Error concealment for sub-band coded audio signals
An audio signal, encoded technology, applied in the direction of forward error control, speech analysis, code conversion, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing unnecessary waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
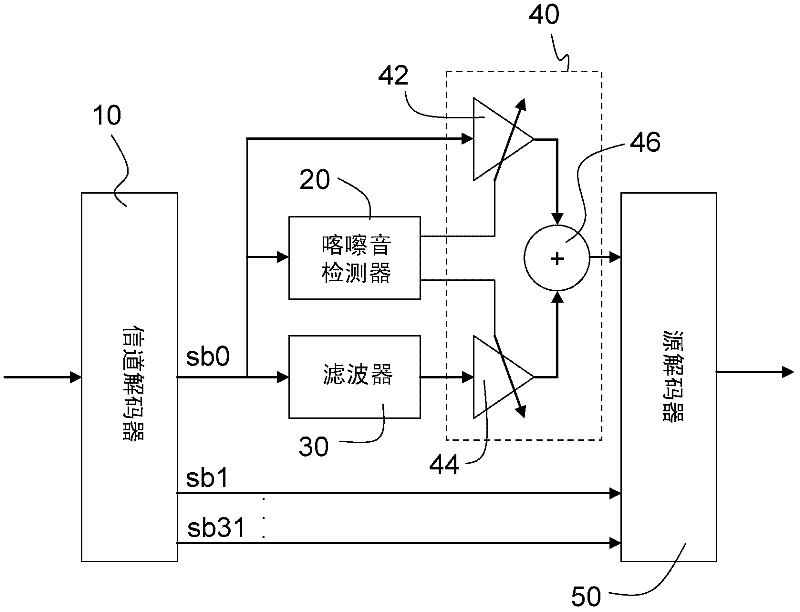
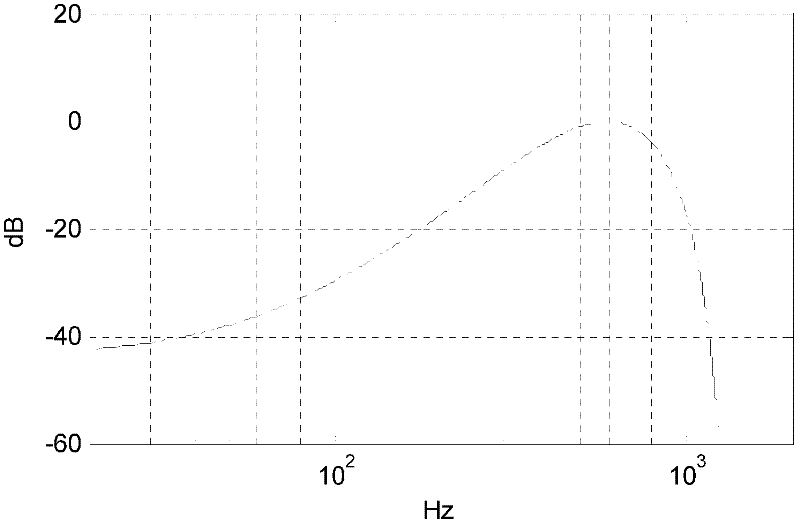
[0049] The MPEG Audio Layer II audio codec used in DAB is a subband codec. Compression is performed in the time domain using a filter bank that generates 32 equally spaced subbands with a bandwidth of 750 Hz at a sampling rate of 48 kHz. All these subbands are not equally perceptually correlated. The first sub-band covers the bandwidth from 0 Hz (DC) to 750 Hz, which corresponds to the 8 critical bands of the human auditory system, while the second sub-band covers only 4 critical bands.
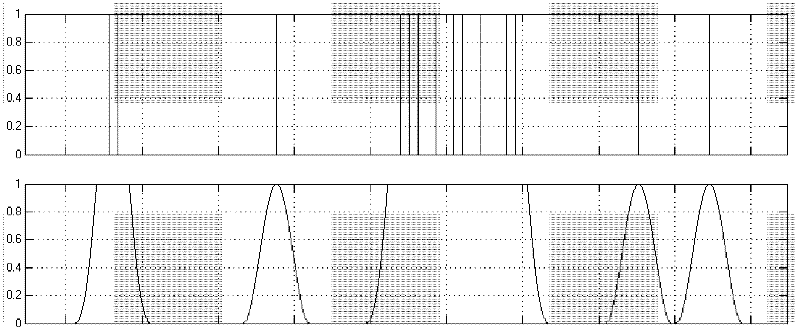
[0050] Isolated bit errors in subbands produce time-domain discontinuities that can typically be heard as band-limited "click" noise. Bursts of bit errors tend to randomize the time-domain signal of the corrupted subbands, which can be heard as band-limited white noise.
[0051] The inventors have observed that these artifacts are most annoying in the first sub-band ranging from 0 to 750 Hz. This is not only due to the relatively low frequency resolution of the MPEG Audio Layer II filterba...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com