Method for inducing ovulation by using non-polypeptide cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cAMP) level modulator
A technology for inducing ovulation and regulating agent, which can be used in pharmaceutical formulations, peptide/protein components, active ingredients of heterocyclic compounds, etc., and can solve the problems of impaired ovulation in mice and weakened sensitivity of granulocytes to gonadotropins.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
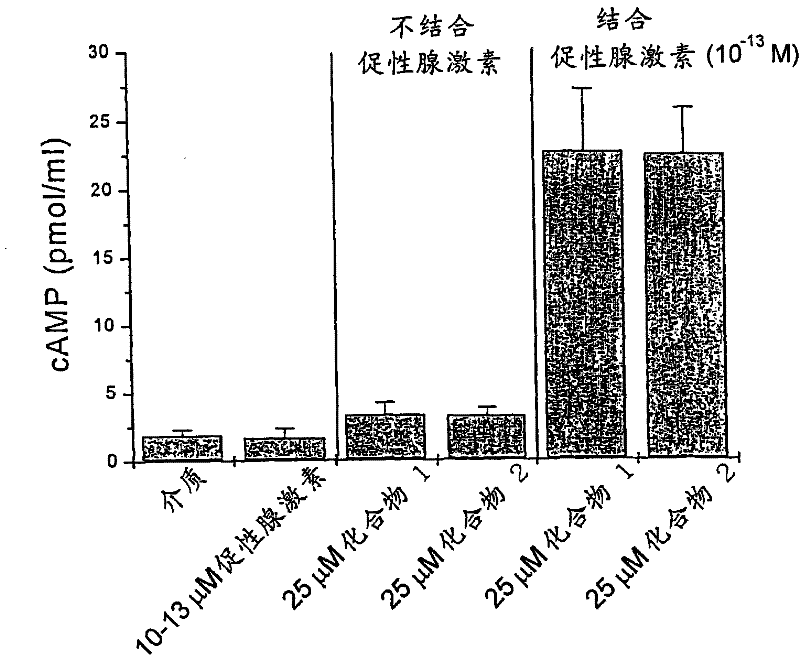
[0150] Example 1 Compound 1 and Compound 2 alone or in combination with gonadotropins have an effect on rat ovarian granules in vitro
[0151] Effect of cellular cAMP levels
[0152] Ovariectomy was performed in 25-day-old Sprague-Dawley rats that had been hypophysectomized and treated with diethylstilbestrol. The ovaries are repeatedly punctured with a 27-gauge needle to release granulocytes from the follicles. After washing, the cells were resuspended in McCoys 5A medium + 1% BSA + 2 μM androstenedione. The number of viable cells was 100,000, all loaded into 1.0 ml 6-well tissue culture dishes (compounds 1 and 2 at a concentration of 25 micromolar, alone or in combination with a low dose of 0.1 pM gonadotropins). The well plates were incubated for 48 hours at 37°C in an incubator with 100% humidity and 5.0% carbon dioxide. Conditioned media were analyzed in a radioimmunoassay (RIA) specific for cAMP. The experimental results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. s...
Embodiment 2
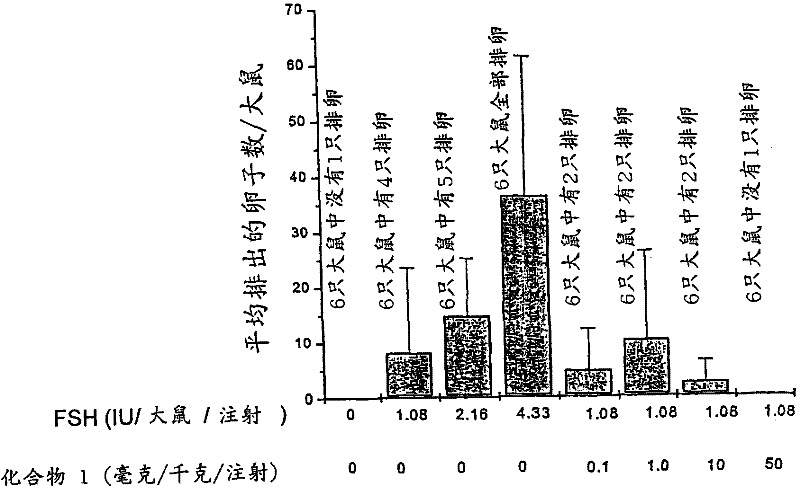
[0153] Example 2 Effect of PDE inhibitor compound 1 on follicle maturation in vivo
[0154] Compound 1 (0.1, 1, 10 and 50 mg / kg / injection; 2 times a day, 3 days) was administered with or without suboptimal dose of FSH (1.08 IU / rat / injection; 2 times a day, 3 days). days), immature female rats were treated to produce mature follicles. A single ovulation dose of hCG (20 IU) is injected, followed by FSH. Administer PDE inhibitors in combination with suboptimal doses of FSH. All injections are by subcutaneous route. Oocytes in the fallopian tubes were counted 18 hours after hCG administration to determine ovulation. The experimental results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. see image 3 , the data represent the average number of oocytes in the fallopian tubes of all rats in each group and the ovulation incidence of ovulating rats. from image 3 It can also be seen that the PDE inhibitor (compound 1) inhibits (rather than stimulates) ovulation at 50 mg / kg. These r...
Embodiment 3
[0155]Example 3 Effect of PDE Inhibitor Compound 1 on Ovulation in Vivo in the Presence of Subeffective Dose of hCG
[0156] Treat immature female rats with an effective dose of FSH (2.16IU / rat / injection; 2 times a day, 2 days) to produce mature follicles, and inject a single dose of hCG to induce ovulation. The amount of hCG administered was a subeffective dose (3 IU) with or without a single injection of compound 1 (50, 10 and 1 mg / kg) at the last injection of FSH. Oocytes in the fallopian tubes were counted 18 hours after hCG administration to determine ovulation. see Figure 4 , injecting a single dose of Compound 1, co-administered with the subovulation amount of hCG, to induce ovulation. All injections are by subcutaneous route. The experimental results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. The data show that non-polypeptide cAMP level modulators, in this example PDE inhibitors, enhance hCG-induced ovulation when administered at suboptimal doses of hCG. The fi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com