Laser multiple degrees of freedom precision measurement system based on telescope system
A telescopic system and precision measurement technology, applied in the field of laser multi-degree-of-freedom precision measurement systems, can solve the problems of multi-degree-of-freedom error magnification limitation and difficulty in obtaining, and achieve the effects of simple structure, convenient installation and adjustment, and fewer optical components.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
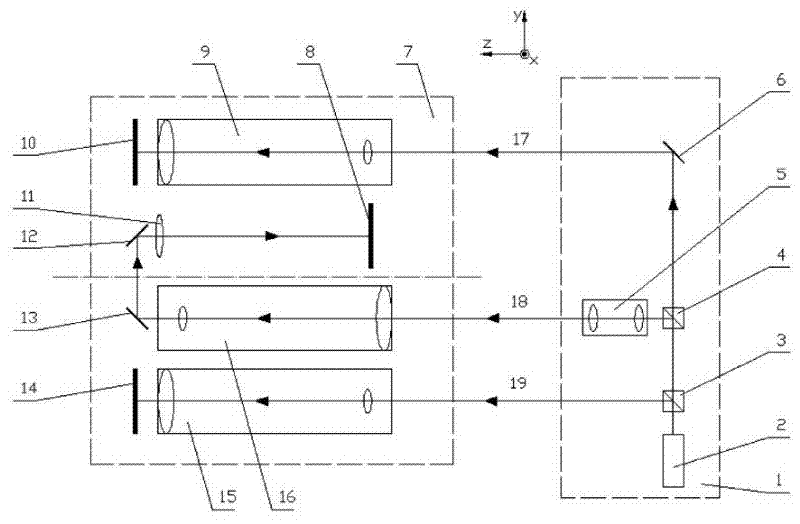
[0027] see figure 1 , the laser multi-degree-of-freedom precision measurement system based on the telescopic system includes a fixed mechanism and a moving mechanism. The moving mechanism 1 is fixed on the kinematic pair of the guide rail, and moves along the linear guide rail with the kinematic pair, and the fixing mechanism 7 is fixed on one end of the measuring guide rail.
[0028] The moving mechanism 1 includes a laser 2 , a first beam splitter 3 , a second beam splitter 4 and a third reflector 6 arranged in sequence, the transmission port of the first beam splitter 3 and the entrance port of the second beam splitter 4 Correspondingly, the transmission port of the second beam splitter 4 corresponds to the incident port of the third reflector 6 ; a laser collimating telescope 5 is provided corresponding to the reflection port of the second beam splitter 4 . Both the first beam splitter 3 and the second beam splitter 4 divide the incident beam into two beams of reflected l...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the first measuring telescopic mechanism 15 , the second measuring telescopic mechanism 16 and the third measuring telescopic mechanism 9 are Galilean telescope systems; the lens 11 is a composite lens.
[0032] All the other structures are with embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0034] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the first photoelectric receiver 14, the second photoelectric receiver 8 and the third photoelectric receiver 10 adopt a charge-coupled device (CCD), and the first reflector 13, the second reflector 12 and the third The reflector 6 adopts a folding prism.
[0035] All the other structures are with embodiment 1.
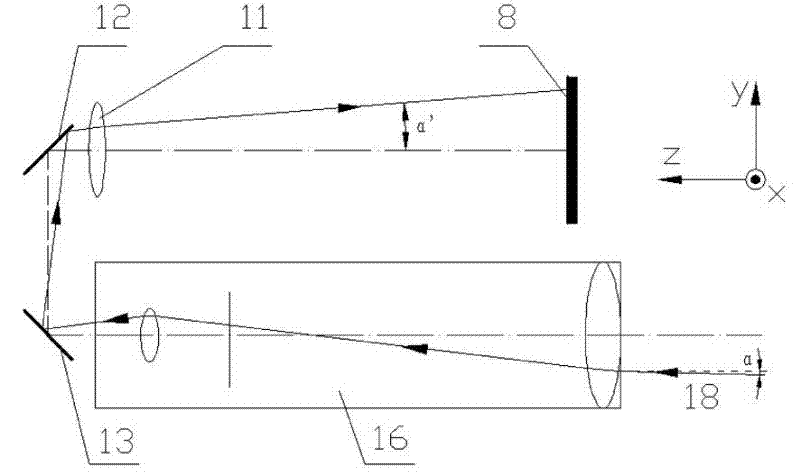
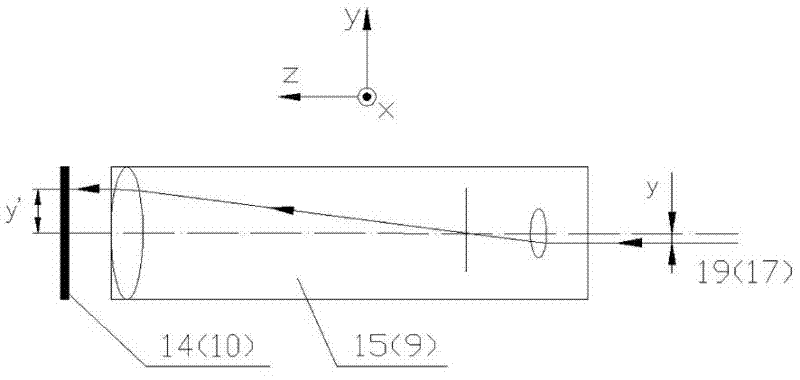
[0036] see figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 , explaining the principle and method of measuring the five-degree-of-freedom error:
[0037] Assume that initially, the posture of the moving part of the linear guideway makes the first laser beam 19, the second laser beam 18 and the third laser beam 17 respectively correspond to the first measuring telescopic mechanism 15, the second measuring telescopic mechanism 16 and the third measuring telescope. The optical axes of the far mechanism 9 coincide.
[0038] The highly stable laser beam emitted by the laser 2 passes through the first beam splitter 3 and is split by the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com