Synchronous motor of permanent magnet
A synchronous motor and permanent magnet technology, applied in synchronous motors with stationary armatures and rotating magnets, magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuit static parts, etc., can solve the problem of permanent magnet magnetic flux drop, torque drop, etc. problems, achieve excellent results, and expand the effect of high-speed operation range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
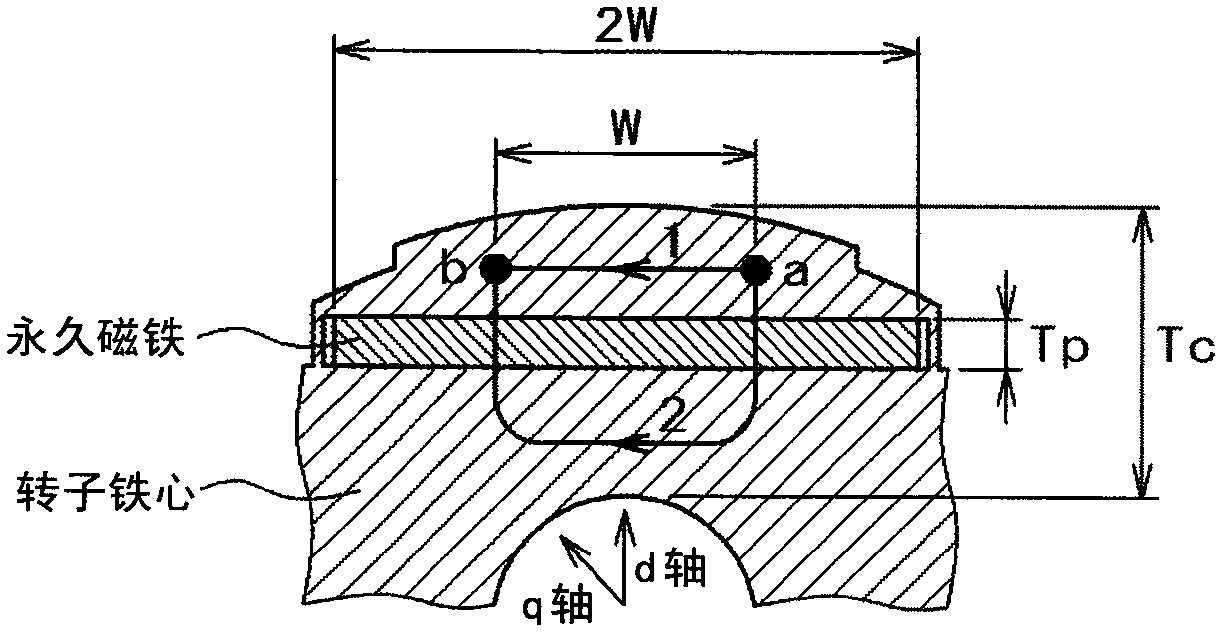
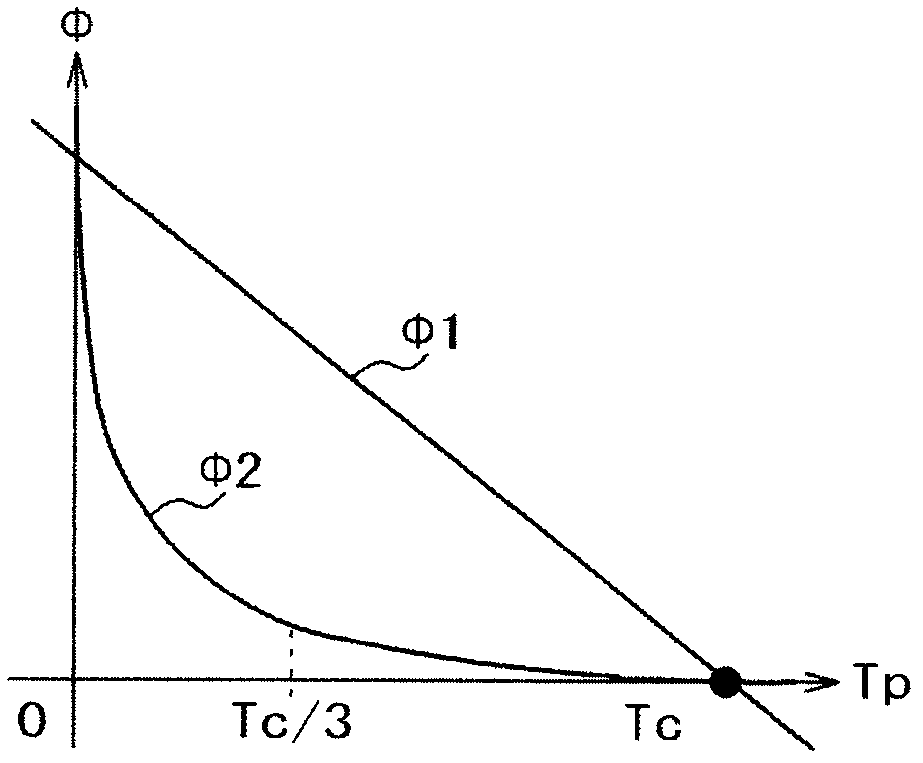
[0080] image 3 It is a radial sectional view of the rotor of the permanent magnet synchronous motor according to the first embodiment of the present invention. and, Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of the magnetic flux lines in the radial section of the permanent magnet synchronous motor according to the first embodiment of the present invention, Figure 5 is used to illustrate the above image 3 Radial sectional view of the rotor with the indicated permanent magnet widths and slot widths provided on the rotor back yoke, Image 6 Indicates the slit width W of this example sl / W pm With no load induced electromotive force E o , Torque M p and q-axis inductance L q Relationship.
