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031]A light-weight optical track distribution system based on an optical track network, including a light-weight optical track distribution scheme for an optical track network, including an optical fiber link containing N unidirectional optical tracks, N>1, And N is a natural number. One of the one-way optical tracks contains M nodes, M≥3, and M is a natural number; each node has a local database for storing optical track information; network service requests are divided into voice type, video type, file There are three types. The lightest load light track distribution system also includes:
[0032] tag value (bid i ) calculation module to calculate the label value of the data request node to determine the priority of the node. The label value calculation adopts the method of setting different weights. The label value calculation formula is as follows:
[0033] bid i = a * t ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The resource allocation system of this embodiment also includes:
[0052] Light track load ratio (P j ) calculation module, which is used to reflect the influence degree of the new arrival request on the load on the light track. The calculation formula is: That is, when track j is assigned to a new request, the ratio of the original load on the track to the total load. The larger the ratio, the heavier the load on the light track. where D j Indicates the size of the existing load on the directly accessible light track j. D. i Indicates the size of the newly requested capacity at node i. D. i +D j Indicates the total load on track j after track j is allocated to new incoming requests.
[0053] Load Adjustment Factor (T j ) computing module, since new requests may cause loss of original requests on the optical track, an adjustment factor is needed to balance the load while reducing the packet loss rate. The load adjustment factor is represented by the ratio of...
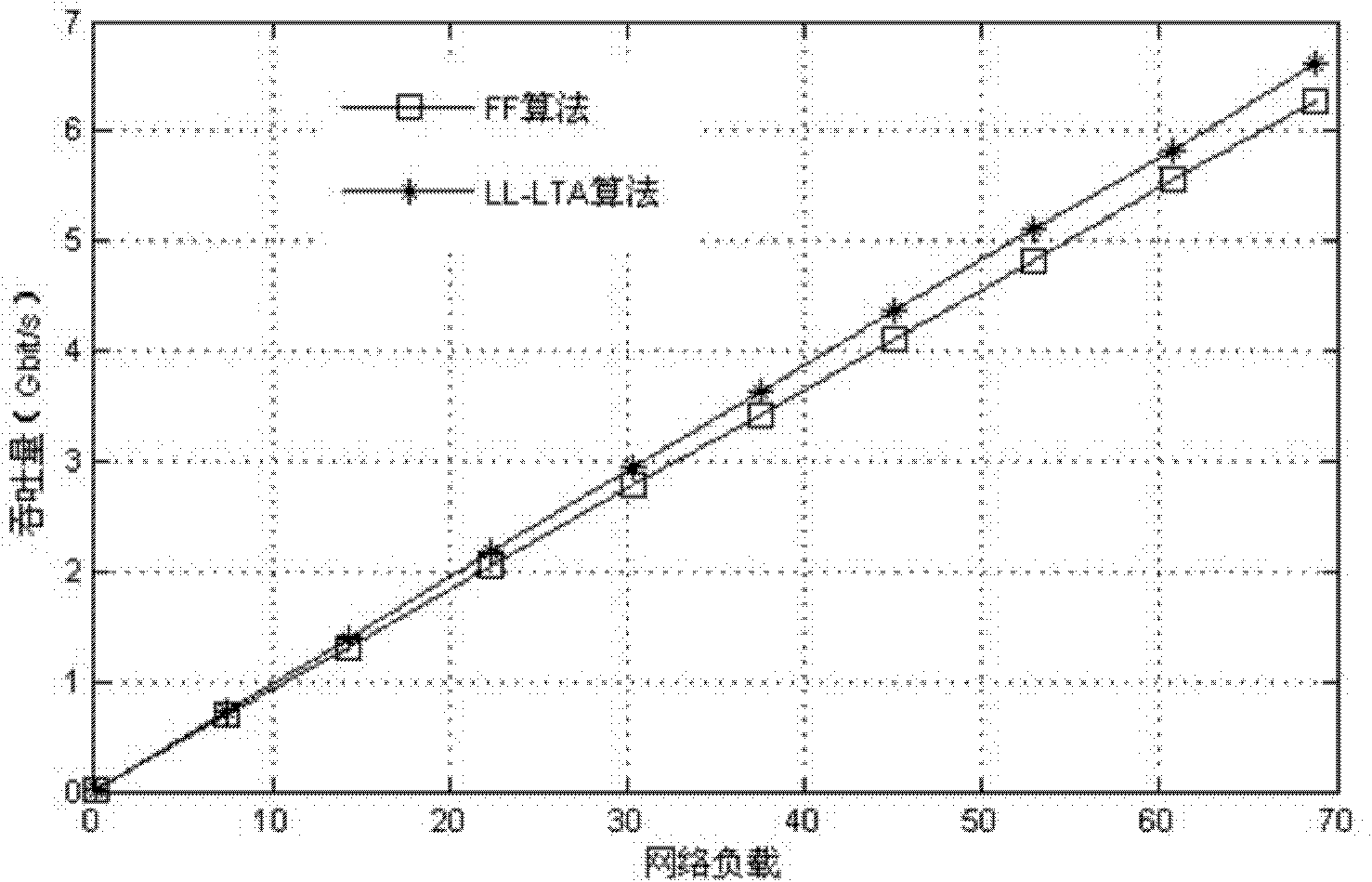
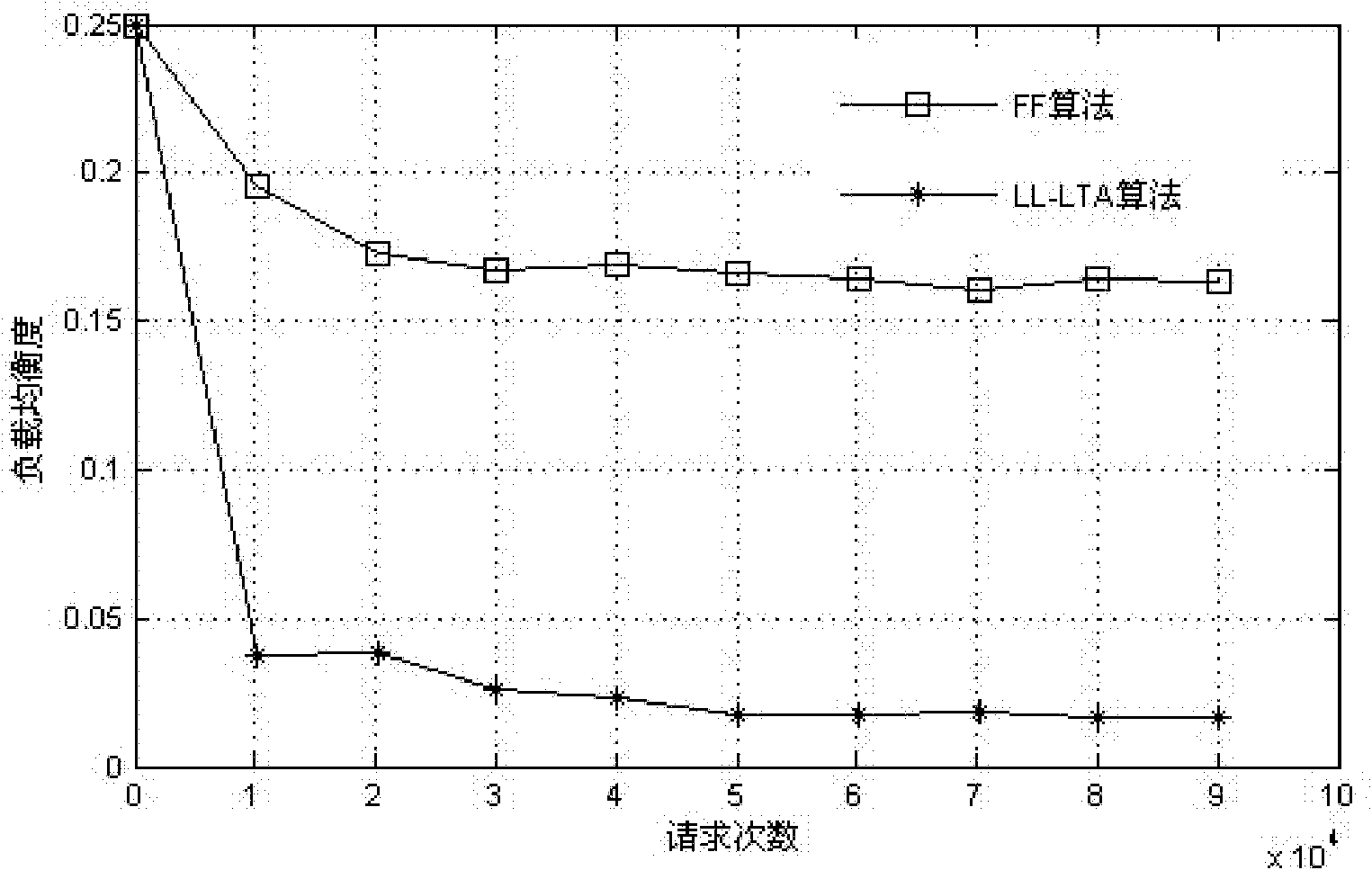
Embodiment 3
[0060] The parameters in this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 2, evaluate the degree of network load balance, and obtain the attached figure 2 The results shown. It can be seen that the light track distribution scheme with the lightest load has a more balanced load distribution.
[0061] Other structures and working processes of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com