Fuel saving control device for working machine and fuel saving control method for working machine
A technology for working vehicles and working devices, which is applied to control devices, lifting devices, vehicle components, etc., and can solve problems such as poor energy recovery and regeneration efficiency, energy conversion loss, and hindrance to fuel-saving effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
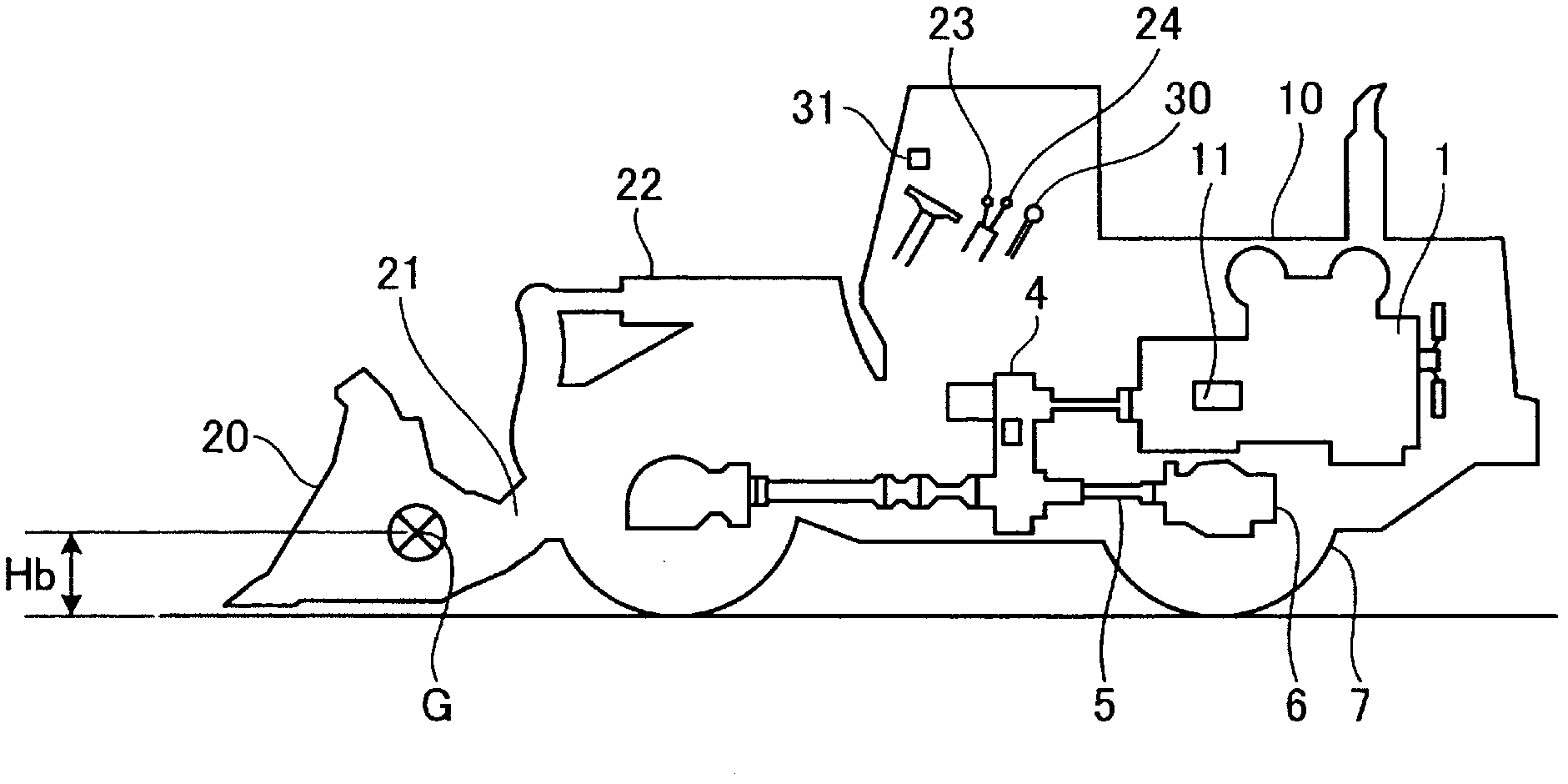
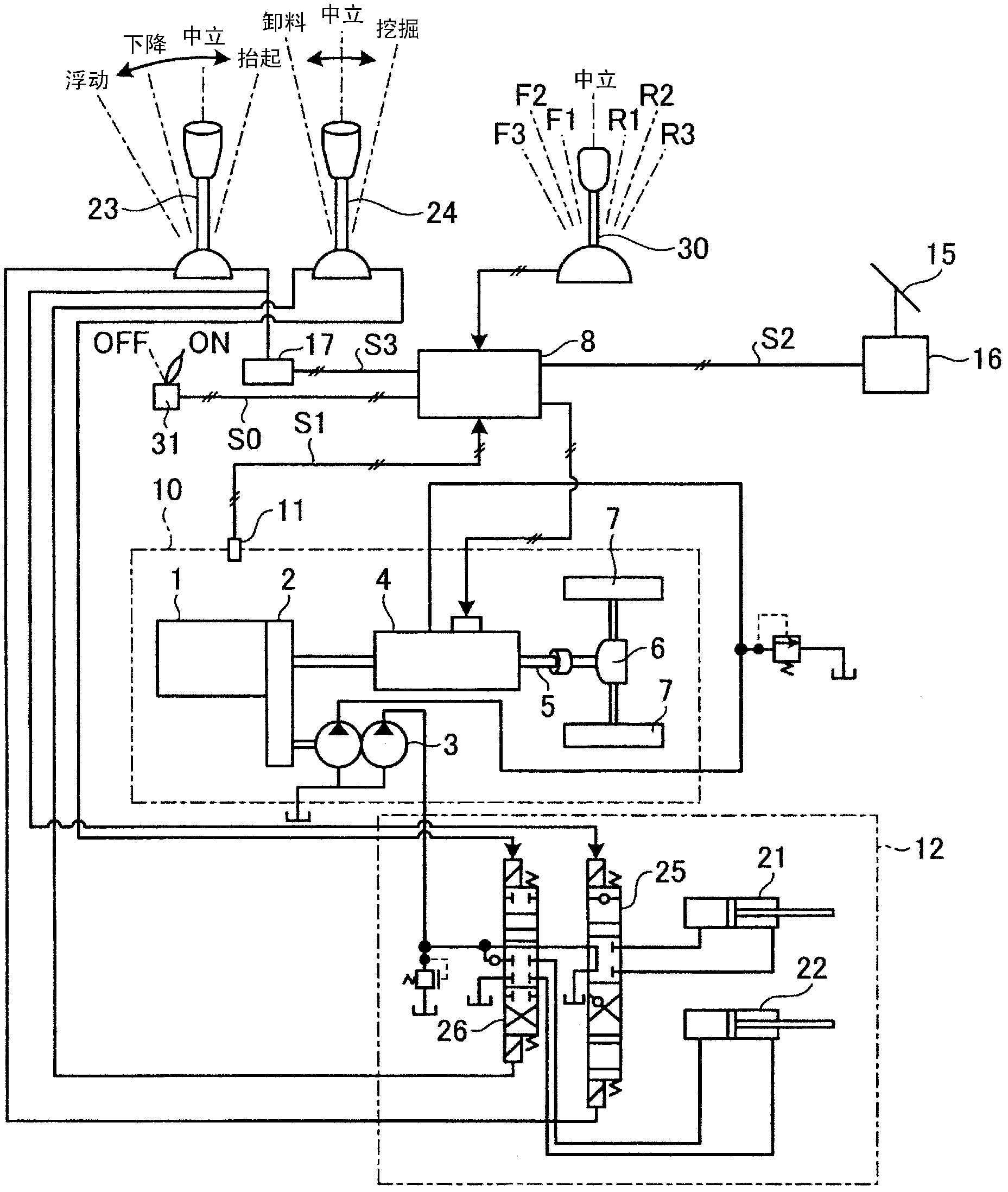
[0030] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram showing a schematic configuration of a wheel loader to which the fuel-saving control device for a work vehicle according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention is applied. figure 2 is included in the figure 1 It is a block diagram showing the structure of the fuel-saving control device of the work vehicle of the wheel loader shown. exist figure 1 and figure 2 In the wheel loader, an engine 1 is mounted on the rear of a vehicle body 10, and is connected to a travel transmission 4 and a fixed displacement hydraulic pump 3 via a PTO 2 that extracts the rotational force of the engine 1 to the outside.
[0031] The travel transmission 4 is a continuously variable transmission, and is realized by an HST (Hydro-Static Transmission) or a belt-type continuously variable transmission. The travel transmission 4 decelerates and speeds up the rotating shaft based on instructions from the controller 8 . The output side of the travel transmi...
Embodiment approach 2
[0044] Next, Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described. In the first embodiment described above, the hydraulic pump 3 is a fixed-displacement hydraulic pump, but in this second embodiment, a variable-displacement hydraulic pump 33 is used as a hydraulic pump of the work implement.
[0045] That is, if Figure 5 As shown, a variable displacement hydraulic pump 33 is provided instead of the fixed displacement hydraulic pump 3 . The hydraulic pump 33 uses the controller 8 to control the inclination of the swash plate of the hydraulic pump 33 , thereby changing the capacity of the hydraulic pump 33 . Furthermore, when the accelerator pedal is released during travel and the arm is raised, the controller 8 performs control to increase the speed reduction ratio of the travel transmission 4 compared to the normal case as in the first embodiment, and Control is performed to increase the capacity of the hydraulic pump 33 . In this case, it is preferable that the capacit...