[0081] in the image 3 Among them, the rotor 1 is composed of laminated steel plates, and transmits power to the outside through the output shaft inserted into the shaft hole 7 . Inside the rotor 1, the permanent magnets 2 embedded in the magnet insertion holes 3 are arranged as four poles, a...
Embodiment 2
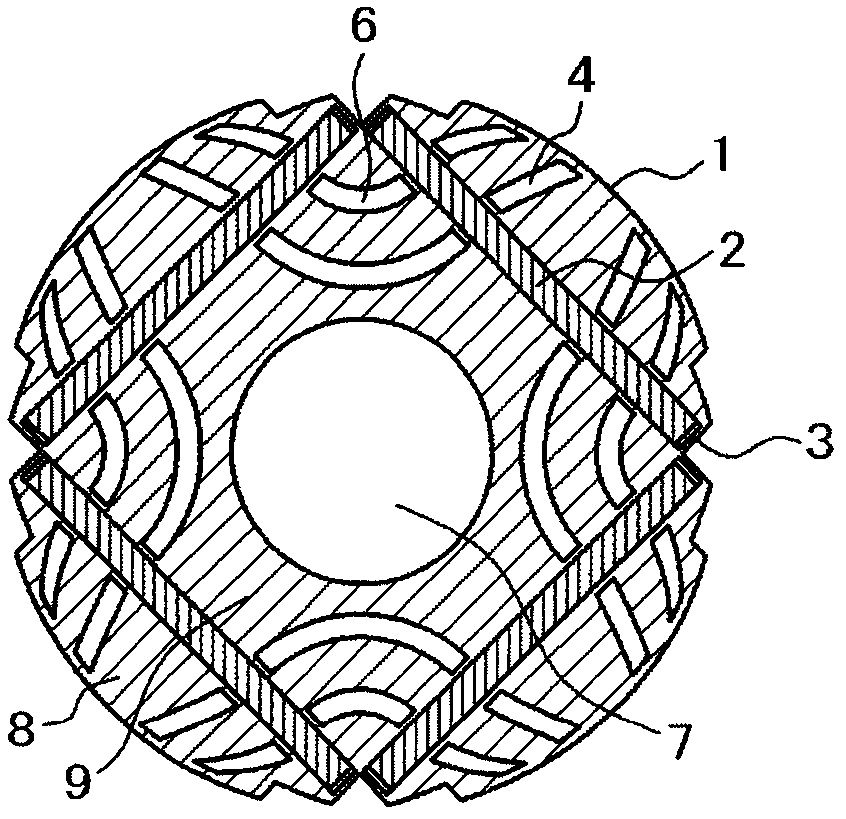
[0101] Next, Figure 8 It is a radial sectional view of the rotor of the permanent magnet synchronous motor according to the second embodiment of the present invention. in the Figure 8 , against the above image 3 The same structural elements are also attached with the same symbols to avoid repeated explanations.
[0102] It should be noted that the Figure 8 The structure shown is the same as the above figure 1 The difference of the shown structure is that the permanent magnet 2 is arranged in six poles, and among the slits 6a to 6d provided four times per pole, the width of the slits 6b and 6c located near the center of the magnetic poles is wider than that of the slits 6a to 6d located at the center of the magnetic poles. Slits 6a, 6d near the ends. In addition, in the illustrated example, no slit is provided in the outer peripheral core portion 8 , however, the present invention is not limited thereto, and the slit may be provided in the outer peripheral core portio...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Figure 9 It is a radial sectional view of the rotor of the permanent magnet synchronous motor according to the third embodiment of the present invention. in the Figure 7 , against the above image 3 The same structural elements are attached with the same symbols to avoid repeated explanations.
[0105] Should Figure 9 The structure shown in Embodiment 3 is the same as the above figure 1 The difference of the shown structure is that there are six slits per pole, and the distance between adjacent slits 6e and 6f located near the center of the magnetic pole among the slits 6a to 6f is smaller than that at the end of the magnetic pole. The distance between adjacent adjacent slits 6a, 6b or the distance between slits 6c, 6d. By adopting such a structure, the effect of reducing the inductance can be further increased. Furthermore, the third embodiment is not limited to the 4-pole motor, and the same effect can be obtained with the same structure in the 6-pole motor,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com