Method for producing beta-mannanase through fermentation by utilizing konjac flour microorganisms
A technology of microbial fermentation and mannanase, which is applied in the field of production of β-mannanase, can solve the problems of medium viscosity, slow heat dissipation, large stirring resistance, etc., and achieve enhanced fluidity, prevention of aging and variation, and stirring resistance small effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
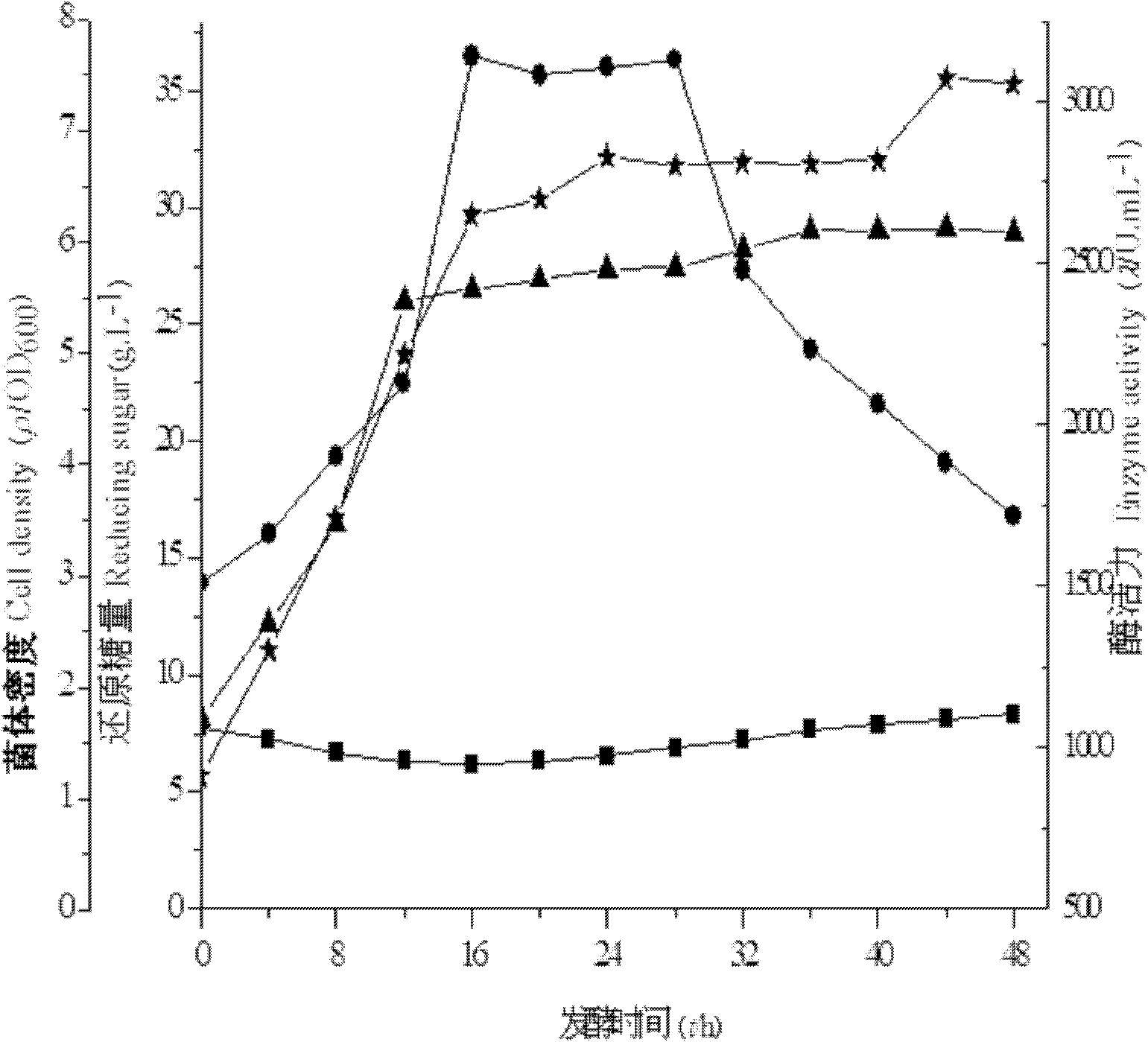
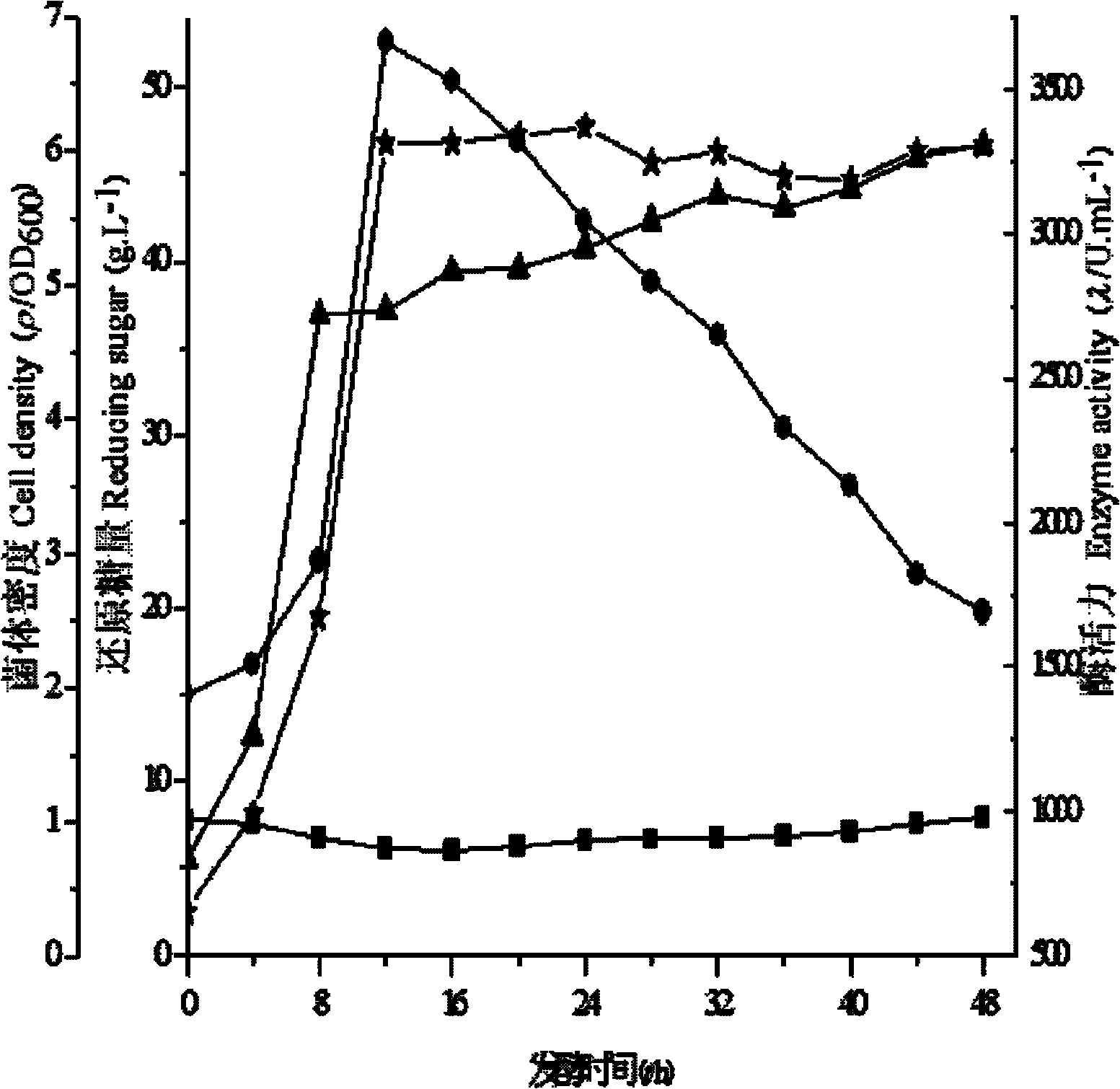
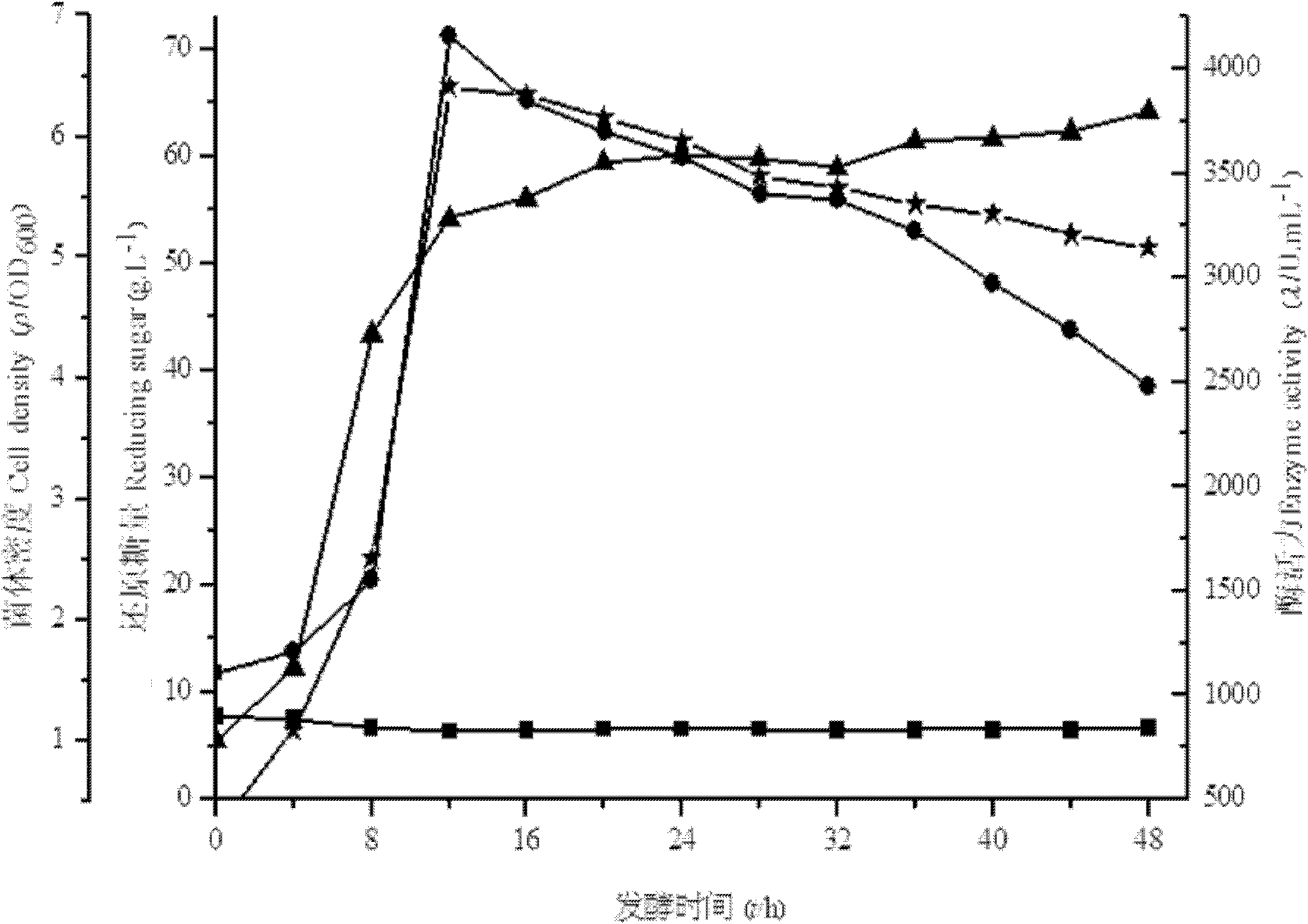
[0011] Specific embodiment one: present embodiment utilizes konjac powder microbial fermentation to produce β-mannanase and realizes by following steps: one, take by weighing fermentation base material, water, fermentation nitrogen source and trace element, mix then, obtain the initial culture of fermentation Base; Two, add konjac flour for the first time in the initial culture medium of fermentation, then insert microbial seed liquid, wherein the addition of konjac flour for the first time is 2% w / v of the initial medium of fermentation; Three, at 37 ℃ Under the conditions of ±2°C, stirring rate of 300r / min, and ventilation rate of 4L / min, ferment until the microbial cell density reaches OD 600 When the value is 4.5, konjac flour is added for the second time, and then fermented for 8-40 hours at 37°C±2°C, stirring speed is 300r / min, and air flow is 4L / min, and the microbial fermentation production using konjac flour is completed. β-mannanase; Wherein, the addition of konjac f...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0013] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in step 1, the fermentation nitrogen source is peptone. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0014] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: in step one, the trace element is MgSO 4 and KH 2 PO 4 , MgSO in the initial fermentation medium 4 The mass concentration is 0.02%, KH 2 PO 4 The mass concentration is 0.5%. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Enzyme activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com