Embodiment approach 3
[0052] Next, Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described. In the first and second embodiments described above, the travel transmission 4 is a continuously variable transmission, but in this third embodiment, the travel transmission 4 is a stepped transmission. Other structures are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
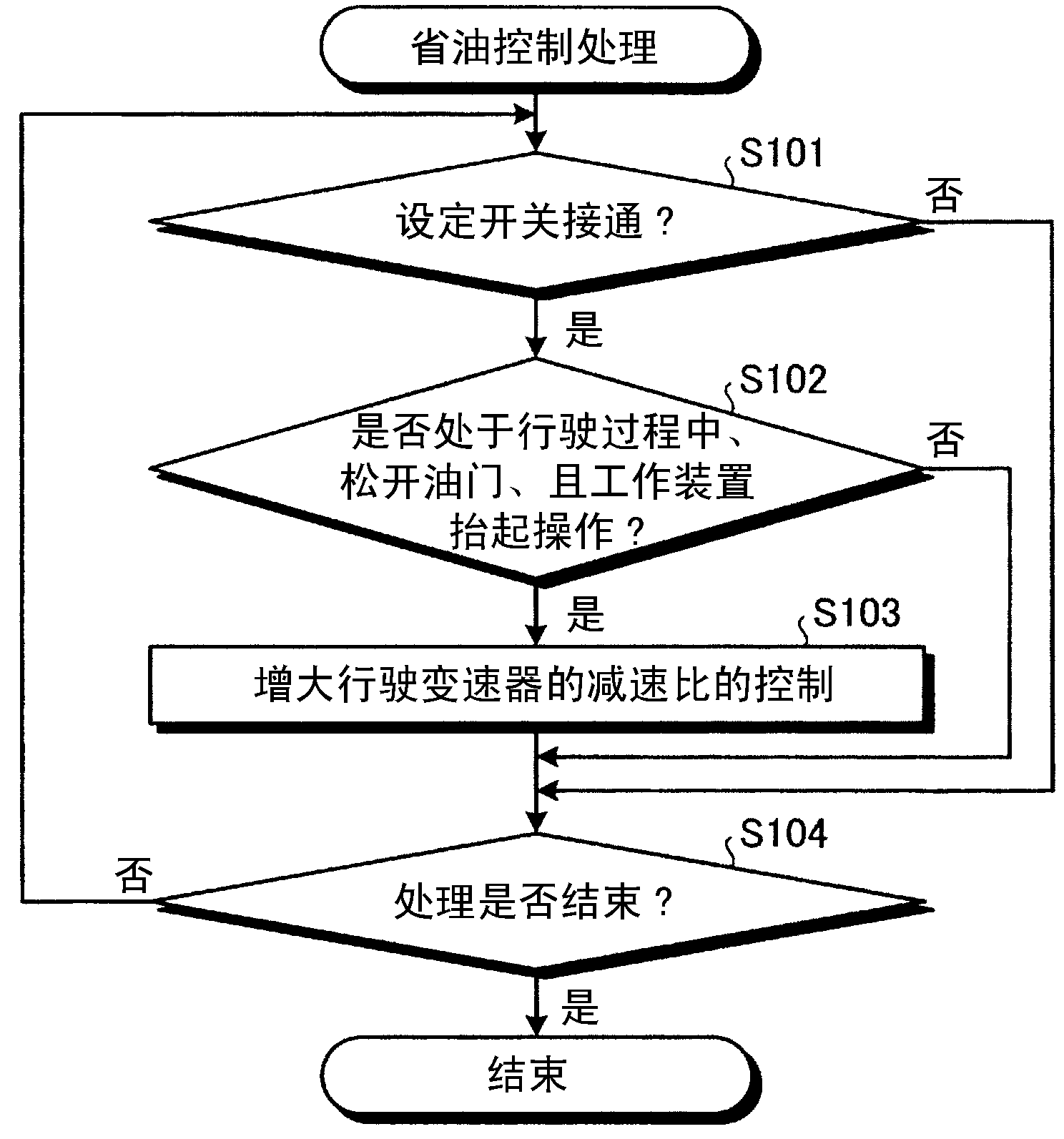
[0053] Here, refer to Figure 8 The timing chart shown here describes the operation of each part when the fuel-saving control process according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention is performed. It should be noted, Figure 8 The dotted line in the circle represents the fuel-saving control processing of the stepped transmission according to the third embodiment, and the solid line represents the fuel-saving control processing of the continuously variable transmission according to the first embodiment. exist Figure 8 , firstly, release the accelerator before time t1 (refer to Figure 8 (a)), the vehicle speed V(S1) is above the fixed value Vth ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com