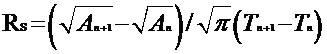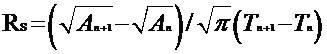Method for quantitatively measuring cell spreading rate based on idealized cell radius
A quantitative measurement and cell technology, applied in measurement devices, material analysis by optical means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult, rough, and no quantitative measurement of spreading rate of cells, and achieve the effect of simple calculation method and simple measurement equipment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Example 1: Quantitative measurement of cell spreading.
[0017] The suspended human umbilical vein endothelial cells were planted on a 24-well plate containing culture medium and placed in CO 2 Incubator (37 0 C, 5% CO 2 ) cultured. After 6 hours, 24 hours, and 48 hours of culture, observe and obtain cell morphology images with a confocal microscope, and measure the adherent area of all individual cells in the image and the average adherent area of all cells, through the formula provided above The average spreading rate of cells for different time periods was calculated. Finally, it was calculated that the average idealized radius at 6 hours, 24 hours and 48 hours during cell spreading was 12.95, 18.19 and 19.01 microns respectively; Over time, the average cell spreading rate (radius change per unit time) was 2.16, 0.29 and 0.03 μm / hour, respectively. The data showed that the cells spread the fastest within 0-6 hours, and the spreading speed gradually decreased...
Embodiment 2
[0018] Example 2: Quantitative measurement of drug effects on cell spreading.
[0019] The suspended human umbilical vein endothelial cells were planted on a 24-well plate containing culture medium and placed in CO 2 Incubator (37 0 C, 5% CO 2 ) cultured. After 24 hours of culture, use a confocal microscope to obtain cell morphology images, then add 20 ug / ml Ox-LDL (oxidized low-density lipoprotein) to the cell solution, and continue to culture for 48 hours, and at 6 hours and 12 hours respectively Topographic images of the cells were acquired using a confocal microscope at , 24, and 48 hours. And measure the adherent area of all single cells in the image and the average adherent area of all cells, and calculate the idealized radius and average spreading rate of cells in different time periods through the formula provided above. Finally, the effect of the drug on cell spreading was calculated: before adding the drug, the idealized radius of the cell was about 20.04 mic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com