Method for preparing titanium dioxide nanotube array
A technology of nanotube arrays and titanium dioxide, applied in electrolytic coatings, surface reaction electrolytic coatings, coatings, etc., can solve the problems of irregular arrays, uneven tube diameters, uneven surface of nanotubes, and achieve structural regularity. sequence, uniform distribution, and consistent surface
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
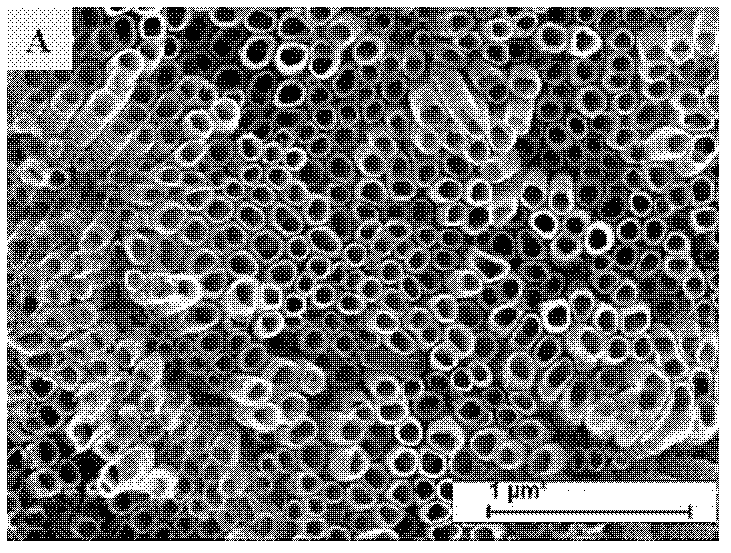
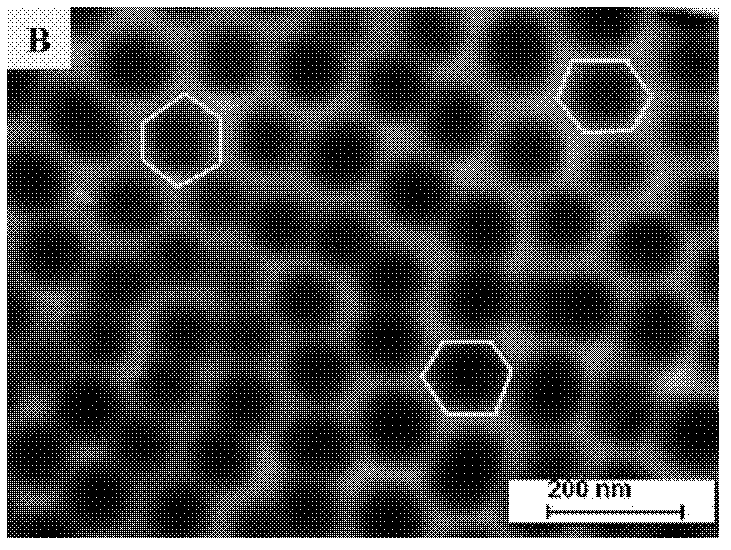
[0023] Titanium sheet (diameter 17mm, thickness 0.5mm) was sanded with sandpaper before anodizing until there was no scratches on the surface, and then mixed acid HF:HNO 3 :H 2 Soak in O=1:3:5 (volume ratio) for 5 minutes, ultrasonically clean with deionized water, and dry with nitrogen gas for use. At room temperature, use a platinum sheet (purity 99.95%) as a counter electrode, take 50 mL of electrolyte solution, apply an anode voltage of 40 V, and perform electrochemical anodic oxidation in an electrolytic cell. Take out the sample and clean it ultrasonically with deionized water, then place the sample in 0.05M HCl for 1 h, rinse with deionized water, and dry. The electrolyte composition and experimental conditions are shown in Table 1. Figure 1~2 It is a nanotube array prepared according to the conditions of Test Example 3 in Table 1. from figure 1 (A) It can be seen that the nanotube array is an upright and hollow structure, but the surface is uneven, the length of e...
Embodiment 2
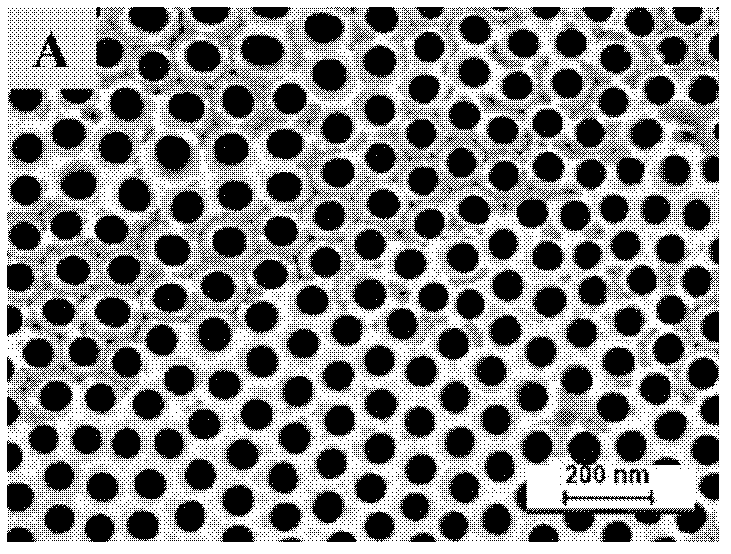
[0027] Similar to Test Examples 1-5, the difference is that the base material used as the anode is the titanium sheet used in Test Examples 1-5 and treated with ultrasonic. At room temperature, using a platinum sheet (purity 99.95%) as a counter electrode, continuously using the electrolyte in Test Examples 1-5, applying an anode voltage of 40V, and performing electrochemical anodic oxidation in an electrolytic cell. The samples were taken out, ultrasonically cleaned with deionized water, and dried. The composition and experimental conditions of the electrolyte are shown in Table 2. Figure 3-5 It is a two-step oxidized nanotube array prepared according to the conditions of Test Example 8 in Table 2. from Figure 3-5 It is obvious that the array of nanotubes formed after the secondary oxidation is arranged regularly, the surface is flat, the diameter of the tubes is uniform, and the morphology characteristics are regular and orderly.
[0028] Table 2
[0029]
[0030] F...
Embodiment 3
[0032] The preparation method of the titanium dioxide nanotube array, the specific steps are to polish the surface of the titanium sheet with sandpaper, polish it with chemical polishing solution, and dry it for later use; prepare the electrolyte solution: the solute is fluoride, the solvent is water, and alcohol additives are added, the content of fluoride is 0.1wt% to 0.5wt% of the total mass of the electrolyte, the content of the alcohol additive is 80% to 99% of the total volume of the electrolyte, and the rest is solvent water; the alcohol additive is ethylene glycol, and the fluoride Ammonium fluoride; prepare a two-electrode system electrolytic cell, use the titanium sheet as the anode, and the platinum sheet as the counter electrode, and perform electrochemical anodic oxidation to form a layer of TiO on the surface of the titanium sheet 2 Nanotube array film; the anodized titanium sheet is ultrasonically cleaned and dried in an acid solution; the titanium sheet is used ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com