Electronic learning synapse with spike-timing dependent plasticity using unipolar memory-switching elements
A spike and synapse technology applied in the field of artificial neural networks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
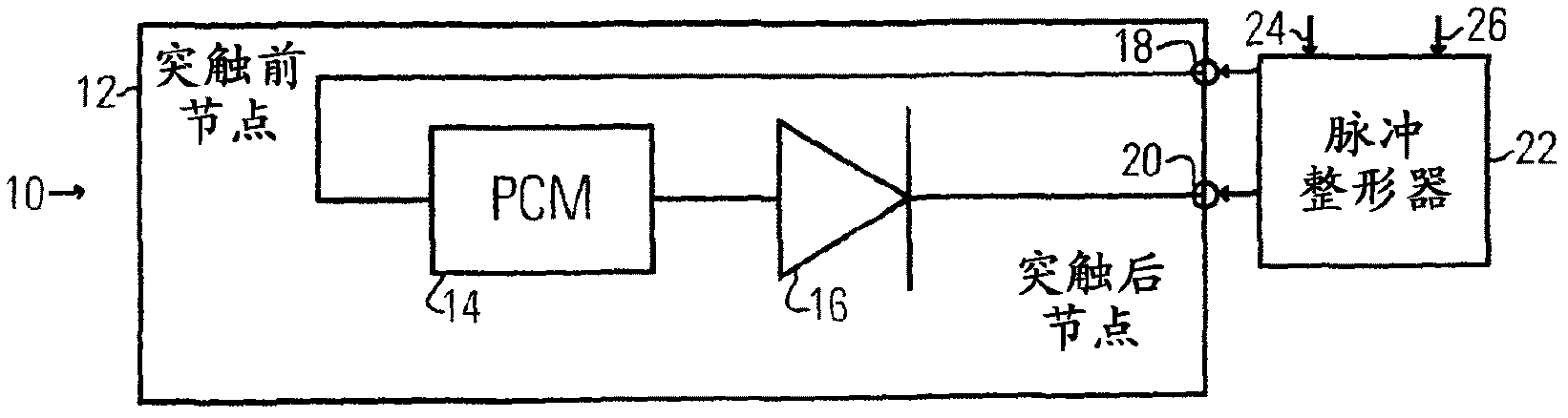
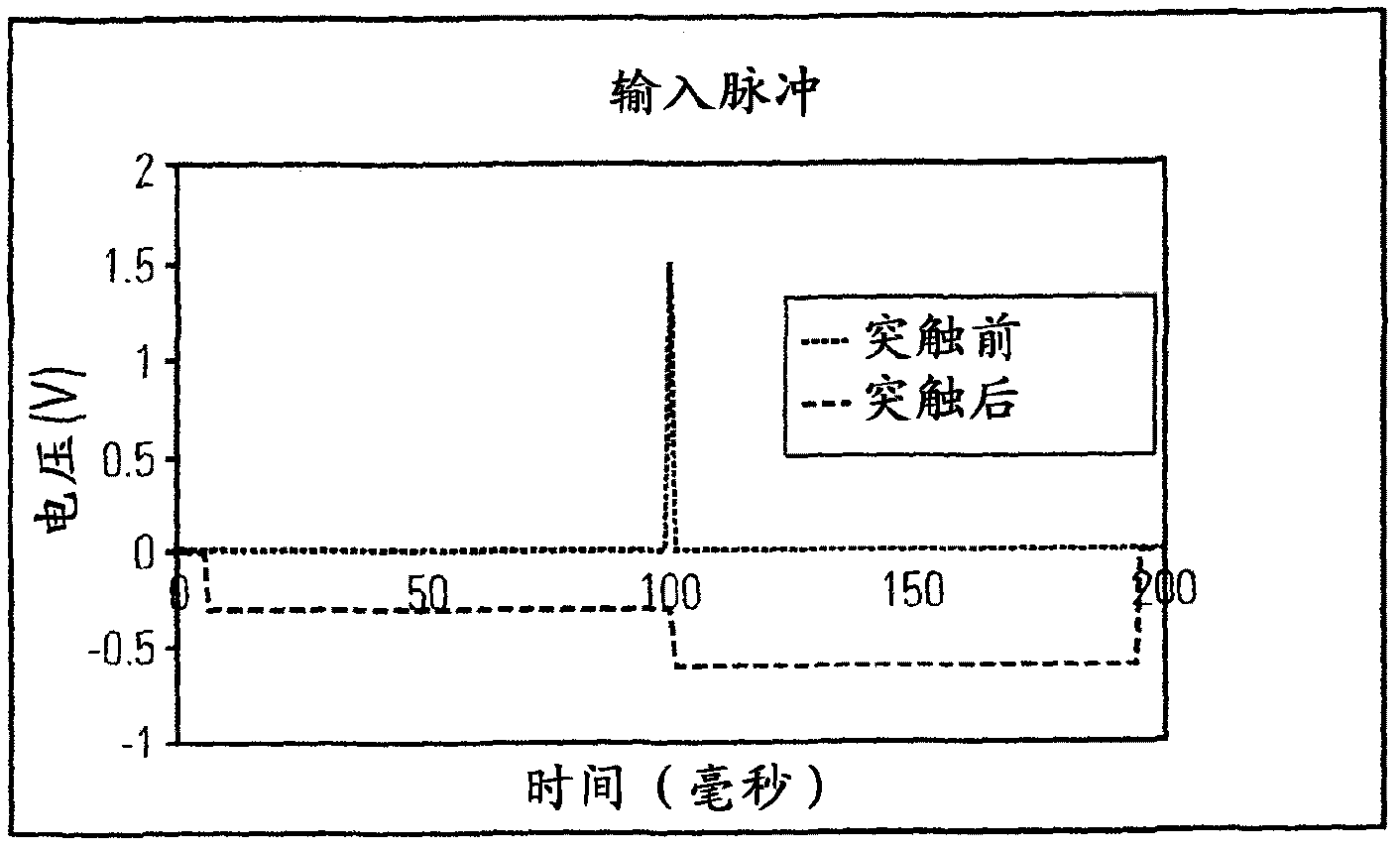
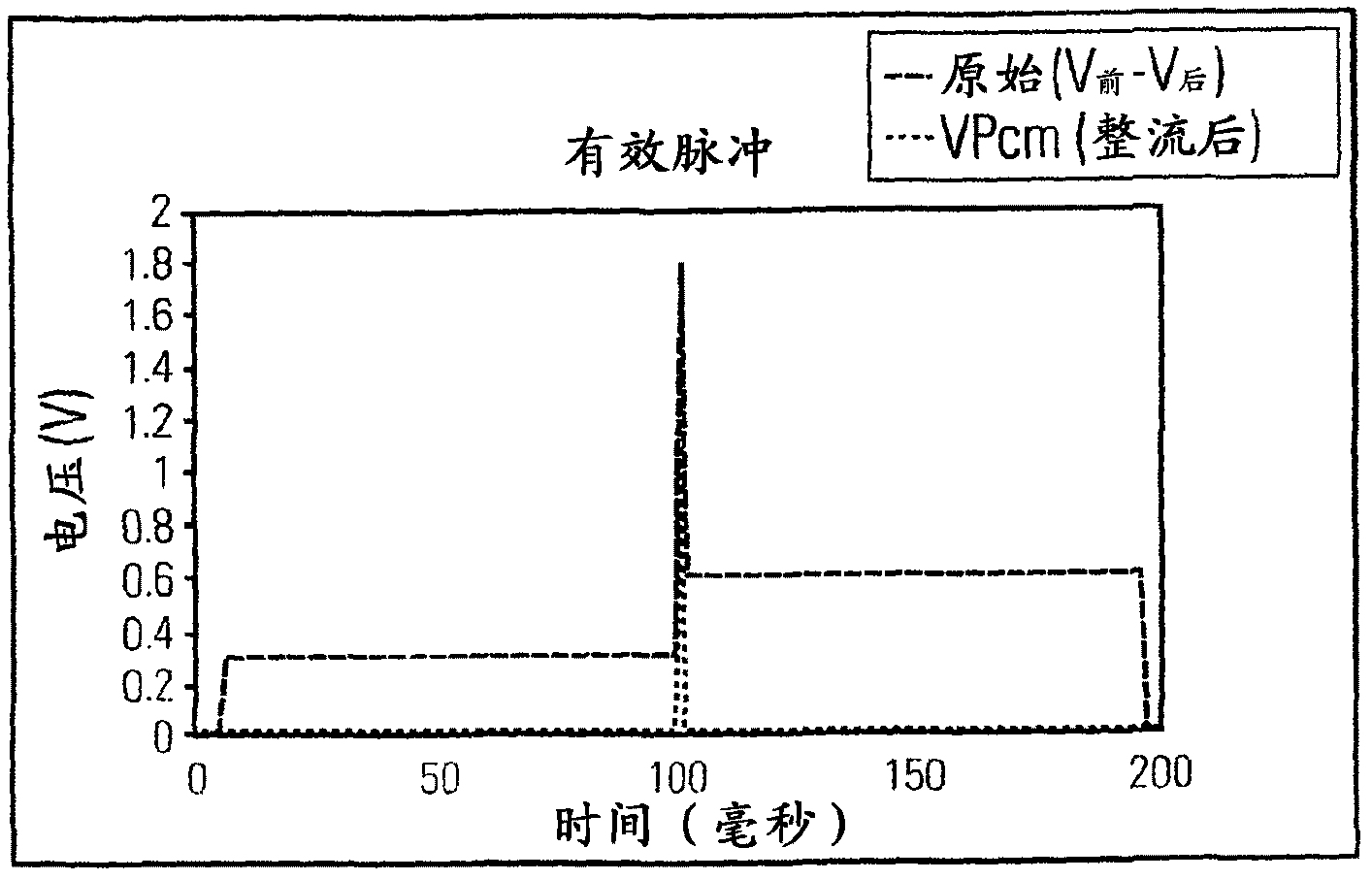
[0017] Embodiments of the present invention provide systems, methods, and computer readable media for electronic learning synapses with spike-dependent plasticity utilizing memory switching elements. The term "neuron" was coined by Heinrich Wilhelm Gottfried von Waldeyer-Hartz in 1891 to represent the discrete information processing unit of the brain. In 1897 Sir Charles Sherrington called the connection between two neurons a "synapse". The flow of information in a synapse only goes in one direction, so you can talk about "pre-synaptic" vs "post-synaptic" neurons. When neurons receive enough input across synapses to become activated, they emit "spikes" that are transmitted to those synapses, ie, the pre-synaptic neurons of those synapses. Neurons can be "excitatory" or "inhibitory".
[0018] The brain can be viewed as a directed graph where nodes are neurons and edges are synapses. The table below shows the rough number of neurons and synapses in mouse, mouse and human. Ea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com