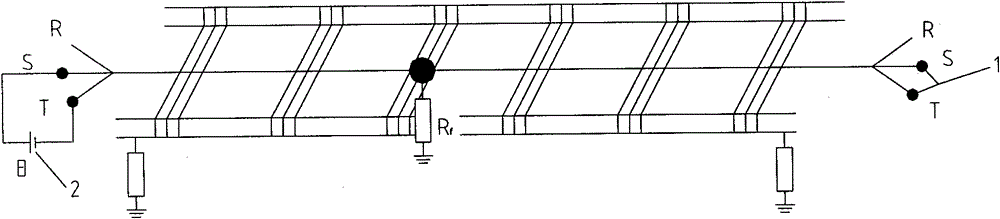
A method for detecting grounding faults of bridge cables
A technology of fault detection and cable grounding, applied in the direction of the fault location, etc., can solve the problems of the eccentric magnetic field requiring special equipment and personnel limitations, the environmental interference of the metallic ground fault audio method, and the difficulty of measuring the ground fault with the audio induction method, etc., to achieve The effect of saving measurement time, high safety, and portable test equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
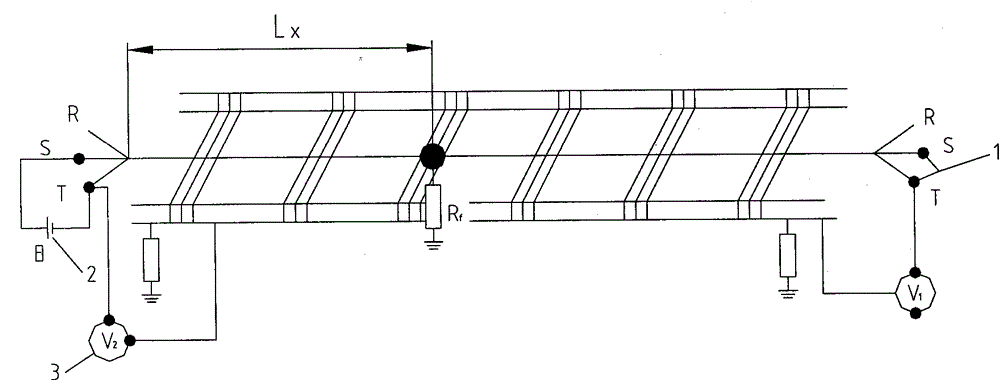
[0066] Embodiment 1: A ground fault occurs in the main insulation of the S phase of the raw power cable, and the specific parameters of the cable are: length L=750 meters, cross-sectional area S=50mm 2 , Ground resistance R f = 15 ohms.
[0067] Loop current output is 10 amps
[0068] The voltage is measured as follows: V 1 =1.531VV 2 =1.169V
[0069] Then L X =(V 2 / V 1 +V 2 )*L=(1.169 / 1.531+1.169)*750=324.7 meters
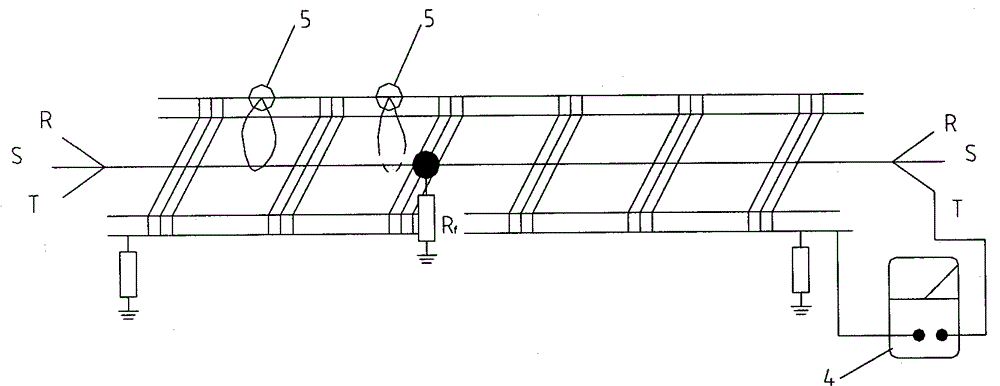
[0070] This measurement method is used for precise determination at a distance of 300 meters near the rough measurement distance. When the insulating rope moves to 320 meters, due to the influence of the insulation of the insulating rope itself, the grounding resistance R f Elimination, the resistance value of the multimeter resistance measurement gear connected to the fault loop immediately changed from 15Ω to infinity, and at this time it can be determined that the fault point is at 320 meters. All the work from the beginning of the measurement to the...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Embodiment 2: A ground fault occurs in the T-phase main insulation of the power cable, and the specific parameters of the cable are: length L=1300 meters, cross-sectional area S=185mm 2 , Ground resistance Rf = 0 ohms.
[0072] Loop current output is 10 amps
[0073] The voltage is measured as follows: V 1 =0.178VV 2 =1.087V
[0074] Then L X =(V 2 / V 1 +V 2 )*L=(1.087 / 0.178+1.087)*1300=1117.1 meters
[0075] The measurement method is used for precise determination at a rough measurement distance of 1100 meters. When the insulating rope 5 moves to 1120 meters, due to the influence of the insulation of the insulating rope itself, the grounding resistance R f Elimination, the resistance value of the multimeter resistance measurement gear connected to the fault circuit changed from 0Ω to infinity immediately, and at this time it can be determined that the fault point is at 1120 meters. Three people completed the whole work from measurement to fault location within...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com