Video sequence coding method aiming at HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding)
An encoding method and video sequence technology, applied in the field of video encoding, can solve problems such as inapplicability to practical applications, high complexity, and inapplicability to transform encoding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
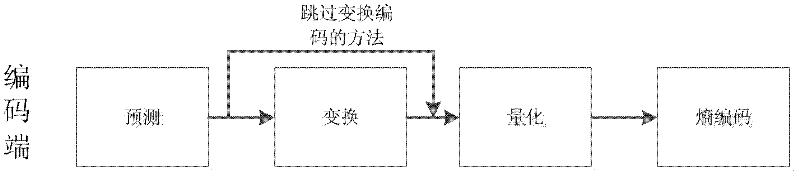
[0016] This encoding method for a HEVC video sequence comprises the following steps:
[0017] (1) For the luminance component in the prediction unit PU, the prediction block is obtained, and then subtracted from the original value to obtain the residual, and the division based on the rate-distortion cost is performed to obtain the transformation unit TU;
[0018] (2) Determine whether the current TU selects whether to perform transformation according to the principle of minimum rate-distortion cost;
[0019] (3) After selection, quantize with a corresponding method, and pass the quantization coefficient and the sign of whether to transform to the decoding end;
[0020] (4) At the decoding end, each TU reads the flag and judges whether to perform inverse transformation;
[0021] (5) Each TU performs corresponding inverse quantization according to the read flag;
[0022] (6) Determine whether to perform inverse transformation according to the read flag, and perform correspondi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com